Abstract
Purpose
Proper tillage management and crop plantation are two established approaches to control soil erosion in red soil slopes of southern China. This study aims to investigate the surface–subsurface runoff and soil losses processes on sloping farmland under different peanut growth stages and ridge treatments, and to quantify the combined effects of proper tillage management and crop plantation.
Methods
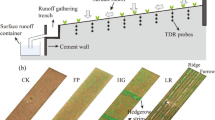
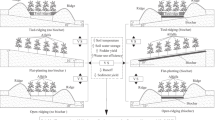
Simulated rainfall experiments with an intensity of 60 mm h−1 were conducted to measure the initiation time and steady rates of surface–subsurface runoff and soil losses under four tillage treatments including flat planting (FP), longitudinal ridge (LR), cross ridge (CR), and alternate distribution of cross and longitudinal ridges (CL) at the bare land and four different growth stages of peanut.
Results
As peanut grew, the mean steady surface runoff rate for all treatments decreased by 19.6%, 38.8%, 54.0%, and 66.3% at the four growth stages respectively, and the mean steady subsurface runoff rate increased by 35.4%, 77.3%, 99.9%, and 118.4% at the four growth stages respectively. The maximum soil loss rate also decreased from 7.33 ~ 25.92 g m−2 min−1 at the seedling stage to 0.31 ~ 4.72 g m−2 min−1 at the full fruit stage. Compared with the FP treatment, the steady surface runoff rate for the LR treatment increased by 8.1 ~ 32.4% and the steady subsurface runoff rate reduced by 7.2 ~ 38.4%; while for the CR treatment, the steady surface runoff rate reduced by 77.6 ~ 92.7% and the steady subsurface runoff rate increased by 26.6 ~ 219.3%. As peanut grew, the contribution index of peanut to surface runoff increased from 0 at bare land stage to 0.80, 0.96, and 0.34 for the LR, CL, and CR treatment at the S4 stage, while the contribution index of ridge tillage to runoff generally decreased.
Conclusions
The inhibitory effects of peanut on surface runoff rate and sediment yield, as well as its promotion effect on subsurface runoff, were enhanced with peanut growth. Conversely, the impact of ridge tillage gradually decreased as peanut grew. On plots with longitudinal ridges, the impact of ridges on runoff was offset by contribution of crop growth after the seedling stage; whereas on plots with only contour ridges, the impact of ridges continued to dominate runoff control as peanut grew.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Geng J, Yang H, Song H, Wang B (2021) Effect of Ridge Height Row Grade and Field Slope on Nutrient Losses in Runoff in Contour Ridge Systems under Seepage with Rainfall Condition. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18042022
An J, Zhang Y, Wang Y (2020) Rainstorm pattern effects on the size distribution of soil aggregate in eroded sediment within contour ridge systems. J Soils Sediments 20:2192–2206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02561-7
Appels WM, Bogaart PW, van der Zee SE (2016) Surface runoff in flat terrain: how field topography and runoff generating processes control hydrological connectivity. J Hydrol 534:493–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.01.021
Balasubramanian A (2017) Soil erosion–causes and effects. In: Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science. Mysore, pp 1-7. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26247.39841
Barbosa F, Bertol I, Luciano R, Gonzalez A (2009) Phosphorus losses in water and sediments in runoff of the water erosion in oat and vetch crops seed in contour and downhill. Soil Tillage Res 106:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.09.004
Baumhardt R, Stewart B, Sainju U (2015) North American soil degradation: processes, practices, and mitigating strategies. Sustainability 7:2936–2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7032936
Bayat F, Monfared AB, Jahansooz MR, Esparza ET, Keshavarzi A, Morera AG, Fernández MP, Cerda A (2019) Analyzing long-term soil erosion in a ridge-shaped persimmon plantation in eastern Spain by means of ISUM measurements. CATENA 183:104176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104176
Bochet E, García-Fayos P (2004) Factors controlling vegetation establishment and water erosion on motorway slopes in Valencia. Spain Restor Ecol 12:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1061-2971.2004.0325.x
