Abstract
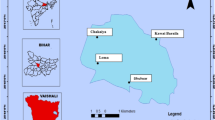
Urban rivers are significantly impacted by anthropogenic pressure. This study presents the updated assessment of the concentrations of 11 metals and other variables (pH, total organic carbon (TOC) and nutrients (total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and total silica)) in the sediments of four urban rivers in inner Hanoi city, Vietnam, during the period 2020–2022. The mean concentrations of Fe, Zn, As, and Cr were higher than the permissible values of the Vietnam National technical regulation on the surface sediment quality. Moreover, Zn and Cr were at the severe effect level of the US EPA guidelines for sediment quality. The calculation of pollution indices (Igeo and EF) demonstrated that Mn, Ni, and Fe were from natural sources whereas other metals were from both anthropogenic and natural sources. The ecological risk index revealed that metals in Hanoi riverine sediments were classified at considerable ecological risk. High values of metals, TOC, and nutrients in the sediments of these urban rivers mostly originate from the accumulation of untreated urban wastewater that is enhanced by low river discharge. Our results may provide scientific base for better management decisions to ensure environmental protection and sustainable development of Hanoi city.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data can be made available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Acharjee A, Ahmed Z, Kumar P, Alam R, Rahman MS, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Assessment of the ecological eisk from heavy metals in the surface sediment of River Surma, Bangladesh: coupled approach of Monte Carlo simulation and multi-component statistical analysis. Water 14:180. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020180
Acosta JA, Gabarron M, Faz A, Martinez-Martinez S, Zornoza R, Arocena JM (2015) Infuence of population density on the concentration and speciation of metals in the soil and street dust from urban areas. Chemosphere 134:328–337
Adenuga AA, Amos OD, Oyekunle JAO, Umukoro EH (2019) Adsorption performance and mechanism of a low-cost biosorbent from spent seedcake of Calophyllum inophyllum in simultaneous cleanup of potentially toxic metals from industrial wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103317
Angela CB, Javier CJ, Teresa GM, Marisa MH (2015) Hydrological evaluation of a peri-urban stream and its impact on ecosystem services potential. Glob Ecol Conserv 3:628–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2015.02.008
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 23rd edn. American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF), Washington, D.C., USA
Ashayeri SY, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Ahmadi A, Hooda PS (2023) Risk assessment, geochemical speciation, and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of an urban river draining into a coastal wetland. Mar Pollut Bull 186:114389
Asokbunyarat V, Sirivithayapakorn S (2020) Heavy metals in sediments and water at the Chao Phraya river mouth. Thailand Thai Environ Eng J 34(3):33–44
Astatkie H, Ambelu A, Mengistie E (2021) Contamination of stream sediment with heavy metals in the Awetu watershed of Southwestern Ethiopia. Front Earth Sci 9:658737
Bhuyan MS, Bakar MA, Rashed-Un-Nabi M, Senapathi V, Chung SY, Islam MS (2019) Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediment of the Old Brahmaputra River. Bangladesh Appl Water Sci 9(5):1–13
Bloesch J (2009) Sediments of aquatic ecosystems encyclopedia of inland waters. Academic Press 479–490 https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012370626-3.00210-6
Cai MT, Ye P, Yang X, Li C (2019) Vegetation and climate change in the Hetao Basin (northern China) during the last interglacial-glacial cycle. J Asian Earth Sci 171:1–8
Cai Y, Mao L, Deng X, Zhou C, Zhang Y (2023) Trace elements in surface sediments from Xinyanggang River of Jiangsu Province, China: spatial distribution, risk assessment and source appointment. Mar Pollut Bull 187:114550
Chakraborty P, Sharma B, Babu PVR, Yao KM, Jaychandran S (2014) Impact of total organic carbon (in sediments) and dissolved organic carbon (in overlying water column) on Hg sequestration by coastal sediments from the central east coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 79(1–2):342–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.11.028
Chen W, Cai Y, Zhu K, Wei J, Lu Y (2022) Spatial heterogeneity analysis and source identification of heavy metals in soil: a case study of Chongqing. Southwest China Chem Biol Technol Agric 9:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-022-00313-3
Chu AD, Pham MC, Nguyen MK (2010) Characteristic of urban wastewater in Hanoi City—nutritive value and potential risk in using for agriculture. VNU J Sci Earth Sci 26:42–47
Dang DN, Carvalho FP, Am NM, Tuan N, Yen NTH, Villeneuve JP, Cattini C (2001) Chlorinated pesticides and PCBs in sediments and molluscs from freshwater canals in the Hanoi region. Environ Pollut 112:311–320
Dang TH (2011) Erosion et transferts de matières en suspension, carbone et métaux dans le bassin versant du fleuve Rouge depuis la fontiere Sino-Vietnamienne jusqu’à l’entrée du delta. (Erosion and transfers of suspended solids, carbon and metals in the Red River watershed from the China‑Vietnam border to the entry of the Delta). PhD thesis. Universite Bordeaux I. p 352
