Abstract
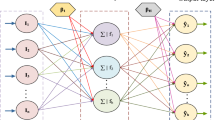
A multilayer perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network (ANN) model has been optimized by the multi-objective ant colony optimization (MOACO) algorithm, which uses three objective functions. A sensitivity analysis to choose MOACO parameter values is carried out by calculating hypervolume metric, and the proposed approach adopts the Vlsekriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) decision method to choose final compromised solution on the Pareto front obtained from MOACO. As a result, we used the MLP-MOACO developed model to estimate the value of engine emissions of NOx in a four stroke, spark ignition (SI) gasoline engine and observed acceptable correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.99978.
Similar content being viewed by others
Refferences
Liu K, Zhu H, Lü J. Cooperative stabilization of a class of lti plants with distributed observers. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2017, 64: 1891–1902
Chen Y, Lü J. Delay-induced discrete-time consensus. Automatica, 2017, 85: 356–361
Shaghaghi E, Jabbarpour M R, Md Noor R, et al. Adaptive green traffic signal controlling using vehicular communication. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng, 2017, 18: 373–393
Zhang J, Liu Y. Application of complete ensemble intrinsic time-scale decomposition and least-square SVM optimized using hybrid DE and PSO to fault diagnosis of diesel engines. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng, 2017, 18: 272–286
Feng D, Xiao M, Liu Y, et al. Finite-sensor fault-diagnosis simulation study of gas turbine engine using information entropy and deep belief networks. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng, 2016, 17: 1287–1304
Feng J, Liu Z, Wu C, et al. AVE: Autonomous vehicular edge computing framework with ACO-based scheduling. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2017, 66: 10660–10675
Zhang X, Wu Z, Hu X, et al. Trajectory optimization-based auxiliary power unit control strategy for an extended range electric vehicle. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2017, 66: 10866–10874
Pei J Z, Su Y X, Zhang D H. Fuzzy energy management strategy for parallel HEV based on pigeon-inspired optimization algorithm. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 60: 425–433
Meseguer J, Toh C, Calafate C, et al. Driving styles: A mobile platform for driving styles and fuel consumption characterization. J Commun Netw, 2017, 19: 162–168
Sakthivel G, Snehitkumar B, Ilangkumaran M. Application of fuzzy logic in internal combustion engines to predict the engine performance. Int J Ambient Energy, 2016, 37: 273–283
Deb M, Majumder P, Majumder A, et al. Application of artificial intelligence (AI) in characterization of the performance-emission profile of a single cylinder CI engine operating with hydrogen in dual fuel mode: An ANN approach with fuzzy-logic based topology optimization. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41: 14330–14350
He G Z, Xie H, He S J. Overall efficiency optimization of controllable mechanical turbo-compounding system for heavy duty diesel engines. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 60: 36–50
Ling X C, Wu F, Yao D W. A reduced combustion kinetic model for the methanol-gasoline blended fuels on SI engines. Sci China Technol Sci, 2016, 59: 81–92
Martinez-Morales J D, Palacios-Hernández E R, Velázquez-Carrillo G A. Artificial neural network based on genetic algorithm for emissions prediction of a SI gasoline engine. J Mech Sci Technol, 2014, 28: 2417–2427
Martinez-Morales J D, Palacios-Hernández E R, Velázquez-Carrillo G A. Modeling engine fuel consumption and NOx with RBF neural network and MOPSO algorithm. Int J Automot Technol, 2015, 16: 1041–1049
Kannan G R, Balasubramanian K R, Anand R. Artificial neural network approach to study the effect of injection pressure and timing on diesel engine performance fueled with biodiesel. Int J Automot Technol, 2013, 14: 507–519
Ilangkumaran M, Sakthivel G, Nagarajan G. Artificial neural network approach to predict the engine performance of fish oil biodiesel with diethyl ether using back propagation algorithm. Int J Ambient Energy, 2016, 37: 446–455
Niu X, Yang C, Wang H, et al. Investigation of ANN and SVM based on limited samples for performance and emissions prediction of a CRDI-assisted marine diesel engine. Appl Thermal Eng, 2017, 111: 1353–1364
Shi D H, Wang S H, Pisu P, et al. Modeling and optimal energy management of a power split hybrid electric vehicle. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 60: 713–725
Muralidharan K, Vasudevan D. Applications of artificial neural networks in prediction of performance, emission and combustion characteristics of variable compression ratio engine fuelled with waste cooking oil biodiesel. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng, 2015, 37: 915–928
Ahmed T, Lim O. A two stroke free piston engine’s performance and exhaust emission using artificial neural networks. J Mech Sci Technol, 2016, 30: 4747–4755
Rahimi-Gorji M, Ghajar M, Kakaee A H, et al. Modeling of the air conditions effects on the power and fuel consumption of the SI engine using neural networks and regression. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng, 2017, 39: 375–384
Channapattana S V, Pawar A A, Kamble P G. Optimisation of operating parameters of DI-CI engine fueled with second generation Biofuel and development of ANN based prediction model. Appl Energy, 2017, 187: 84–95
Karthickeyan V, Balamurugan P, Rohith G, et al. Developing of ANN model for prediction of performance and emission characteristics of VCR engine with orange oil biodiesel blends. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng, 2017, 39: 2877–2888
Jiang Y Y, Xiang J W, Li B, et al. A hybrid multiple damages detection method for plate structures. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 60: 726–736
Lee M C. Effects of H2/CO/CH4 syngas composition variation on the NOx and CO emission characteristics in a partially-premixed gas turbine combustor. Sci China Technol Sci, 2016, 59: 1804–1813
Hagan M, Demuth H, Beale M. Neural Network Design. Boston: PWS Publising Company, 1996
Demuth H, Beale M. Hagan M. Neural Network Toolbox TM 6 User’s Guide. Natick: The Math Works Inc., 2008
Hagan M T, Menhaj M B. Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 1994, 5: 989–993
Chiam S, Tan K, Mamun A. Multiobjective Evolutionary Neural Networks for Time Series Forecasting. In: Obayashi S, Deb K, Poloni C, et al, eds. Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. EMO 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2007, 4403: 346–360
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B, 1996, 26: 29–41
Doerner K, Gutjahr W J, Hartl R F, et al. Pareto ant colony optimization: A metaheuristic approach to multiobjective portfolio selection. Ann Operations Res, 2004, 131: 79–99
Coello C, Lamont G, Van D. Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems. New York: Springer, 2007
Opricovic S, Tzeng G H. Compromise solution by MCDM methods: A comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Operational Res, 2004, 156: 445–455
Vapnik V. Statistical Learning Theory. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1998
Zitzler E, Thiele L. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: A comparative case study and the strength pareto approach. IEEE Trans Evol Computat, 1999, 3: 257–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Morales, J., Quej-Cosgaya, H., Lagunas-Jiménez, J. et al. Design optimization of multilayer perceptron neural network by ant colony optimization applied to engine emissions data. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62, 1055–1064 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9235-y