Abstract
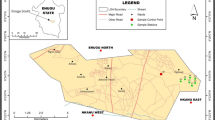
The shifting of tannery industries from Hazaribagh to Savar adjacent to Dhaleshwari River might have inevitable adverse impacts, especially the heavy metal contamination of both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. The study was carried out to investigate the concentrations of four heavy metals in the soil, water, and plant samples collected from around Dhaleshwari River adjacent to the Bangladesh Small & Cottage Industries Corporation Tannery Industrial Estate, Dhaka. This study revealed that average concentrations of cadmium and chromium in soil exceeded the maximum permissible limit of World Health Organization (1996) and average concentrations of lead, cadmium, and chromium in water exceeded the maximum permissible limit of World Health Organization (2011) and Environmental Conservation Rules (1997). The average concentrations of lead, cadmium, and chromium in the roots and shoots of both Eichhornia crassipes and Cynodon dactylon exceeded the maximum permissible limit of Food and Agriculture Organization/ World Health Organization (2016). Ecological risk assessment using indices model for soil pollution indicated that soil is mostly contaminated with cadmium and chromium which can pose strong ecological risk Health risk assessment using indices model for water pollution revealed the high degree of contamination and unacceptable non-carcinogenic risk and carcinogenic risk for adults as well as children through ingestion of water. Average bioconcentration factor and bioaccumulation factor were higher in Eichhornia crassipes than Cynodon dactylon for lead, cadmium, and chromium. Average translocation factor was also higher in Eichhornia crassipes for all the metals except cadmium. It is suggested remedial and mitigation measures be instituted to control environmental degradation of the newly established Tannery Industrial Estate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Satar AM, Ali MH, Goher ME (2017) Indices of water quality and metal pollution of Nile River, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 43(1):21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.12.006
Abioye OP, Oyewole OA, Oyeleke SB, Adeyemi MO, Orukotan AA (2018) Biosorption of lead, chromium and cadmium in tannery effluent using indigenous microorganisms. Brazilian J Biol Sci 5(9):25–32. https://doi.org/10.21472/bjbs.050903
Ahmed ATA, Mandal S, Chowdhury DA, Tareq ARM, Rahman MM (2012) Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in ayre fish (Sperata Aor Hamilton, 1822), sediment and water of Dhaleshwari River in dry season. Bangladesh J Zool 40(1):147–153. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjz.v40i1.12904
Alam MS, Han B, Al-Mizan, Pichtel J (2019) Assessment of soil and groundwater contamination at a former Tannery district in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Geochem Health 42(7):1905–1920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00457-6
Alam MS, Han B, Al-Mizan, Pichtel J (2020) Assessment of soil and groundwater contamination at a former Tannery district in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Geochem Health 42(7):1905–1920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00457-6
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang M-Q (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030042
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Ali MM, Hossain D, Imran A, Khan MS, Begum M, Osman MH (2021) Environmental pollution with heavy metals: a public health concern. In Heavy Metals- Their Environmental Impacts and Mitigation. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.96805
Al-Mizan, Juel MAI, Alam MS, Pichtel J, Ahmed T (2020) Environmental and health risks of metal-contaminated soil in the former tannery area of Hazaribagh, Dhaka. SN Appl Sci 2(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03680-4
Alves RIS, Sampaio CF, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Segura-Muñoz SI (2014) Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo River, Brazil: Human health risks. Environ Res 133:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.05.012
Arefin MT, Rahman MM, Wahid-U-Zzaman M, Kim J-E (2016) Heavy metal contamination in surface water used for irrigation: functional assessment of the Turag River in Bangladesh. J Appl Biol Chem 59(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.3839/jabc.2016.015
Atiemo MS, Ofosu GF, Kuranchie-Mensah HA, Tutu ONDM, Palm L, Blankson SA (2011) Contamination assessment of heavy metals in road dust from selected roads in Accra, Ghana. Res J Environ Earth Sci 3(5):473–480
Backman B, Bodiš D, Lahermo P, Rapant S, Tarvainen T (1998) Application of a groundwater contamination index in Finland and Slovakia. Environ Geol 36(1–2):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050320
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M (2021) Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front Pharmacol 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Ben Salem Z, Capelli N, Laffray X, Elise G, Ayadi H, Aleya L (2014) Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecol Eng 69:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.072
Bhuiyan MAH, Suruvi NI, Dampare SB, Islam MA, Quraishi SB, Ganyaglo S, Suzuki S (2010) Investigation of the possible sources of heavy metal contamination in lagoon and canal water in the tannery industrial area in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 175(1–4):633–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1557-6
