Abstract
Purpose
Degraded soils are unable to perform key functions and, thus, it is very important to develop effective reclamation methods. To restore utility or natural values to degraded ecosystems, various compounds are applied. In this study, the impacts of additives of various origin and composition on Polish (Eutric Cambisol) and Bulgarian (Epicalcic Chernozem) soils were compared. The main goal of the study was to make a comprehensive assessment of the validity of using popular soil additives in a real context.
Materials and methods
Physicochemical and hydrophysical parameters including pH, variable surface charge, porosity, specific surface area, wettability, sorption capacity relative to trace metals, and water retention of soils were taken into account. Surface charge and porosity of soils were determined using potentiometric titration and nitrogen adsorption/desorption method, respectively. Wettability was measured by sessile-drop method, whereas water retention, using different matric potentials (pF curves). Sorption study on trace metals included isotherm and kinetics determination as well as experimental data modeling.
Results and discussion
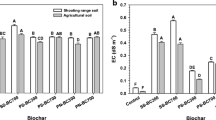
The most positive effect on soil surface charge, porosity, wettability, and cadmium (Cd) sorption was observed for synthetic zeolite, zeolite-carbon composite, and vermicompost. This effect was noted only for Polish soil characterized by poor porosity, low content of organic carbon, and moderately acidic reaction. For eroded Bulgarian soil, the condition of which was definitely better, the impact of modifiers was not spectacular. Among tested amendments, only divergan increased water retention properties of both examined soils significantly.
Conclusions
Zeolite, zeolite-carbon composite, and vermicompost can be apply for degraded soils of low organic carbon content, poor porosity, and moderately acidic pH to improve their physicochemical parameters and sorption ability toward trace metals. Divergan should be used to improve water retention of degraded soils during their reclamation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request/reasonable request.
References
Abdeen SA (2020) Evaluation of vermicompost and zeolite ability to improve water and nutrients retention in a sandy soil. J Soil Sci Agric Eng 11(8):403–409
Amanullah I, Hussain I, Ali I, Ullah S, Iqbal A, Al-Tawara AR, Al-Tawara AR, Thangadurai D, Sangeetha J (2021) Agricultural soil reclamation and restoration of soil organic matter and nutrients via application of organic, inorganic and bio fertilization (Mini review). IOP Conf. Ser Earth Environ. Sci. 788, 012165.
Aparicio JD, Raimondo EE, Saez JM, Costa-Gutierrez SB, Alvarez A, Benimeli CS, Polti MA (2022) The current approach to soil remediation: a review of physicochemical and biological technologies, and the potential of their strategic combination. J Env Chem Eng 10(2):107141
Azizian S, Eris S (2021) Chapter 6 - Adsorption isotherms and kinetics. Editor(s): M. Ghaedi. Interface Sci. Technol. 33, 445–509.
Bachmann J, Horton R, Van der Ploeg RR, Woche S (2000) Modified sessile drop method for assessing initial soil–water contact angle of sandy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:564–567
Bandura L, Panek R, Madej J, Franus W (2021) Synthesis of zeolite-carbon composites using high-carbon fly ash and their adsorption abilities towards petroleum substances. Fuel 283:119173
Belviso C (2020) Zeolite for potential toxic metal uptake from contaminated soil: a brief review. Processes 8:820
Belviso C, Satriani A, Lovelli S, Comegna A, Coppola A, Dragonetti G, Cavalcante F, Rivelli AR (2022) Impact of zeolite from coal fly ash on soil hydrophysical properties and plant growth. Agriculture 12:356
Benlikaya R, Kahrıman M (2022) Chemical inferences drawn from basalt volcanic pumice. CBUJOS 18(2):225–231
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem so 60:309–319
Ceritoğlu M, Şahin S, Erman M (2018) Effects of vermicompost on plant growth and soil structure. Selcuk J Agric Food Sci 32(3):607–615
Contin M, Miho L, Pellegrini E, Gjoka F, Shkurta E (2019) Effects of natural zeolites on ryegrass growth and bioavailability of Cd, Ni, Pb, and Zn in an Albanian contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 19:4052–4062
Cui L, Li L, Bian R, Yan J, Quan G, Liu Y, Ippolito JA, Wang H (2020) Short- and long-term biochar cadmium and lead immobilization mechanisms. Environments 7:53
Dahiya HS, Budania YK (2018) Prospects of fly ash application in agriculture: a global review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7:397–409
Danesh N, Ghorbani M, Marjani A (2021) Separation of copper ions by nanocomposites using adsorption process. Sci Rep 11:1676
Das SK, Mukherjee I, Kumar A (2015) Effect of soil type and organic manure on adsorption-desorption of flubendiamide. Environ Monit and Assess 187(7):403
Das SK, Ghosh GK, Avasthe RK (2017) Biochar amendments on physico-chemical and biological properties of soils. Agrica Intern J Plant Sci Related Ind 6(2):19–27
Dexter AR (2006) Application of S-theory in tillage research. In: 17th Triennial Conference. Proceedings of ISTRO 17. Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany, 429–442.
