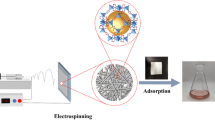
Abstract
The need to effectively remove toxic organic dyes from aquatic systems has become an increasingly critical issue in the recent years. In pursuit of this objective, polydopamine (PDA)-binary ZIF-8/UiO-66 (MOFs) was synthesized and incorporated into cellulose acetate (CA), producing ZIF-8/UiO-66/PDA@CA composite nanofibers under meticulously optimized conditions. The potential of fabricated nanofibers to remove cationic methylene blue (MB) dye was investigated. Various analysis tools including FTIR, XRD, SEM, zeta potential, BET, tensile strength testing, and XPS were employed. Results revealed a substantial leap in tensile strength, with ZIF-8/UiO-66/PDA@CA registering an impressive 2.8 MPa, as a marked improvement over the neat CA nanofibers (1.1 MPa). ZIF-8/UiO-66/PDA@CA nanofibers exhibit an outstanding adsorption capacity of 82 mg/g, notably outperforming the 22.4 mg/g capacity of neat CA nanofibers. In binary dye systems, these nanofibers exhibit a striking maximum adsorption capacity of 108 mg/g, establishing their eminence in addressing the complexities of wastewater treatment. Furthermore, the adsorption data fitted to the Langmuir isotherm, and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The fabricated nanofiber demonstrates good reproducibility and durability, consistently upholding its performance over five cycles. This suite of remarkable attributes collectively underscores its potential as a robust, durable, and highly promising solution for the effective and efficient removal of pernicious MB dye, in the context of both water quality improvement and environmental preservation.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Monaem EM, Omer AM, Khalifa RE, Eltaweil AS (2022) Floatable cellulose acetate beads embedded with flower-like zwitterionic binary MOF/PDA for efficient removal of tetracycline. J Colloid Interface Sci 620:333–345
Abdelfatah AM, Fawzy M, El-Khouly ME, Eltaweil AS (2021) Efficient adsorptive removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution using phytosynthesized nano-zero valent iron. J Saudi Chem Soc 25;101365
Ali ASM, El-Aassar MR, Hashem FS, Moussa NA (2019) Surface modified of cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibers by polyaniline/β-cyclodextrin composite for removal of cationic dye from aqueous medium. Fibers Polym 20(10):2057–2069
Ali Khan AS (2012) Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption on sand from Temkin adsorption isotherm. Turk J Chem 36(3):437–443
Asif I, Rafique U (2021) Cellulose acetate-based hybrid materials: fascinating material as a potential adsorbent for Congo red removal. Desalin Water Treat 244:302–324
Ayiania M, Smith M, Hensley AJR, Scudiero L, McEwen JS, Garcia-Perez M (2020) Deconvoluting the XPS spectra for nitrogen-doped chars: an analysis from first principles. Carbon 162:528–544
Bespalov I, Datler M, Buhr S, Drachsel W, Rupprechter G, Suchorski Y (2015) Initial stages of oxide formation on the Zr surface at low oxygen pressure: an in situ FIM and XPS study. Ultramicroscopy 159:147–151
Chang PH, Lee YT, Peng CH (2020) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid metal zeolitic imidazolate framework membrane for efficient H2/Co2 gas separation. Materials 13(21):1–15
Chen J, Li J, Zhan X, Han X, Chen C (2010) Effect of PEG additives on properties and morphologies of polyetherimide membranes prepared by phase inversion. Front Chem Eng China 4(3):300–306
Chen Q, He Q, Lv M, Xu Y, Yang H, Liu X, Wei F (2015) Selective adsorption of cationic dyes by UiO-66-NH2. Appl Surf Sci 327:77–85
Chen R, Lin B, Luo R (2022) Recent progress in polydopamine-based composites for the adsorption and degradation of industrial wastewater treatment. Heliyon 8(12):e12105
Cheng J, Zhan C, Wu J, Cui Z, Si J, Wang Q, Peng X, Turng LS (2020) Highly efficient removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution using cellulose acetate nanofibrous membranes modified by polydopamine. ACS Omega 5(10):5389–5400
Ding M, Cai X, Jiang HL (2019) Improving MOF stability: approaches and applications. Chem Sci 10(44):10209–10230
Elmaghraby NA, Omer AM, Kenawy ER, Gaber M, El Nemr A (2022) Electrospun composites nanofibers from cellulose acetate/carbon black as efficient adsorbents for heavy and light machine oil from aquatic environment. J Iran Chem Soc 19(7):3013–3027
Elmaghraby NA, Omer AM, Kenawy ER, Gaber M, Hassaan MA, Ragab S, Hossain I, Nemr AE (2023) Electrospun cellulose acetate/activated carbon composite modified by EDTA (rC / AC - EDTA) for efficient methylene blue dye removal. Sci Rep 13:19919
Eltaweil AS, Abd El-Monaem EM, El-Subruiti GM, Abd El-Latif MM, Omer AM (2020a) Fabrication of UiO-66/MIL-101(Fe) binary MOF/carboxylated-GO composite for adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 10(32):19008–19019
Eltaweil AS, Elgarhy GS, El-Subruiti GM, Omer AM (2020b) Carboxymethyl cellulose/carboxylated graphene oxide composite microbeads for efficient adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye. Int J Biol Macromol 154:307–318
