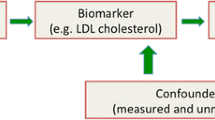
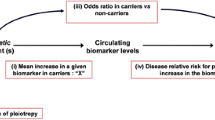
Abstract
Epidemiological research has revealed a galaxy of biomarkers, such as genes, molecules or traits, which are associated with increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVD). However, the etiological basis remains poorly characterized. Mendelian randomization (MR) involves the use of observational genetic data to ascertain the roles of disease-associated risk factors and, in particular, differentiate those reflecting the presence or severity of a disease from those contributing causally to a disease. Over the past decade, MR has evolved into a fruitful approach to clarifying the causal relation of a biomarker with ASCVD and to verifying potential therapeutic targets for ASCVD. In this review, we selected high-quality MR studies on ASCVD, examined the causal relationship of a series of biomarkers with ASCVD, and elucidated the role of MR in validating biomarkers as a therapeutic target by comparing the results from MR studies and randomized clinical trials (RCTs) for the treatment of ASCVD. The good agreement between the results derived by MR and RCTs suggests that MR could be performed as a screening process before novel drug development. However, when designing and interpreting a MR study, the assumptions and limitations inherent in this approach should be taken into account. Novel methodological developments, such as sensitivity analysis, will help to strengthen the validity of MR studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, O.S., Morris, J.A., Mujammami, M., Forgetta, V., Leong, A., Li, R., Turgeon, M., Greenwood, C.M.T., Thanassoulis, G., Meigs, J.B., et al. (2015). A Mendelian randomization study of the effect of type-2 diabetes on coronary heart disease. Nat Commun 6, 7060.
Au Yeung, S.L., Lin, S.L., Li, A.M., and Schooling, C.M. (2016). Birth weight and risk of ischemic heart disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Sci Rep 6, 38420.
Benn, M., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., McCarthy, M.I., Jensen, G.B., Grande, P., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2012). Nonfasting glucose, ischemic heart disease, and myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 59, 2356–2365.
Bergholdt, H.K.M., Nordestgaard, B.G., Varbo, A., and Ellervik, C. (2015). Milk intake is not associated with ischaemic heart disease in observational or Mendelian randomization analyses in 98529 Danish adults. Int J Epidemiol 44, 587–603.
Bochud, M., and Rousson, V. (2010). Usefulness of Mendelian randomization in observational epidemiology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7, 711–728.
Borges, M.C., Lawlor, D.A., de Oliveira, C., White, J., Horta, B.L., and Barros, A.J.D. (2016). Role of adiponectin in coronary heart disease risk. Circ Res 119, 491–499.
Brendum-Jacobsen, P., Benn, M., Afzal, S., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2015). No evidence that genetically reduced 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with increased risk of ischaemic heart disease or myocardial infarction: a Mendelian randomization study. Int J Epidemiol 44, 651–661.
Burgess, S., Freitag, D.F., Khan, H., Gorman, D.N., and Thompson, S.G. (2014). Using multivariable mendelian randomization to disentangle the causal effects of lipid fractions. PLoS ONE 9, e108891.
Burgess, S., Timpson, N.J., Ebrahim, S., and Davey Smith, G. (2015). Mendelian randomization: where are we now and where are we going? Int J Epidemiol 44, 379–388.
Burgess, S., and Harshfield, E. (2016). Mendelian randomization to assess causal effects of blood lipids on coronary heart disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 23, 124–130.
Burgess, S., Bowden, J., Fall, T., Ingelsson, E., and Thompson, S.G. (2017). Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from Mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants. Epidemiology 28, 30–42.
Björkegren, J.L.M., Kovacic, J.C., Dudley, J.T., and Schadt, E.E. (2015). Genome-wide significant loci: How important are they? J Am Coll Cardiol 65, 830–845.
C Reactive Protein Coronary Heart Disease Genetics Collaboration (CCGC). (2011). Association between C reactive protein and coronary heart disease: mendelian randomisation analysis based on individual participant data. BMJ 342, d548..
Cannon, C.P., Blazing, M.A., Giugliano, R.P., McCagg, A., White, J.A., Theroux, P., Darius, H., Lewis, B.S., Ophuis, T.O., Jukema, J.W., et al. (2015). Ezetimibe added to statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 372, 2387–2397.
