Abstract
Purpose
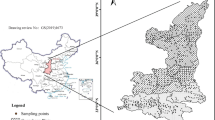
The present study aimed to reveal the spatial distribution of soil nutrients in southwest China and to quantitatively evaluate the effect of environmental factors on spatial variability of soil nutrients under different cropping systems.
Methods
Semivariogram, random forest (RF), and partial dependence plots (PDP) were applied to investigate the relationships between environmental factors and soil nutrients variability. A total of 142 samples were collected from topsoil under rice and maize cropping systems in southwest China.
Results
Soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) in the topsoil of the study area were higher than their corresponding background and geochemical baseline values of China. Semivariogram analysis indicated that SOC and TN have weak spatial dependence, and TP has strong spatial dependence. The soil nutrient contents were predicted well by the RF models. The mean absolute error, root mean square error, and coefficient of determination were 0.14–0.47 g/kg, 0.19–3.67 g/kg, and 0.30–0.46, respectively. For different soil nutrients, the relative importance of environmental variables varied greatly. Cropping system, topographic wetness index (TWI), and slope were critical factors that controlled SOC variability. Cropping system, TWI, and mean annual temperature explained most variation of TN. Soil pH, aspect, and cropping system were dominant factors affecting TP variability.
Conclusion
In this study, SOC and TN had weak spatial autocorrelation, while TP had strong spatial autocorrelation. Meanwhile, cropping system and topography had greatly impact on the variability of soil nutrients, which should be considered in formulating agricultural measures in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and material used in this research will be available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Adhikari D, Jiang T, Kawagoe T et al (2017) Relationship among phosphorus circulation activity, bacterial biomass, ph, and mineral concentration in agricultural soil. Microorganisms 5:79. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5040079
Apley DW, Zhu J (2020) Visualizing the effects of predictor variables in black box supervised learning models. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 82:1059–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/rssb.12377
Bangroo SA, Najar GR, Rasool A (2017) Effect of altitude and aspect on soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Himalayan Mawer Forest Range. CATENA 158:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.06.017
Bao SD (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, China
Berk RA, Bleich J (2013) Statistical Procedures for Forecasting Criminal Behavior: A Comparative Assessment Berk and Bleich Forecasting Criminal Behavior. Criminol Public Policy 12:513–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-9133.12047
Beullens J, Van de Velde D, Nyssen J (2014) Impact of slope aspect on hydrological rainfall and on the magnitude of rill erosion in Belgium and northern France. CATENA 114:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.10.016
Blyth S (1994) Karl Pearson and the Correlation Curve. International Statistical Review / Revue Internationale de Statistique 62(3):393. https://doi.org/10.2307/1403769
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Cao Q, Li J, Wang G et al (2021) On the spatial variability and influencing factors of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks in a desert oasis ecotone of northwestern China. CATENA 206:105–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105533
Chen Z, Wang L, Wei A et al (2019) Land-use change from arable lands to orchards reduced soil erosion and increased nutrient loss in a small catchment. Sci Total Environ 648:1097–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.141
da Cerozi BS, Fitzsimmons K (2016) The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour Technol 219:778–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.08.079
Deng L, Zhu GY, Tang ZS, S G, et al (2016) Global patterns of the effects of land-use changes on soil carbon stocks. Glob Ecol Conserv 5:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2015.12.004
Duan L, Li Z, Xie H et al (2020) Regional pattern of soil organic carbon density and its influence upon the plough layers of cropland. L Degrad Dev 31:2461–2474. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3610
Elith J, Leathwick JR, Hastie T (2008) A working guide to boosted regression trees. J Anim Ecol 77:802–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01390.x
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Kerkhoff AJ et al (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186:593–608. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03214.x
Fang XM, Zhang XL, Chen FS et al (2019) Phosphorus addition alters the response of soil organic carbon decomposition to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 133:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.03.005
Finzi AC, Austin AT, Cleland EE et al (2011) Responses and feedbacks of coupled biogeochemical cycles to climate change: Examples from terrestrial ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 9:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1890/100001
Friedman JH (2001) Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann Stat 29:1189–1232. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013203451
Gallaher RN, Weldon CO, Boswell FC (1976) A Semiautomated Procedure for Total Nitrogen in Plant and Soil Samples. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40:887–889. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1976.03615995004000060026x
Gao XS, Xiao Y, Deng LJ et al (2019) Spatial variability of soil total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in Renshou County of Sichuan Basin, China. J Integr Agric 18:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62069-6
