Abstract
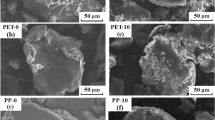
Microplastics (MPs) migrate by adsorbing heavy metals in aquatic environments and act as their carriers. However, the aging mechanisms of MPs in the environment and the interactions between MPs and heavy metals in aquatic environments require further study. In this study, two kinds of materials, polyamide (PA) and polylactic acid (PLA) were used as target MPs, and the effects of UV irradiation on the physical and chemical properties of the MPs and the adsorption behavior of Cu(II) were investigated. The results showed that after UV irradiation, pits, folds and pores appeared on the surface of aged MPs, the specific surface area (SSA) increased, the content of oxygen-containing functional groups increased, and the crystallinity decreased. These changes enhanced the adsorption capacity of aged MPs for Cu(II) pollutants. The adsorption behavior of the PA and PLA MPs for Cu(II) conformed to the pseudo-second-order model and Langmuir isotherm model, indicating that the monolayer chemical adsorption was dominant. The maximum amounts of aged PA and PLA reached 1.415 and 1.398 mg/g, respectively, which were 1.59 and 1.76 times of virgin MPs, respectively. The effects of pH and salinity on the adsorption of Cu(II) by the MPs were significant. Moreover, factors such as pH, salinity and dosage had significant effects on the adsorption of Cu(II) by MPs. Oxidative complexation between the oxygen-containing groups of the MPs and Cu(II) is an important adsorption mechanism. These findings reveal that the UV irradiation aging of MPs can enhance the adsorption of Cu(II) and increase their role as pollutant carriers, which is crucial for assessing the ecological risk of MPs and heavy metals coexisting in aquatic environments.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahechti M, Benomar M, El Alami M, Mendiguchía C (2022) Metal adsorption by microplastics in aquatic environments under controlled conditions: exposure time, pH and salinity. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102:1118–1125. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1733546
Alimi OS, Budarz JF, Hernandez LM, Tufenkji N (2018) Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ Sci Technol 52:1704–1724. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05559
Allouss D, Essamlali Y, Chakir A, Khadhar S, Zahouily M (2020) Effective removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution over graphene oxide encapsulated carboxymethylcellulose-alginate hydrogel microspheres: towards real wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7476–7492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06950-w
Ammala A, Bateman S, Dean K, Petinakis E, Sangwan P, Wong S, Yuan Q, Yu L, Patrick C, Leong KH (2011) An overview of degradable and biodegradable polyolefins. Prog Polym Sci 36:1015–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.12.002
Arp HPH, Kühnel D, Rummel C, MacLeod M, Potthoff A, Reichelt S, Rojo-Nieto E, Schmitt-Jansen M, Sonnenberg J, Toorman E, Jahnke A (2021) Weathering Plastics as a Planetary Boundary Threat: Exposure, Fate, and Hazards. Environ Sci Technol 55:7246–7255. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01512
Bao RQ, Fu DD, Fan ZQ, Peng XZ, Peng LC (2022) Aging of microplastics and their role as vector for copper in aqueous solution. Gondwana Res 108:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2021.12.002
Bergmann M, Mützel S, Primpke S, Tekman MB, Trachsel J, Gerdts G (2019) White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci Adv 5:10. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax1157
Betianu CS, Cozma P, Rosca M, Ungureanu EDC, Mamaliga I, Gavrilescu M (2020) Sorption of Organic Pollutants onto Soils: Surface Diffusion Mechanism of Congo Red Azo Dye. Processes 8:19. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121639
Brennecke D, Duarte B, Paiva F, Caçador I, Canning-Clode J (2016) Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 178:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.003
Carbery M, O’Connor W, Thavamani P (2018) Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environ Int 115:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.007
Chaturvedi G, Kaur A, Umar A, Khan MA, Algarni H, Kansal SK (2020) Removal of fluoroquinolone drug, levofloxacin, from aqueous phase over iron based MOFs, MIL-100(Fe). J Solid State Chem 281:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2019.121029
Chen LY, Liu WX, Yang T, Nowack B (2023) Probabilistic material flow analysis of eight commodity plastics in China: Comparison between 2017 and 2020. Resour Conserv Recycl 191:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.106880
Cherono F, Mburu N, Kakoi B (2021) Adsorption of lead, copper and zinc in a multi-metal aqueous solution by waste rubber tires for the design of single batch adsorber. Heliyon 7:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08254
Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS (2011) Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2588–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025
Crespo M, Gómez-del Río T, Rodríguez J (2019) Failure of polyamide 12 notched samples manufactured by selective laser sintering. J Strain Anal Eng Des 54:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309324719847817
De Gisi S, Gadaleta G, Gorrasi G, La Mantia FP, Notarnicola M, Sorrentino A (2022) The role of (bio)degradability on the management of petrochemical and bio-based plastic waste. J Environ Manage 310:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114769
Ding JF, Ju P, Ran Q, Li JX, Jiang FH, Cao W, Zhang J, Sun CJ (2023) Elder fish means more microplastics? Alaska pollock microplastic story in the Bering Sea. Sci Adv 9:10. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adf5897
Dong JW, Xia XH, Liu ZX, Zhang XT, Chen QW (2019) Variations in concentrations and bioavailability of heavy metals in rivers during sediment suspension-deposition event induced by dams: insights from sediment regulation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir in the Yellow River. J Soils Sediments 19:403–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2016-1
Du S, Wei YH, Ahmed S, Zhou FY, Tan YH, Li Y, Wang M, Chen XX, Zhou WT (2022) Enhanced thermal stability and UV resistance of polyamide 6 filament fabric via in-situ grafting with methyl methacrylate. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp 651:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129371
Fan XL, Gan R, Liu JQ, Xie Y, Xu DZ, Xiang Y, Su JK, Teng Z, Hou J (2021a) Adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotics by tire wear particles and polyethylene microplastics with or without aging processes. Sci Total Environ 771:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145451
Fan XL, Zou YF, Geng N, Liu JQ, Hou J, Li DD, Yang CF, Li Y (2021b) Investigation on the adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotics by degradable MPs with or without UV ageing process. J Hazard Mater 401:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmal.2020.123363
Fan XL, Shi S, Xiang Y, Xie Y, Chen Q, Yang YY, Liu JQ, Zhang JK, Hou J (2022) Insights into the Characteristics, Adsorption, and Desorption Behaviors of Polylactic Acid Aged with or without Salinities. J Environ Eng-ASCE 148.https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ee.1943-7870.0002025
Fan XL, Xie Y, Qian SW, Xiang Y, Chen Q, Yang YY, Liu JQ, Zhang JK, Hou J (2023) Insights into the characteristics, adsorption and desorption behaviors of microplastics aged with or without fulvic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:10484–10494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22897-x
Fiore M, Garofalo SF, Migliavacca A, Mansutti A, Fino D, Tommasi T (2022) Tackling Marine Microplastics Pollution: an Overview of Existing Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 233:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05715-5
Foshtomi MY, Oryan S, Taheri M, Bastami KD, Zahed MA (2019) Composition and abundance of microplastics in surface sediments and their interaction with sedimentary heavy metals, PAHs and TPH (total petroleum hydrocarbons). Mar Pollut Bull 149:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110655
Fu QM, Tan XF, Ye SJ, Ma LL, Gu YL, Zhang P, Chen Q, Yang YY, Tang YQ (2021) Mechanism analysis of heavy metal lead captured by natural-aged microplastics. Chemosphere 270:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128624
Gao L, Fu DD, Zhao JJ, Wu WS, Wang ZZ, Su YY, Peng LC (2021) Microplastics aged in various environmental media exhibited strong sorption to heavy metals in seawater. Mar Pollut Bull 169:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112480
Geng Y, He H, Liu H, Jing HS (2020) Preparation of polycarbonate/poly(lactic acid) with improved printability and processability for fused deposition modeling. Polym Adv Technol 31:2848–2862. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5013
Guo CX, Wang LL, Lang DN, Qian QQ, Wang W, Wu RL, Wang JD (2023) UV and chemical aging alter the adsorption behavior of microplastics for tetracycline. Environ Pollut 318:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120859
Guo X, Wang JL (2019) The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment: A review. Mar Pollut Bull 142:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.019
Han XX, Wang SY, Yu X, Vogt RD, Feng JF, Zhai LF, Ma WQ, Zhu L, Lu XQ (2021) Kinetics and Size Effects on Adsorption of Cu(II), Cr(III), and Pb(II) Onto Polyethylene, Polypropylene, and Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastic Particles. Front Mar Sci 8:6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.785146
