Abstract
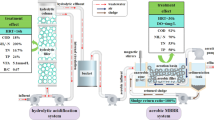
Domestic wastewater source-separated treatment has attracted wide attention due to the efficiency improvement of sewage treatment systems, energy saving, resource reuse, and the construction and operation cost saving of pipeline networks. Nonetheless, the excess source-separated urine still demands further harmless treatment. Sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR), a new type of composite biofilm reactor developed by filling different fillers into the sequential batch reactor (SBR) reactor, has higher pollutant removal performance and simpler operation and maintenance. However, the phosphorus removal ability of the SBBR filling with conventional fillers is still limited and needs further improvement. In this study, we developed two new fillers, the self-fabricated filler A and B (SFA/SFB), and compared their source-separated urine treatment performance. Long-term treatment experimental results demonstrated that the SBBR systems with different fillers had good removal performance on the COD and TN in the influent, and the removal rate increased with the increasing HRT. However, only the SBBR system with the SFA showed excellent PO43−-P and TP removal performance, with the removal rates being 83.7 ± 11.9% and 77.3 ± 13.7% when the HRT was 1 d. Microbial community analysis results indicated that no special bacteria with strong phosphorus removal ability were present on the surface of the SFA. Adsorption experimental results suggested that the SFA had better adsorption performance for phosphorus than the SFB, but it could not always have stronger phosphorus adsorption and removal performance during long-term operation due to the adsorption saturation. Through a series of characterizations such as SEM, XRD, and BET, it was found that the SFA had a looser structure due to the use of different binder and production processes, and the magnesium in the SFA gradually released and reacted with PO43− and NH4+ in the source-separated urine to form dittmarite and struvite, thus achieving efficient phosphorus removal. This study provides a feasible manner for the efficient treatment of source-separated urine using the SBBR system with self-fabricated fillers.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Altmann J, Rehfeld D, Träder K, Sperlich A, Jekel M (2016) Combination of granular activated carbon adsorption and deep-bed filtration as a single advanced wastewater treatment step for organic micropollutant and phosphorus removal. Water Res 92:131–139
Bayuseno AP, Schmahl WW (2020) Crystallization of struvite in a hydrothermal solution with and without calcium and carbonate ions. Chemosphere 250:126245
Capodaglio AG, Callegari A, Cecconet D, Molognoni D (2017) Sustainability of decentralized wastewater treatment technologies. Water Pract Technol 12(2):463–477
Chrispim MC, Scholz M, Nolasco MA (2019) Phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater treatment: critical review of challenges and opportunities for developing countries. J Environ Manage 248:109268
Dan NH, Le Luu T (2021) High organic removal of landfill leachate using a continuous flow sequencing batch biofilm reactor (CF-SBBR) with different biocarriers. Sci Total Environ 787:147680
Del Bubba M, Arias CA, Brix H (2003) Phosphorus adsorption maximum of sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds as measured by the Langmuir isotherm. Water Res 37(14):3390–3400
Du M, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Lv M, Xu Q, Chen Z, Wen Q, Li A (2022) La-doped activated carbon as high-efficiency phosphorus adsorbent: DFT exploration of the adsorption mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 298:121585
Du X, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Feng S, Zhang Y, Kou H, Sun Y (2023) The synergistic effect of chemical oxidation and microbial activity on improving volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production during the animal wastewater anaerobic digestion process treated with persulfate/biochar. Sci Total Environ 857:159276
Fan C, Lv C, Wang Z, Wu S, Jin Z, Bei K, He S, Kong H, Zhao J, Zhao M, Zheng X (2022) Influence of regular addition of ore on treatment efficiency and aquatic organisms in living machine system for black water treatment. J Clean Prod 341:130928
Ghosh S, Lobanov S, Lo VK (2019) An overview of technologies to recover phosphorus as struvite from wastewater: advantages and shortcomings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19063–19077
