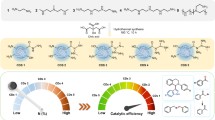
Abstract
Mn3O4/ZnO-Al2O3-CeO2 catalyst was synthesized through a solid-state process from a 3% Mn-doped Zn-(Al/Ce) layered double hydroxide structure. Detailed structural and optical characterization using XRD, FTIR, UV–visible DRS, and TEM was conducted. By investigating clofibric acid (CA) degradation in aqueous solution, Mn3O4/ZnO-Al2O3-CeO2 photocatalytic activity was evaluated. The results show that the heterostructure mixed oxide catalyst has excellent CA photodegradation performance. Further, the characterization reveals that such photocatalytic efficiency can be attributed to two facts that are summarized in the optical properties and the synergic effect between Mn and Ce elements. The sample demonstrated a narrow band gap of 2.34 eV based on DRS. According to the experimental results of the photodegradation, after 120 min of irradiation, the photocatalyst exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity, with a degradation efficiency of 93.6%. Optimization outcomes indicated that maximum degradation efficiency was attained under the following optimum conditions: catalyst dose of 0.3 g/L, initial dye concentration of 20 mg/L, pH 3.86, and 120 min of reaction time. The quenching test demonstrates that photogenerated electrons and superoxide radicals are the most powerful reactive species. The catalyst could be useful in decreasing the photogenerated charges recombination, which offers more redox cycles simultaneously during the catalytic process. The strong Ce-Mn interaction and the formation of their different oxidation states offer a high degradation efficiency by facilitating electron–hole transfer. The introduction of Mn3O4 in the catalyst can effectively improve the visible absorption properties, which are beneficial in the photocatalytic process by reaching a high catalytic efficiency at a low cost.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdi M, Mahdikhah V, Sheibani S (2020) Visible light photocatalytic performance of La-Fe co-doped SrTiO3 perovskite powder. Opt Mater (amst) 102:109803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109803
Ajala OJ, Tijani JO, Salau RB et al (2022) A review of emerging micro-pollutants in hospital wastewater: environmental fate and remediation options. Results Eng 16:100671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100671
Akir S, Hamdi A, Addad A et al (2017) Facile synthesis of carbon-ZnO nanocomposite with enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Appl Surf Sci 400:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.212
Aydın S, Ulvi A, Bedük F, Aydın ME (2022) Pharmaceutical residues in digested sewage sludge: occurrence, seasonal variation and risk assessment for soil. Sci Total Environ 817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152864
Beausse J (2004) Selected drugs in solid matrices: a review of environmental determination, occurrence and properties of principal substances. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 23:753–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2004.08.005
Binas V, Stefanopoulos V, Kiriakidis G, Papagiannakopoulos P (2019) Photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous benzene, toluene and xylene under UV and visible irradiation over Mn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Mater 5:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2018.12.003
Cerrato E, Calza P, Cristina Paganini M (2022) Photocatalytic reductive and oxidative ability study of pristine ZnO and CeO2-ZnO heterojunction impregnated with Cu2O. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 427:113775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.113775
Chafi S, Azzouz A, Ballesteros E (2022) Occurrence and distribution of endocrine disrupting chemicals and pharmaceuticals in the river Bouregreg (Rabat, Morocco). Chemosphere 287:132202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132202
Chaudhari SM, Gonsalves OS, Nemade PR (2021) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Diclofenac with Agl/CeO2: a comparison with Mn, Cu and Ag-doped CeO2. Mater Resear Bull 143:111463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111463
Chen P, Wang F, Zhang Q et al (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of clofibric acid by g-C3N4/P25 composites under simulated sunlight irradiation: the significant effects of reactive species. Chemosphere 172:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.015
Cheng G, Yuan C, Ruan W et al (2023) Visible light enhanced persulfate activation for degradation of tetracycline via boosting adsorption of persulfate by ligand-deficient MIL-101(Fe) icosahedron. Chemosphere 317:137857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137857
Dias JA, Gualdi AJ, Costa LJD et al (2020) Effects of bismuth/lanthanum-substitution on optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of bismuth–iron titanate. Mater Today Commun 24:101193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101193
Elhalil A, Elmoubarki R, Farnane M et al (2018) Synthesis, characterization and efficient photocatalytic activity of novel Ca/ ZnO-Al2O3 nanomaterial. Mater Today Commun 16:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.06.005
