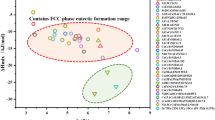
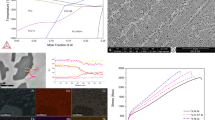
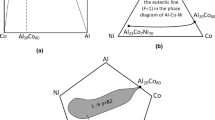
Abstract
Eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys (HEAs) have recently attracted a great deal of interest because of their promising properties, such as an excellent castability and unique combination of good ductility and high strength. However, in the absence of a phase diagram, it remains a non-trivial task to find a eutectic or near-eutectic composition for a HEA system, which usually demands a tremendous amount of efforts if a trial-and-error approach is followed. In this paper, we briefly review the thermodynamics that governs the eutectic solidification in regular binary and ternary alloys, and proceed to the discussion for the design of eutectic HEAs. Based on the data reported, we then propose an improved strategy which may enable an efficient search for the eutectic or near eutectic HEA compositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wattis J A D. A Becker-Döring model of competitive nucleation. J Phys A-Math Gen, 1999, 32: 8755–8784
Sato T, Sayama Y. Completely and partially co-operative growth of eutectics. J Cryst Growth, 1974, 22: 259–271
Goetzinger R, Barth M, Herlach D M. Mechanism of formation of the anomalous eutectic structure in rapidly solidified Ni-Si, Co-Sb and Ni-Al-Ti alloys. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 1647–1655
Zhao S, Li J F, Liu L, et al. Cellular growth of lamellar eutectics in undercooled Ag-Cu alloy. Mater Charact, 2009, 60: 519–524
Jordan R M, Hunt J D. The growth of lamellar eutectic structures in the Pb-Sn and Al-CuAl2 systems. Metall Mater Trans B, 1971, 2: 3401–3410
Johnson D R, Chen X F, Oliver B F, et al. Processing and mechanical properties of in-situ composites from the NiAlCr and the NiAl(Cr,Mo) eutectic systems. Intermetallics, 1995, 3: 99–113
Bei H, George E P, Kenik E A, et al. Directional solidification and microstructures of near-eutectic Cr-Cr3Si alloys. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 6241–6252
Bei H, George E P. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a directionally solidified NiAl-Mo eutectic alloy. Acta Mater, 2005, 53: 69–77
Yang W, Felton L E, Messler R W. The effect of soldering process variables on the microstructure and mechanical properties of eutectic Sn-Ag/Cu solder joints. J Electron Mater, 1995, 24: 1465–1472
Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater, 2004, 6: 299–303
Ma S G, Zhang S F, Qiao J W, et al. Superior high tensile elongation of a single-crystal CoCrFeNiAl0.3 high-entropy alloy by Bridgman solidification. Intermetallics, 2014, 54: 104–109
Shun T T, Du Y C. Microstructure and tensile behaviors of FCC Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J Alloy Compd, 2009, 479: 157–160
Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Woodward C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2014, 68: 214–228
Senkov O N, Woodward C, Miracle D B. Microstructure and properties of aluminum-containing refractory high-entropy alloys. Jom-Us, 2014, 66: 2030–2042
Stepanov N D, Shaysultanov D G, Salishchev G A, et al. Effect of V content on microstructure and mechanical properties of the CoCr-FeMnNiVx high entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd, 2015, 628: 170–185
Hsu C Y, Wang W R, Tang W Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of new AlCoxCrFeMo0.5 Ni high-entropy alloys. Adv Eng Mater, 2010, 12: 44–49
Otto F, Dlouhý A, Somsen C, et al. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi highentropy alloy. Acta Mater, 2013, 61: 5743–5755
Senkov O N, Wilks G B, Miracle D B, et al. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 1758–1765
Wang F, Zhang Y, Chen G, et al. Tensile and compressive mechanical behavior of a CoCrCuFeNiAl0.5 high entropy alloy. Int J Mod Phys B, 2009, 23: 1254–1259
Lu Y, Dong Y, Guo S, et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci Rep, 2015, 4: 6200
Guo S, Ng C, Liu C T. Anomalous solidification microstructures in Co-free AlxCrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd, 2013, 557: 77–81
Jiang H, Zhang H, Huang T, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Co2MoxNi2VWx eutectic high entropy alloys. Mater Des, 2016, 109: 539–546
Jiang L, Lu Y, Dong Y, et al. Effects of Nb addition on structural evolution and properties of the CoFeNi2V0.5 high-entropy alloy. Appl Phys A, 2015, 119: 291–297
He F, Wang Z, Cheng P, et al. Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J Alloy Compd, 2016, 656: 284–289
Lu Y, Gao X, Jiang L, et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and neareutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater, 2017, 124: 143–150
Jiang L, Cao Z Q, Jie J C, et al. Effect of Mo and Ni elements on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the CoFeNixVMoy high entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd, 2015, 649: 585–590
