Abstract
Purpose
Evaluate the efficiency of Populus alba clone Villafranca in the uptake and translocation of Zn from contaminated soils.
Materials and methods
The effects of 48 days of zinc treatment (Zn t ) on the growth and the photosynthetic activities of P. alba L. clone Villafranca were studied using ZnSO4 (375 ppm per unit of soil dry weight) added in sand and peat moss substrate at the beginning of the treatment (T 0) and again after 30 days (T 1) in order to reach a target Zn concentration of 375 ppm at T 0 and 750 ppm at T 1 per unit of soil dry weight.
Results and discussion
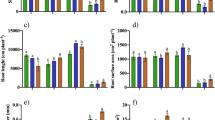
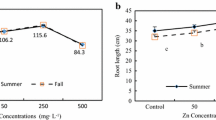
Zn uptake in the different organs was analyzed after 30 (T 1) and 48 days (T 2) from the beginning of treatment, showing the following order: root ≫ leaves ≥ woody cutting = stem. The leaf area increased by 12 % in comparison to control plants at the end of second treatment (48 days). Cutting radial growth showed a high synchronicity in the growth rate fluctuation among control and Zn t plants, but a higher increase in radial diameter of Zn t cutting was observed starting from day 38 (after 8 days of second Zn t ) reaching after 48 days 38 % higher than control plants.
Conclusions
Although our data of leaf Zn concentration were in the range usually reported as toxic for plants, Villafranca clone in Zn t substrate were unaffected in terms of net CO2 assimilation and stomatal conductance to water vapor.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ (2009) Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and human. Environ Geochem Health 31:537–548
Azzarello E, Pandolfi C, Giordano C, Rossi M, Mugnai S, Mancuso S (2012) Ultramorphological and physiological modifications induced by high zinc levels in Paulownia tomentosa. Environ Exp Bot 81:11–17
Baize D (1997) Teneurs totales en elements traces metalligues dans les sols (France). INRA Editions, Paris, p 409
Bernardini A, Salvatori E, Di Re S, Fusaro L, Nervo G, Manes F (2015) Natural and commercial Salix clones differ in their ecophysiological response to Zn stress. Photosynthetica. doi:10.1007/s11099-015-0155-9
Bonari E (2001) Potenzialità e problematiche agronomiche della silvicoltura a breve rotazione come coltura da energia negli ambienti mediterranei. Riv Agron 35:188–199
Borghi M, Tognetti R, Monteforti G, Sebastiani L (2008) Responses of two poplar species (Populus alba and Populus x canadensis) to high copper concentrations. Environ Exp Bot 62:290–299
Confalonieri M, Belenghi B, Balestrazzi A, Negri S, Facciotto G, Schenone G, Delledonne M (2000) Transformation of elite white poplar (Populus alba L.) cv. ‘Villafranca’ and evaluation of herbicide resistance. Plant Cell Rep 19:978–982
Di Baccio D, Tognetti R, Sebastiani L, Vitagliano C (2003) Responses of Populus deltoides × Populus nigra (Populus × euramericana) clone I-214 to high zinc concentrations. New Phytol 2:443–452
Di Baccio D, Minnocci A, Sebastiani L (2010) Leaf structural modifications in Populus × euramericana subjected to Zn excess. Biol Plant 54(3):502–508
Dos Santos Utmazian MN, Wieshammer G, Vega R, Wenzel WW (2007) Hydroponic screening for metal resistance and accumulation of cadmium and zinc in twenty clones of willows and poplars. Environ Pollut 148:155–165
Durand TC, Hausman JF, Carpin S, Alberic P, Baillif P, Label P, Morabito D (2010) Zinc and cadmium effects on growth and ion distribution in Populus tremula × Populus alba. Biol Plant 54:191–194
Fedorkov A (2007) Effect of heavy metal pollution of forest soil on radial growth of Scots pine. For Pathol 37:136–142
Fernàndez J, Zacchini M, Fleck I (2012) Photosynthetic and growth responses of Populus clones eridano and I-214 submitted to elevated Zn concentrations. J Geochem Explor 123:77–86
Franchin C, Fossati T, Pasquini E, Lingua G, Castiglione S, Torrigiani P (2007) High concentrations of Zn and Cu induce differential polyamine responses in micropropagated white poplar (Populus alba L. ‘Villafranca’). Physiol Plant 130:77–90
Giachetti G, Sebastiani L (2006) Metal accumulation in poplar plant grown with industrial wastes. Chemosphere 64:446–454