Fan T-T, Sun Q, Cui P-X, Xuan L, Wang Y-J (2022) Sorption mechanism of cadmium on soils: a combination of batch experiment, path analysis, and EXAFS techniques. Geoderma 422:115950
Ferreira CSS, Seifollahi-Aghmiuni S, Destouni G, Ghajarnia N, Kalantari Z (2022) Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: processes, status and consequences. Sci Tot Environ 805:150106
Filcheva E, Tsadilas C (2002) Influence of cliniptilolite and compost on soil properties. Commun Soil Sci Plan 33(3–4):595–607
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Env Res Pub He 17(11):3782
Geng N, Kang X, Yan X, Yin N, Wang H, Pan H, Yang Q, Lou Y, Zhuge, (2022) Biochar mitigation of soil acidification and carbon sequestration is influenced by materials and temperature. Ecotoxicol and Environ Saf 232:113241
Gil E, Kijowska-Strugała M, Demczuk P (2021) Soil erosion dynamics on a cultivated slope in the Western Polish Carpathians based on over 30 years of plot studies. CATENA 207:105682
Główny Urząd Statystyczny (2021) Wskaźnik 15.1.b - Udział gruntów zdewastowanych i zdegradowanych wymagających rekultywacji w powierzchni ogółem. Available at: https://sdg.gov.pl/statistics_nat/15-1-b/
Główny Urząd Statystyczny (2022) Kategoria K9 – Stan i ochrona środowiska, Grupa G304 - Ochrona powierzchni ziemi i gleby, Podgrupa P1986 - Grunty zdewastowane i zdegradowane wymagające rekultywacji. Available at: https://bdl.stat.gov.pl/bdl/dane/podgrup/tablica
Gudeta K, Bhagat A, Julka JM, Sinha R, Verma R, Kumar A, Kumari S, Ameen F, Bhat SA, Amarowicz R, Sharma M (2022) Vermicompost and its derivatives against phytopathogenic fungi in the soil: A review. Horticulturae 8(4):311
Gupta Ch, Prakash D, Gupta S, Nazareno MA (2019) Role of vermicomposting in agricultural waste management. In: Shah S, Venkatramanan V, Prasad R (eds) Sustainable green technologies for environmental management. Springer, Singapore, pp 283–295
Hasanabadi T, Lack S, Modhej A, Lavifazel HGM, Ardakani MR (2019) Feasibility study on reducing lead and cadmium absorption by Alfalfa (Medicago scutellata L.) in a contaminated soil using nano-activated carbon and natural based nano-zeolite. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj Napoca 47:1185–1193
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second-order model for sorption process. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Houssou AA, Jeyakumar P, Niazi NK, Van Zwieten L, Li X, Huang L, Wei L, Ibrahim HM, Alghamdi AG (2021) Effect of the particle size of clinoptilolite zeolite on water content and soil water storage in a loamy sand soil. Water 13:607
Ibrahim HM, Alghamdi AG (2021) Effect of the particle size of clinoptilolite zeolite on water content and soil water storage in a loamy sand soil. Water 13(5):607
Ifthikar J, Jiao X, Ngambia A, Wang T, Khan A, Jawad A, Xue Q, Liu L, Chen Z (2018) Facile one-pot synthesis of sustainable carboxymethyl chitosan – sewage sludge biochar for effective heavy metal chelation and regeneration. Bioresour Technol 262:22–31