He WT, Yu QD, Wang N, Ouyang XK (2020a) Efficient adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions by acid-resistant and recyclable ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid-grafted polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan beads. J Mol Liq 316:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113856
He XP, Yao B, Xia Y, Huang H, Gan YP, Zhang WK (2020b) Coal fly ash derived zeolite for highly efficient removal of Ni2+ in waste water. Powder Technol 367:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.11.037
Hu MF, Hou N, Li YF, Liu YM, Zhang H, Zeng DQ, Tan HH (2021) The effect of microplastics on behaviors of chiral imidazolinone herbicides in the aquatic environment: Residue, degradation and distribution. J Hazard Mater 418:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126176
Huang BY, Liu YG, Li B, Liu SB, Zeng GM, Zeng ZW, Wang XH, Ning QM, Zheng BH, Yang CP (2017) Effect of Cu(II) ions on the enhancement of tetracycline adsorption by Fe3O4@SiO2-Chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 157:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.025
Huang W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Gao H, Xu W, Xia X (2024) Insights into adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cu(II) onto biodegradable and conventional microplastics: Effect of aging process and environmental factors. Environ Pollut 342:123061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.123061
Jang M, Shim WJ, Cho Y, Han GM, Song YK, Hong SH (2020) A close relationship between microplastic contamination and coastal area use pattern. Water Res 171:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115400
Kalcíková G, Skalar T, Marolt G, Kokalj AJ (2020) An environmental concentration of aged microplastics with adsorbed silver significantly affects aquatic organisms. Water Res 175:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115644
Kataoka T, Nihei Y, Kudou K, Hinata H (2019) Assessment of the sources and inflow processes of microplastics in the river environments of Japan. Environ Pollut 244:958–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.111
Khalid N, Aqeel M, Noman A, Khan SM, Akhter N (2021) Interactions and effects of microplastics with heavy metals in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Environ Pollut 290:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118104
Lang MF, Yu XQ, Liu JH, Xia TJ, Wang TC, Jia HZ, Guo XT (2020) Fenton aging signi ficantly affects the heavy metal adsorption capacity of polystyrene microplastics. Sci Total Environ 722:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137762
Leng YF, Wang W, Cai HP, Chang FY, Xiong W, Wang J (2023) Sorption kinetics, isotherms and molecular dynamics simulation of 17β-estradiol onto microplastics. Sci Total Environ 858:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159803
Li CR, Busquets R, Campos LC (2020) Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: A review. Sci Total Environ 707:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135578
Li J, Yu SG, Cui M (2023) Aged polyamide microplastics enhance the adsorption of trimethoprim in soil environments. Environ Monit Assess 195:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11350-2
Li JY, Liu HH, Chen JP (2018) Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res 137:362–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.056
Li L, Xue B, Lin H, Lan W, Wang X, Wei J, Li M, Li M, Duan Y, Lv J, Chen Z (2024) The adsorption and release mechanism of different aged microplastics toward Hg(II) via batch experiment and the deep learning method. Chemosphere 350:141067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.141067
Li SS, Ma RX, Zhu XH, Liu C, Li LZ, Yu ZL, Chen XC, Li ZR, Yang Y (2021) Sorption of tetrabromobisphenol A onto microplastics: Behavior, mechanisms, and the effects of sorbent and environmental factors. Ecotox Environ Safe 210:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111842
Li YC, Wang JZ, Xue BQ, Wang SH, Qi P, Sun J, Li HF, Gu XY, Zhang S (2022a) Enhancing the flame retardancy and UV resistance of polyamide 6 by introducing ternary supramolecular aggregates. Chemosphere 287:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132100
Li YH, Zhang Y, Su F, Wang YY, Peng LL, Liu DZ (2022b) Adsorption behaviour of microplastics on the heavy metal Cr(VI) before and after ageing. Chemosphere 302:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134865
Liang JN, Wu JH, Zeng Z, Li MZ, Liu WZ, Zhang TP (2023) Behavior and mechanisms of ciprofloxacin adsorption on aged polylactic acid and polyethlene microplastics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:62938–62950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26390-x