Elhalil A, Elmoubarki R, Farnane M et al (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of caffeine as a model pharmaceutical pollutant on Mg doped ZnO-Al2O3 heterostructure. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 10:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.02.002
Favier L, Rusu L, Simion AI, Hlihor RM, Pacala ML, Augustyniak A (2019) Efficient degradation of clofibric acid by heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation process. Environ Eng Manag J 18(8):1683–1692
Hussain MM, Rahman MM, Asiri AM (2016) Efficient 2-nitrophenol chemical sensor development based on Ce2O3 nanoparticles decorated CNT nanocomposites for environmental safety. PLoS ONE 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166265
Ighalo JO, Ajala OJ, Umenweke G, et al (2020) Mitigation of clofibric acid pollution by adsorption: a review of recent developments. J Environ Chem Eng 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104264
Iqbal J, Shah NS, Khan ZUH et al (2022) Visible light driven doped CeO2 for the treatment of pharmaceuticals in wastewater: a review. J Water Process Eng 49:103130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103130
Janani FZ, Khiar H, Taoufik N et al (2022) ZnO-Zn2TiO4 heterostructure for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22791-6
Janani FZ, Khiar H, Taoufik N et al (2021) ZnO–Al2O3–CeO2–Ce2O3 mixed metal oxides as a promising photocatalyst for methyl orange photocatalytic degradation. Mater Today Chem 21.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100495
Kijlstra WS, Poels EK, Bliek A et al (1997) Characterization of Al2O3-supported manganese oxides by electron spin resonance and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 101:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp962343i
Korkmaz NE, Savun-Hekimoğlu B, Aksu A et al (2022) Occurrence, sources and environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Sci Total Environ 819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152996
Liang X, Wang P, Gao Y et al (2020) Design and synthesis of porous M-ZnO/CeO2 microspheres as efficient plasmonic photocatalysts for nonpolar gaseous molecules oxidation: insight into the role of oxygen vacancy defects and M=Ag, Au Nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 260:118151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118151
Lin H, Tang X, Wang J et al (2021) Enhanced visible-light photocatalysis of clofibric acid using graphitic carbon nitride modified by cerium oxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 405:124204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124204
Ma B, Liu Z, Wang L et al (2024) Significantly boosting photocatalytic degradation efficiency through simple Br modification. Mater Sci Semicond Process 169:107941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107941
Mohan R, Krishnamoorthy K, Kim SJ (2012) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods. Solid State Commun 152:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2011.12.008
Morales-mendoza G, Tzompantzi F, García-mendoza C et al (2015) Mn-doped Zn / Al layered double hydroxides as photocatalysts for the 4-chlorophenol photodegradation. Appl Clay Sci 118:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.08.030
Nagendran S, Periyasamy G, Kamath PV (2018) Hydration-induced interpolytype transformations in the bayerite-derived nitrate-intercalated layered double hydroxide of Li and Al. J Solid State Chem 266:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2018.07.016
Olfs HW, Torres-Dorante LO, Eckelt R, Kosslick H (2009) Comparison of different synthesis routes for Mg-Al layered double hydroxides (LDH): characterization of the structural phases and anion exchange properties. Appl Clay Sci 43:459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.10.009
Pratt GW, Coelho R (1959) Optical absorption of CoO and MnO above and below the Néel temperature. Phys Rev 116:281–286. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.116.281
Rebelo D, Correia AT, Nunes B (2020) Acute and chronic effects of environmental realistic concentrations of clofibric acid in Danio rerio: behaviour, oxidative stress, biotransformation and lipid peroxidation endpoints. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 80:103468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103468
Reza RA, Ahmaruzzaman M, Sil AK, Gupta VK (2014) Comparative adsorption behavior of ibuprofen and clofibric acid onto microwave assisted activated bamboo waste. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:9331–9339. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie404162p
Sahoo GP, Samanta S, Bhui DK et al (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis of hexagonal ZnO microstructures in HPMC polymer matrix and their catalytic activities. J Mol Liq 212:665–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.10.019
Sescu AM, Harja M, Favier L et al (2020) Zn/La mixed oxides prepared by coprecipitation: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic studies. Materials (basel) 13:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214916