Zhu J M, Fu H M, Zhang H F, et al. Microstructures and compressive properties of multicomponent AlCoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2010, 527: 6975–6979
Mishra A K, Samal S, Biswas K. Solidification behaviour of Ti-Cu-Fe-Co-Ni high entropy alloys. Trans Ind Inst Met, 2012, 65: 725–730
He F, Wang Z, Shang X, et al. Stability of lamellar structures in CoCr-FeNiNbx eutectic high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Mater Des, 2016, 104: 259–264
Guo S, Ng C, Liu C T. Sunflower-like solidification microstructure in a near-eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater Res Lett, 2013, 1: 228–232
Tsai K Y, Tsai M H, Yeh J W. Sluggish diffusion in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2013, 61: 4887–4897
Wani I S, Bhattacharjee T, Sheikh S, et al. Ultrafine-grained AlCoCr-FeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater Res Lett, 2016, 4: 174–179
Dong Y, Lu Y, Kong J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-component AlCrFeNiMox high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd, 2013, 573: 96–101
Boyer H E, Gall T L. Metals Handbook Desk Edition. Metals Park: American Society for Metals, 1985
Ma S G, Zhang Y. Effect of Nb addition on the microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2012, 532: 480–486
Tong C J, Chen Y L, Yeh J W, et al. Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall Mat Trans A, 2005, 36: 881–893
Ivashenko A V, Titov V V, Kovshev E I. Liquid crystalline compounds: III on applicability of Schröder-Van Laar equations to liquid crystals mixtures. Mol Crysts Liquid Crysts, 1976, 33: 195–200
Lee H-G. Chemical Thermodynamics for Metals and Materials. Place Published: Imperial College Press, 1999
Petzow G, Effenberg G. Ternary alloys. A comprehensive compendium of evaluated constitutional data and phase diagrams. 1991, 4
Dinsdale A T. SGTE data for pure elements. Calphad, 1991, 15: 317–425
Ternary Phase Diagrams for Materials Science. Place Published: Elsevier Science & Technology, 2001
Ye Y F, Wang Q, Lu J, et al. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater Today, 2016, 19: 349–362
He Q F, Ye Y F, Yang Y. The configurational entropy of mixing of metastable random solid solution in complex multicomponent alloys. J Appl Phys, 2016, 120: 154902
Wang D, Tan H, Li Y. Multiple maxima of GFA in three adjacent eutectics in Zr-Cu-Al alloy system—A metallographic way to pinpoint the best glass forming alloys. Acta Mater, 2005, 53: 2969–2979
Ding S, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. Combinatorial development of bulk metallic glasses. Nat Mater, 2014, 13: 494–500
Yeh J W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM, 2013, 65: 1759–1771
Ye Y F, Liu X D, Wang S, et al. The general effect of atomic size misfit on glass formation in conventional and high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2016, 78: 30–41
Takeuchi A, Amiya K, Wada T, et al. Entropies in alloy design for high-entropy and bulk glassy alloys. Entropy, 2013, 15: 3810–3821
Ye Y F, Wang Q, Lu J, et al. The generalized thermodynamic rule for phase selection in multicomponent alloys. Intermetallics, 2015, 59: 75–80
Guo S, Liu C T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog Nat Sci-Mater Int, 2011, 21: 433–446
Zhang Y, Lu Z P, Ma S G, et al. Guidelines in predicting phase formation of high-entropy alloys. MRC, 2014, 4: 57–62
Yang X, Zhang Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater Chem Phys, 2012, 132: 233–238
Zhang Y, Peng W. Microstructural control and properties optimization of high-entrop alloys. Procedia Eng, 2012, 27: 1169–1178
Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1–93
Mansoori G A, Carnahan N F, Starling K E, et al. Equilibrium thermodynamic properties of the mixture of hard spheres. J Chem Phys, 1971, 54: 1523–1525
Ye Y F, Liu C T, Yang Y. A geometric model for intrinsic residual strain and phase stability in high entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2015, 94: 152–161
Zhang Y, Zhou Y J, Lin J P, et al. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv Eng Mater, 2008, 10: 534–538
Troparevsky M C, Morris J R, Kent P R C, et al. Criteria for predicting the formation of single-phase high-entropy alloys. Phys Rev X, 2015, 5: 011041
Highmore R J, Greer A L. Eutectics and the formation of amorphous alloys. Nature, 1989, 339: 363–365
Turnbull D. Under what conditions can a glass be formed? Contemp Phys, 1969, 10: 473–488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Z., He, Q. & Yang, Y. Exploring the design of eutectic or near-eutectic multicomponent alloys: From binary to high entropy alloys. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 61, 159–167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9051-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9051-6