Busari MA, Kukal SS, Kaur A, Bhatt R, Dulazi AA (2015) Conservation tillage impacts on soil, crop and the environment. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 3:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.05.002
Carretta L, Tarolli P, Cardinali A, Nasta P, Romano N, Masin R (2021) Evaluation of runoff and soil erosion under conventional tillage and no-till management: a case study in northeast Italy. Catena 197:104972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104972
Carter MR (2005) CONSERVATION TILLAGE. In: Hillel D (ed) Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 306–311
Carvalho DFd, Eduardo EN, Almeida WSd, Santos LA, Alves Sobrinho T (2015) Water erosion and soil water infiltration in different stages of corn development and tillage systems. Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambiental 19:1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v19n11p1072-1078
Cecchi GA, Kröpfl AI, Villasuso NM, Distel RA (2006) Stemflow and soil water redistribution in intact and disturbed plants of Larrea divaricata in southern Argentina. Arid Land Res Manage 20:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324980600705669
Chen N, Ma T, Zhang X (2016) Responses of soil erosion processes to land cover changes in the Loess Plateau of China: A case study on the Beiluo River basin. CATENA 136:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.02.022
Dai C, Liu Y, Wang T, Li Z, Zhou Y (2018) Exploring optimal measures to reduce soil erosion and nutrient losses in southern China. Agric Water Manage 210:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.07.032
De Baets S, Poesen J, Meersmans J, Serlet L (2011) Cover crops and their erosion-reducing effects during concentrated flow erosion. CATENA 85:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.01.009
Ebabu K, Tsunekawa A, Haregeweyn N, Tsubo M, Adgo E, Fenta AA, Meshesha DT, Berihun ML, Sultan D, Vanmaercke M (2022) Global analysis of cover management and support practice factors that control soil erosion and conservation. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 10:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.12.002
El Kateb H, Zhang H, Zhang P, Mosandl R (2013) Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: a field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. CATENA 105:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.12.012
Fang NF, Wang L, Shi ZH (2017) Runoff and soil erosion of field plots in a subtropical mountainous region of China. J Hydrol 552:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.048
Feng T, Wei W, Chen L, Rodrigo-Comino J, Die C, Feng X, Ren K, Brevik EC, Yu Y (2018) Assessment of the impact of different vegetation patterns on soil erosion processes on semiarid loess slopes. Earth Surf Process Landf 43:1860–1870. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.4361
Free GR (1956) Investigations of tillage for soil and water conservation I. A comparison of crop yields for contour vs. up and downslope tillage. Soil Sci Soc Am J 20:427–429. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1956.03615995002000030035x
García-Díaz A, Bienes R, Sastre B, Novara A, Gristina L, Cerdà A (2017) Nitrogen losses in vineyards under different types of soil groundcover. A field runoff simulator approach in central Spain. Agric Ecosyst Environ 236:256–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.12.013
García-Ruiz JM (2010) The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: a review. CATENA 81:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2010.01.001
Ghosal K, Das Bhattacharya S, Ghosal K (2020) A review of RUSLE model. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48:689–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01097-0
Grum B, Assefa D, Hessel R, Woldearegay K, Kessler A, Ritsema C, Geissen V (2017) Effect of in situ water harvesting techniques on soil and nutrient losses in semi-arid Northern Ethiopia. Land Degrad Dev 28:1016–1027. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2603
Hombegowda H, Adhikary PP, Jakhar P, Madhu M, Barman D (2020) Hedge row intercropping impact on run-off, soil erosion, carbon sequestration and millet yield. Nutr Cycling Agroecosyst 116:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10031-2
Huang B, Yuan Z, Zheng M, Liao Y, Nguyen KL, Nguyen TH, Sombatpanit S, Li D (2022) Soil and water conservation techniques in tropical and subtropical Asia: a review. Sustainability 14:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095035