Lionetto F, Corcione CE, Messa F, Perrone S, Salomone A, Maffezzoli A (2023) The Sorption of Amoxicillin on Engineered Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastics. J Polym Environ 31:1383–1397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02690-0
Liu H, Zhang X, Ji B, Qiang ZM, Karanfil T, Liu C (2023) UV aging of microplastic polymers promotes their chemical transformation and byproduct formation upon chlorination. Sci Total Environ 858:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159842
Liu P, Qian L, Wang HY, Zhan X, Lu K, Gu C, Gao SX (2019) New Insights into the Aging Behavior of Microplastics Accelerated by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ Sci Technol 53:3579–3588. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b00493
Liu P, Lu K, Li JL, Wu XW, Qian L, Wang MJ, Gao SX (2020) Effect of aging on adsorption behavior of polystyrene microplastics for pharmaceuticals: Adsorption mechanism and role of aging intermediates. J Hazard Mater 384:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121193
Liu X, Zhou DD, Chen M, Cao YW, Zhuang LY, Lu ZH, Yang ZH (2022a) Adsorption behavior of azole fungicides on polystyrene and polyethylene microplastics. Chemosphere 308:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136280
Liu XW, Zheng MG, Wang L, Ke RH, Lou YH, Zhang XJ, Dong XF, Zhang Y (2018) Sorption behaviors of tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate and hexabromocyclododecanes on polypropylene microplastics. Mar Pollut Bull 135:581–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.061
Liu YX, Zhang J, Cao WG, Hu Y, Shen WB (2022b) The influence of Pb(II) adsorption on (Non) biodegradable microplastics by UV/O3 oxidation treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 10:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108615
Loncarski M, Gvoic V, Prica M, Cveticanin L, Agbaba J, Tubic A (2021) Sorption behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on biodegradable polylactic acid and various nondegradable microplastics: Model fitting and mechanism analysis. Sci Total Environ 785:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147289
Luo HW, Liu CY, He DQ, Xu J, Sun JQ, Li J, Pan XL (2022) Environmental behaviors of microplastics in aquatic systems: A systematic review on degradation, adsorption, toxicity and biofilm under aging conditions. J Hazard Mater 423:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126915
Luo HW, Tu CL, He DQ, Zhang AP, Sun JQ, Li J, Xu J, Pan XL (2023) Interactions between microplastics and contaminants: A review focusing on the effect of aging process. Sci Total Environ 899:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165615
Lv MJ, Jiang B, Xing Y, Ya HB, Zhang T, Wang X (2022) Recent advances in the breakdown of microplastics: strategies and future prospectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:65887–65903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22004-0
Ma J, Zhao JH, Zhu ZL, Li LQ, Yu F (2019) Effect of microplastic size on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of triclosan on polyvinyl chloride. Environ Pollut 254:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113104
Mao RF, Lang MF, Yu XQ, Wu RR, Yang XM, Guo XT (2020) Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 393:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122515
Marsic-Lucic J, Lusic J, Tutman P, Bojanic Varezic D, Siljic J, Pribudic J (2018) Levels of trace metals on microplastic particles in beach sediments of the island of Vis, Adriatic Sea. Croatia Mar Pollut Bull 137:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.10.027
Mejías C, Martín J, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2023) Role of polyamide microplastics as vector of parabens in the environment: An adsorption study. Environ Technol Innov 32:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103276
Naji A, Azadkhah S, Farahani H, Uddin S, Khan FR (2021) Microplastics in wastewater outlets of Bandar Abbas city (Iran): A potential point source of microplastics into the Persian Gulf. Chemosphere 262:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128039
Napper IE, Bakir A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2015) Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar Pollut Bull 99:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.029
O’Connor D, Hou DY, Ok YS, Lanphear BP (2020) The effects of iniquitous lead exposure on health. Nat Sustain 3:77–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-0475-z
Obbard RW, Sadri S, Wong YQ, Khitun AA, Baker I, Thompson RC (2014) Global warming releases microplastic legacy frozen in Arctic Sea ice. Earth Future 2:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014ef000240
Oni BA, Ayeni AO, Agboola O, Oguntade T, Obanla O (2020) Comparing microplastics contaminants in (dry and raining) seasons for Ox-Bow Lake in Yenagoa Nigeria. Ecotox Environ Safe 198:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110656