Casas, J.P., Ninio, E., Panayiotou, A., Palmen, J., Cooper, J.A., Ricketts, S. L., Sofat, R., Nicolaides, A.N., Corsetti, J.P., Fowkes, F.G.R., et al. (2010). PLA2G7 genotype, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity, and coronary heart disease risk in 10494 cases and 15624 controls of European ancestry. Circulation 121, 2284–2293.
Codd, V., Nelson, C.P., Albrecht, E., Mangino, M., Deelen, J., Buxton, J.L., Hottenga, J.J., Fischer, K., Esko, T., Surakka, I., et al. (2013). Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat Genet 45, 422–427.
Cole, C.B., Nikpay, M., Stewart, A.F.R., and McPherson, R. (2016). Increased genetic risk for obesity in premature coronary artery disease. Eur J Hum Genet 24, 587–591.
CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. (2008). Collaborative pooled analysis of data on C-reactive protein gene variants and coronary disease: judging causality by Mendelian randomisation. Eur J Epidemiol 23, 531–540.
Dale, C.E., Fatemifar, G., Palmer, T.M., White, J., Prieto-Merino, D., Zabaneh, D., Engmann, J.E.L., Shah, T., Wong, A., Warren, H.R., et al. (2017). Causal associations of adiposity and body fat distribution with coronary heart disease, stroke subtypes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 135, 2373–2388.
Davey Smith, G., and Hemani, G. (2014). Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet 23, R89–R98.
Do, R., Willer, C.J., Schmidt, E.M., Sengupta, S., Gao, C., Peloso, G.M., Gustafsson, S., Kanoni, S., Ganna, A., Chen, J., et al. (2013). Common variants associated with plasma triglycerides and risk for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 45, 1345–1352.
Elliott, P., Chambers, J.C., Zhang, W., Clarke, R., Hopewell, J.C., Peden, J. F., Erdmann, J., Braund, P., Engert, J.C., Bennett, D., et al. (2009). Genetic loci associated with C-reactive protein levels and risk of coronary heart disease. JAMA 302, 37–48.
Ference, B.A., Yoo, W., Alesh, I., Mahajan, N., Mirowska, K.K., Mewada, A., Kahn, J., Afonso, L., Williams Sr, K.A., and Flack, J.M. (2012). Effect of long-term exposure to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol beginning early in life on the risk of coronary Heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 60, 2631–2639.
Ference, B.A., Majeed, F., Penumetcha, R., Flack, J.M., and Brook, R.D. (2015). Effect of naturally random allocation to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on the risk of coronary heart disease mediated by polymorphisms in NPC1L1, HMGCR, or both. J Am Coll Cardiol 65, 1552–1561.
Ference, B.A., Robinson, J.G., Brook, R.D., Catapano, A.L., Chapman, M. J., Neff, D.R., Voros, S., Giugliano, R.P., Davey Smith, G., Fazio, S., et al. (2016). Variation in PCSK9 and HMGCR and risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. N Engl J Med 375, 2144–2153.
Fernández-Solà, J. (2015). Cardiovascular risks and benefits of moderate and heavy alcohol consumption. Nat Rev Cardiol 12, 576–587.
Fisher, E., Stefan, N., Saar, K., Drogan, D., Schulze, M.B., Fritsche, A., Joost, H.G., Haring, H.U., Hubner, N., Boeing, H., et al. (2009). Association of AHSG gene polymorphisms with fetuin-A plasma levels and cardiovascular diseases in the EPIC-Potsdam Study. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2, 607–613.
Frikke-Schmidt, R., Nordestgaard, B.G., Stene, M.C.A., Sethi, A.A., Remaley, A.T., Schnohr, P., Grande, P., and Tybjaerg-Hansen, A. (2008). Association of loss-of-function mutations in the ABCA1 gene with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and risk of ischemic heart disease. JAMA 299, 2524–2532.
Gaudet, D., Alexander, V.J., Baker, B.F., Brisson, D., Tremblay, K., Singleton, W., Geary, R.S., Hughes, S.G., Viney, N.J., Graham, M.J., et al. (2015). Antisense inhibition of apolipoprotein C-III in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med 373, 438–447.
Gill, D., Del Greco M., F., Walker, A.P., Srai, S.K.S., Laffan, M.A., and Minelli, C. (2017). The effect of iron status on risk of coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37, 1788–1792.