Deng X, Mao L, Wu Y et al (2022) Pollution, risks, and sources of heavy metals in sediments from the urban rivers flowing into Haizhou Bay, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:38054–38065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18151-5
Duong HT, Kadokami K, Pan S, Matsuura N, Nguyen TQ (2014) Screening and analysis of 940 organic micro-pollutants in river sediments in Vietnam using an automated identification and quantification database system for GC–MS. Chemosphere 107:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.064
Edokpayi JN, Odiyo JO, Popoola EO, Msagati TAM (2017) Evaluation of temporary seasonal variation of heavy metals and their potential ecological risk in Nzhelele River. South Africa Open Chem 15(1):272–282. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2017-0033
Garcia-Flores E, Wakida FT, Espinoza-Gomez JH (2013) Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwaterrunoff in Tijuana. Mexico Int J Environ Res 7(2):387–394
Ge Y, Lou Y, Xu M, Wu C, Meng J, Shi L, Xu Y (2021) Spatial distribution and influencing factors on the variation of bacterial communities in an urban river sediment. Environ Pollut 272:115984
Gorme JB, Maniquiz MC, Song P, Kim L-H (2010) The water quality of the Pasig River in the city of Manila, Philippines: current status, management and future recovery. Environ Eng Res 15(3):173–179. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2010.15.3.173
Gu YG, Gao YP, Lin Q (2016) Contamination, bioaccessibility and human health risk of heavy metals in exposed-lawn soils from 28 urban parks in southern China’s largest city. Guangzhou Appl Geochem 67:52–58
Gu X, Lin C, Wang B, Wang J, Ouyang W (2022) A comprehensive assessment of anthropogenic impacts, contamination, and ecological risks of toxic elements in sediments of urban rivers: a case study in Qingdao. East China Adv Environ 7:100143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100143
Gunes G (2022) The change of metal pollution in the water and sediment of the Bartın River in rainy and dry seasons. Environ Eng Res 27(2):200701. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.701
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentological Approach Water Res 14:975–1001
Han L, Chang C, Yan S, Qu C, Tian Y, Guo J, Guo J (2023) Distribution, sources and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from Beiluo River. Toxics 11:139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020139
Hanoi-GSO (2021) General Statistical Official of Hanoi. Statistical Yearbook of Hanoi 2020. p 672. http://thongkehanoi.gov.vn. Accessed 3 Dec 2021
Hanoi-GSO (2022) General Statistical Official of Hanoi. Statistical Yearbook of Hanoi 2021. p 685. http://thongkehanoi.gov.vn. Accessed 3 Dec 2021
Hoang AQ, Takahashi S, Le ND, Duong TT, Pham TMH, Pham TNM, Nguyen TAH, Tran TM, Tu MB, Le TPQ (2021a) Comprehensive determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and brominated flame retardants in surface sediment samples from Hanoi urban area, Vietnam: contamination status, accumulation profiles, and potential ecological risks. Environ Res 197:111158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111158
Hoang AQ, Takahashi S, Le ND, Hoang TTH, Duong TT, Pham TMH, Nguyen TD, Phung TXB, Nguyen TAH, Le HT, Nguyen MT, Tu MB, Nguyen YTH, Nguyen TML, Phung VP, Le TPQ (2021b) Unsubstituted and methylated PAHs in surface sediment of urban rivers in the Red River Delta (Hanoi, Vietnam): concentrations, profiles, sources, and ecological risk assessment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107:475–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03174-y
Holm PE, Rootze NH, Borggaard OK, Møberg JP, Christensen TH (2003) Correlation of cadmium distribution coefficients to soil characteristics. J Environ Qual 32:138–145
Ingvertsen ST, Marcussen H, Holm PE (2013) Pollution and potential mobility of Cd, Ni and Pb in the sediments of a wastewater-receiving river in Hanoi. Vietnam Environ Monit Assess 185:9531–9548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3271-7
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah–Al-Mamun M, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Indic 48:282–291
Islam MS, Hossain MB, Matin A, Islam Sarker MS (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and source apportionment in the sediment from Feni River estuary, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 202:25–32
Islam Md.S, Shammi RS, Jannat R, Kabir MdH, Islam Md.S (2022). Spatial distribution and ecological risk of heavy metal in surface sediment of Old Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh. Chem Ecol 39(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2022.2152015
Khan R, Islam MS, Tareq ARM et al (2020) Distribution, sources and ecological risk of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from a polluted urban river in central Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100318
Kobayashi Y, Ogata F, Nakamura T, Kawasaki N (2020) Synthesis of novel zeolites produced from fly ash by hydrothermal treatment in alkaline solution and its evaluation as an adsorbent for heavy metal removal. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103687