Ivanova N, Obaeed GLO, Sulkarnaev F, Buchkina N, Gubin A, Yurtaev, (2023) Effect of biochar aging in agricultural soil on its wetting properties and surface structure. Biochar 5:75
Janu R, Mrlik V, Ribitsh D, Hofman J, Sedláček P, Bielská L, Soja G (2021) Biochar surface functional groups as affected by biomass feedstock, biochar composition and pyrolysis temperature. CRC 4:36–46
Jeffery S, Bezemer TM, Cornelissen G, Kuyper TW, Lehmann J, Mommer L, Sohi SP, van de Voorde TFJ, Wardle DA, van Groenigen JW (2015) The way forward in biochar research: targeting trade-offs between the potential wins. GCB Bioenergy 7(1):1–13
Jeppu GP, Clement TP (2012) A modified Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model for simulating pH-dependent adsorption effects. J Contam Hydrol 129–130:46–53
Jia Y, Shi S, Liu J, Su S, Liang Q, Zeng X, Li T (2018) Study of the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of biochar. Appl Sci 8:1019
Józefaciuk G (2002) Effect of acid and alkali treatments on surface-charge properties of selected minerals. Clay Clay Miner 50(5):647–656
Józefaciuk G, Szatanik-Kloc A, Ambrożewicz-Nita A (2018) The surface area of zeolite-amended soils exceeds the sum of the inherent surface areas of soil and zeolite. Eur J Soil Sci 69(5):787–790
Kaplan H, Ratering S, Felix-Henningsen P, Schnell S (2019) Stability of in situ immobilization of trace metals with different amendments revealed by microbial 13C-labelled wheat root decomposition and efflux-mediated metal resistance of soil bacteria. Sci Total Environ 659:1082–1089
Kasera N, Augoustides V, Kolar P, Hall SG, Vicente B (2022) Effect of surface modification by oxygen-enriched chemicals on the surface properties of pine bark biochars. Processes 10:2136
Kubier A, Wilkin RT, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in soils and groundwater: a review. Appl Geochem 108:104388
Kuncheva G, Kercheva M, Enchev Ev, Paparkova Ts, Kolchakov V (2023) Factors controlling water-stable macroaggregation of Kastanozems exposed to water erosion. Bulg J Agric Sci 29(2):262–271
Kunecki P, Panek R, Wdowin M (2016) Na-P1 zeolite synthesis and its crystalline structure ripening through hydrothermal process using coal combustion by-products as substrates. Geology Geophys Environ 42(1):90–91
Kunecki P, Panek R, Wdowin M, Bień T, Franus W (2021) Influence of the fly ash fraction after grinding process on the hydrothermal synthesis efficiency of Na-A, Na-P1, Na-X and sodalite zeolite types. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8:291–311
Li L, Zhang Y-J, Novak A, Yang Y, Wang J (2021) Role of biochar in improving sandy soil water retention and resilience to drought. Water 13:407
Liu Z, Ogunmokun FA, Wallach R (2022) Does biochar affect soil wettability and flow pattern? Geoderma 417:115826
Loeppert RH, Suarez DL (1996) Carbonate and gypsum. In: Bigham, J.M., Bartels, J.M. (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 3: chemical methods. SSSA, ASA, Madison, 437–474.
Lowell S, Shields JE, Thomas MA, Thommes M (2004) Mesopore analysis. In: Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density. Particle Technology Series, 16, Springer, Dordrecht.
