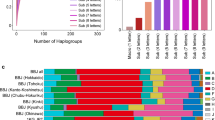
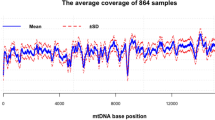
Abstract
Genetic variants of whole mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) that predispose to exceptional longevity need to be systematically identified and appraised. Here, we conducted a case-control study with 237 exceptional longevity subjects (aged 95–107) and 444 control subjects (aged 40–69) randomly recruited from a “longevity town”—the city of Rugao in China—to investigate the effects of mtDNA variants on exceptional longevity. We sequenced the entire mtDNA genomes of the 681 subjects using a next-generation platform and employed a complete mtDNA phylogenetic analytical strategy. We identified T3394C as a candidate that counteracts longevity, and we observed a higher load of private nonsynonymous mutations in the COX1 gene predisposing to female longevity. Additionally, for the first time, we identified several variants and new subhaplogroups related to exceptional longevity. Our results provide new clues for genetic mechanisms of longevity and shed light on strategies for evaluating rare mitochondrial variants that underlie complex traits.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexe G, Fuku N, Bilal E et al (2007) Enrichment of longevity phenotype in mtDNA haplogroups D4b2b, D4a, and D5 in the Japanese population. Hum Genet 121:347–356. doi:10.1007/s00439-007-0330-6
Ballard JWO, Rand DM (2005) The population biology of mitochondrial DNA and its phylogenetic implications. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 36:621–642. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.36.091704.175513
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Rohl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Cai XY, Wang XF, Li SL et al (2009) Association of mitochondrial DNA haplogroups with exceptional longevity in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 4:e6423. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006423
Camus MF, Clancy DJ, Dowling DK (2012) Mitochondria, maternal inheritance, and male aging. Curr Biol CB 22:1717–1721. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.018
Christensen K, Johnson TE, Vaupel JW (2006) The quest for genetic determinants of human longevity: challenges and insights. Nat Rev Genet 7:436–448. doi:10.1038/nrg1871
Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB (2010) Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 11:415–425. doi:10.1038/nrg2779
Collerton J, Ashok D, Martin-Ruiz C et al (2013) Frailty and mortality are not influenced by mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in the very old. Neurobiol Aging 34(2889):e2881–e2884. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.04.001
Cronn R, Liston A, Parks M, Gernandt DS, Shen R, Mockler T (2008) Multiplex sequencing of plant chloroplast genomes using Solexa sequencing-by-synthesis technology. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e122. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn502
Dato S, Passarino G, Rose G et al (2004) Association of the mitochondrial DNA haplogroup J with longevity is population specific. Eur J Hum Genet 12:1080–1082. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201278
De Benedictis G, Rose G, Carrieri G et al (1999) Mitochondrial DNA inherited variants are associated with successful aging and longevity in humans. FASEB J 13:1532–1536
Feng J, Zhang J, Liu M et al (2011) Association of mtDNA haplogroup F with healthy longevity in the female Chuang population, China. Exp Gerontol 46:987–993. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2011.09.001
Ferguson M, Mockett RJ, Shen Y, Orr WC, Sohal RS (2005) Age-associated decline in mitochondrial respiration and electron transport in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J 390:501–511. doi:10.1042/BJ20042130
Frank SA, Hurst LD (1996) Mitochondria and male disease. Nature 383:224. doi:10.1038/383224a0
Gemmell NJ, Metcalf VJ, Allendorf FW (2004) Mother’s curse: the effect of mtDNA on individual fitness and population viability. Trends Ecol Evol 19:238–244. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2004.02.002
Gibson G (2011) Rare and common variants: twenty arguments. Nat Rev Genet 13:135–145. doi:10.1038/nrg3118
Guan MX (2011) Mitochondrial 12S rRNA mutations associated with aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Mitochondrion 11:237–245. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2010.10.006
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syq010
Harpending HC, Batzer MA, Gurven M, Jorde LB, Rogers AR, Sherry ST (1998) Genetic traces of ancient demography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:1961–1967
Innocenti P, Morrow EH, Dowling DK (2011) Experimental evidence supports a sex-specific selective sieve in mitochondrial genome evolution. Science 332:845–848. doi:10.1126/science.1201157
Ji F, Sharpley MS, Derbeneva O et al (2012) Mitochondrial DNA variant associated with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and high-altitude Tibetans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7391–7396. doi:10.1073/pnas.1202484109
Katzman SM, Strotmeyer ES, Nalls MA et al (2014) Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation associated with peripheral nerve function in the elderly. J Gerontol. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu175
Kong QP, Bandelt HJ, Sun C et al (2006) Updating the East Asian mtDNA phylogeny: a prerequisite for the identification of pathogenic mutations. Hum Mol Genet 15:2076–2086. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl130
Lam ET, Bracci PM, Holly EA et al (2012) Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation and risk of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 72:686–695. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1682