Jonard F, Mahmoudzadeh M, Roisin C, Weihermüller L, André F, Minet J, Vereecken H, Lambot S (2013) Characterization of tillage effects on the spatial variation of soil properties using ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic induction. Geoderma 207:310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.05.024
Jost G, Schume H, Hager H, Markart G, Kohl B (2012) A hillslope scale comparison of tree species influence on soil moisture dynamics and runoff processes during intense rainfall. J Hydrol 420:112–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.11.057
Kurothe R, Kumar G, Singh R, Singh H, Tiwari S, Vishwakarma A, Sena D, Pande V (2014) Effect of tillage and cropping systems on runoff, soil loss and crop yields under semiarid rainfed agriculture in India. Soil Tillage Res 140:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.03.005
Li J, Yu X, Liu Q, Wu Y (2012) Soil and water losses and phosphorus output at the places between ridges in sloping peanut land under different planting modes in Yimeng mountainous area of Shandong Province, East China. Chin J Appl Ecol 23:3347–3354. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.2012.0422
Li H, Han X, Zhang Z (2013) Research on runoff and erosion sediment under simulate rainfall conditions of black soil in Northeast China. J Soil Water Conserv 27:49–52+57. https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2013.04.024
Li H, Shen H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Gao Q (2021) Effects of ridge tillage and straw returning on runoff and soil loss under simulated rainfall in the Mollisol Region of Northeast China. Sustainability 13:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910614
Lin Q, Xu Q, Wu F, Li T (2019) Effects of wheat in regulating runoff and sediment on different slope gradients and under different rainfall intensities. Catena 183:104196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104196
Liu Q, Singh V, Singh V (2004) Effect of microtopography, slope length and gradient, and vegetative cover on overland flow through simulation. J Hydrol Eng 9:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2004)9:5(375)
Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang X, Ding G, Cruse R (2011) Soil erosion control practices in Northeast China: A mini-review. Soil Tillage Res 117:44–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2011.08.005
Liu QJ, Shi ZH, Yu XX, Zhang HY (2014) Influence of microtopography, ridge geometry and rainfall intensity on soil erosion induced by contouring failure. Soil Tillage Res 136:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2013.09.006
Liu Y-J, Yang J, Hu J-M, Tang C-J, Zheng H-J (2016) Characteristics of the surface–subsurface flow generation and sediment yield to the rainfall regime and land-cover by long-term in-situ observation in the red soil region, Southern China. J Hydrol 539:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.058
Ma B, Liu G, Ma F, Li Z, Wu F (2018) Effects of crop-slope interaction on slope runoff and erosion in the Loess Plateau. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 69:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2018.1488988
Ma Y, Li Z, Deng C, Yang J, Tang C, Duan J, Zhang Z, Liu Y (2022) Effects of tillage-induced soil surface roughness on the generation of surface–subsurface flow and soil loss in the red soil sloping farmland of southern China. Catena 213:106230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106230
Mloza-Banda M, Cornelis W, Mloza-Banda H, Makwiza C, Verbist K (2014) Soil properties after change to conservation agriculture from ridge tillage in sandy clay loams of mid-altitude C entral M alawi. Soil Use Manage 30:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12139
Mohammad AG, Adam MA (2010) The impact of vegetative cover type on runoff and soil erosion under different land uses. CATENA 81:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2010.01.008
Mohamoud YM (2012) Effect of contour ridging on runoff and soil loss. Afr J Agric Res 7:6115–6124. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR11.2307
Moreno RG, Requejo AS, Altisent JMD, Álvarez MCD (2011) Significance of soil erosion on soil surface roughness decay after tillage operations. Soil Tillage Res 117:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2011.08.006