Biswas P, Alam M, Ahmed M, Kumar Biswas P, Uddin N, Alam S, Sultana S, Ahmed T (2017) Cite This Article: Pradip Kumar Biswas, Nasir Uddin, Sha Alam, Tamjid-Us-Sakib, Sharmin Sultana, and Tofayal Ahmed. Am J Water Resour 5(5):146–151. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-5-5-2
Bosnic M, Buljan J, Daniels RP (2000) Pollutants in Tannery Effluents. Regional Programme for Pollution Control in the Tanning Industry in South-East Asia 3–26
Briffa J, Sinagra E, Blundell R (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 6(9):e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Chen SH, Cheow YL, Ng SL, Ting ASY (2020) Bioaccumulation and Biosorption Activities of Indoor Metal-Tolerant Penicillium simplicissimum for Removal of Toxic Metals. Int J Environ Res 14(2):235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00253-6
Das S, Goswami S, Das Talukdar A (2016) Physiological responses of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms, to cadmium and its phytoremediation potential. Turk J Biol 40:84–94. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1411-86
Duman F, Leblebici Z, Aksoy A (2009) Growth and bioaccumulation characteristics of watercress (Nasturtium officinaleR. BR.) exposed to cadmium, cobalt and chromium. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 21(4):257–265. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422909x12578511366924
Eckel H, Roth U, Döhler H, Nicholson F, Unvin R (2005) Assessment and reduction of heavy metal input into agro-ecosystems - Final report of the EU-Concerted Action AROMIS. KTBL-Schrift 432
ECR. (1997). Government of the people’s republic of Bangladesh, ministry of environment and forest: Dhaka, Bangladesh
FAO/WHO (2016) General standard for contaminants and toxins in food and feed.Codex Alimentarius International Food Standards. CODEX STAN 193–1995
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Haldar S, Ghosh A (2020) Microbial and plant-assisted heavy metal remediation in aquatic ecosystems: a comprehensive review. 3 Biotech 10(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02195-4
Hasan SMM, Akber MA, Bahar MM, Islam MA, Akbor MA, Siddique MAB, Islam MA (2021) Chromium contamination from tanning industries and phytoremediation potential of native plants: A Study of savar tannery industrial Estate in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106(6):1024–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03262-z
Hassan M, Rahman MATMT, Saha B, Kamal AKI (2015) Status of heavy metals in water and sediment of the Meghna River, Bangladesh. Am J Environ Sci 11(6):427–439. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2015.427.439
Hossain MdM, Chowdhury MdA, Hasan MdJ, Rashid M-A, Acter T, Khan MN, Mahatabuddin S, Uddin N (2021) Heavy metal pollution in the soil-vegetable system of Tannery Estate. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 16:100557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100557
Hosseini NS, Sobhanardakani S, Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Merrikhpour H (2020) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside plants (Achillea wilhelmsii and Cardaria draba) and soils along some highways in Hamedan, west of Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07874-6
Hseu Z-Y, Tsai C-C (2004) Digestion methods for total heavy metals in sediments and soils. Biores Technol 95(2004):53–59
Islam M, Karim Md, Zheng X, Li X (2018) Heavy metal and metalloid pollution of soil, water and foods in Bangladesh: a critical review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(12):2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122825
Islam MdS, Kormoker T, Mazumder M, Anika SE, Islam MdT, Hemy DH, Mimi US, Proshad R, Kabir MdH, Idris AM (2021) Trace elements concentration in soil and plant within the vicinity of abandoned tanning sites in Bangladesh: an integrated chemometric approach for health risk assessment. Toxin Rev 41(3):752–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2021.1925919
Islam Md. D, Hasan MM, Rahaman A, Haque P, Islam Md. S, Rahman MM (2020) Translocation and bioaccumulation of trace metals from industrial effluent to locally grown vegetables and assessment of human health risk in Bangladesh. SN Appl Sci 2(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-3123-3
Jallouli S, Wali A, Buonerba A, Zarra T, Belgiorno V, Naddeo V, Ksibi M (2020) Efficient and sustainable treatment of tannery wastewater by a sequential electrocoagulation-UV photolytic process. J Water Process Eng 38:101642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101642
Jorfi S, Maleki R, Jaafarzadeh N, Ahmadi M (2017) Pollution load index for heavy metals in Mian-Ab plain soil, Khuzestan. Iran Data in Brief 15:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.017
Jumbe AS, Nandini N (2009) Impact assessment of heavy metals pollution of Vartur lake, Bangalore. J Appl Natl Sci 1(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v1i1.35
Karim MdR, Manshoven S, Islam MdR, Gascon JA, Ibarra M, Diels L, Rahman MdM (2013) Assessment of an urban contaminated site from Tannery Industries in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 17(1):52–61. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hz.2153-5515.0000139
