Abstract
Purpose
Long-term excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer under diverse land uses has caused serious environmental problems on the North China Plain. Current studies focus on denitrifiers and bacterial communities in topsoil under diverse land-use types; however, few studies have studied denitrifiers and microbial communities in subsoils.
Materials and methods
The variations in soil bacterial communities and denitrifiers with soil profiles (0–300 cm) under crop, apple orchard, and vegetable fields were investigated through high-throughput sequencing and quantitative PCR technologies.
Results and discussion
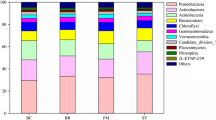
NO3−-N largely accumulated in the deeper soil layers (100–300 cm) in the apple orchard, resulting in a higher risk of NO3−-N leaching. The soil bacterial community structure at the 0–100 cm soil depth had a marketable difference from that at 100–300 cm under these three land-use types, and the C:N ratio was the main driving factor for their vertical distribution. The bacterial α-diversity decreased with soil depth; the crop field had the highest α-diversity across all horizons except 100–200 cm, and total carbon was the most important factor driving α-diversity. In addition, the absolute abundance of the nirK, nirS, and nosZ genes decreased with soil depth and varied with land-use type, which was deeply affected by multiple soil properties, such as soil organic matter and total nitrogen.
Conclusion
Our findings highlighted that potentially important and unique functions remain to be revealed in subsoils, which may provide new insights into mitigating nitrate leaching in various land-use types.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Acosta-Martinez V, Dowd S, Sun Y, Allen V (2008) Tag-encoded pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in a single soil type as affected by management and land use. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2762–2770
Babin D, Deubel A, Jacquiod S, Sorensen SJ, Geistlinger J, Grosch R, Smalla K (2019) Impact of long-term agricultural management practices on soil prokaryotic communities. Soil Biol Biochem 129:17–28
Banerjee S, Schlaeppi K, van der Heijden MGA (2018) Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:567–576
Barberán A, Ladau J, Leff JW, Pollard KS, Menninger HL, Dunn RR, Fierer N (2015) Continental-scale distributions of dust-associated bacteria and fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:5756–5761
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Bolyen E, Knight R, Huttley GA, Caporaso JG (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2 ’ s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6:90
Bolyen E et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Boot CM, Hall EK, Denef K, Baron JS (2016) Long-term reactive nitrogen loading alters soil carbon and microbial community properties in a subalpine forest ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 92:211–220
Bowles TM, Acosta-Martinez V, Calderon F, Jackson LE (2014) Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol Biochem 68:252–262
Braker G, Matthies D, Hannig M, Brandt FB, Brenzinger K, Groengroeft A (2015) Impact of land use management and soil properties on denitrifier communities of namibian savannas. Microb Ecol 70:981–992
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Chai X, Yang Y, Wang X, Hao P, Wang L, Wu T, Zhang X, Xu X, Han Z, Wang Y (2021) Spatial variation of the soil bacterial community in major apple producing regions of China. J Appl Microbiol 130:1294–1306
Chen J, Wang P, Wang C, Wang X, Miao L, Liu S, Yuan Q, Sun S (2020) Fungal community demonstrates stronger dispersal limitation and less network connectivity than bacterial community in sediments along a large river. Environ Microbiol 22:832–849
Chen S, Wang F, Zhang Y, Qin S, Wei S, Wang S, Hu C, Liu B (2018) Organic carbon availability limiting microbial denitrification in the deep vadose zone. Environ Microbiol 20:980–992
Chu H, Fujii T, Morimoto S, Lin X, Yagi K (2008) Population size and specific nitrification potential of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria under long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1960–1963
