Abstract
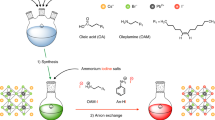
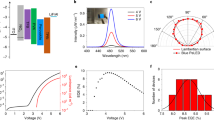
Perovskite materials can realize the transition from green light to full-visible light spectrum by halogen anion exchange. Here, we designed an in-situ solid-phase anion-exchange method combined with inkjet printing to achieve full-color perovskite quantum dot light-emitting diodes (PeQD-LEDs). It was revealed that, in addition to the concentration, the anion-exchange rate was affected by the dielectric constant of the anion-exchange medium solvent. Without destroying the PeQD film, the higher the dielectric constant of the solvent, the faster the reaction rate. And at the same time, the solvent with higher dielectric constant will cause more defects, so the morphology, structure and properties of the perovskite films varied with solvents. The chain length of amine salts in anion-exchange medium solute also played a key role in the stability of electroluminescence spectra. The obtained blue-light devices had a maximum EQE of 4.6% at 481 nm and 6.6% at 493 nm prepared by spin-coating. For inkjet printing, instead of printing red-, green- and blue-luminescent materials, we printed halogen-containing materials to achieve the in-situ solid-phase anion-exchange with underlying PeQDs, and the inkjet-printed full-color device showed the current efficiency of 0.78 cd A−1. The method to achieve full-color devices by inkjet-printing halogen-containing materials can not only simplify the process, but also broaden the range of material selection, making the ink preparation more selective.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kovalenko MV, Protesescu L, Bodnarchuk MI. Science, 2017, 358: 745–750
Lin K, Wei Z. Sci China Chem, 2023, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-023-1568-0
Zhang F, Zhong H, Chen C, Wu X, Hu X, Huang H, Han J, Zou B, Dong Y. ACS Nano, 2015, 9: 4533–4542
Wang KH, Zhu BS, Yao JS, Yao HB. Sci China Chem, 2018, 61: 1047–1061
Chiba T, Hayashi Y, Ebe H, Hoshi K, Sato J, Sato S, Pu YJ, Ohisa S, Kido J. Nat Photon, 2018, 12: 681–687
Dong Y, Wang YK, Yuan F, Johnston A, Liu Y, Ma D, Choi MJ, Chen B, Chekini M, Baek SW, Sagar LK, Fan J, Hou Y, Wu M, Lee S, Sun B, Hoogland S, Quintero-Bermudez R, Ebe H, Todorovic P, Dinic F, Li P, Kung HT, Saidaminov MI, Kumacheva E, Spiecker E, Liao LS, Voznyy O, Lu ZH, Sargent EH. Nat Nanotechnol, 2020, 15: 668–674
Zhu H, Tong G, Li J, Xu E, Tao X, Sheng Y, Tang J, Jiang Y. Adv Mater, 2022, 34: 2205092
Kim JS, Heo JM, Park GS, Woo SJ, Cho C, Yun HJ, Kim DH, Park J, Lee SC, Park SH, Yoon E, Greenham NC, Lee TW. Nature, 2022, 611: 688–694
Jiang Y, Sun C, Xu J, Li S, Cui M, Fu X, Liu Y, Liu Y, Wan H, Wei K, Zhou T, Zhang W, Yang Y, Yang J, Qin C, Gao S, Pan J, Liu Y, Hoogland S, Sargent EH, Chen J, Yuan M. Nature, 2022, 612: 679–684
Akkerman QA, D’Innocenzo V, Accornero S, Scarpellini A, Petrozza A, Prato M, Manna L. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137: 10276–10281
Nedelcu G, Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk MI, Grotevent MJ, Kovalenko MV. Nano Lett, 2015, 15: 5635–5640
Zhou Y, Fang T, Liu G, Xiang H, Yang L, Li Y, Wang R, Yan D, Dong Y, Cai B, Zeng H. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31: 2106871
Yoon YJ, Lee KT, Lee TK, Kim SH, Shin YS, Walker B, Park SY, Heo J, Lee J, Kwak SK, Kim GH, Kim JY. Joule, 2018, 2: 2105–2116
Liu Y, Zhang Y. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13: 47072–47080
Yao J, Wang L, Wang K, Yin Y, Yang J, Zhang Q, Yao H. Sci Bull, 2020, 65: 1150–1153
Yoon YJ, Shin YS, Jang H, Son JG, Kim JW, Park CB, Yuk D, Seo J, Kim GH, Kim JY. Nano Lett, 2021, 21: 3473–3479
Kim J, Seo KW, Lee SJ, Kim K, Kim C, Lee JY. Adv Sci, 2022, 9: 2200073
He S, Lee HB, Kumar N, Ko KJ, Song M, Kim W, Kang JW. Mater Today Chem, 2022, 26: 101012
Ahn J, Lee YM, Jeon J, Bang J, Jeon S, Woo HK, Lee SY, Bae JH, Kim W, Choi YK, Kim SJ, Oh SJ. Adv Mater Technologies, 2022, 7: 2200031
Hoshi K, Chiba T, Sato J, Hayashi Y, Takahashi Y, Ebe H, Ohisa S, Kido J. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10: 24607–24612
Chiba T, Hoshi K, Pu YJ, Takeda Y, Hayashi Y, Ohisa S, Kawata S, Kido J. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9: 18054–18060
Guo Y, Apergi S, Li N, Chen M, Yin C, Yuan Z, Gao F, Xie F, Brocks G, Tao S, Zhao N. Nat Commun, 2021, 12: 644
Lin K, Xing J, Quan LN, de Arquer FPG, Gong X, Lu J, Xie L, Zhao W, Zhang D, Yan C, Li W, Liu X, Lu Y, Kirman J, Sargent EH, Xiong Q, Wei Z. Nature, 2018, 562: 245–248
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key R&D Plan of Guangdong Province (2022B0303010001), the National Natural Science Foundations of China (52073104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supporting information The supporting information is available online at https://chem.scichina.com and https://link.springer.com/journal/11426. The supporting materials are published as submitted, without typesetting or editing. The responsibility for scientific accuracy and content remains entirely with the authors.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wang, J., Wang, J. et al. In-situ solid-phase anion-exchange full-color perovskite light-emitting devices. Sci. China Chem. 66, 1707–1713 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-023-1631-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-023-1631-8