Lipy EP, Hakim M, Mohanta LC, Islam D, Lyzu C, Roy DC, Jahan I, Akhter S, Raknuzzaman M, Abu Sayed Md (2020) Assessment of heavy metal concentration in water, sediment and common fish species of Dhaleshwari River in Bangladesh and their health implications. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(11):4295–4307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02552-7
Liu W-X, Liu J-W, Wu M-Z, Li Y, Zhao Y, Li S-R (2009) Accumulation and translocation of toxic heavy metals in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growing in agricultural soil of Zhengzhou, China. Bullet Environ Contam Toxicol 82(3):343–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9575-6
Liu Z, Yu X, Jia L, Wang Y, Song Y, Meng H-D (2021) The influence of distance weight on the inverse distance weighted method for ore-grade estimation. Sci Rep 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82227-y
Lofrano G, Carotenuto M, Gautam RK, Chattopadhyaya MC (2014) CHAPTER 12. Heavy metals in tannery wastewater and sludge: Environmental concerns and future challenges. in heavy metals in water (pp 249–260). https://doi.org/10.1039/9781782620174-00249
Lu GY, Wong DW (2008) An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. Comput Geosci 34(9):1044–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.010
Madan S, Chanchal K, Kaushik N (2017) Uptake of chromium in water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and its impact on biochemical structure. Environ Conserv J 18(1&2):143–148. https://doi.org/10.36953/ecj.2017.181220
Masindi V, Muedi KL (2018) Environmental contamination by heavy metals. Heavy Metals. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76082
McLennan SM (2001) Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 2(4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2000gc000109
Milton AH, Rahman H, Smith W, Shrestha R, Dear K (2006) Water consumption patterns in rural Bangladesh: are we underestimating total arsenic load? J Water Health 4(4):431–436. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2006.010
Mitra S, Sarkar SK, Raja P, Biswas JK, Murugan K (2018) Dissolved trace elements in Hooghly (Ganges) River Estuary, India: Risk assessment and implications for management. Mar Pollut Bull 133:402–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.057
Mitra S, Chakraborty AJ, Tareq AM, Emran TB, Nainu F, Khusro A, Idris AM, Khandaker MU, Osman H, Alhumaydhi FA, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J King Saud Univ-Sci 34(3):101865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101865
Mizan A, Mamun MAH, Islam MS (2023) Metal contamination in soil and vegetables around Savar tannery area, Dhaka, Bangladesh: A preliminary study for risk assessment. Heliyon 9(3):e13856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13856
Mizan A, Zohra F, Ahmed S, Nurnabi M, Alam M (2016) Low cost adsorbent for mitigation of water pollution caused by tannery effluents at Hazaribagh. Bangladesh J Sci Indust Res 51(3):215–220. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjsir.v51i3.29433
Mouhsine E, Ouazzani N, Avila M, Perez G (2012) Heavy metal contamination of soils and water resources kettara abandoned mine the chemistry of iron in biosystems view project traitement des eaux -water traitment view project. Am J Environ Sci 8(3):253–261
Muller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2(3):108–118
Nirola R, Megharaj M, Palanisami T, Aryal R, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R (2015) Evaluation of metal uptake factors of native trees colonizing an abandoned copper mine – a quest for phytostabilization. J Sustain Mining 14(3):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsm.2015.11.001
Olowoyo JO, van Heerden E, Fischer JL, Baker C (2010) Trace metals in soil and leaves of Jacaranda mimosifolia in Tshwane area, South. Africa Atmos Environ 44(14):1826–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.01.048
Paul H, Antunes APM, Covington AD, Evans P, Phillips PS (2013) Bangladeshi leather industry: an overview of recent sustainable developments. J Soc Leather Technol Chem 97:25–31
Rahimzadeh MR, Rahimzadeh MR, Kazemi S, Moghadamnia A (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update. Caspian J Int Med 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.2.67
Rahman MS, Molla AH, Saha N, Rahman A (2012) Study on heavy metals levels and its risk assessment in some edible fishes from Bangshi River, Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Chem 134(4):1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.099
Rahman MS, Hossain MB, Babu SMOF, Rahman M, Ahmed ASS, Jolly YN, Choudhury TR, Begum BA, Kabir J, Akter S (2019) Source of metal contamination in sediment, their ecological risk, and phytoremediation ability of the studied mangrove plants in ship breaking area, Bangladesh. Mar Pollut Bull 141:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.02.032
Rahman MS, Kumar P, Ullah M, Jolly YN, Akhter S, Kabir J, Begum BA, Salam A (2021) Elemental analysis in surface soil and dust of roadside academic institutions in Dhaka city, Bangladesh and their impact on human health. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2021.06.001
Rahman M, Ahmed Z, Seefat S, Alam R, Md R, Islam T, Choudhury T, Begum A, Idris A (2022) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment at the newly established tannery industrial Estate in Bangladesh: a case study. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 87(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2021.10.001
