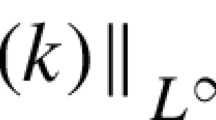Abstract
The author shows the existence of long-time averages to turbulent solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations and determines the equations satisfied by them, involving a Reynolds stress that is shown to be dissipative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrouche, C. and Girault, V., On the existence and regularity of the solutions of Stokes problem in arbitrary dimension, Proc. Japan Acad., 67(5), 1991, 171–175.
Batchelor, G. K., An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1967.
Boussinesq, J., Essai sur la théorie des eaux courantes, Mémoires Présentés par Divers Savants à l’Académie des Sciences, 23(1), 1877, 1–660.
Caffarelli, L., Kohn, R. and Nirenberg, L., Partial regularity of suitable weak solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations, Comm. Pure Appl. Math., 35(5–6), 1982. 771–831.
Chácon Rebollo, T. and Lewandowski, R., Mathematical and Numerical Foundations of Turbulence Models and Applications, Modeling and Simulation in Science, Engineering and Technology, Birkhäuser, Basel; Springer-Verlag, New York, 2014.
Hopf, E., Ber die Anfangswertaufgabe fr die hydrodynamischen Grundgleichungen, Math. Nachr., 4, 1951, 213–231 (in German).
Kolmogorov, A. N., The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluids for very large Reynolds number, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSR, 30, 1941, 9–13.
Girault, V. and Raviart, P. A., Finite Element Approximation of the Navier-Stokes Equations, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1979.
Feireisl, E., Dynamics of Viscous Incompressible Fluids, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004.
Layton, W., The 1877 Boussinesq conjecture: Turbulent fluctuation are dissipative on the mean flow, 2014. to appear.
Leray, J., Sur le mouvement d’un liquide visqueux emplissant l’espace, Acta Mathematica, 63, 1934, 193–248.
Lions, J. L., Quelques Méthodes de Résolution des Problèmes aux Limites non Linéaires, Dunod, Paris, 1969.
Prandtl, L., Über die ausgebildeten Turbulenz, Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 5, 1925, 136–139 (in German).
Reynolds, O., An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous, and of the law of resistance in parallel channels, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 174, 1883, 935–982.
Ruelle, D., Chance and Chaos, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1991.
Sobolev, V. I., Bochner integral, Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2001.
Stokes, G., On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums, Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 9, 1851, 8–106.
Tartar, L., An introduction to Navier-Stokes equation and oceanography, Lecture Notes of the Unione Matematica Italiana, 1, Springer-Verlag, Berlin; UMI, Bologna, 2006.
Tartar, L., An introduction to Sobolev spaces and interpolation spaces, Lecture Notes of the Unione Matematica Italiana, 3, Springer-Verlag, Berlin; UMI, Bologna, 2007.
Taylor, G. I., Statistical theory of turbulence, Part I-IV, Proc. Roy. Soc. A., 151, 1935, 421–478.
Temam, R., Navier-Stokes Equations, Theory and Numerical Analysis, Reprint of the 1984 Edition, A. M. S. Chelsea Publishing, Providence, RI, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In Honor of the Scientific Contributions of Professor Luc Tartar
This work was supported by ISFMA, Fudan University, China, and CNRS, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewandowski, R. Long-time turbulence model deduced from the Navier-Stokes equations. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 36, 883–894 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11401-015-0982-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11401-015-0982-9