Csardi G, Nepusz T (2006) The igraph software package for complex network research. Int J Complex Syst 1695:1–9
Cui M, Zeng L, Qin W, Feng J (2020) Measures for reducing nitrate leaching in orchards: a review. Environ Pollut 263:114553
Curtis P, Nakatsu CH, Konopka A (2002) Aciduric Proteobacteria isolated from pH 2.9 soil. Arch Microbiol 178:65–70
DeBruyn JM, Nixon LT, Fawaz MN, Johnson AM, Radosevich M (2011) Global biogeography and quantitative seasonal dynamics of Gemmatimonadetes in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6295–6300
Ding L, Zhou J, Li Q, Tang J, Chen X (2022) Effects of land-use type and flooding on the soil microbial community and functional genes in reservoir riparian zones. Microb Ecol 83:393–407
Eilers KG, Debenport S, Anderson S, Fierer N (2012) Digging deeper to find unique microbial communities: the strong effect of depth on the structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 50:58–65
Emadi M, Emadi M, Baghernejad M, Fathi H, Saffari M (2008) Effect of land use change on selected soil physical and chemical properties in North Highlands of Iran. J Appl Sci 8:496–502
Fan Z, Lin S, Zhang X, Jiang Z, Yang K, Jian D, Chen Y, Li J, Chen Q, Wang J (2014) Conventional flooding irrigation causes an overuse of nitrogen fertilizer and low nitrogen use efficiency in intensively used solar greenhouse vegetable production. Agric Water Manag 144:11–19
Fetene EM, Amera MY (2018) The effects of land use types and soil depth on soil properties of Agedit watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Sci Technol 11:39–56
Fierer N (2017) Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:579–590
Fierer N, Lauber CL, Ramirez KS, Zaneveld J, Bradford MA, Knight R (2012) Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J 6:1007–1017
Fierer N, Schimel JP, Holden PA (2003) Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biol Biochem 35:167–176
Francioli D, Schulz E, Lentendu G, Wubet T, Buscot F, Reitz T (2016) Mineral vs. organic amendments: microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front Microbiol 7:1446
Gao J, Wang S, Li Z, Wang L, Chen Z, Zhou J (2021) High nitrate accumulation in the vadose zone after land-use change from croplands to orchards. Environ Sci Technol 55:5782–5790
Gao W, Yang H, Kou L, Li S (2015) Effects of nitrogen deposition and fertilization on N transformations in forest soils: a review. J Soils Sediments 15:863–879
Goberna M, Insam H, Klammer S, Pascual JA, Sanchez J (2005) Microbial community structure at different depths in disturbed and undisturbed semiarid Mediterranean forest soils. Microb Ecol 50:315–326
Goldfarb KC, Karaoz U, Hanson CA, Santee CA, Bradford MA, Treseder KK, Wallenstein MD, Brodie EL (2011) Differential growth responses of soil bacterial taxa to carbon substrates of varying chemical recalcitrance. Front Microbiol 2:94
Gu Y, Wei Y, Xiang Q, Zhao K, Yu X, Zhang X, Li C, Chen Q, Xiao H, Zhang X (2019) C: N ratio shaped both taxonomic and functional structure of microbial communities in livestock and poultry breeding wastewater treatment reactor. Sci Total Environ 651:625–633
Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, Maeder P, Widmer F (2015) Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J 9:1177–1194
He H, Miao Y, Zhang L, Chen Y, Gan Y, Liu N, Dong L, Dai J, Chen W (2020) The structure and diversity of nitrogen functional groups from different cropping systems in Yellow River Delta. Microorganisms 8:424
He S, Guo L, Niu M, Miao F, Jiao S, Hu T, Long M (2017) Ecological diversity and co-occurrence patterns of bacterial community through soil profile in response to long-term switchgrass cultivation. Sci Rep 7:3608
Jimenez-Bueno NG, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, Ortiz-Gutierrez D, Verhulst N, Govaerts B, Dendooven L, Navarro-Noya YE (2016) Bacterial indicator taxa in soils under different long-term agricultural management. J Appl Microbiol 120:921–933
Ju X, Kou C, Zhang F, Christie P (2006) Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 143:117–125