Rasul MG, Faisal I, Khan MMK (2006) Environmental pollution generated from process industries in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Pollut 28(1/2):144. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijep.2006.010881
Saha N, Mollah MZI, Alam MF, Safiur Rahman M (2016) Seasonal investigation of heavy metals in marine fishes captured from the Bay of Bengal and the implications for human health risk assessment. Food Control 70:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.05.040
Saha N, Rahman MS, Ahmed MB, Zhou JL, Ngo HH, Guo W (2017) Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J Environ Manage 185:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.023
Šajn R, Halamić J, Peh Z, Galović L, Alijagić J (2011) Assessment of the natural and anthropogenic sources of chemical elements in alluvial soils from the Drava River using multivariate statistical methods. J Geochem Explor 110(3):278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.06.009
Salhotra, A. M. (2012). Human health risk assessment for contaminated properties 285–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-415813-9.00010-6
Sarker A, Kim J-E, Islam, AR Md. T, Bilal M, Rakib Md. RJ, Nandi R, Rahman MM, Islam T (2021) Heavy metals contamination and associated health risks in food webs—a review focuses on food safety and environmental sustainability in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17153-7
Seleem EM, Mostafa A, Mokhtar M, Salman SA (2021) Risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water on the human health, Assiut City, and its environs, Egypt. Arabian J Geosci 14(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06784-2
Sivaram NM, Barik D (2019) Toxic Waste From Leather Industries. Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-102528-4.00005-5
Soleimani M, Hajabbasi M, Afyuni M, Charkhabi A, Shariatmadari H (2009) Bioaccumulation of Nickel and Lead by Bermuda Grass (Cynodon dactylon) and Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea) from Two Contaminated Soils. Caspian J Env Sci 7(2):59–70
Sulaiman FR, Hamzah HA (2018) Heavy metals accumulation in suburban roadside plants of a tropical area (Jengka, Malaysia). Ecol Proc 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-018-0139-3
Sultan MB, Choudhury TR, Alam Md. N-E, Doza Md. B, Rahmana Md. M (2022) Soil, dust, and leaf-based novel multi-sample approach for urban heavy metal contamination appraisals in a megacity, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Adv 7:100154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100154
Taylor S, McLennan S (1985) The continental crust : its composition and evolution : an examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2014) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Experientia Suppl 101(1):133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tisha SM, Chowdhury TR, Hossain MD (2020) Heavy Metal Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment in the Soil of Tannery Industry at Savar. Chem Eng Res Bullet 106–113. https://doi.org/10.3329/cerb.v22i1.54308
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 33(1–4):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02414780
Tüzen M (2003) Determination of heavy metals in soil, mushroom and plant samples by atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J 74(3):289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-265x(03)00035-3
US EPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for Superfund. Volume I: human health evaluation manual (Part A), Interim Final. 1989. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response (EPA/540/1–89/002)
US EPA (1996) Soil Screening Guidance: Technical Background Document. EPA/540/R-95/128. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response
US EPA (2001) US Environmental Protection Agency.Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites. OSWER 9355.4–24. Office of SolidWaste and Emergency Response
US EPA (2002) Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites OSWER 9355.4-24
US EPA (2020) USEPA Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table. https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables
WHO (1996) Permissible limits of heavy metals in soil and plants. Geneva, Switzerland.
WHO (2011) Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, 4th ed.; NLM classification: WA 67
Wilkinson JM, Hill J, Phillips CJC (2003) The accumulation of potentially-toxic metals by grazing ruminants. Proc Nutr Soc 62(2):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1079/pns2003209
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and research design. Intehum Taufique Aurnab collected, validated and analyzed the data as well as prepared the original draft. Md. Jashim Uddin commented on draft and Alamgir Kabir prepared the final version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Alamgir Kabir supervised the total study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aurnab, I.T., Uddin, M.J. & Kabir, A. Risk assessment of four toxic heavy metals in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems around BSCIC tannery industrial estate of Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33503-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33503-7