Grundy, S.M., Cleeman, J.I., Merz, C.N.B., Brewer, H.B., Clark, L.T., Hunninghake, D.B., Pasternak, R.C., Smith, S.C., Stone, N.J., Stone, N. J., et al. (2004). Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation 110, 227–239.
Guardiola, M., Exeter, H.J., Perret, C., Folkersen, L., Van’t Hooft, F., Eriksson, P., Franco-Cereceda, A., Paulsson-Berne, G., Palmen, J., Li, K.W., et al. (2015). PLA2G10 gene variants, sPLA2 activity, and coronary heart disease risk. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 8, 356–362.
Haase, C.L., Tybjœrg-Hansen, A., Ali Qayyum, A., Schou, J., Nordestgaard, B.G., and Frikke-Schmidt, R. (2012). LCAT, HDL cholesterol and ischemic cardiovascular disease: A Mendelian randomization study of HDL cholesterol in 54,500 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97, E248–E256.
Hägg, S., Fall, T., Ploner, A., Mägi, R., Fischer, K., Draisma, H.H.M., Kals, M., de Vries, P.S., Dehghan, A., Willems, S.M., et al. (2015). Adiposity as a cause of cardiovascular disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Int J Epidemiol 44, 578–586.
Han, C., Liu, F., Yang, X., Chen, J., Li, J., Cao, J., Li, Y., Shen, C., Yu, L., Liu, Z., et al. (2018). Ideal cardiovascular health and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among Chinese adults: the China-PAR project. Sci China Life Sci 61, 504–514.
Helgadottir, A., Gretarsdottir, S., Thorleifsson, G., Hjartarson, E., Sigurdsson, A., Magnusdottir, A., Jonasdottir, A., Kristjansson, H., Sulem, P., Oddsson, A., et al. (2016). Variants with large effects on blood lipids and the role of cholesterol and triglycerides in coronary disease. Nat Genet 48, 634–639.
Hingorani, A.D., and Casas, J.P. (2012). The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 379, 1214–1224.
HPS3/TIMI55-REVEAL Collaborative. (2017). Effects of anacetrapib in patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease. N Engl J Med 377, 1217–1227.
Holmes, M.V., Asselbergs, F.W., Palmer, T.M., Drenos, F., Lanktree, M.B., Nelson, C.P., Dale, C.E., Padmanabhan, S., Finan, C., Swerdlow, D.I., et al. (2015). Mendelian randomization of blood lipids for coronary heart disease. Eur Heart J 36, 539–550.
Holmes, M.V., Dale, C.E., Zuccolo, L., Silverwood, R.J., Guo, Y., Ye, Z., Prieto-Merino, D., Dehghan, A., Trompet, S., Wong, A., et al. (2014). Association between alcohol and cardiovascular disease: Mendelian randomisation analysis based on individual participant data. BMJ 349, g4164.
IL6R Genetics Consortium Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. (2012). Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 9822, 1205–1213.
Jang, Y., Waterworth, D., Lee, J.E., Song, K., Kim, S., Kim, H.S., Park, K. W., Cho, H.J., Oh, I.Y., Park, J.E., et al. (2011). Carriage of the V279F null allele within the gene encoding Lp-PLA2 is protective from coronary artery disease in South Korean males. PLoS ONE 6, e18208.
Keavney, B., Danesh, J., Parish, S., Palmer, A., Clark, S., Youngman, L., Delépine, M., Lathrop, M., Peto, R., and Collins, R. (2006). Fibrinogen and coronary heart disease: test of causality by ‘Mendelian randomization’. Int J Epidemiology 35, 935–943.
Jansen, H., Samani, N.J., and Schunkert, H. (2014). Mendelian randomization studies in coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 35, 1917–1924.
Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., and Chen, Z.Y. (2011). Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cardiovascular risk factors and prognosis in angina pectoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 415, 99–103.
Jørgensen, A.B., Frikke-Schmidt, R., West, A.S., Grande, P., Nordestgaard, B.G., and Tybjœrg-Hansen, A. (2013). Genetically elevated non-fasting triglycerides and calculated remnant cholesterol as causal risk factors for myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 34, 1826–1833.