Gao Y, He N, Yu G et al (2014) Long-term effects of different land use types on C, N, and P stoichiometry and storage in subtropical ecosystems: A case study in China. Ecol Eng 67:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.013
Guo PT, Wu W, Liu HB et al (2011) Effects of land use and topographical attributes on soil properties in an agricultural landscape. Soil Res 49(7):606. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR11134
Haileslassie A, Priess J, Veldkamp E et al (2005) Assessment of soil nutrient depletion and its spatial variability on smallholders’ mixed farming systems in Ethiopia using partial versus full nutrient balances. Agric Ecosyst Environ 108:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2004.12.010
Han Y, Ma W, Zhou B et al (2020) Effects of straw-return method for the maize-rice rotation system on soil properties and crop yields. Agronomy 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040461
Hoylman ZH, Jencso KG, Hu J et al (2018) Hillslope Topography Mediates Spatial Patterns of Ecosystem Sensitivity to Climate. J Geophys Res Biogeosciences 123:353–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JG004108
Hu W, Shen Q, Zhai X et al (2021) Impact of environmental factors on the spatiotemporal variability of soil organic matter: a case study in a typical small Mollisol watershed of Northeast China. J Soils Sediments 21:736–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02863-1
Inglis A, Parnell A, Hurley CB (2022) Visualizing Variable Importance and Variable Interaction Effects in Machine Learning Models. J Comput Graph Stat 0:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2021.2007935
Ishwaran H, Lu M (2019) Standard errors and confidence intervals for variable importance in random forest regression, classification, and survival. Stat Med 38:558–582. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.7803
IUSS Working Group WRB (2006) World reference base for soil resources. World Soil Resour. Rep 103
Jenny H (1994) Factors of soil formation: a system of quantitative pedology. Courier Corporation
Jiang F, Wu XH, Xiang WH et al (2017) Spatial variations in soil organic carbon nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations related to stand characteristics in subtropical areas. Plant and Soil 413(1-2):289–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-3101-0
Jin Z, Shang J, Zhu Q et al (2020) RFRSF: Employee Turnover Prediction Based on Random Forests and Survival Analysis. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 12343 LNCS:503–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62008-035
Kumar S, Singh RP (2016) Spatial distribution of soil nutrients in a watershed of Himalayan landscape using terrain attributes and geostatistical methods. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5098-8
Li D, Niu S, Luo Y (2012) Global patterns of the dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks following afforestation: A meta-analysis. New Phytol 195:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04150.x
Li T, Zeng J, He B, Chen Z (2021) Changes in soil c, n, and p concentrations and stoichiometry in karst trough valley area under ecological restoration: The role of slope aspect, land use, and soil depth. Forests 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020144
Li Y, Qing Y, Lyu M et al (2018) Effects of artificial warming on different soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in a subtropical plantation. Soil Biol Biochem 124:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.06.007
Liao W, Menge DNL, Lichstein JW, Ángeles-Pérez G (2017) Global climate change will increase the abundance of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing trees in much of North America. Glob Chang Biol 23:4777–4787. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13716
Liu F, Wang X, Chi Q, Tian M (2021a) Spatial variations in soil organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus contents and controlling factors across the “Three Rivers” regions of southwest China. Sci Total Environ 794:148795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148795
Liu F, Zhang GL, Song X et al (2020) High-resolution and three-dimensional mapping of soil texture of China. Geoderma 361:114061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.114061
Liu J, Gou X, Zhang F et al (2021b) Spatial patterns in the C:N: P stoichiometry in Qinghai spruce and the soil across the Qilian Mountains. China Catena 196:104814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104814
Liu S, Zhang W, Wang K et al (2015) Factors controlling accumulation of soil organic carbon along vegetation succession in a typical karst region in Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 521–522:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.074
Liu X, Ma J, Ma ZW, Li LH (2017) Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry as affected by land-use in an agro-pastoral region of northwest China. CATENA 150:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.020
Lu Y, Jenkins A, Ferrier RC et al (2015) Addressing China’s grand challenge of achieving food security while ensuring environmental sustainability. Sci Adv 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1400039
Maharajan T, Ceasar SA, Krishna TPA, Ignacimuthu S (2021) Management of phosphorus nutrient amid climate change for sustainable agriculture. J Environ Qual 50:1303–1324. https://doi.org/10.1002/jeq2.20292
Måren IE, Karki S, Prajapati C et al (2015) Facing north or south: Does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley? J Arid Environ 121:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2015.06.004
Moore ID, Grayson RB, Ladson AR (1991) Digital terrain modelling: A review of hydrological, geomorphological, and biological applications. Hydrol Process 5:3–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050103