Kramer C, Gleixner G (2008) Soil organic matter in soil depth profiles: distinct carbon preferences of microbial groups during carbon transformation. Soil Biol Biochem 40:425–433
Kramer SB, Reganold JP, Glover JD, Bohannan BJM, Mooney HA (2006) Reduced nitrate leaching and enhanced denitrifier activity and efficiency in organically fertilized soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4522–4527
Lauber CL, Strickland MS, Bradford MA, Fierer N (2008) The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2407–2415
Li C, Yan K, Tang L, Jia Z, Li Y (2014) Change in deep soil microbial communities due to long-term fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 75:264–272
Li H, Zhang Y, Wang T, Feng S, Ren Q, Cui Z, Cao C (2019) Responses of soil denitrifying bacterial communities carrying nirS, nirK, and nosZ genes to revegetation of moving sand dunes. Ecol Indic 107:105541
Lian J, Wang H, Deng Y, Xu M, Liu S, Zhou B, Jangid K, Duan Y (2022) Impact of long-term application of manure and inorganic fertilizers on common soil bacteria in different soil types. Agric Ecosyst Environ 337:108044
Lindsay EA, Colloff MJ, Gibb NL, Wakelin SA (2010) The abundance of microbial functional genes in grassy woodlands is influenced more by soil nutrient enrichment than by recent weed invasion or livestock exclusion. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5547–5555
Liu C, Yan J, Huang Q, Liu H, Qiao C, Li R, Shen B, Shen Q (2022a) The addition of sawdust reduced the emission of nitrous oxide in pig manure composting by altering the bacterial community structure and functions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:3733–3742
Liu G, Chen L, Deng Q, Shi X, Lock TR, Kallenbach RL, Yuan Z (2020a) Vertical changes in bacterial community composition down to a depth of 20 m on the degraded Loess Plateau in China. Land Degrad Dev 31:1300–1313
Liu M, Min L, Wu L, Pei H, Shen Y (2022b) Evaluating nitrate transport and accumulation in the deep vadose zone of the intensive agricultural region. North China Plain Sci Total Environ 825:153894
Liu M, Zhang W, Wang X, Wang F, Dong W, Hu C, Liu B, Sun R (2020b) Nitrogen leaching greatly impacts bacterial community and denitrifiers abundance in subsoil under long-term fertilization. Agric Ecosyst Environ 294:106885
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M (2016) Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 353:1272–1277
Lv X, Ma B, Sun L, Cai Y, Chang SX (2022) Long-term nitrogen fertilization, but not short-term tillage reversal, affects bacterial community structure and function in a no-till soil. J Soils Sediments 22:630–639
Merloti LF, Mendes LW, Pedrinho A, de Souza LF, Ferrari BM, Tsai SM (2019) Forest-to-agriculture conversion in Amazon drives soil microbial communities and N-cycle. Soil Biol Biochem 137:107567
Muhammad I, Yang L, Ahmad S, Zeeshan M, Farooq S, Ali I, Khan A, Zhou X (2022) Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization alter soil bacterial communities, soil enzyme activities, and nutrient availability in maize crop. Front Microbiol 13:833758
Rao D, Meng F, Yan X, Zhang M, Yao X, Kim KS, Zhao J, Qiu Q, Xie F, Zhang W (2021) Changes in soil microbial activity, bacterial community composition an d function in a long-term continuous soybean cropping system after corn insertion and fertilization. Front Microbiol 12:638326
Reverchon F, Bai SH, Liu X, Blumfield TJ (2015) Tree plantation systems influence nitrogen retention and the abundance of nitrogen functional genes in the Solomon Islands. Front Microbiol 6:1439
Romdhane S, Spor A, Banerjee S, Breuil M-C, Bru D, Chabbi A, Hallin S, van der Heijden MGA, Saghai A, Philippot L (2022) Land-use intensification differentially affects bacterial, fungal and protist communities and decreases microbiome network complexity. Environ Microbiome 17:1
Schlatter DC, Kahl K, Carlson B, Huggins DR, Paulitz T (2020) Soil acidification modifies soil depth-microbiome relationships in a no-till wheat cropping system. Soil Biol Biochem 149:107939
Semenov MV, Krasnov GS, Semenov VM, Ksenofontova N, Zinyakova NB, van Bruggen AHC (2021) Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J Environ Manag 294:113018
