Abstract
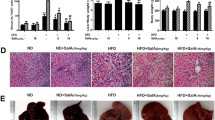
Scutellaria baicalensis has been reported to improve the lipid metabolism of high-fat diet-induced liver dysfunction, but direct evidence is rare. This study aimed to explore the effects and mechanisms of S. baicalensis and its major constituent baicalin on hepatic lipotoxicity. KK-Ay mice and orotic acid (OA)-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) rats were used to evaluate lipid metabolism regulatory effects. Sodium oleate-induced triglyceride-accumulated HepG2 cells were used for the mechanism study, pretreated with or without compound C or STO-609 or transfected with liver kinase B1 (LKB1) siRNA. In KK-Ay mice, S. baicalensis extract showed a decreased effect on serum and hepatic triglycerides, total cholesterols, and free fatty acid (FFA) levels after 8 weeks of treatment. In OA-induced NAFLD rats, 18 days of treatment with baicalin significantly inhibited hepatic lipid accumulation, attenuating hepatocyte hypertrophy, vacuolization and necrosis. S. baicalensis and baicalin treatment significantly suppressed the sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) transcriptional program with downregulation of gene and protein expression of SREBP-1c (both precursor and mature fraction) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, fatty acid synthase and stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and upregulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and nuclear respiratory factor 2 in the liver. Furthermore, activation of AMPK by baicalin was observed to be relative to the increase in phosphorylation of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase. Taken together, S. baicalensis conferred preventive effects against FFA-induced lipotoxicity through the AMPK-mediated SREBP signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lonardo A, Nascimbeni F, Maurantonio M, Marrazzo A, Rinaldi L, Adinolfi L (2017) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: evolving paradigms. World J Gastroenterol 23(36):6571–6592
Meng G, Zhang B, Yu F, Li C, Zhang Q, Liu L, Wu H, Xia Y, Bao X, Shi H, Su Q, Gu Y, Fang L, Yang H, Yu B, Sun S, Wang X, Zhou M, Jia Q, Jiao H, Wang B, Guo Q, Carvalhoa L, Sun Z, Song K, Yu M, Niu K (2017) Soft drinks consumption is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease independent of metabolic syndrome in Chinese population. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1485-0
Benedict M, Zhang X (2017) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an expanded review. World J Hepatol 9(16):715–732
Bechmann LP, Hannivoort RA, Gerken G, Hotamisligil GS, Trauner M, Canbay A (2012) The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases. J Hepatol 56(4):952–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.08.025
Shimano H, Sato R (2017) SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: convergent physiology–divergent pathophysiology. Nat Rev Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.91
Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA, Brown MS (2006) Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell 124(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.022
Li S, Brown MS (2010) Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1 required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(8):3441
Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Lobaccaro JM, Shimomura I, Shan B, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Mangelsdorf DJ (2000) Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Gene Dev 14(22):2819–2830
Javary Joaquim, Allain-Courtois Nathalie, Saucisse Nicolas, Costet Pierre, Heraud Capucine, Benhamed Fadila, Pierre Rémi, Bure Corinne, Pallares-Lupon Nestor, Cruzeiro Marcio Do, Postic Catherine, Cota Daniela, Dubus Pierre, Rosenbaum Jean, Benhamouche-Trouillet S (2017) Liver Reptin/RUVBL2 controls glucose and lipid metabolism with opposite actions on mTORC1 and mTORC2 signalling. Gut. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314208
Schultze S, Hemmings B, Niessen M, Tschopp O (2012) PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev Mol Med 14:e1
He MY, Deng YX, Shi QZ, Zhang XJ, Lv Y (2014) Comparative pharmacokinetic investigation on baicalin and wogonoside in type 2 diabetic and normal rats after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine Huanglian Jiedu decoction. J Ethnopharmacol 155(1):334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.033
Song KH, Lee SH, Kim BY, Park AY, Kim JY (2013) Extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis reduced body weight and blood triglyceride in db/db mice. Phytother Res 27(2):244–250. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4691
Li C, Lin G, Zuo Z (2011) Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics properties of radix Scutellariae and its bioactive flavones. Biopharm Drug Dispos 32(8):427–445. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.771
Waisundara VY, Hsu A, Tan BK, Huang D (2009) Baicalin reduces mitochondrial damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Diabetes Metab Res 25(7):671–677. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.1005
Guo HX, Liu DH, Ma Y, Liu JF, Wang Y, Du ZY, Wang X, Shen JK, Peng HL (2009) Long-term baicalin administration ameliorates metabolic disorders and hepatic steatosis in rats given a high-fat diet. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30(11):1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.150