Müller M, Oelmann Y, Schickhoff U et al (2017) Himalayan treeline soil and foliar C:N: P stoichiometry indicate nutrient shortage with elevation. Geoderma 291:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.12.015
Nelson DWA, Sommers L (1983) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods soil Anal Part 2 Chem Microbiol Prop 9:539–579
Ngaba MJY, Hu YL, Bol R et al (2019) Effects of land use change from natural forest to plantation on C, N and natural abundance of 13C and 15N along a climate gradient in eastern China. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52959-z
Niederberger J, Kohler M, Bauhus J (2019) Distribution of phosphorus fractions with different plant availability in German forest soils and their relationship with common soil properties and foliar P contents. Soil 5:189–204. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-5-189-2019
NSSO, National Soil Survey Office (1998) Soil of China. Beijing, China, pp 318–336
Okin GS, Mladenov N, Wang L et al (2008) Spatial patterns of soil nutrients in two southern African savannas. J Geophys Res Biogeosciences 113:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JG000584
Penn CJ, Camberato JJ (2019) A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil ph affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agric 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060120
Ren T, Bu R, Liao S et al (2019) Differences in soil nitrogen transformation and the related seed yield of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.)under paddy-upland and continuous upland rotations. Soil Tillage Res 192:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.05.008
Rodrigues M, Withers PJA, Soltangheisi A et al (2021) Tillage systems and cover crops affecting soil phosphorus bioavailability in Brazilian Cerrado Oxisols. Soil Tillage Res 205:104770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104770
Scharlemann JPW, Tanner EVJ, Hiederer R, Kapos V (2014) Global soil carbon: Understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool. Carbon Manag 5:81–91. https://doi.org/10.4155/cmt.13.77
Shangguan W, Dai Y, Liu B et al (2012) A soil particle-size distribution dataset for regional land and climate modelling in China. Geoderma 171–172:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.01.013
Song X, Peng C, Zhou G et al (2014) Chinese Grain for Green Program led to highly increased soil organic carbon levels: A meta-analysis. Sci Rep 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04460
Sun S, Zhang G, He T et al (2021) Effects of landscape positions and landscape types on soil properties and chlorophyll content of citrus in a sloping orchard in the three gorges reservoir area, china. Sustain. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084288
Sun W, Zhu H, Guo S (2015) Soil organic carbon as a function of land use and topography on the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol Eng 83:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.06.030
Talkner U, Jansen M, Beese FO (2009) Soil phosphorus status and turnover in central-european beech forest ecosystems with differing tree species diversity. Eur J Soil Sci 60:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01117.x
Tan Q, Wang G, Smith MD et al (2021) Temperature patterns of soil carbon: nitrogen: phosphorus stoichiometry along the 400 mm isohyet in China. CATENA 203:105338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105338
Teng M, Zeng L, Xiao W et al (2017) Spatial variability of soil organic carbon in Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Sci Total Environ 599–600:1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.085
Turmel MS, Speratti A, Baudron F et al (2015) Crop residue management and soil health: A systems analysis. Agric Syst 1346–1316. S0308521X14000651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2014.05.009
Wan W, Hao X, Xing Y et al (2021) Spatial differences in soil microbial diversity caused by pH-driven organic phosphorus mineralization. L Degrad Dev 32:766–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3734
Wang HJ, Shi XZ, Yu DS et al (2009) Factors determining soil nutrient distribution in a small-scaled watershed in the purple soil region of Sichuan Province, China. Soil Tillage Res 105:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2008.08.010
Wang J, Zhang Q, Gou T et al (2018a) Spatial-temporal changes of urban areas and terrestrial carbon storage in the Three Gorges Reservoir in China. Ecol Indic 95:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.06.036
Wang M, Chen H, Zhang W, Wang K (2018b) Soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios as affected by land use and lithology at county scale in a karst area, southwest China. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1299–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.175
Wang M, Chen H, Zhang W, Wang K (2019) Influencing factors on soil nutrients at different scales in a karst area. CATENA 175:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.040
Wang S, Adhikari K, Wang Q et al (2018c) Role of environmental variables in the spatial distribution of soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and C: N ratio from the northeastern coastal agroecosystems in China. Ecol Indic 84:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.08.046
Wang SF, Wang XK, Ouyang ZY (2012) Effects of land use, climate, topography and soil properties on regional soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the Upstream Watershed of Miyun Reservoir, North China. J Environ Sci 24:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60789-4
Wang T, Kang F, Cheng X et al (2017) Spatial variability of organic carbon and total nitrogen in the soils of a subalpine forested catchment at Mt. Taiyue. China Catena 155:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.03.004
Wang W, Sardans J, Zeng C et al (2014) Responses of soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry to different human land uses in a subtropical tidal wetland. Geoderma 232–234:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.06.004