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E et al (2010) The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. doi:10.1101/gr.107524.110
Montoya J, Lopez-Gallardo E, Diez-Sanchez C, Lopez-Perez MJ, Ruiz-Pesini E (2009) 20 years of human mtDNA pathologic point mutations: carefully reading the pathogenicity criteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:476–483. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.09.003
Namslauer I, Brzezinski P (2009) A mitochondrial DNA mutation linked to colon cancer results in proton leaks in cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3402–3407. doi:10.1073/pnas.0811450106
Niemi AK, Hervonen A, Hurme M, Karhunen PJ, Jylhä M, Majamaa K (2003) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms associated with longevity in a Finnish population. Hum Genet 112(1):29–33. doi:10.1007/s00439-002-0843-y
Pakendorf B, Stoneking M (2005) Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 6:165–183. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.6.080604.162249
Pinos T, Nogales-Gadea G, Ruiz JR et al (2012) Are mitochondrial haplogroups associated with extreme longevity? A study on a Spanish cohort. AGE 34:227–233. doi:10.1007/s11357-011-9209-5
Population Census Office of Rugao (20000 Tabulation on the 2000 population census of Rugao City, Jiangsu Province. p. 8
Raule N, Sevini F, Li S et al (2014) The co-occurrence of mtDNA mutations on different oxidative phosphorylation subunits, not detected by haplogroup analysis, affects human longevity and is population specific. Aging Cell 13:401–407. doi:10.1111/acel.12186
Ross OA, McCormack R, Curran MD, Duguid RA, Barnett YA, Rea IM, Middleton D (2001) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism: its role in longevity of the Irish population. Exp Gerontol 36:1161–1178. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(01)00094-8
Ruiz-Pesini E, Mishmar D, Brandon M, Procaccio V, Wallace DC (2004) Effects of purifying and adaptive selection on regional variation in human mtDNA. Science 303:223–226. doi:10.1126/science.1088434
Schork NJ, Murray SS, Frazer KA, Topol EJ (2009) Common vs. rare allele hypotheses for complex diseases. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19:212–219. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.010
Seibel P, Di Nunno C, Kukat C et al (2008) Cosegregation of novel mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene mutations with the age-associated T414G variant in human cybrids. Nucleic Acids Res 36:5872–5881. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn592
Sohal RS, Sohal BH, Orr WC (1995) Mitochondrial superoxide and hydrogen peroxide generation, protein oxidative damage, and longevity in different species of flies. Free Radic Bio Med 19:499–504
Soto IC, Fontanesi F, Liu J, Barrientos A (2012) Biogenesis and assembly of eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase catalytic core. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817:883–897. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.09.005
Tanaka M, Fuku N, Nishigaki Y et al (2007) Women with mitochondrial haplogroup N9a are protected against metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 56:518–521. doi:10.2337/db06-1105
Tanno Y, Okuizumi K, Tsuji S (1998) mtDNA polymorphisms in Japanese sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 19:S47–S51
Tennessen JA, Bigham AW, O’Connor TD et al (2012) Evolution and functional impact of rare coding variation from deep sequencing of human exomes. Science 337:64–69. doi:10.1126/science.1219240
Tranah GJ, Lam ET, Katzman SM et al (2012) Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation is associated with free-living activity energy expenditure in the elderly. BBA-Bioenergetics 1817:1691–1700. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.05.012
van Oven M, Kayser M (2009) Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation. Hum Mutat 30:E386–E394. doi:10.1002/humu.20921
Vaupel JW (2010) Biodemography of human ageing. Nature 464:536–542. doi:10.1038/nature08984
Wallace DC (2005) A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: a dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet 39:359–407. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.39.110304.095751
Wallace DC (2010) Mitochondrial DNA mutations in disease and aging. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:440–450. doi:10.1002/em.20586
Wolff JN, Gemmell NJ (2013) Mitochondria, maternal inheritance, and asymmetric fitness: why males die younger. Bioessays 35:93–99. doi:10.1002/bies.201200141
Zhang M, Zhou X, Li C et al (2010) Mitochondrial haplogroup M9a specific variant ND1 T3394C may have a modifying role in the phenotypic expression of the LHON-associated ND4 G11778A mutation. Mol Genet Metab 101:192–199. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.07.014
Zheng HX, Yan S, Qin ZD, Wang Y, Tan JZ, Li H, Jin L (2011) Major population expansion of East Asians began before neolithic time: evidence of mtDNA genomes. PLoS ONE 6:e25835. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025835
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (31171216), the National Basic Research Program (2012CB944600), the Ministry of Science and Technology (2011BAI09B00), and the Ministry of Health (201002007) of China.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interests were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Lei Li and Hong-Xiang Zheng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 71 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zheng, HX., Liu, Z. et al. Mitochondrial genomes and exceptional longevity in a Chinese population: the Rugao longevity study. AGE 37, 14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9750-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9750-8