Guo G, Ekama GA, Wang Y, Dai J, Biswal BK, Chen G, Wu D (2019) Advances in sulfur conversion-associated enhanced biological phosphorus removal in sulfate-rich wastewater treatment: a review. Bioresour Technol 285:121303
Hu X, Wang J, Wu F, Li D, Yang J, Chen J, Liang J, Lou X, Chen H (2023) Phosphorus recovery and resource utilization from phosphogypsum leachate via membrane-triggered adsorption and struvite crystallization approach. Chem Eng J 471:144310
Imwene KO, Ngumba E, Kairigo PK (2022) Emerging technologies for enhanced removal of residual antibiotics from source-separated urine and wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manage 322:116065
Jagaba AH, Kutty SRM, Lawal IM, Abubakar S, Hassan I, Zubairu I, Umaru I, Abdurrasheed AS, Adam AA, Ghaleb AAS, Almahbashi NMY, Al-dhawi BNS, Noor A (2021) Sequencing batch reactor technology for landfill leachate treatment: a state-of-the-art review. J Environ Manage 282:111946
Jiang C, Jia L, Zhang B, He Y, Kirumba G (2014) Comparison of quartz sand, anthracite, shale and biological ceramsite for adsorptive removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 26(2):466–477
Jin Z, Xie X, Zhou J, Bei K, Zhang Y, Huang X, Zhao M, Kong H, Zheng X (2018) Blackwater treatment using vertical greening: efficiency and microbial community structure. Bioresour Technol 249:175–181
Jucherski A, Walczowski A, Bugajski P, Jóźwiakowski K (2019) Technological reliability of domestic wastewater purification in a small Sequencing Batch Biofilm Reactor (SBBR). Sep Purif Technol 224:340–347
Kumar R, Pal P (2015) Assessing the feasibility of N and P recovery by struvite precipitation from nutrient-rich wastewater: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(22):17453–17464
Kumari S, Jagadevan S (2022) Phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater through struvite biomineralization using model gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial strains. J Clean Prod 366:132992
Li H, Liu F, Luo P, Xie G, Xiao R, Hu W, Peng J, Wu J (2018) Performance of integrated ecological treatment system for decentralized rural wastewater and significance of plant harvest management. Ecol Eng 124:69–76
Li W, Liu J, Zhen Y, Lin M, Sui X, Zhao W, Bing X, Lin J, Zhai L (2021a) Simultaneous removal of nitrite and organics in a biofilm-enhanced high-salt wastewater treatment system via mixotrophic denitrification coupled with sulfate reduction. J Water Process Eng 40:101976
Li Y, Zhu S, Zhang Y, Lv M, Joël Roland Kinhoun J, Qian T, Fan B (2021b) Constructed wetland treatment of source separated washing wastewater in rural areas of southern China. Sep Purif Technol. 272:118725
Liu X, Yang S, Liu S, Yang Y (2021) Performance and mechanism of phosphorus removal by slag ceramsite filler. Process Saf Environ Protect 148:858–866
Min KJ, Kim D, Lee J, Lee K, Park KY (2019) Characteristics of vegetable crop cultivation and nutrient releasing with struvite as a slow-release fertilizer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(33):34332–34344
Ongena S, de Walle AV, Mosquera-Romero S, Driesen N, Gutierrez L, Rabaey K (2023) Comparison of MBR and MBBR followed by UV or electrochemical disinfection for decentralized greywater treatment. Water Res 235:119818
Rajab AR, Salim MR, Sohaili J, Anuar AN, Salmiati, Lakkaboyana SK (2017) Performance of integrated anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactor treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 313:967–974
Saerens B, Geerts S, Weemaes M (2021) Phosphorus recovery as struvite from digested sludge – experience from the full scale. J Environ Manage 280:111743
Sarikaya Y, Onal M, Baran B, Alemdaroglu T (2000) The effect of thermal treatment of some of the physicochemical properties of a bentonite. Clay Clay Min 48(5):557–562
Scrivener KL, Nonat A (2011) Hydration of cementitious materials, present and future. Cem Concr Res 41(7):651–665
Shen X, Hussain T, Mitchek M, Wong J, Reible D (2023) Evaluating the sorption kinetics of polychlorinated biphenyls in powdered and granular activated carbon. Water Res 236:119978
Shi L, Zhang P, He Y, Zeng F, Xu J, He L (2021) Enantioselective effects of cyflumetofen on microbial community and related nitrogen cycle gene function in acid-soil. Sci Total Environ 771:144831
Simbeye C, Courtney C, Simha P, Fischer N, Randall DG (2023) Human urine: a novel source of phosphorus for vivianite production. Sci Total Environ 892:164517