Xi Y, Wu M, Li H, Dong S, Luo E, Gu M, Shen X, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Liu H (2015) Baicalin attenuates high fat diet-induced obesity and liver dysfunction: dose-response and potential role of CaMKKbeta/AMPK/ACC pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(6):2349–2359. https://doi.org/10.1159/000374037
Jung EJ, Kwon SW, Jung BH, Oh SH, Lee BH (2011) Role of the AMPK/SREBP-1 pathway in the development of orotic acid-induced fatty liver. J Lipid Res 52(9):1617–1625. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M015263
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226(1):497–509
Zhang Y, Liu X, Han L, Gao X, Liu E, Wang T (2013) Regulation of lipid and glucose homeostasis by mango tree leaf extract is mediated by AMPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Food Chem 141(3):2896–2905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.121
Gao J, Li J, An Y, Liu X, Qian Q, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang T (2014) Increasing effect of Tangzhiqing formula on IRS-1-dependent PI3K/AKT signaling in muscle. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:198. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-198
Gao Y, Gu C, Wang K, Wang H, Ruan K, Xu Z, Feng Y (2017) The effects of hypoglycemia and weight loss of total lignans from Fructus Arctii in KKAy mice and its mechanisms of the activity. Phytother Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6003
Burnett BP, Silva S, Mesches MH, Wilson S, Jia Q (2007) Safety evaluation of a combination, defined extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu. J Food Biochem 31(6):797–825
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X, Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, Gao B, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, Shaw RJ, Cohen RA, Zang M (2011) AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 13(4):376–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.009
Qing-ming C, Xin-li H, Yan-mei L, Zhang K, Akao T, Tori MH (2001) Studies on metabolites of baicalin in human urine. China J Chin Mater Med 26(11):768–769
Zhang J, Cai W, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wu X, Li Y, Lu J, Qiao Y (2015) Profiling and identification of the metabolites of baicalin and study on their tissue distribution in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. J Chromatogr B 985:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.01.018
Malhi H, Gores G (2008) Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 28(4):360–369
Leamy A, Egnatchik R, Young J (2013) Molecular mechanisms and the role of saturated fatty acids in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Prog Lipid Res 52(1):165–174
Rotman Y, Sanyal AJ (2017) Current and upcoming pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 66(1):180–190. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312431
Neuschwander-Tetri B (2010) Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 52(2):774–788
Akao T, Kawabata K, Yanagisawa E, Ishihara K, Mizuhara Y, Wakui Y, Sakashita Y, Kobashi K (2000) Baicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J Pharm Pharmacol 52(12):1563–1568
Hou Y-C, Lin S-P, Tsai S-Y, Ko M-H, Chang Y-C, Chao P-D (2010) Flavonoid pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution after repeated dosing of the roots of Scutellaria baicalensisin rats. Planta Med 77(05):455–460. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250433
Ma Y, Yang F, Wang Y, Du Z, Liu D, Guo H, Shen J, Peng H (2012) CaMKKbeta is involved in AMP-activated protein kinase activation by baicalin in LKB1 deficient cell lines. PLoS One 7(10):e47900. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047900
Chen Q, Wang T, Li J, Wang S, Qiu F, Yu H, Zhang Y, Wang T (2017) Effects of natural products on fructose-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020096
Li J, Liu X, Ran X, Chen J, Li X, Wu W, Huang H, Huang H, Long Y, Liang J, Cheng J, Tian H (2010) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c knockdown protected INS-1E cells from lipotoxicity. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(1):35–46
Kwak DH, Lee JH, Song KH, Ma JY (2014) Inhibitory effects of baicalin in the early stage of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes differentiation by down-regulation of PDK1/Akt phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biochem 385(1–2):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1834-0
Fang Penghua, Mei Yu, Zhang Lei, DanWan Mingyi Shi, Zhu Yan, Bo Ping, Zhang Z (2017) Baicalin against obesity and insulin resistance through activation of AKT/AS160/GLUT4 pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 448(2017):77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.03.027
Zeng X, Yang J, Hu O, Huang J, Ran L, Chen M, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Yi L, Mi M (2018) Dihydromyricetin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by improving mitochondrial respiratory capacity and redox homeostasis through modulation of SIRT3 signaling. Antioxid Redox Sign. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7172
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81430095; 81673703; 81173524), Important Drug Development Fund, Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2017ZX09305–002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Liu, M., Yu, H. et al. Scutellaria baicalensis regulates FFA metabolism to ameliorate NAFLD through the AMPK-mediated SREBP signaling pathway. J Nat Med 72, 655–666 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1199-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1199-5