Oni BA, Sanni SE (2022) Occurrence of Microplastics in Borehole Drinking Water and Sediments in Lagos. Nigeria Environ Toxicol Chem 41:1721–1731. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5350
Petersen F, Hubbart JA (2021) The occurrence and transport of microplastics: The state of the science. Sci Total Environ 758:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143936
Rahman A, Sarkar A, Yadav OP, Achari G, Slobodnik J (2021) Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Sci Total Environ 757:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
Reinaldo JS, Pereira LM, Silva ES, Macedo TCP, Damasceno IZ, Ito EN (2020) Thermal, mechanical and morphological properties of multicomponent blends based on acrylic and styrenic polymers. Polym Test 82:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106265
Rochman CM, Hoh E, Hentschel BT, Kaye S (2013) Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ Sci Technol 47:1646–1654. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303700s
Romero D, Chlala D, Labaki M, Royer S, Bellat JP, Bezverkhyy I, Giraudon JM, Lamonier JF (2015) Removal of Toluene over NaX Zeolite Exchanged with Cu2+. Catalysts 5:1479–1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5031479
Rubio L, Marcos R, Hernández A (2020) Potential adverse health effects of ingested micro- and nanoplastics on humans. Lessons learned from in vivo and in vitro mammalian models. J Toxicol Env Health-Pt b-Crit Rev. 23:51–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2019.1700598
Sackey EA, Song YL, Yu Y, Zhuang HF (2021) Biochars derived from bamboo and rice straw for sorption of basic red dyes. PLoS ONE 16:20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254637
Shen XC, Li DC, Sima XF, Cheng HY, Jiang H (2018) The effects of environmental conditions on the enrichment of antibiotics on microplastics in simulated natural water column. Environ Res 166:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.034
Sheng DR, Meng XH, Wen XH, Wu J, Yu HJ, Wu M (2022) Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 841:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156733
Su XY, Chen Y, Li YF, Li J, Song W, Li XG, Yan LG (2022) Enhanced adsorption of aqueous Pb(II) and Cu(II) by biochar loaded with layered double hydroxide: Crucial role of mineral precipitation. J Mol Liq 357:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119083
Sun C, Wei SY, Tan HY, Huang YL, Zhang YH (2022) Progress in upcycling polylactic acid waste as an alternative carbon source: A review. Chem Eng J 446:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136881
Sun Y, Peng BY, Wang Y, Wang XJ, Xia SQ, Zhao JF (2023) Evaluating the adsorption and desorption performance of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) microplastics towards Cu(II): The roles of biofilms and biodegradation. Chem Eng J 464:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142714
Tan DJ, Bilal GS, Komal B (2020) Impact of Carbon Emission Trading System Participation and Level of Internal Control on Quality of Carbon Emission Disclosures: Insights from Chinese State-Owned Electricity Companies. Sustainability 12:14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051788
Thompson RC, Olsen Y, Mitchell RP, Davis A, Rowland SJ, John AWG, McGonigle D, Russell AE (2004) Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 304:838–838. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094559
Torres FG, Dioses-Salinas DC, Pizarro-Ortega CI, De-la-Torre GE (2021) Sorption of chemical contaminants on degradable and non-degradable microplastics: Recent progress and research trends. Sci Total Environ 757:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143875
Upadhyay R, Singh S, Kaur G (2022) Sorption of pharmaceuticals over microplastics’ surfaces: interaction mechanisms and governing factors. Environ Monit Assess 194:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10475-0
Velusamy S, Roy A, Sundaram S, Mallick TK (2021) A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem Rec 21:1570–1610. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000153
Velzeboer I, Kwadijk C, Koelmans AA (2014) Strong Sorption of PCBs to Nanoplastics, Microplastics, Carbon Nanotubes, and Fullerenes. Environ Sci Technol 48:4869–4876. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405721v
Wang CH, Zhao J, Xing BS (2021a) Environmental source, fate, and toxicity of microplastics. J Hazard Mater 407:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124357
Wang H, Qiu C, Song YL, Bian SC, Wang Q, Chen YM, Fang CR (2022a) Adsorption of tetracycline and Cd(II) on polystyrene and polyethylene terephthalate microplastics with ultraviolet and hydrogen peroxide aging treatment. Sci Total Environ 845:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157109
