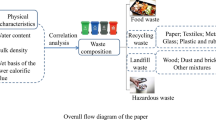
Abstract
Inorganic chlorine is susceptible to water and soil salinization due to its non-degradability and high mobility. To clarify the environmental risks associated with the active inorganic chlorine in municipal solid waste (MSW), the specific characteristics and contributions of inorganic chlorine in different MSW categories were investigated in this study. MSW samples were collected from eight representative waste classification residential areas in Hangzhou, China. It was found that the inorganic chlorine content in different MSW categories varied significantly (0–113 mg/g). Perishable waste, paper, and plastic were found to be the main sources of inorganic chlorine in MSW. A four-category classification system was used to quantify the contribution of inorganic chlorine from each waste category. It was found that the misclassification of inorganic chlorine contributions from perishable waste and other waste accounted for 51.96% and 48.04%, respectively. However, when correctly classified into the four-category system, their contributions were reduced to 67.14% and 30.65%, respectively. Therefore, MSW classification showed a significant reduction in the overall contribution of inorganic chlorine. The misclassification reduces the contribution of inorganic chlorine to 48.04%, while correct classification increases the reduction to 69.35%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian R, Chen J, Zhang T, Gao C, Niu Y, Sun Y, Zhan M, Zhao F, Zhang G (2022) Influence of the classification of municipal solid wastes on the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: a case study of Qingdao City, China. J Clean Prod 376:134275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134275
Cai Z, Du B, Dai X, Wang T, Wang J, Zhang Y (2023) Coupling of alkaline and mechanical modified fly ash for HCl and SO2 removal in the municipal solid waste incineration plant. Fuel 346:128354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128354
Cheng S, Ding X, Dong X, Zhang M, Tian X, Liu Y, Huang Y, Jin B (2023) Immigration, transformation, and emission control of sulfur and nitrogen during gasification of MSW: fundamental and engineering review. Carbon Resour Convers 6:184–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2023.03.003
Deng Y, Chen N, Feng C, Chen F, Wang H, Kuang P, Feng Z, Liu T, Gao Y, Hu W (2019) Treatment of organic wastewater containing nitrogen and chlorine by combinatorial electrochemical system: taking biologically treated landfill leachate treatment as an example. Chem Eng J 364:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.176
Gu B, Jiang S, Wang H, Wang Z, Jia R, Yang J, He S, Cheng R (2017) Characterization, quantification and management of China’s municipal solid waste in spatiotemporal distributions: a review. Waste Manag 61:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.11.039
Honma S, Hu J (2021) Cost efficiency of recycling and waste disposal in Japan. J Clean Prod 284:125274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125274
Kassman H, Pettersson J, Steenari BM, Åmand LE (2013) Two strategies to reduce gaseous KCl and chlorine in deposits during biomass combustion — injection of ammonium sulphate and co-combustion with peat. Fuel Process Technol 105:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.06.025
Kruta de Araujo NC, Sato T (2018) A descriptive study of work ability and health problems among Brazilian recyclable waste pickers. J Commun Health 43:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-017-0432-6
Li H, Liu H, Huang Y, Chen X, Zhang X, Li J, Xu L, Yao H (2024a) Mechanism of coupling corrosion caused by flue gas and deposits in municipal solid waste incinerator: roles of H2O(g), HCl, and SO2. Corros Sci 231:111933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2024.111933
Li S, Zhang M, Hu H, Guo G, Gong L, Dong L, Xu S, Yao H (2024b) Fate of sulfur and chlorine during co-incineration of municipal solid waste and industrial organic solid waste. Sci Total Environ 920:171040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171040
Liu Y, Wang J (2023) Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of carbon emissions from municipal solid waste treatment in China. Waste Manag 168:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2023.05.043
Liu Y, Xing P, Liu J (2017) Environmental performance evaluation of different municipal solid waste management scenarios in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 125:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.06.005
Liu B, Han Z, Liang X (2023) Dioxin emissions from municipal solid waste incineration in the context of waste classification policy. Atmos Pollut Res 14:101842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2023.10184
Long Y, Shen D, Wang H, Lu W, Zhao Y (2011) Heavy metal source analysis in municipal solid waste (MSW): case study on Cu and Zn. J Hazard Mater 186:1082–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.106
Long Y, Liu D, Xu J, Fang Y, Du Y, Shen D (2018) Release behavior of chloride from MSW landfill simulation reactors with different operation modes. Waste Manag 77:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.018
Lv L, Sun P, Gu Z, Du H, Pang X, Tao X, Xu R, Xu L (2009) Removal of chloride ion from aqueous solution by ZnAl-NO3 layered double hydroxides as anion-exchanger. J Hazard Mater 161:1444–1449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.114
Lv J, Dong H, Geng Y, Li H (2020) Optimization of recyclable MSW recycling network: a Chinese case of Shanghai. Waste Manag 102:763–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.11.041
Ma W, Wenga T, Frandsen FJ, Yan B, Chen G (2020) The fate of chlorine during MSW incineration: vaporization, transformation, deposition, corrosion and remedies. Prog Energy Combust Sci 76:100789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2019.100789
McSorley K, Rutter A, Cumming R, Zeeb BA (2016) Phytoextraction of chloride from a cement kiln dust (CKD) contaminated landfill with Phragmites australis. Waste Manag 51:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.009
Shan L, Tian S, Hu Q (2016) Effect of deicing chloride salts on roadside plants and soil. Saf Environ Eng 23:89–95. https://doi.org/10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2016.03.015
Song Y, Xian X, Zhang C, Zhu F, Yu B, Liu J (2023) Residual municipal solid waste to energy under carbon neutrality: challenges and perspectives for China. Resour Conserv Recycl 198:107177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.107177
Tai J, Zhang W, Che Y, Feng D (2011) Municipal solid waste source-separated collection in China: a comparative analysis. Waste Manag 31:1673–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.03.014
Tang L, Guo J, Wan R, Jia M, Qu J, Li L, Bo X (2023) Air pollutant emissions and reduction potentials from municipal solid waste incineration in China. Environ Pollut 319:121021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121021
Teakle NL, Tyerman SD (2010) Mechanisms of Cl-transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 33:566–589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02060.x
Vehlow J (1996) Municipal solid waste management in Germany. Waste Manag 16:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(96)00081-5
Yang N, Zhang H, Chen M, Shao L, He P (2012) Greenhouse gas emissions from MSW incineration in China: impacts of waste characteristics and energy recovery. Waste Manag 32:2552–2560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.06.008
Zhao F, Bian R, Zhang T, Fang X, Chai X, Xin M, Li W, Sun Y, Yuan L, Chen J, Lin X, Liu L (2022) Characteristics of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins/dibenzofurans from a full-scale municipal solid waste (MSW) incinerator in China by MSW classification. Process Saf Environ 161:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.03.012
Zhou H, Long Y, Meng A, Li Q, Zhang Y (2015) Thermogravimetric characteristics of typical municipal solid waste fractions during co-pyrolysis. Waste Manag 38:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.027
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Scientific Research Project of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education (Y202147303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuyang Long: project administration, supervision, writing—review and editing; Ying Hu: investigation, data curation, visualization; Dongyun Liu: data curation, visualization; Dongsheng Shen: supervision, resources; Foquan Gu: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, formal analysis, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Y., Hu, Y., Liu, D. et al. Source analysis of chlorine in municipal solid waste under waste classification: a case study of Hangzhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 31054–31063 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33243-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33243-8