Kaess, B.M., Preis, S.R., Lieb, W., Beiser, A.S., Yang, Q., Chen, T.C., Hengstenberg, C., Erdmann, J., Schunkert, H., Seshadri, S., et al. (2015). Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the community. J Am Heart Assoc 4, e001544.
Kamstrup, P.R., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., Steffensen, R., and Nordestgaard, B. G. (2009). Genetically elevated lipoprotein(a) and increased risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA 301, 2331–2339.
Kastelein, J.J.P., Akdim, F., Stroes, E.S.G., Zwinderman, A.H., Bots, M.L., Stalenhoef, A.F.H., Visseren, F.L.J., Sijbrands, E.J.G., Trip, M.D., Stein, E.A., et al. (2008). Simvastatin with or without Ezetimibe in familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 358, 1431–1443.
Keenan, T., Zhao, W., Rasheed, A., Ho, W.K., Malik, R., Felix, J.F., Young, R., Shah, N., Samuel, M., Sheikh, N., et al. (2016). Causal assessment of serum urate levels in cardiometabolic diseases through a Mendelian randomization study. J Am Coll Cardiol 67, 407–416.
Kobylecki, C.J., Afzal, S., Davey Smith, G., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2015). Genetically high plasma vitamin C, intake of fruit and vegetables, and risk of ischemic heart disease and all-cause mortality: a Mendelian randomization study. Am J Clin Nutrit 101, 1135–1143.
Lawlor, D.A., Nordestgaard, B.G., Benn, M., Zuccolo, L., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., and Davey Smith, G. (2013). Exploring causal associations between alcohol and coronary heart disease risk factors: findings from a Mendelian randomization study in the Copenhagen General Population Study. Eur Heart J 34, 2519–2528.
Lieb, W., Jansen, H., Loley, C., Pencina, M.J., Nelson, C.P., Newton-Cheh, C., Kathiresan, S., Reilly, M.P., Assimes, T.L., Boerwinkle, E., et al. (2013). Genetic predisposition to higher blood pressure increases coronary artery disease risk. Hypertension 61, 995–1001.
Linsel-Nitschke, P., Götz, A., Erdmann, J., Braenne, I., Braund, P., Hengstenberg, C., Stark, K., Fischer, M., Schreiber, S., El Mokhtari, N. E., et al. (2008). Lifelong reduction of LDL-cholesterol related to a common variant in the LDL-receptor gene decreases the risk of coronary artery disease—a Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS ONE 3, e2986.
Lloyd-Jones, D.M., Morris, P.B., Ballantyne, C.M., Birtcher, K.K., Daly, D. D. Jr., DePalma, S.M., Minissian, M.B., Orringer, C.E., and Smith, S.C. Jr. (2016). ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on the role of non-statin therapies for LDL-Cholesterol lowering in the management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. J Am Coll Cardiol 68, 92–125.
Madamanchi, N.R., Tchivilev, I., and Runge, M.S. (2006). Genetic markers of oxidative stress and coronary atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 8, 177–183.
Manousaki, D., Mokry, L.E., Ross, S., Goltzman, D., and Richards, J.B. (2016). Mendelian randomization studies do not support a role for vitamin D in coronary artery disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 9, 349356.
Merino, J., Leong, A., Posner, D.C., Porneala, B., Masana, L., Dupuis, J., and Florez, J.C. (2017). Genetically driven hyperglycemia increases risk ofcoronary artery disease separately from type 2 diabetes. Dia Care 40, 687–693.
Mokry, L.E., Ahmad, O., Forgetta, V., Thanassoulis, G., and Richards, J.B. (2015). Mendelian randomisation applied to drug development in cardiovascular disease: a review. J Med Genet 52, 71–79.
Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium Investigators. (2014). Inactivating mutations in NPC1L1 and protection from coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 371, 2072–2082.
Nelson, C.P., Hamby, S.E., Saleheen, D., Hopewell, J.C., Zeng, L., Assimes, T.L., Kanoni, S., Willenborg, C., Burgess, S., Amouyel, P., et al. (2015). Genetically determined height and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 372, 1608–1618.
Nicholls, S.J., Cavender, M.A., Kastelein, J.J.P., Schwartz, G., Waters, D. D., Rosenson, R.S., Bash, D., and Hislop, C. (2012). Inhibition of secretory phospholipase A2 in patients with acute coronary syndromes: rationale and design of the vascular inflammation suppression to treat acute coronary syndrome for 16 weeks (VISTA-16) trial. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 26, 71–75.