Giovannelli A, Deslauriers A, Fragnelli G, Scaletti L, Castro G, Rossi S, Crivellaro A (2007) Evaluation of drought response of two poplar clones (Populus x canadensis Monch ‘I-214’ and P. deltoides Marsh. ‘Dvina’) through high resolution analysis of stem growth. J Exp Bot 58:2673–2683
Guerra F, Gainza F, Pérez R, Zamudio F (2011) Phytoremediation of heavy metals using poplars (Populus spp): a glimpse of the plant responses to copper, cadmium and zinc stress. In: Ivan A. (ed) Handbook of Phytoremediation. Golubev© Nova Science Publishers, Inc. ISBN: 978-1-61728-753-4
Hassan Z, Aarts MGM (2011) Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environ Exp Bot 72:53–63
Hermle S, Günthardt-Goerg MS, Schulin R (2006) Effects of metal-contaminated soil on the performance of young trees growing in model ecosystems under field conditions. Environ Pollut 144:703–714
Hunt R (1978) Plant growth analysis. Camelot Press Ltd Southampton, UK
Körner C (2003) Alpine plant life: functional plant ecology of high mountain ecosystems. Springer, Berlin
Langer I, Krpata D, Fitz WJ, Wenzel WW, Schweiger PF (2009) Zinc accumulation potential and toxicity threshold determined for a metal-accumulating Populus canescens clone in a dose–response study. Environ Pollut 157:2871–2877
Manara A (2012) Plant responses to heavy metal toxicity. In: Furini A (ed) Plants and heavy metals. Springer briefs in biometals. Springer, New York, pp 27–53
Markert B (1992) Presence and significance of naturally occurring chemical elements of the periodic system in the plant organism and consequences for future investigations on inorganic environmental chemistry in ecosystems. Vegetatio 103:1–30
Morabito D, Caruso A, Carpin S, Carli C, Laurans F, Depierreux C et al (2006) Cambial activity of Populus tremula x Populus alba clone 717-1B4 in hydroponic culture. Can J Forest Res 36:719–724
Mukhtar N, Hameed M, Ashraf M, Ahmed R (2013) Modifications in stomatal structure and function in Cenchrus ciliaris L. and Cynodon dactylion (L.) Pers. In response to cadmium stress. Pak J Bot 45:351–357
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Oberhuber W, Gruber A, Kofler W, Swidrak I (2014) Radial stem growth in response to microclimate and soil moisture in a drought-prone mixed coniferous forest at an inner Alpine site. Eur J For Res 133:467–479
Romeo S, Francini A, Ariani A, Sebastiani L (2014a) Phytoremediation of Zn: identify the diverging resistance, uptake and biomass production behaviours of poplar clones under high zinc stress. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1813–1825
Romeo S, Trupiano D, Ariani A, Renzone G, Scippa GS, Scaloni A, Sebastiani L (2014b) Proteomic analysis of Populus × euramericana (clone I-214) roots to identify key factors involved in zinc stress response. J Plant Physiol 171:1054–1063
Sagardoy R, Morales F, Lόpez-Millán AF, Abadía A, Abadía J (2009) Effects of zinc toxicity on sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) plants grown in hydroponics. Plant Biol 11:339–35
Sebastiani L, Scebba F, Tognetti R (2004) Heavy metal accumulation and growth responses in poplar clones Eridano (Populus deltoides x maximowiczii) and I-214 (P. x euramericana) exposed to industrial waste. Environ Exp Bot 52:79–88
Sebastiani L, Francini A, Romeo S, Ariani A, Minnocci A (2014) Heavy metals stress on poplar: molecular and anatomical modifications. In: Gaur RK, Sharma P (eds) Approaches to plant stress and their management. Springer, India, pp 267–279
Unterbrunner R, Puschenreiter M, Simmer P, Wieshammer G, Tlustos P, Zupan M, Wenzel WW (2007) Heavy metal accumulation in trees growing on contaminated sites in Central Europe. Environ Pollut 148:107–114
Yang Z, Midmore DJ (2005) Modelling plant resource allocation and growth partitioning in response to environmental heterogeneity. Ecol Model 181:59–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jaume Bech
Stefania Romeo and Alessandra Francini contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romeo, S., Francini, A., Sebastiani, L. et al. High Zn concentration does not impair biomass, cutting radial growth, and photosynthetic activity traits in Populus alba L.. J Soils Sediments 17, 1394–1402 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1251-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1251-y