Sronsri C, Sittipol W, U-yen K (2021) Luminescence characterization of Mn-doped LiMgPO4 synthesized using different precursors. J Solid State Chem 297:122083
Tang X, Wu M, Li R, Wang Z (2017) Prospect of recovering phosphorus in magnesium slag-packed wetland filter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(29):22808–22815
Tian T, Qiao W, Han Z, Wen X, Yang M, Zhang Y (2021) Effect of temperature on the persistence of fecal bacteria in ambient anaerobic digestion systems treating swine manure. Sci Total Environ 791:148302
Udomkittayachai N, Xue W, Xiao K, Visvanathan C, Tabucanon AS (2021) Electroconductive moving bed membrane bioreactor (EcMB-MBR) for single-step decentralized wastewater treatment: performance, mechanisms, and cost. Water Res 188:116547
Wang H, Biswal BK, Mao Y, Chen G, Wu D (2019) Multiple-cycle operation of sulphur-cycle-enhanced biological phosphorus removal to maintain stable performance at high temperatures. Bioresour Technol 289:121736
Xia Z, Wang Q, She Z, Gao M, Zhao Y, Guo L, Jin C (2019) Nitrogen removal pathway and dynamics of microbial community with the increase of salinity in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process. Sci Total Environ 697:134047
Xu Z, Xu W, Zhang L, Ma Y, Li Y, Li G, Nghiem LD, Luo W (2021) Bacterial dynamics and functions driven by bulking agents to mitigate gaseous emissions in kitchen waste composting. Bioresour Technol 332:125028
Yakamercan E, Aygün A (2020) Anaerobic/aerobic cycle effect on di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and pentachlorophenol removal from real textile wastewater in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. J Clean Prod 273:122975
Yang K, Ji B, Wang H, Zhang H, Zhang Q (2014) Bio-augmentation as a tool for improving the modified sequencing batch biofilm reactor. J Biosci Bioeng 117(6):763–768
Yang G, Wang J, Zhang H, Jia H, Zhang Y, Gao F (2019) Applying bio-electric field of microbial fuel cell-upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor catalyzed blast furnace dusting ash for promoting anaerobic digestion. Water Res 149:215–224
Zhang X, Liu Y (2022) Resource recovery from municipal wastewater: a critical paradigm shift in the post era of activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 363:127932
Zhang Z, Han Y, Xu C, Ma W, Han H, Zheng M, Zhu H, Ma W (2018) Microbial nitrate removal in biologically enhanced treated coal gasification wastewater of low COD to nitrate ratio by coupling biological denitrification with iron and carbon micro-electrolysis. Bioresour Technol 262:65–73
Zhang B, Yu Z, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Qiu D, Xiao E, Wu Z (2023) Effects of salinity on the performance of bioflocs with activated sludge as inoculum. Chem Eng J Adv 14:100451
Zhu W, Chen J, Yuan S, Sang W, Ban Y, Zhang S (2023) Impact of aeration frequency on performance of mixotrophic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) treating real domestic wastewater: removal efficiency, pathways, and mechanisms. J Clean Prod 385:135747
Zou J, Ma L, Su Z, Huang D, Li J (2012) Domestic wastewater treatment using sequencing batch biofilm reactor in low temperature. ICBEB 1357–1360
Funding
This work was supported by the Major projects of the National Social Science Fund (21ZDA028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weinan Zhang: investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, conceptualization, methodology.
Ke Bei: validation, investigation, data curation.
Zhan Jin: validation, investigation, data curation.
Min Zhao: supervision, project administration.
Suqing Wu: data curation, methodology.
Shunfeng Jiang: writing—original draft, conceptualization, methodology.
Huachang Jin: validation, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft.
Xiangyong Zheng: validation, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Subtle magnesium liberation filler was applied in SBBR system for urine treating.
• SBBR system with the SFA showed excellent phosphorus removal performance.
• Dittmarite and struvite were formed by gradually released magnesium.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Bei, K., Jin, Z. et al. Subtle magnesium liberation of self-fabricated functional filler actuates highly efficient phosphorus removal from source-separated urine by SBBR. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 24360–24374 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32727-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32727-x