Medykowska M, Wiśniewska M, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Panek R (2022) Interaction mechanism of heavy metal ions with the nanostructured zeolites surface – adsorption, electrokinetic and XPS studies. J Mol Liq 357:119144
Medykowska M, Wiśniewska M, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Panek R (2023) Study on electrical double layer nanostructure on zeolitic materials’ surface in the presence of impurities of different nature. Appl. Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02747-5
Moeen M, Qi T, Hussain Z, Ge Q, Maqbool Z, Jianjie X, Kaiqing F (2020) Use of zeolite to reduce the bioavailability of heavy metals in a contaminated soil. J Ecol Eng 21(7):186–196
Mokrzycki J, Franus W, Panek R, Sobczyk M, Rusiniak P, Szerement J, Jarosz R, Marcińska-Mazur L, Bajda T, Mierzwa-Hersztek M (2023) Zeolite composite materials from fly ash: an assessment of physicochemical and adsorption properties. Materials 16(6):2142
National Statistical Institute (2021) Land use distribution of the Republic of Bulgaria as of 31.12.2021. Available at: https://www.nsi.bg/en/content/19674/land-use-distribution-republic-bulgaria
Ndede EO, Kurebito S, Idowu O, Tokunari T, Jindo K (2022) The potential of biochar to enhance the water retention properties of sandy agricultural soils. Agronomy 12:311
Nibou D, Mekatel H, Amokrane S, Barkat M, Trari M (2010) Adsorption of Zn2+ ions onto NaA and Na-X zeolites: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):637–646
Obalum SE, Chibuike GU, Peth S, Ouyang Y (2017) Soil organic matter as sole indicator of soil degradation. Environ Monit Assess 189:176
Ogunmokun FA, Wallach R (2021) Remediating the adverse effects of treated wastewater irrigation by repeated on surface surfactant application. Water Resour. Res. 57, e2020WR029429.
Olle M (2019) Review: vermicompost, its importance and benefit in agriculture. J Agric Sci 2(XXX):93–98
Panek R, Medykowska M, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Wiśniewska M (2021a) Comparison of physicochemical properties of fly ash precursor, Na-P1(C) zeolite–carbon composite and Na-P1 zeolite – adsorption affinity to divalent Pb and Zn cations. Materials 14(11):3018
Panek R, Medykowska M, Wiśniewska M, Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Jędruchniewicz K, Franus M (2021b) Simultaneous removal of Pb2+ and Zn2+ heavy metals using fly ash Na-X zeolite and its carbon Na-X(C) Composite. Materials 14(11):2832
Paparkova T (2023) Application of evaporation method to determine the soil water retention curve. Bulg J Soil Sci Agrochemisty Ecol 57(2):3–11
Parker A, Rae JE (2013) Environmental interactions of clays: clays and the environment. Springer, Berlin
Pomianek I (2014) Socio-economic development of agricultural problem areas in Poland. Econ Sociol 7(2):218–235
Qi F, Lamb D, Naidu R, Bolan NS, Yan Y, Sik Ok Y, Mahmudur Rahman M, Choppala G (2018) Cadmium solubility and bioavailability in soils amended with acidic and neutral biochar. Sci Total Environ 610–611:1457–1466
Ramezanzadeh H, Reyhanitabar A, Oustan S, Mohammadi MH, van der Zee SEATM (2021) Enhanced sorption of cadmium by using biochar nanoparticles from ball milling in a sandy soil. Eurasian Soil Sci 54:201–211
Razzaghi F, Obour PB, Arthur E (2020) Does biochar improve soil water retention? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Geoderma 361:114055
Reynolds WD, Drury CF, Tan CS, Fox CA, Yang XM (2009) Use of indicators and pore volume-function characteristics to quantify soil physical quality. Geoderma 152:252–263
Rousseva Sv, Malinov I, Stefanova V (2016) Soil erosion risk assessments using GIS technologies – Bulgarian experience. Bulg J Agric Sci 22(2):205–208
Saravanan P, Kathireswari P, Kulandaivelu S (2022) Spectroscopic assessment of sugarcane bagasse mediated vermicompost for qualitative enrichment of animal wastes Elephus maximus and Bos taurus. Waste Biomass Valori 14:2133–2149
Stancheva M, Stanchev H, Young R, Parlichev G (2021) Coastal erosion driven land-sea interactions in maritime spatial planning – a case of Bulgaria. J Coast Conserv 25:54
Sulaiman S, Azis RS, Ismail I, Che Man H, Faezach K, Yusof M et al (2021) Adsorptive removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution using a magnetite nano-adsorbent from mill scale waste: synthesis, characterization, adsorption and kinetic modelling studies. Nanoscale Res Lett 16:168
