Abstract
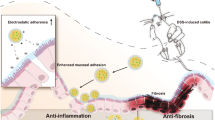
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term, recurrent inflammatory bowel disease for which no effective cure is yet available in the clinical setting. Repairing the barrier dysfunction of the colon and reducing intestinal inflammation are considered key objectives to cure UC. Here we demonstrate a novel therapeutic strategy based on a C60 fullerene suspension (C60FS) to treat dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced UC in an animal model. C60FS can repair the barrier dysfunction of UC and effectively promote the healing of ulcers; it also manifests better treatment effects compared with mesalazine enema. C60FS can reduce the numbers of basophils in the blood of UC rats and mast cells in the colorectal tissue, thereby effectively alleviating inflammation. The expression of H1R, H4R, and VEGFR2 receptors in colorectal tissues is inhibited by C60FS, and the levels of histamine and prostaglandin in the rat blood are reduced. This work presents a reliable strategy based on fullerene to cure UC and provides a novel guide for UC treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bharadwaj, S., Narula, N., Tandon, P., and Yaghoobi, M. (2018). Role of endoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Rep 6, 75–82.
Byelinska, I.V., Kuznietsova, H.M., Dziubenko, N.V., Lynchak, O.V., Rybalchenko, T.V., Prylutskyy, Y.I., Kyzyma, O.A., Ivankov, O., Rybalchenko, V.K., and Ritter, U. (2018). Effect of C60 fullerenes on the intensity of colon damage and hematological signs of ulcerative colitis in rats. Mater Sci Eng C 93, 505–517.
Carter, M.J., Lobo, A.J., and Travis, S.P.L. (2004). Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 53, v1–v16.
Chan, H.C.H., and Ng, S.C. (2017). Emerging biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol 52, 141–150.
Corman, M.L., Bergamaschi, R., Nicholls, R.J., and Fazio, V.W. (2013). Corman’s Colon and Rectal Surgery Sixth Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wikins.
Dias, C.C., Rodrigues, P.P., da Costa-Pereira, A., and Magro, F. (2015). Clinical predictors of colectomy in patients with ulcerative colitis: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J Crohns Colitis 9, 156–163.
Dresselhaus, M.S., Dresselhaus, G., and Eklund, P.C. (1996). Science of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes. New York: Academic Press.
Dukes, C.E., and Lockhart-mummery, H.E. (2010). Practical points in the pathology and surgical treatment of ulcerative colitis. A critical review. Br J Surg 45, 25–36.
Eswaran, S.V. (2018). Water soluble nanocarbon materials: a panacea for all? Curr Sci 114, 1846.
Farmer, R.G., Michener, W.M., and Mortimer, E.A. (1980). Studies of family history among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol 9, 271–278.
Faubion, W.A.Jr., LoftusJr., E.V., Harmsen, W.S., Zinsmeister, A.R., and Sandborn, W.J. (2001). The natural history of corticosteroid therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology 121, 255–260.
Ferreira, C.A., Ni, D., Rosenkrans, Z.T., and Cai, W. (2018). Scavenging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species with nanomaterials. Nano Res 11, 4955–4984.
Halenova, T.I., Vareniuk, I.M., Roslova, N.M., Dzerzhynsky, M.E., Savchuk, O.M., Ostapchenko, L.I., Prylutskyy, Y.I., Ritter, U., and Scharff, P. (2016). Hepatoprotective effect of orally applied water-soluble pristine C60 fullerene against CCl4-induced acute liver injury in rats. RSC Adv 6, 100046–100055.
Hattori, Y., and Seifert, R. (2017). Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease. Cham: Springer.
Hawkins, J.V., Emmel, E.L., Feuer, J.J., Nedelman, M.A., Harvey, C.J., Klein, H.J., Rozmiarek, H., Kennedy, A.R., Lichtenstein, G.R., and Billings, P.C. (1997). Protease activity in a hapten-induced model of ulcerative colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 42, 1969–1980.
Jensen, A.W., Wilson, S.R., and Schuster, D.I. (1996). Biological applications of fullerenes. Bioorg Med Chem 4, 767–779.
Kawakami, A., Tanaka, M., Ochiai, R., Naganuma, M., Kunisaki, R., and Kazuma, K. (2016). Difficulties in performing mesalazine enemas and factors related to discontinuation among patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol Nurs 40, 101–108.
Kucharzik, T., Dignass, A.U., Atreya, R., Bokemeyer, B., and Zemke, J. (2018). Aktualisierte S3-leitlinie colitis ulcerosa der deutschen gesellschaft für gastroenterologie, verdauungs- und stoffwechselkrankheiten (DGVS). Z Gastroent 56, 1087–1169.
Kuriyama, T., Yamato, M., Homma, J., Tobe, Y., and Tokushige, K. (2020). A novel rat model of inflammatory bowel disease developed using a device created with a 3D printer. Regen Ther 14, 1–10.
Laharie, D., Bourreille, A., Branche, J., Allez, M., Bouhnik, Y., Filippi, J., Zerbib, F., Savoye, G., Nachury, M., Moreau, J., et al. (2012). Ciclosporin versus infliximab in patients with severe ulcerative colitis refractory to intravenous steroids: a parallel, open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet 380, 1909–1915.
Lashner, B.A., Evans, A.A., Kirsner, J.B., and Hanauer, S.B. (1986). Prevalence and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in family members. Gastroenterology 91, 1396–1400.
Levine, A., Yerushalmi, B., Kori, M., Broide, E., Mozer-Glassberg, Y., Shaoul, R., Kolho, K.L., Shteyer, E., Shamaly, H., Ledder, O., et al. (2017). Mesalamine enemas for induction of remission in oral mesalamine-refractory pediatric ulcerative colitis: a prospective cohort study. J Crohns Colitis 11, 970–974.