Muoni T, Koomson E, Öborn I, Marohn C, Watson CA, Bergkvist G, Barnes A, Cadisch G, Duncan A (2020) Reducing soil erosion in smallholder farming systems in east Africa through the introduction of different crop types. Exp Agric 56:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479719000280
Nearing M, Lane LJ, Lopes VL (2017) Modeling soil erosion. Soil erosion research methods. Routledge, New York, pp 127–158
Park S-I, Yang HI, Park H-J, Seo B-S, Lee D-H, Jeong Y-J, Yoon K-S, Kim H-Y, Choi W-J (2020) Vegetated ridge and sandbag may not reduce soil erosion and loss of carbon and nutrients from upland fields. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 66:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2019.1696152
Prasuhn V (2012) On-farm effects of tillage and crops on soil erosion measured over 10 years in Switzerland. Soil Tillage Res 120:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2012.01.002
Reeder RC (1990) Extension programs and farmer experiences with ridge tillage. Soil Tillage Res 18:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-1987(90)90066-M
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, Porter JP (1991) RUSLE: revised universal soil loss equation. J Soil Water Conserv 46:30–33
Rong L, Duan X, Zhang G, Gu Z, Feng D (2019) Impacts of tillage practices on ephemeral gully erosion in a dry-hot valley region in southwestern China. Soil Tillage Res 187:72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.11.012
Rose C (2017) Research progress on soil erosion processes and a basis for soil conservation practices. Soil erosion research methods, New York, pp 159–180
Singh R, Panda R, Satapathy K, Ngachan S (2011) Simulation of runoff and sediment yield from a hilly watershed in the eastern Himalaya, India using the WEPP model. J Hydrol 405:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.022
Steudel T, Bugan R, Kipka H, Pfennig B, Fink M, de Clercq W, Flügel W-A, Helmschrot J (2015) Implementing contour bank farming practices into the J2000 model to improve hydrological and erosion modelling in semi-arid Western Cape Province of South Africa. Hydrol Res 46:192–211. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2013.164
Stevens CJ, Quinton JN, Bailey AP, Deasy C, Silgram M, Jackson DR (2009) The effects of minimal tillage, contour cultivation and in-field vegetative barriers on soil erosion and phosphorus loss. Soil Tillage Res 106:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.04.009
Stocking M (2017) Assessing vegetative cover and management effects. Soil erosion research methods. Routledge, New York, pp 211–234
Strohmeier S, Fukai S, Haddad M, AlNsour M, Mudabber M, Akimoto K, Yamamoto S, Evett S, Oweis T (2021) Rehabilitation of degraded rangelands in Jordan: The effects of mechanized micro water harvesting on hill-slope scale soil water and vegetation dynamics. J Arid Environ 185:104338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2020.104338
Sun W, Mu X, Gao P, Zhao G, Li J, Zhang Y, Chiew F (2019) Landscape patches influencing hillslope erosion processes and flow hydrodynamics. Geoderma 353:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.07.003
Thomaz EL, Marcatto FS, Antoneli V (2022) Soil erosion on the Brazilian sugarcane cropping system: An overview. Geogr Sustain 3:129–138
Urgeghe AM, Mayor ÁG, Turrión D, Rodríguez F, Bautista S (2021) Disentangling the independent effects of vegetation cover and pattern on runoff and sediment yield in dryland systems—uncovering processes through mimicked plant patches. J Arid Environ 193:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2021.104585
Wang L, Dalabay N, Lu P, Wu F (2017) Effects of tillage practices and slope on runoff and erosion of soil from the Loess Plateau, China, subjected to simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res 166:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.09.007
Wang S, Sun B, Chaodong L, Zhanbin L, Bo M (2018) Runoff and soil erosion on slope cropland: a review. J Resour Ecol 9:461–470. https://doi.org/10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.05.002
Wang L, Zheng F, Zhang XJ, Wilson GV, Qin C, He C, Liu G, Zhang J (2020) Discrimination of soil losses between ridge and furrow in longitudinal ridge-tillage under simulated upslope inflow and rainfall. Soil Tillage Res 198:104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104541
Wang Z, Chen Z, Ai Z, Zhang G, Zhang Y (2012) Erosion and desertification with Mountain Yimeng typical surface soil caused by different rainfall intensity and slope. J Soil Water Conserv 26:17–20+26. https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2012.06.024
