Abstract
Purpose
The stoichiometric characteristics of plants are significantly affected by soil nutrients and moisture, which regulate photosynthesis. In wheat, they can be assessed to determine environmental adaptability.
Methods
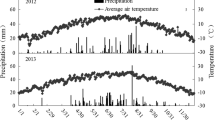
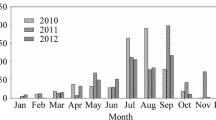
The selected spring wheat was investigated in a field experiment conducted from 2015 to 2017 in a semiarid area. The three treatments were (1) plastic-soil mulching (PMS), (2) gravel mulching (SM), and (3) without mulching (CK). The soil chemical properties and the net photosynthetic rate in flag leaves were recorded; the stoichiometric parameters of soil and flag leaves were calculated.
Results
The soil organic carbon (C) of PMS increased significantly in the 0–30-cm profile when compared with SM and CK, respectively. The soil nitrogen (N)/phosphorus (P) ratio of PMS increased in the filling stage when compared with SM and CK, respectively. The C/N ratio in flag leaves of wheat under PMS significantly decreased and increased compared with SM and CK at the filling stage during a wet year, respectively, and significantly decreased compared with CK during a drought year. The C/N and C/P ratios were significantly correlated between soil and wheat flag leaves in SM, and the net photosynthetic rates and the C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios of flag leaves under PMS and SM were also significantly correlated.
Conclusions
The PMS treatment relieved soil nutrient limitations in flag leaves and increased the net photosynthetic rate by optimizing foliar C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios. This resulted in increased photosynthesis under drought conditions and significantly increased the yield and water-use efficiency.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao SD (1999) Analysis of soil agrochemical. Beijing, China
Cannell GH, Bingham FT, Lingle JC, Garber MJ (2008) Yield and nutrient composition of tomatoes in relation to soil temperature, moisture, and phosphorus levels. Soil Sci Soc Am J 27(5):560–565
Dong QH, Yang YC, Yu K, Feng H (2018) Effects of straw mulching and plastic film mulching on improving soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions, crop yield and water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric Water Manag 201(31):133–143
Du WL, Gao J, Hu FL, Guo DL, Zhang GS, Zhang RH, Xue JQ (2013) Responses of drought stress on photosynthetic trait and osmotic adjustment in two maize cultivars. Acta Agron Sin 39(3):530–536
Fu WG, Wang FK, Zhao Y, Teng BQ, Wang YX (2016) Effects of soil nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics on photosynthetic gas exchange and chlorophyII fluorescence of wheat. Acta Botan Boreali-Occiden Sin 36(7):1435–1442
Fu W, Fan J, Hu YT, Zhao J, Hao MD (2017) Effects of fertilization and film mulching on soil physical and chemical properties and winter wheat yield on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer 23(5):1158–1167
Garcia NS, Bonachela JA, Martiny AC (2016) Interactions between growth-dependent changes in cell size, nutrient supply and cellular elemental stoichiometry of marine Synechococcus. ISME J 10:2715–2724
He JS, Han XG (2010) Ecological stoichiometry: searching for unifying principles from individuals to ecosystems. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology 34(1):2–6
Hong JT, Wang XD, Wu JB (2015) Effects of soil fertility on the N: P stoichiometry of herbaceous plants on a nutrient-limited alpine steppe on the northern Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 391:179–194
Hou HZ, Lv JF, Guo TW, Zhang GP, Dong B, Zhang XC (2014) Effects of whole field soil-plastic mulching on spring wheat water consumption, yield, and soil water balance in semiarid region. Scientia Agricultural Sinica 47(22):4392–4404
Huysen TL, Perakis SS, Harmon ME (2016) Decomposition drives convergence of forest litter nutrient stoichiometry following phosphorus addition. Plant Soil 406:1–14
Kattge J, Knorr W, Raddatz T, Wirth C (2009) Quantifying photosynthetic capacity and its relationship to leaf nitrogen content for global-scale terrestrial biosphere models. Glob Change Biol 15:976–991