Eze E, Omer AM, Hassanin AH, Eltaweil AS, El-Khouly ME (2023) Efficient removal of noxious methylene dye by low-cost and reusable composite beads based on cellulose acetate/banana pseudo-stem fiber. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, in press
Fendi W, Naser J (2018) Adsorption isotherms study of methylene blue dye on membranes from electrospun nanofibers. Orient J Chem 34(6):2884–2894
Feng Y, Li Y, Xu M, Liu S, Yao J (2016) Fast adsorption of methyl blue on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 and its adsorption mechanism. RSC Adv 6(111):109608–109612
Franciski MA, Peres EC, Godinho M, Perondi D, Foletto EL, Collazzo GC, Dotto GL (2018) Development of CO2 activated biochar from solid wastes of a beer industry and its application for methylene blue adsorption. Waste Manage 78:630–638
Ganguly A, Sharma S, Papakonstantinou P, Hamilton J (2011) Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using high-resolution in situ X-ray-based spectroscopies. J Phys Chem C 115(34):17009–17019
Gondal MA, Fasasi TA, Baig U, Mekki A (2017) Effects of oxidizing media on the composition, morphology and optical properties of colloidal zirconium oxide nanoparticles synthesized via pulsed laser ablation in liquid technique. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(6):4030–4039
Gopi S, Pius A, Kargl R, Kleinschek KS, Thomas S (2019) Fabrication of cellulose acetate/chitosan blend films as efficient adsorbent for anionic water pollutants. Polym Bull 76(3):1557–1571
Hakro RA, Mehdi M, Qureshi RF, Mahar RB, Khatri M, Ahmed F, Khatri Z, Kim IS (2021) Efficient removal of reactive blue-19 dye by co-electrospun nanofibers. Mater Res Express 8(5):1–11
Hastuti B, Nur Afifah S, Mulyani B, Susilowati E (2020) Adsorption of methylene blue dyes using pectin membrane. J Phys Confer Ser 1503 (1)
Katz MJ, Brown ZJ, Colón YJ, Siu PW, Scheidt KA, Snurr RQ, Hupp JT, Farha OK (2013) A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem Commun 49(82):9449–9451
Khan I, Saeed K, Zekker I, Zhang B, Hendi AH, Ahmad A, Khan I (2022) Review on methylene blue: its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water 14(2):242
Kim EY, Kim HS, Kim D, Kim J, Lee PS (2019) Preparation of mixed matrix membranes containing ZIF-8 and UiO-66 for multicomponent light gas separation. Crystals 9(1):15
Koriem OA, Kamel AM, Shaaban W, Elkady MF (2022) Enhancement of dye separation performance of eco-friendly cellulose acetate-based membranes. Sustainability 14(22):14665
Lee YR, Jang MS, Cho HY, Kwon HJ, Kim S, Ahn WS (2015) ZIF-8: a comparison of synthesis methods. Chem Eng J 271:276–280
Li Y, Zhou K, He M, Yao J (2016) Synthesis of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 using mixed-base and their dye adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 234:287–292
Li T, Liu L, Zhang Z, Han Z (2020) Preparation of nanofibrous metal-organic framework filter for rapid adsorption and selective separation of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Sep Purif Technol 237:116360
Liang XX, Omer AM, Hu Z, Wang Y, Yu D, Ouyang X (2019) Efficient adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions using magnetic amine-functionalized chitosan. Chemosphere 217:270–278
Liebscher J (2019) Chemistry of polydopamine-scope, variation, and limitation. Eur J Org Chem 19(32):4976–4994
Luan Tran B, Chin HY, Chang BK, Chiang AST (2019) Dye adsorption in ZIF-8: the importance of external surface area. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 277:149–153
Mandal S, Natarajan S, Mani P, Pankajakshan A (2021) Post-synthetic modification of metal–organic frameworks toward applications. Adv Func Mater 31(4):2006291
Mirhosseini H, Shamspur T, Mostafavi A, Sargazi G (2021) A novel ultrasonic reverse micelle-assisted electrospun efficient route for Eu-MOF and Eu-MOF/CA composite nanofibers: a high-performance photocatalytic treatment for removal of BG pollutant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(4):4317–4328
Modi S, Yadav VK, Gacem A, Ali IH, Dave D, Khan SH, Yadav KK, Rather SU, Ahn Y, Son CT, Jeon BH (2022) Recent and emerging trends in remediation of methylene blue dye from wastewater by using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Water 14(11):1749
Mohammadi AA, Alinejad A, Kamarehie B, Javan S, Ghaderpoury A, Ahmadpour M, Ghaderpoori M (2017) Metal-organic framework Uio-66 for adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(9):1959–1968
Mondal NK, Das K, Das B, Sadhukhan B (2016) Effective utilization of calcareous soil towards the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18(3):867–881
Morcos GS, Ibrahim AA, El-Sayed MMH, El-Shall MS (2021) High performance dunctionalized UiO metal organic frameworks for the efficient and selective adsorption of Pb(II) ions in concentrated multi-ion systems. J Env Chem Eng 3;105191
Muneshwar T, Cadien K (2018) Comparing XPS on bare and capped ZrN films grown by plasma enhanced ALD: effect of ambient oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 435:367–376