Nüesch, E., Dale, C., Palmer, T.M., White, J., Keating, B.J., van Iperen, E. P., Goel, A., Padmanabhan, S., Asselbergs, F.W., Asselbergs, F.W., etal. (2016). Adult height, coronary heart disease and stroke: a multi-locus Mendelian randomization meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiology 45, 19271937.
Palmer, T.M., Nordestgaard, B.G., Benn, M., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., Davey Smith, G., Lawlor, D.A., and Timpson, N.J. (2013). Association of plasma uric acid with ischaemic heart disease and blood pressure: Mendelian randomisation analysis of two large cohorts. BMJ 347, f4262.
Polfus, L.M., Gibbs, R.A., and Boerwinkle, E. (2015). Coronary heart disease and genetic variants with low phospholipase A2 activity. N Engl J Med 372, 295–296.
Polisecki, E., Peter, I., Simon, J.S., Hegele, R.A., Robertson, M., Ford, I., Shepherd, J., Packard, C., Jukema, J.W., de Craen, A.J.M., et al. (2010). Genetic variation at the NPC1L1 gene locus, plasma lipoproteins, and heart disease risk in the elderly. J Lipid Res 51, 1201–1207.
Relton, C.L., and Davey Smith, G. (2015). Mendelian randomization: applications and limitations in epigenetic studies. Epigenomics 7, 12391243.
Ridker, P.M., Everett, B.M., Thuren, T., MacFadyen, J.G., Chang, W.H., Ballantyne, C., Fonseca, F., Nicolau, J., Koenig, W., Anker, S.D., et al. (2017). Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med 377, 1119–1131.
Ringstedt, T., Kraemer, R., Hahn, R., Wang, S., Ibanez, C.F., Rafii, S., and Hempstead, B.L. (2000). Brain derived neurotrophic factor is an endothelial cell survival factor required for intramyocardial vessel stabilization. Development 127, 4531–4540.
Ross, S., Gerstein, H.C., Eikelboom, J., Anand, S.S., Yusuf, S., and Paré, G. (2015). Mendelian randomization analysis supports the causal role of dysglycaemia and diabetes in the risk of coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 36, 1454–1462.
Sabatine, M.S., Giugliano, R.P., Wiviott, S.D., Raal, F.J., Blom, D.J., Robinson, J., Ballantyne, C.M., Somaratne, R., Legg, J., Wasserman, S. M., et al. (2015). Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med 372, 1500–1509.
Sabatine, M.S., Giugliano, R.P., Keech, A.C., Honarpour, N., Wiviott, S.D., Murphy, S.A., Kuder, J.F., Wang, H., Liu, T., Wasserman, S.M., et al. (2017). Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 376, 1713–1722.
Shah, S., Casas, J.P., Drenos, F., Whittaker, J., Deanfield, J., Swerdlow, D. I., Holmes, M.V., Kivimaki, M., Langenberg, C., Wareham, N., et al. (2013). Causal relevance of blood lipid fractions in the development of carotid atherosclerosis. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 6, 63–72.
Stender, S., Frikke-Schmidt, R., Nordestgaard, B.G., Grande, P., and Tybjaerg-Hansen, A. (2013). Genetically elevated bilirubin and risk of ischaemic heart disease: three Mendelian randomization studies and a meta-analysis. J Intern Med 273, 59–68.
Svensson-Färbom, P., Almgren, P., Hedblad, B., Engström, G., Persson, M., Christensson, A., and Melander, O. (2015). Cystatin C is not causally related to coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 10, e0129269.
Tang, W.H.W., Hartiala, J., Fan, Y., Wu, Y., Stewart, A.F.R., Erdmann, J., Kathiresan, S., Kathiresan, S., Roberts, R., McPherson, R., et al. (2012). Clinical and genetic association of serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities with cardiovascular risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32, 2803–2812.
Thomsen, M., Varbo, A., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2014). Low nonfasting triglycerides and reduced all-cause mortality: a Mendelian randomization study. Clin Chem 60, 737–746.
Trenkwalder, T., Kessler, T., Schunkert, H., and Erdmann, J. (2015). Genetics of coronary artery disease: Short people at risk? Expert Rev Cardiovascular Ther 13, 1169–1172.