Wang X, Zhang S, Zhong Q et al (2021) Interaction effects of environmental factors on soil nitrogen fractions based on a novel sequential extraction method. Eur J Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.13146
Wang X, Zhou J, XU S et al (2016) China soil geochemical baselines networks: Data characteristics. Geol China 1469–1480
Wei X, Shao M, Fu X, Horton R (2010) Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen after 28 years grassland afforestation: Effects of tree species, slope position, and soil order. Plant Soil 331:165–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0243-3
Wiesmeier M, Barthold F, Blank B, Kögel-Knabner I (2011) Digital mapping of soil organic matter stocks using Random Forest modeling in a semi-arid steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil 340:7–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0425-z
Wu J (2011) Carbon accumulation in paddy ecosystems in subtropical China: Evidence from landscape studies. Eur J Soil Sci 62:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01325.x
Xue JF, Pu C, Liu SL et al (2015) Effects of tillage systems on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in a double paddy cropping system in Southern China. Soil Tillage Res 153:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.06.008
Yang RM, Zhang GL, Liu F et al (2016) Comparison of boosted regression tree and random forest models for mapping topsoil organic carbon concentration in an alpine ecosystem. Ecol Indic 60:870–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.08.036
Yu H, Zha T, Zhang X et al (2020a) Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon may be predominantly regulated by topography in a small revegetated watershed. CATENA 188:104459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104459
Yu X, Zhou W, Chen Y et al (2020b) Spatial variation of soil properties and carbon under different land use types on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 703:134946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134946
Zeraatpisheh M, Ayoubi S, Jafari A et al (2019) Digital mapping of soil properties using multiple machine learning in a semi-arid region, central Iran. Geoderma 338:445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.09.006
Zhang H, Wang D, Su B et al (2021) Distribution and determinants of organic carbon and available nutrients in tropical paddy soils revealed by high–resolution sampling. Agric Ecosyst Environ 320:107580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107580
Zhang H, Wu P, Fan M et al (2018) Dynamics and driving factors of the organic carbon fractions in agricultural land reclaimed from coastal wetlands in eastern China. Ecol Indic 89:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.01.039
Zhang L, tao, Gao Z liang, Yang S wei, et al (2015) Dynamic processes of soil erosion by runoff on engineered landforms derived from expressway construction: A case study of typical steep spoil heap. CATENA 128:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.01.020
Zhang X, Li MJ, Yang C et al (2022) The stratification of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen affected by parent material and cropping system. CATENA 210:105898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105898
Zhang Y, Ni J, Yang J et al (2017) Citrus stand ages regulate the fraction alteration of soil organic carbon under a citrus/Stropharua rugodo-annulata intercropping system in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:18363–18371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9269-x
Zhang Z, Yu X, Qian S, Li J (2010) Spatial variability of soil nitrogen and phosphorus of a mixed forest ecosystem in Beijing, China. Environ Earth Sci 60:1783–1792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0314-z
Zheng H, Huang H, Zhang C, Li J (2016) National-scale paddy-upland rotation in Northern China promotes sustainable development of cultivated land. Agric Water Manag 170:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.01.009
Zheng S, Xia Y, Hu Y et al (2021) Stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil: Effects of agricultural land use and climate at a continental scale. Soil Tillage Res 209:104903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104903
Zhou W, Han G, Liu M et al (2020) Determining the distribution and interaction of soil organic carbon, nitrogen, pH and texture in soil profiles: A case study in the Lancangjiang river Basin. Southwest China Forests 11:532. https://doi.org/10.3390/F11050532
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support provided by the farmers in southwest China during data collection, which allowed us to conduct this study. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their careful reading and valuable comments, which helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Heshuang Wan, Hongbin Liu and Weichun Zhang; Methodology: Heshuang Wan and Weichun Zhang; Formal analysis and investigation: Heshuang Wan and Wei Wu; Writing-original draft preparation: Heshuang Wan and Wei Wu; Writing-review and editing: Heshuang Wan, Wei Wu and Hongbin Liu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors undertake that this article has not been published in any other journal and that no plagiarism has occurred.
Consent to participate
The authors agree to participate in the journal.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish in the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jianming Xue
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, HS., Zhang, WC., Wu, W. et al. Environmental factors affecting soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus under two cropping systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. J Soils Sediments 23, 831–844 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03373-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03373-y