Sun L, Zhang G, Li X, Zhang X, Hang W, Tang M, Gao Y (2023) Effects of biochar on the transformation of cadmium fractions in alkaline soil. Heliyon 9(1):e12949
Szatanik-Kloc A, Szerement J, Adamczuk A, Józefaciuk G (2021) Effect of low zeolite doses on plants and soil physicochemical properties. Materials 14:2617
Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Rzepa G, Bajda T, Wiśniewska M, Urban T, Kukowska S, Tomczyk A, Grygorczuk-Płaneta K, Kondracki B (2022b) Aggregation mechanism of natural schwertmannite particles covered with two-component layers of high molecular weight tackifier and trace metal ions. J Mol Liq 368:120746
Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Tomczyk A, Grygorczuk-Płaneta K, Naveed S (2022c) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii exopolysaccharide and sunflower husk biochar as factors affecting immobilization of both tetracycline and Cd ions on soil solid phase. J. Soil Sediment. 22(11):1–20
Szewczuk-Karpisz K, Bajda T, Tomczyk A, Kuśmierz M, Komaniecka I (2022a) Immobilization mechanism of Cd2+/HCrO4-/CrO42- ions and carboxin on montmorillonite modified with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii exopolysaccharide. J Hazard Mater 428, 128228.
Tiziano G (2016) Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 8:281
Tomczyk A, Boguta A, Sokołowska Z (2019) Biochar efficiency in copper removal from Haplic soils. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:4899–4912
Tomczyk A, Sokołowska Z, Boguta P (2020) Biochar physicochemical properties: pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev Environ Sci Bio/technol 19:191–215
Tomczyk A, Kubaczyński A, Szewczuk-Karpisz K (2023) Assessment of agricultural waste biochars for remediation of degraded water-soil environment: dissolved organic carbon release and immobilization of impurities in one- or two-adsorbate systems. Waste Manag 155:87–98
Van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898
Wang Z, Wallach R (2021) Water infiltration into subcritical water-repellent soils with time-dependent contact angle. J Hydrol 595:126044
Wen X, Wang Y, Cheng P, Liu D, Ma S, Zhang C, Liu T, Tao L (2020) Surface charge properties of variable charge soils influenced by environmental factors. Appl Clay Sci 189:105522
Woche SK, Goebel M-O, Kirkham MB, Horton R, Van der Ploeg RR, Bachmann, (2004) Contact angle of soils as affected by depth, texture, and land management. Eur J Soil Sci 56(2):239–251
Xuan K, Li X, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Ma B, Liu J (2023) Effects of organic amendments on soil pore structure under waterlogging stress. Agronomy 13:289
Zahedifar M (2020) Effect of biochar on cadmium fractions in some polluted saline and sodic soils. Environ Manag 66:1133–1141
Zhang C, Liu Z, Deng P (2016) Contact angle of soil minerals: a molecular dynamics study. Comput Geotech 75:48–56
Zhang M, Riaz M, Zhang L, El-desouki Z, Jiang C (2019) Biochar induces changes to basic soil properties and bacterial communities of different soils to varying degrees at 25 mm rainfall: more effective on acidic soils. Front Microbiol 10:1321
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Vincent J.M.N.L. Felde for providing divergan.
Funding
The work was partially financed by the National Science Fund under the grant agreement КП-06 H 46/1 2020 (project “Efficiency of erosion control agrotechnologies for improvement of soil quality and water regime and mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions”) as well as by the National Science Centre, Poland (2021/41/B/NZ9/03059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Modification of degraded soils of different origin was performed.
• Its impact was the most significant for Polish soil–Eutric Cambisol.
• Zeolitic materials and vermicompost improved Cd sorption even by 41.6%.
• In the case of Bulgarian soil, the effects of used amendments were minimal.
• Divergan improved water retention of degraded soils by 22% maximally.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Szewczuk-Karpisz, K., Tomczyk, A., Kercheva, M. et al. Reclamation of degraded soils: Analysis of selected parameters after organic/inorganic modifications. J Soils Sediments (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03760-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03760-7