Shan K, Zhai F, Yi ZZ et al (2021) Mixed conductivity and the conduction mechanism of the orthorhombic CaZrO3 based materials. Surf Interfaces 23:100905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100905
Shang K, Li W, Wang X et al (2019) Degradation of p-nitrophenol by DBD plasma/Fe2+/persulfate oxidation process. Sep Purif Technol 218:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.02.046
Shehu Z, Nyakairu GWA, Tebandeke E, Odume ON (2022) Overview of African water resources contamination by contaminants of emerging concern. Sci Total Environ 852:158303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158303
Shi Y, Geng J, Li X et al (2022) Effects of DOM characteristics from real wastewater on the degradation of pharmaceutically active compounds by the UV/H2O2 process. J Environ Sci (china) 116:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.12.017
Silori R, Shrivastava V, Singh A et al (2022) Global groundwater vulnerability for pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs): the scenario of second decade of 21st century. J Environ Manage 320:115703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115703
Taoufik N, Boumya W, Elmoubarki R et al (2022) Experimental design, machine learning approaches for the optimization and modeling of caffeine adsorption. Mater Today Chem 23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100732
Velu S, Shah N, Jyothi TM, Sivasanker S (1999) Effect of manganese substitution on the physicochemical properties and catalytic toluene oxidation activities of Mg-Al layered double hydroxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 33:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(99)00123-7
Wan J, Tao F, Shi Y et al (2022) Designed preparation of nano rod shaped CeO2-MnOx catalysts with different Ce/Mn ratios and its highly efficient catalytic performance for chlorobenzene complete oxidation: new insights into structure–activity correlations. Chem Eng J 433:133788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133788
Wang Y, He X, Gao P et al (2024) Enhanced photocatalytic gaseous formaldehyde degradation using N-CQDs/OVs-TiO2 composite under visible light: unraveling the synergistic effects of N-CQDs and oxygen vacancies. Environ Res 247:118301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.118301
Wu C, Shen L, Zhang YC, Huang Q (2011) Solvothermal synthesis of Cr-doped ZnO nanowires with visible light-driven photocatalytic activity. Mater Lett 65:1794–1796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.03.070
Wu S, Wang Z, Wan L et al (2022) Electrocatalytic hydrodechlorination of clofibric acid (CA) using Pd/Ni foam electrodes: the effects of Ni(OH)2 and complexing agents on electrode preparation. J Electroanal Chem 915:116358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116358
Yang ZM, Huang GF, Huang WQ et al (2014) Novel Ag3PO4/CeO2 composite with high efficiency and stability for photocatalytic applications. J Mater Chem A 2:1750–1756. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta14286h
Zhang L, Dai CH, Zhang XX et al (2016) Synthesis and highly efficient photocatalytic activity of mixed oxides derived from ZnNiAl layered double hydroxides. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (English Ed) 26:2380–2389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64360-1
Zhao Q, Liu Q, Han J et al (2019) The effect of cerium incorporation on the catalytic performance of cobalt and manganese containing layer double oxides for acetone oxidation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94:3753–3762. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5868
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Center for Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST) of Morocco for microscopic analysis performed in their technical facilities. The authors also acknowledge the financial support through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R768), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This study was funded by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R768), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fatima Zahra Janani: performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, and writing: original draft. Habiba Khiar: performed the experiments and analyzed and interpreted the data. Nawal Taoufik: analyzed and interpreted the data and data curation. Mhamed Sadiq: analyzed and interpreted the data and data curation. Lidia Favier: analyzed and interpreted the data, writing: review and editing, and data curation. Abdelrahman Osama Ezzat: writing: review and editing. Alaâeddine Elhalil: analyzed and interpreted the data and writing: review and editing. Noureddine Barka: conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, writing: review and editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Janani, F.Z., Khiar, H., Taoufik, N. et al. Mn3O4/ZnO-Al2O3-CeO2 mixed oxide catalyst derived from Mn-doped Zn-(Al/Ce)-LDHs: efficient visible light photodegradation of clofibric acid in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 25373–25387 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32841-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32841-w