Wilcox BP, Breshears DD, Allen CD (2003) Ecohydrology of a resource-conserving semiarid woodland: Effects of scale and disturbance. Ecol Monogr 73:223–239. https://doi.org/10.1890/00129615(2003)073[0223:EOARSW]2.0.CO;2
Wysocka-Czubaszek A, Czubaszek R (2014) Tillage erosion: the principles, controlling factors and main implications for future research. J Ecol Eng 15:150–159. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993.1125470
Xie S, Mo M, Tu A, Liu Y (2014) Characteristics of vertical runoff output on red-soil slope under natural rainfall condition. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 30:132–138. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.19.016
Xie S, Tu A, Mo M, Liu Y (2015) Analysis on the characteristic of interflow production processes on red soil slopes in the case of natural rainfall events. Adv Water Sci 26:526–534. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2015.04.009
Xu X, Zheng F, Wilson GV, He C, Lu J, Bian F (2018) Comparison of runoff and soil loss in different tillage systems in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res 177:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.10.005
Xu Q, Wang T, Li Z, Cai C, Shi Z (2010) Characteristics of interflow in purple soil of hillslope. Advances in Water Science 21:299–234. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2010.02.006
Yakupoglu T, Gundogan R, Dindaroglu T, Kusvuran K, Gokmen V, Rodrigo-Comino J, Gyasi-Agyei Y, Cerdà A (2021) Tillage impacts on initial soil erosion in wheat and sainfoin fields under simulated extreme rainfall treatments. Sustainability 13:789. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020789
Yang Z, Li C, Liu Y, Duan J, Zhang L, Li Z, Zhou X, Li Q, Ma Y, Tian L (2023) Roles of the stolon and erect grass species in surface–subsurface flow generation and red soil loss. J Hydrol 617:128827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128827
Zhang X, Yu GQ, Li ZB, Li P (2014) Experimental study on slope runoff, erosion and sediment under different vegetation types. Water Resour Manag 28:2415–2433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0603-5
Zhao X, Huang J, Gao X, Wu P, Wang J (2014) Runoff features of pasture and crop slopes at different rainfall intensities, antecedent moisture contents and gradients on the Chinese Loess Plateau: a solution of rainfall simulation experiments. CATENA 119:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.03.007
Zheng H, Liu Z, Zuo J, Wang L, Nie X (2018) Characteristics of nitrogen loss through surface-subsurface flow on red soil slopes of Southeast China. Eurasian Soil Sci 50:1506–1514. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1064229317130063
Zheng H, Li H, Mo M, Song Y, Liu Z, Zhang H (2020) Quantified benefits of cultivating day-lily (Hemerocallis citrina) hedgerows over multiple years on sloped red-soil farmland, Southern China. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 21:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00343-6
Zheng H, Hu J, Huang P, Wang L, Wan J (2014) Comparative study of nitrogen and phosphorus through surface-flow and interflow on red soil farmland. J Soil Water Conserv 28:41–45+70. https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2014.06.008
Zheng H, Nie X, Liu Z, Mo M, Song Y (2021) Identifying optimal ridge practices under different rainfall types on runoff and soil loss from sloping farmland in a humid subtropical region of Southern China. Agric Water Manage 255:107043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107043
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42007066 and 42067020), the Major Discipline Academic and Technical Leaders Training Program of Jiangxi Province (20225BCJ23005), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M721427), and the Jiangxi Water Resources Science and Technology Project (202223YBKT20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: David Allen Lobb
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, K., Liu, Z., Han, X. et al. Effects of ridge tillage and peanut growth on the surface–subsurface runoff generation and soil loss in the red soil sloping farmland of southern China. J Soils Sediments 24, 1431–1446 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03734-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03734-9