Muqeet M, Khalique A, Qureshi UA, Mahar RB, Ahmed F, Khatri Z, Kim IS, Brohi KM (2018) Aqueous hardness removal by anionic functionalized electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Cellulose 25(10):5985–5997
Omer AM, Khalifa RE, Hu Z, Zhang H, Liu C, Ouyang X (2019) Fabrication of tetraethylenepentamine functionalized alginate beads for adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 125:1221–1231
Omer AM, Elgarhy GS, El-Subruiti GM, Khalifa RE, Eltaweil AS (2020) Fabrication of novel iminodiacetic acid-functionalized carboxymethyl cellulose microbeads for efficient removal of cationic crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 148:1072–1083
Paclijan SS, Franco SMB, Abella RB, Lague JCH, Tan NPB (2021) Fresh and uncalcined solution blow spinning - spun PAN and PVDF nanofiber membranes for methylene blue dye removal in water. J Membr Sci Res 7(3):173–184
Pi Y, Li X, Xia Q, Wu J, Li Y, Xiao J, Li Z (2018) Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in water by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Eng J 337:351–371
Pottathara YB, Narwade VN, Bogle KA, Kokol V (2020) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils–graphene oxide composite films with improved dye adsorption properties. Polym Bull 77(12):6175–6189
Ruan H, Pan N, Wang C, Yu L, Liao J, Shen J (2021) Functional UiO-66 series membranes with high perm selectivity of monovalent and bivalent anions for electrodialysis applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 60(10):4086–4096
Sağlam S, Türk FN, Arslanoğlu H (2023) Use and applications of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) in dye adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 11(5):110568
Tag El-Din AF, El-Khouly ME, Elshehy EA, Atia AA, El-Said WA (2018) Cellulose acetate assisted synthesis of worm-shaped mesopores of MgP ion-exchanger for cesium ions removal from seawater. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 265:211–218
Tang B, Wu D, Xu T (2005) Effect of PEG additives on properties and morphologies of membranes prepared from poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) by benzyl bromination and in situ amination. J Appl Polym Sci 98(6):2414–2421
Vadi M, Mansoorabad AO, Mohammadi M, Rostami N (2013) Investigation of Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin adsorption isotherm of tramadol by multi-wall carbon nanotube. Asian J Chem 25(10):5467–5469
Večeř M, Pospíšil J (2012) Stability and rheology of aqueous suspensions. Proc Eng 42:1720–1725
Wang Z, Wang J, Li M, Sun K, Liu CJ (2014) Three-dimensional printed acrylonitrile butadiene styrene framework coated with Cu-BTC metal-organic frameworks for the removal of methylene blue. Sci Rep 4:4–10
Wee Lik H, Janssens Nikki, Sree Sreeprasanth P, Wiktor Christian, Gobechiya Elena, Fischer Roland A, Kirschhock Christine EA, Martens Johan A (2014) Local transformation of ZIF-8 powders and coatings into ZnO nanorods for photocatalytic application. Nanoscale 6(4):2056–2060
Yang X, Zhou Y, Sun Z, Yang C, Tang D (2021) Polydopamine assists the continuous growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 on electrospun polyacrylonitrile fibers as efficient adsorbents for the improved removal of Cr(vi). New J Chem 45(34):15503–15513
Zha Q, Sang X, Liu D, Wang D, Shi G, Ni C (2019) Modification of hydrophilic amine-functionalized metal-organic frameworks to hydrophobic for dye adsorption. J Solid State Chem 275:23–29
Zhang M, Yang K, Cui J, Yu H, Wang Y, Shan W, Lou Z, Xiong Y (2020) 3D-agaric like core-shell architecture UiO-66-NH2@ZIF-8 with robust stability for highly efficient REEs recovery. Chem Eng J 386:124023
Zhou HC, Long JR, Yaghi OM (2012) Introduction to metal–organic frameworks. Chem Rev 112(2):673–674
Acknowledgements
Esther Eze would like to express gratitude to Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD) for the scholarship. Ahmed Hassanin acknowledges Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STIFA), Egypt, Project 33431 DDP for supporting the manufacturing of all the nanofiber samples on the project’s devices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Esther Eze: fabrication and characterization of the materials, running the experiments for adsorption of MB, writing the manuscript. Ahmed M. Omer: conceptualization, data analysis, writing the manuscript, and supervision. Ahmed Hassanin: methodology for fabrication of nanofiber, and supervision. Abdelazeem S. Eltaweil: conceptualization, methodology, writing the manuscript, and supervision. Mohamed E. El-Khouly: conceptualization, fabrication, and characterization of the materials, editing the manuscript, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eze, E., Omer, A.M., Hassanin, A.H. et al. Cellulose acetate nanofiber modified with polydopamine polymerized MOFs for efficient removal of noxious organic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 29992–30008 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33050-1