Triglyceride Coronary Disease Genetics Consortium and Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. (2010). Triglyceride-mediated pathways and coronary disease: collaborative analysis of 101 studies. Lancet 375, 1634–1639.
van der Laan, S.W., Fall, T., Soumaré, A., Teumer, A., Sedaghat, S., Baumert, J., Zabaneh, D., van Setten, J., Isgum, I., Galesloot, T.E., et al. (2016). Cystatin C and cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 68, 934–945.
Vandenbroucke, J.P. (2004). When are observational studies as credible as randomised trials? Lancet 363, 1728–1731.
van Meurs, J.B.J., Pare, G., Schwartz, S.M., Hazra, A., Tanaka, T., Vermeulen, S.H., Cotlarciuc, I., Yuan, X., Mälarstig, A., Bandinelli, S., et al. (2013). Common genetic loci influencing plasma homocysteine concentrations and their effect on risk of coronary artery disease. Am J Clin Nutrit 98, 668–676.
Varbo, A., Benn, M., Tybjœrg-Hansen, A., Jørgensen, A.B., Frikke-Schmidt, R., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2013). Remnant cholesterol as a causal risk factor for ischemic heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 61, 427–436.
Varbo, A., Benn, M., Tybjœrg-Hansen, A., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2013). Elevated remnant cholesterol causes both low-grade inflammation and ischemic heart disease, whereas elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol causes ischemic heart disease without inflammation. Circulation 128, 1298–1309.
Voight, B.F., Peloso, G.M., Orho-Melander, M., Frikke-Schmidt, R., Barbalic, M., Jensen, M.K., Hindy, G., Hólm, H., Ding, E.L., Johnson, T., et al. (2012). Plasma HDL cholesterol and risk of myocardial infarction: A mendelian randomisation study. Lancet 380, 572–580.
White, J., Sofat, R., Hemani, G., Shah, T., Engmann, J., Dale, C., Shah, S., Kruger, F.A., Giambartolomei, C., Swerdlow, D.I., et al. (2016). Plasma urate concentration and risk of coronary heart disease: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 4, 327–336.
Wu, Z., Lou, Y., Qiu, X., Liu, Y., Lu, L., Chen, Q., and Jin, W. (2014). Association of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) gene polymorphism, high density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis using a Mendelian randomization approach. BMC Med Genet 15, 118.
Würtz, P., Kangas, A.J., Soininen, P., Lehtimäki, T., Kähönen, M., Viikari, J.S., Raitakari, O.T., Järvelin, M.R., Davey Smith, G., and Ala-Korpela, M. (2013). Lipoprotein subclass profiling reveals pleiotropy in the genetic variants of lipid risk factors for coronary heart disease. J Am College Cardiology 62, 1906–1908.
Yaghootkar, H., Lamina, C., Scott, R.A., Dastani, Z., Hivert, M.F., Warren, L.L., Stancáková, A., Buxbaum, S.G., Lyytikäinen, L.P., Henneman, P., et al. (2013). Mendelian randomization studies do not support a causal role for reduced circulating adiponectin levels in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 62, 3589–3598.
Yang, Q., Bailey, L., Clarke, R., Flanders, W.D., Liu, T., Yesupriya, A., Khoury, M.J., and Friedman, J.M. (2012). Prospective study of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) variant C677T and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among 6000 US adults. Am J Clin Nutrit 95, 1245–1253.
Yau, C., and Campbell, K. (2019). Bayesian statistical learning for big data biology. Biophys Rev 11, 95–102.
Zacho, J., Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., Jensen, J.S., Grande, P., Sillesen, H., and Nordestgaard, B.G. (2008). Genetically elevated C-reactive protein and ischemic vascular disease. N Engl J Med 359, 1897–1908.
Zhao, J.V., and Schooling, C.M. (2016). Endogenous androgen exposures and ischemic heart disease, a separate sample Mendelian randomization study. Int J Cardiol 222, 940–945.
Zhao, J.V., and Schooling, C.M. (2017). Homocysteine-reducing B vitamins and ischemic heart disease: a separate-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 71, 267–273.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (81530014), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370410, 81425004, 81770442, 81571689) and the Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Hao, P., Liu, Q. et al. Mendelian randomization studies on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: evidence and limitations. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 758–770 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-9537-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-9537-4