Li, L., Zhen, M., Wang, H., Sun, Z., Jia, W., Zhao, Z., Zhou, C., Liu, S., Wang, C., and Bai, C. (2020). Functional gadofullerene nanoparticles trigger robust cancer immunotherapy based on rebuilding an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Nano Lett 20, 4487–4496.
Li, X., Zhen, M., Zhou, C., Deng, R., Yu, T., Wu, Y., Shu, C., Wang, C., and Bai, C. (2019). Gadofullerene nanoparticles reverse dysfunctions of pancreas and improve hepatic insulin resistance for type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment. ACS Nano 13, 8597–8608.
Lynchak, O.V., Prylutskyy, Y.I., Rybalchenko, V.K., Kyzyma, O.A., Soloviov, D., Kostjukov, V.V., Evstigneev, M.P., Ritter, U., and Scharff, P. (2017). Comparative analysis of the antineoplastic activity of C60 fullerene with 5-fluorouracil and pyrrole derivative in vivo. Nanoscale Res Lett 12, 1–6.
Mardini, H.E. (2005). Azathioprine-induced pancreatitis in Crohn’s disease: a smoking gun or guilt by association. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21, 195.
Mayberry, J.F., and Rhodes, J. (1984). Epidemiological aspects of Crohn’s disease: a review of the literature. Gut 25, 886–899.
Navaneethan, U., and Shen, B. (2010). Hepatopancreatobiliary manifestations and complications associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16, 1598–1619.
Ng, S.C., and Kamm, M.A. (2009). Therapeutic strategies for the management of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15, 935–950.
Ordás, I., Eckmann, L., Talamini, M., Baumgart, D.C., and Sandborn, W.J. (2012). Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 380, 1606–1619.
Orholm, M., Munkholm, P., Langholz, E., Nielsen, O.H., Sørensen, T.I.A., and Binder, V. (1991). Familial occurrence of inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 324, 84–88.
Pellino, G., and Selvaggi, F. (2015). From colon-sparing techniques to pelvic ileal pouch: history and evolution of surgery for ulcerative colitis. Eur Surg 47, 81–90.
Prylutska, S.V., Grynyuk, I.I., Matyshevska, O.P., Prylutskyy, Y.I., Ritter, U., and Scharff, P. (2008). Anti-oxidant properties of C60 fullerenes in vitro. Fullerenes Nanotubes Carbon Nanostruct 16, 698–705.
Prylutska, S., Grynyuk, I., Matyshevska, O., Prylutskyy, Y., Evstigneev, M., Scharff, P., and Ritter, U. (2014). C60 fullerene as synergistic agent in tumor-inhibitory Doxorubicin treatment. Drugs R D 14, 333–340.
Prylutskyy, Y.I., Vereshchaka, I.V., Maznychenko, A.V., Bulgakova, N.V., Gonchar, O.O., Kyzyma, O.A., Ritter, U., Scharff, P., Tomiak, T., Nozdrenko, D.M., et al. (2017). C60 fullerene as promising therapeutic agent for correcting and preventing skeletal muscle fatigue. J Nanobiotechnol 15, 1–2.
Purrmann, J., Bertrams, J., Borchard, F., Miller, B., Cleveland, S., Stolze, T., and Strohmeyer, G. (1986). Monozygotic triplets with Crohn’s disease of the colon. Gastroenterology 91, 1553–1559.
Sachar, D.B., Auslander, M.O., and Walfish, J.S. (1980). Aetiological theories of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol 9, 231–257.
Schirmer, B., Lindemann, L., Bittkau, K.S., Isaev, R., Bøsche, D., Juchem, M., Seifert, R., and Neumann, D. (2020). Mouse colonic epithelial cells functionally express the histamine H4 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 373, 167–174.
Shale, M., Kanfer, E., Panaccione, R., and Ghosh, S. (2008). Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 57, 1639–1641.
Simmonds, N.J., and Rampton, D.S. (1993). Inflammatory bowel disease—a radical view. Gut 34, 865–868.
Snook, J. (1990). Are the inflammatory bowel diseases autoimmune disorders? Gut 31, 961–963.
Steele, S.R., Hull, T.L., Hyman, N., Maykel, J.A., Read, T.E., and Whitlow, C.B. (2016). The Ascrs Textbook of Colon and Rectal Surgery. Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing.
Sutherland, L., and Macdonald, J.K. (2006). Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 19, CD000543.
Wang, T., Lu, H., Li, F., and Zhang, Q. (2021). Effect of kangfuxin liquid enema combined with mesalazine on gestational outcomes and quality of life in child-bearing female with active ulcerative colitis. Medicine 100, e23915.
Wehkamp, J., and Stange, E.F. (2018). Recent advances and emerging therapies in the non-surgical management of ulcerative colitis. F1000Research 7, 1207.
Weterman, I.T., and Peña, A.S. (1984). Familial incidence of Crohn’s disease in the netherlands and a review of the literature. Gastroenterology 86, 449–452.
Zhang, J., Xu, J., Ma, H., Bai, H., Liu, L., Shu, C., Li, H., Wang, S., and Wang, C. (2019). Designing an amino-fullerene derivative C70-(EDA)8 to fight superbacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11, 14597–14607.
Zhou, C., Zhen, M., Yu, M., Li, X., Yu, T., Liu, J., Jia, W., Liu, S., Li, L., Li, J., et al. (2020). Gadofullerene inhibits the degradation of apolipoprotein B100 and boosts triglyceride transport for reversing hepatic steatosis. Sci Adv 6, eabc1586.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51832008, 51772300, and 52072374). We thank Beijing FULLCAN Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for providing valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, X., Zhao, Z., Li, H. et al. Fullerene nanoparticles for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 1146–1156 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2001-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2001-0