Körschens M, Albert E, Armbruster M, Barkusky D, Baumecker M, Behle-Schalk L, Bischoff R, Čergan Z, Ellmer F, Herbst F, Hoffmann S, Hofmann B, Kismanyoky T, Kubat J, Kunzova E, Lopez-Fando C, Merbach I, Merbach W, Pardor MT, Rogasik J, Rühlmann J, Spiegel H, Schulz E, Tajnsek A, Toth Z, Wegener H, Zorn W (2013) Effect of mineral and organic fertilization on crop yield, nitrogen uptake, carbon and nitrogen balances, as well as soil organic carbon content and dynamics: results from 20 European long-term field experiments of the twenty-first century. Arch Agron Soil Sci 59(8):1017–1040
Li SQ, Li FM, Song QH, Wang J (2001) Effect of plastic film mulching periods on the soil nitrogen availability in semiarid areas. Acta Ecol Sin 21(9):1519–1526
Li YS, Wu LH, Zhao LM, Lu XH, Fan QL, Zhang FS (2007) Influence of continuous plastic film mulching on yield, water use efficiency and soil properties of rice fields under non-flooding condition. Soil Tillage Res 93(2):370–378
Li X, Wang H, Gan SH, Jiang DQ, Tian GM, Zhang ZJ (2013) Eco-stoichiometric alterations in paddy soil ecosystem driven by phosphorus application. PLoS One 8(5):1–9
Liu C, Wang Y, Wang N, Wang GX (2012) Advances research in plant nitrogen, phosphorus and their stoichiometry in terrestrial ecosystems: a review. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology 36(11):1205–1216
Lü XT, Kong DL, Pan QM, Simmons ME, Han XG (2012) Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 168(2):301–310
Luo SS, Zhu L, Liu JL, Bu LD, Yue SC, Shen YF, Li SQ (2015) Mulching effects on labile soil organic nitrogen pools under a spring maize cropping system in semiarid farmland. Agron J 107(4):1465–1472
Miller JJ, Beasley BW, Larney FJ, Olson BM (2004) Barley dry matter yield, crop uptake, and soil nutrients under fresh and composted manure containing straw or wood-chip bedding. Can J Plant Sci 84(4):987–999
Reich PB, Oleksyn J (2004) Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. PNAS 101:11001–11006
Sheng YG (2000). The most important chemical reaction on earth – photosynthesis. Beijing, China
Veiga MD, Reinert DJ, Reichert JM (2010) Tillage systems and nutrient sources affecting soil cover, temperature and moisture in a clayey oxisol under corn. Revista Brasileira De Ciência Do Solo 34(6):2011–2020
Wang X, Li HG, Cheng LY, Wang BL, Shen JB (2017a) Advances of root-soil interface effect of phosphorus and water interaction and mechanisms of their efficient use. J Plant Nutr Fertil 23(4):1054–1064
Wang M, Liu GH, Jin TT, Li ZS, Gong L, Wang H, Ye X (2017b) Age-related changes of leaf traits and stoichiometry in an alpine shrub (Rhododendron agglutinatum) along altitudinal gradient. J Mountain Sci 14(1):106–118
Yan ZB, Jin NY, Han TS, Fang JY, Han WX (2013) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on leaf carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of Arabidopsis thaliana. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology 37(6):551–557
Yan S, Zhang L, Jing YS, He HL, Yu GR (2014) Variations in the relationship between maximum leaf carboxylation rate and leaf nitrogen concentration. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology 38(6):640–652
Yan K, Duan CQ, Fu DG, Li J, Michelle HGW, Qian L, Tian YX (2015) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of plant communities in geochemically phosphorus-enriched soils in a subtropical mountainous region, SW China. Environ Earth Sci 74(5):3867–3876
Zhang YW, Shangguan ZP (2018) Interaction of soil water storage and stoichiometrical characteristics in the long-term natural vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau. Ecol Eng 116:7–13
Zhang XC, Yu XF, Ma YF (2013) Effect of nitrogen application and elevated CO2 on photosynthetic gas exchange and electron transport in wheat leaves. Photosynthetic 51(4):593–602
Acknowledgments
We thank Lesley Benyon, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31960398, 31560355), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0200403), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Projects of the Gansu Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2020GAAS32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jianming Xue
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, H., Zhang, X., Wang, J. et al. Plastic-soil mulching increases the photosynthetic rate by relieving nutrient limitations in the soil and flag leaves of spring wheat in a semiarid area. J Soils Sediments 20, 3158–3170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02659-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02659-3