Abstract
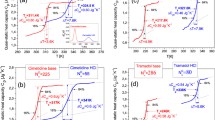
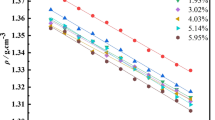
In this work, 16 kinds of [FeCl4]--based magnetic ionic liquids (ILs) with different cation structures have been designed and synthesized, and their structures are characterized by IR and Raman spectroscopy. Then the lower critical solution temperature (LCST)-type phase behavior of these magnetic ILs in water is investigated as a function of concentration. It is shown that cation structure, alkyl chain length and molar ratio of FeCl3/chloride IL have a significant influence on the LCST of the mixtures. The phase separation temperature can be tuned efficiently by these factors. Meanwhile, the LCST-type phase separation process is also investigated by dynamic light scattering. The results support the mechanism that the hydrogen bonds of the [FeCl4]- anion with water have been gradually disrupted to form ILs aggregates with increasing temperature. In addition, the stability of the ILs in water is also examined in some details. These LCST-type phase separation systems may have potential applications in extraction and separation techniques at room temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wasserscheid P, Welton T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis. 2nd Ed. Weinheim: John Wiley-VCH, 2007. 1–6
Hallett JP, Welton T. Chem Rev, 2011, 111: 3508–3576
Wang H, Tan B, Wang J, Li Z, Zhang S. Langmuir, 2014, 30: 3971–3978
Kohno Y, Deguchi Y, Ohno H. Chem Commun, 2012, 48: 11883–11885
Brown P, Wasbrough MJ, Gurkan BE, Hatton TA. Langmuir, 2014, 30: 4267–4272
Yang J, Wang H, Wang J, Zhang Y, Guo Z. Chem Commun, 2014, 50: 14979–14982
Santos E, Albo J, Irabien A. RSC Adv, 2014, 4: 40008–40018
Hayashi S, Hamaguchi H. Chem Lett, 2004, 33: 1590–1591
Wang H, Yan R, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhang S. Catal Commun, 2010, 11: 763–767
Clark KD, Nacham O, Yu H, Li T, Yamsek MM, Ronning DR, Anderson JL. Anal Chem, 2015, 87: 1552–1559
Nie Y, Gong X, Gao H, Zhang X, Zhang S. Sci China Chem, 2014, 57: 1766–1773
Misuk V, Mai A, Giannopoulos K, Alobaid F, Epplec B, Loewe H. Lab Chip, 2013,13: 4542–4548
Santos E, Albo J, Rosatella A, Afonso CAM, Irabien Á. J Chem Technol Biotechnol, 2014, 89: 866–871
Klee A, Prevost S, Gasser U, Gradzielski M. J Phys Chem B, 2015, 119: 4133–4142
Yamauchi H, Maeda Y. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111: 12964–12968
Lee H, Rosen BM, Fenyvesi G, Sunkara HB. J PolymSci Part A: Polym Chem, 2012, 50: 4311–4315
Maia FM, Rodríguez O, Macedo EA. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2010, 296: 184–191
Fukumoto K, Ohno H. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2007, 46: 1852–1855
Kohno Y, Arai H, Saita S, Ohno H. Australian J Chem, 2011, 64: 1560–1567
Kohno Y, Arai H, Ohno H. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 4772–4774
Saita S, Kohno Y, Ohno H. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 93–95
Deguchi Y, Kohno Y, Ohno H. Chem Lett, 2015, 44: 238–240
Nitta A, Morita T, Saita S, Kohno Y, Ohno H, Nishikawa K. Chem Phys Lett, 2015, 628: 108–112
Saita S, Kohno Y, Nakamura N, Ohno H. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 8988–8990
Saita S, Mieno Y, Kohno Y, Ohno H. Chem Commun, 2014, 50: 15450–15452
Xie Z, Taubert A. ChemPhysChem, 2011, 12: 364–368
Pei Y, Huang Y, Li L, Wang J. J Chem Thermodynamics, 2014, 74: 231–237
Pernak J, Syguda A, Mirska I, Pernak A, Nawrot J, Pradzynska A, Griffin ST, Rogers RD. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13: 6817–6827
Brown P, Bushmelev A, Butts CP, Cheng J, Eastoe J, Grillo I, Heenan RK, Schmidt AM. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51: 2414–2416
Costa AJL, Soromenho MRC, Shimizu K, Esperança JMSS, Lopes JNC, Rebelo LPN. RSC Adv, 2013, 3: 10262–10271
Costa AJL, Soromenho MRC, Shimizu K, Marrucho IM, Esperança JMSS, Lopes JNC, Rebelo LPN. J Phys Chem B, 2012, 116: 9186–9195
Li JG, Hu YF, Sun SF, Ling S, Zhang JZ. J Phys Chem B, 2012, 116: 6461–6464
Sitze MS, Schreiter ER, Patterson EV, Freeman RG. Inorg Chem, 2001, 40: 2298–2304
Stober R, Herrmann W. J Phys Chem A, 2013, 117: 3960–3971
Estager J, Holbrey JD, Swadzba-Kwasny M. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43: 847–886
Tang Y, Hu X, Guan P, Lin X, Li X. J Phys Org Chem, 2014, 27: 498–503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, Y., Cao, Y., Huang, Y. et al. Tunable LCST-type phase behavior of [FeCl4]--based ionic liquids in water. Sci. China Chem. 59, 587–593 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5577-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5577-0