Wang LL, Guo CX, Qian QQ, Lang DN, Wu RL, Abliz S, Wang W, Wang JD (2023) Adsorption behavior of UV aged microplastics on the heavy metals Pb(II) and Cu(II) in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 313:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137439
Wang QJ, Zhang Y, Wangjin XX, Wang YL, Meng GH, Chen YH (2020) The adsorption behavior of metals in aqueous solution by microplastics effected by UV radiation. J Environ Sci 87:272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.07.006
Wang SW, Zhong S, Zheng XY, Xiao D, Zheng LL, Yang Y, Zhang HD, Ai BL, Sheng ZW (2021b) Calcite modification of agricultural waste biochar highly improves the adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 9:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106215
Wang XX, Zhang RX, Li ZY, Yan B (2022b) Adsorption properties and influencing factors of Cu(II) on polystyrene and polyethylene terephthalate microplastics in seawater. Sci Total Environ 812:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152573
Wang ZZ, Fu DD, Gao L, Qi HY, Su YY, Peng LC (2021c) Aged microplastics decrease the bioavailability of coexisting heavy metals to microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotox Environ Safe 217:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112199
Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (2013) The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ Pollut 178:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031
Wu TF, Zhu GW, Chen JH, Yang TT (2020) In-situ observations of internal dissolved heavy metal release in relation to sediment suspension in lake Taihu China. J Environ Sci 97:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.05.004
Xie FY, Yu MC, Yuan QK, Meng Y, Qie YK, Shang ZM, Luan FB, Zhang DL (2022) Spatial distribution, pollution assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in the Yellow River. J Hazard Mater 436:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129309
Yan MT, Nie HY, Xu KH, He YH, Hu YT, Huang YM, Wang J (2019) Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city and Pearl River estuary, China. Chemosphere 217:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.093
Zhang GY, Yang ZC, Teng Q, Han YQ, Zhang SH, Liu SY (2023) Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) by magnetic beads loaded with xanthan gum. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:33624–33635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24620-2
Zhang K, Xiong X, Hu HJ, Wu CX, Bi YH, Wu YH, Zhou BS, Lam PKS, Liu JT (2017) Occurrence and Characteristics of Microplastic Pollution in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. China Environ Sci Technol 51:3794–3801. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00369
Zhao JM, Ran W, Teng J, Liu YL, Liu H, Yin XN, Cao RW, Wang Q (2018) Microplastic pollution in sediments from the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. China Sci Total Environ 640:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.346
Zhao YX, Yang YN, Yang SJ, Wang QH, Feng CP, Zhang ZY (2013) Adsorption of high ammonium nitrogen from wastewater using a novel ceramic adsorbent and the evaluation of the ammonium-adsorbed-ceramic as fertilizer. J Colloid Interface Sci 393:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.10.028
Zhou YY, He YZ, Xiang YJ, Meng SJ, Liu XC, Yu JF, Yang J, Zhang JC, Qin PF, Luo L (2019) Single and simultaneous adsorption of pefloxacin and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions by oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube. Sci Total Environ 646:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.267
Zhuang ST, Wang JL (2023) Interaction between antibiotics and microplastics: Recent advances and perspective. Sci Total Environ 897:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165414
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review and also thank to editage Editor (https://www.editage.com/) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270215) and Research Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (15Q119, and Q20131708).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chun Hu: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, project administration, and funding acquisition; Yaodong Xiao: investigation, data curation, formal analysis, and writing-original draft; Qingrong Jiang: investigation, and data curation; Mengyao Wang: investigation, and writing-review and editing; Tingdan Xue: investigation and conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, C., Xiao, Y., Jiang, Q. et al. Adsorption properties and mechanism of Cu(II) on virgin and aged microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 29434–29448 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33131-1