Seuradge BJ, Oelbermann M, Neufeld JD (2017) Depth-dependent influence of different land-use systems on bacterial biogeography. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fiw239
Song Y, Xu M, Li X, Bian Y, Wang F, Yang X, Gu C, Jiang X (2018) Long-term plastic greenhouse cultivation changes soil microbial community structures: a case study. J Agric Food Chem 66:8941–8948
Sun R, Guo X, Wang D, Chu H (2015) Effects of long-term application of chemical and organic fertilizers on the abundance of microbial communities involved in the nitrogen cycle. Appl Soil Ecol 95:171–178
Sun R, Li W, Dong W, Tian Y, Hu C, Liu B (2018) Tillage changes vertical distribution of soil bacterial and fungal communities. Front Microbiol 9:699
Surey R, Lippold E, Heilek S, Sauheitl L, Henjes S, Horn MA, Mueller CW, Merbach I, Kaiser K, Boettcher J, Mikutta R (2020) Differences in labile soil organic matter explain potential denitrification and denitrifying communities in a long-term fertilization experiment. Appl Soil Ecol 153:103630
Throback IN, Enwall K, Jarvis A, Hallin S (2004) Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 49:401–417
Walters W, Hyde ER, Berg-Lyons D, Ackermann G, Humphrey G, Parada A, Gilbert JA, Jansson JK, Caporaso JG, Fuhrman JA, Apprill A, Knight R (2016) Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4–5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys. mSystems 1:e00009
Wang F, Chen S, Qin S, Sun R, Zhang Y, Wang S, Hu C, Hu H, Liu B (2021) Long-term nitrogen fertilization alters microbial community structure and denitrifier abundance in the deep vadose zone. J Soils Sediments 21:2394–2403
Wang F, Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Hu C, Liu B (2018) Long-term nitrogen fertilization elevates the activity and abundance of nitrifying and denitrifying microbial communities in an upland soil: implications for nitrogen loss from intensive agricultural systems. Front Microbiol 9:2424
Wang R, Liu Z, Yao Z, Lei Y (2014) Modeling the risk of nitrate leaching and nitrate runoff loss from intensive farmland in the Baiyangdian Basin of the North China Plain. Environ Earth Sci 72:3143–3157
Wang Y, Chen P, Wang F, Han W, Qiao M, Dong W, Hu C, Zhu D, Chu H, Zhu Y (2022) The ecological clusters of soil organisms drive the ecosystem multifunctionality under long-term fertilization. Environ Int 161:107133
Wang Y, Ying H, Yin Y, Zheng H, Cui Z (2019) Estimating soil nitrate leaching of nitrogen fertilizer from global meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 657:96–102
Wheeler DC, Nolan BT, Flory AR, DellaValle CT, Ward MH (2015) Modeling groundwater nitrate concentrations in private wells in Iowa. Sci Total Environ 536:481–488
Xun W, Liu Y, Li W, Ren Y, Xiong W, Xu Z, Zhang N, Miao Y, Shen Q, Zhang R (2021) Specialized metabolic functions of keystone taxa sustain soil microbiome stability. Microbiome 9:35
Zhang Q, Han Y, Chen W, Guo Y, Wu M, Wang Y, Li H (2022) Soil type and pH mediated arable soil bacterial compositional variation across geographic distance in North China Plain. Appl Soil Ecol 169:104220
Zhang Z, Han X, Yan J, Zou W, Wang E, Lu X, Chen X (2020) Keystone microbiomes revealed by 14 years of field restoration of the degraded agricultural soil under distinct vegetation scenarios. Front Microbiol 11:1915
Zhou J, Gu B, Schlesinger WH, Ju X (2016) Significant accumulation of nitrate in Chinese semi-humid croplands. Sci Rep 6:25088
Zhou J, Jiang X, Wei D, Zhao B, Ma M, Chen S, Cao F, Shen D, Guan D, Li J (2017) Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in black soils for two crop seasons in China. Sci Rep 7:3267
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41930865, No. 42077358, No. 41877425) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB40020204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hang-Wei Hu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, W., Wang, F., Zhang, L. et al. Variations of soil bacterial community and denitrifier abundance with depth under different land-use types. J Soils Sediments 23, 1889–1900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03428-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03428-8