Koppel DJ, Price GAV, Brown KE, Adams MS, King CK, Gore DB et al (2021) Assessing metal contaminants in Antarctic soils using difusive gradients in thin-flms. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128675
Lawati WMA, Rizoulis A, Eiche E, Boothman C, Poly DA, Lloyd JR, Berg M, Aguilar PV, van Dongen BA (2012) Characterization of organic matter and microbial communities in contrasting arsenic-rich Holocene and arsenic-poor Pleistocene aquifers, Red River Delta. Vietnam Appl Geochemistry 27:315–325
Le TPQ, Le ND, Hoang TTH, Rochelle-Newall E, Nguyen TAH, Dinh LM, Duong TT, Pham TMH, Nguyen TD, Phung TXB, Nguyen TQT, Vu TH, Le PT, Phung VP (2022) Surface sediment quality of the Red River (Vietnam): impacted by anthropogenic and natural factors. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19:12477–12496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03936-z
Li H, Shi A, Li M, Zhang X (2013) Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and fow rate of overlying water on heavy metals rlease from storm sewer sediments. J Chem 434012:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/434012
Li L, Jiang M, Liu Y, Shen X (2019) Heavy metals inter-annual variability and distribution in the Yangtze River estuary sediment. China Mar Pollut Bull 141:514–520
Liang MJ, Xiong F, Zeng JW, Yu WD, Zhang YL, Zhou SJ (2021) Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of farmland soil around three types of industrial enterprises in Guangzhou Suburb. Guangdong Agric Sci 48:103–110
Liao J, Cui X, Feng H, Yan S (2022) Environmental background values and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in watershed sediments: a comparison of assessment methods. Water 14:51. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010051
Liu R, Wang M, Chen W, Peng C (2016) Spatial pattern of heavy metals accumulation risk in urban soils of Beijing and its influencing factors. Environ Pollut 210:174–181
Lohani MB, Singh A, Rupainwar DC et al (2008) Seasonal variations of heavy metal contamination in river Gomti of Lucknow city region. Environ Monit Assess 147:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0117-1
Luu ML, Pham TTH, Nguyen TH, Nguyen LA, Duong MN, Hoang TTT, Vu VT (2022) Initial study of the pollution load assessment from domestic wastewater and the application of microorganic products for treatment of organic matter in To Lich River. TNU J Sci Technol 227(08):182–190. https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.5584
Manno E, Varrica D, Dongarrà G (2006) Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela. Sicily Atmos Environ 40:5929–5941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.020
Marcussen H, Dalsgaard A, Holm PE (2008) Content, distribution and fate of 33 elements in sediments of rivers receiving wastewater in Hanoi. Vietnam Environ Pollut 155:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.001
Martin J-M, Meybeck M (1979) Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar Chem 7:173–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(79)90039-2
Mcgrane SJ (2016) Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: a review. Hydrol Sci J 61(13):2295–2311. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2015.1128084
MONRE (Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resource and Environment) (2017) National technical regulation on sediment quality QCVN 43:2017/BTNMT. http://vea.gov.vn. Accessed 03 June 2020
MONRE (Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment) (2019) Report on the state of the national environment in 2018: water environment in river basins. Issued by Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment dated on 31 Jul 2019. p 158. Available at http://dwrm.gov.vn/uploads/download/files/ bao-caohtmt-quoc-gia-2018-moi-truong-nuoc-cac-lvs_signed.pdf
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J 2:108–118
Nasiruddin M, Islam ARMT, Siddique MAB et al (2023) Distribution, sources, and pollution levels of toxic metal(loid)s in an urban river (Ichamati), Bangladesh using SOM and PMF modeling with GIS tool. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:20934–20958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23617-1
Nguyen HD, Nguyen VN (2021) Analysis study of current transportation status in Vietnam’s urban traffic and the transition to electric two-wheelers mobility. Sustain 13:5577. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105577
Nguyen TLH, Ohtsubo M, Loretta LY, Higashi T (2007a) Heavy metal pollution of the To-Lich and Kim-Nguu Rivers in Hanoi City and the industrial source of the pollutants. J Agric Fac Kyushu Univ 52(1):141–146
Nguyen TLH, Otsubo M, Li L, Higashi T (2007b) Mobility of heavy metals in the sediment of the To Lich River and the Kim Nguu River in Hanoi City. J Agric Fac Kyushu Univ 52:179–185. https://doi.org/10.5109/9303
Nguyen DD, Telichenko VI, Slesarev MYu (2018) Sources and causes of surface water pollution in Hanoi (Vietnam). Vestnik MGSU. Proceedings Moscow State Univ Civil Eng 13(10):1234–1242. https://doi.org/10.22227/1997-0935.2018.10.1234-1242
Nguyen TM, Lin TH, Chan HP (2019) The environmental effects of urban development in Hanoi, Vietnam from satellite and meteorological observations from 1999–2016. Sustainability 11:1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061768
Nguyen BT, Do DD, Nguyen XT, Nguyen VN, Nguyen DTP, Nguyen MH, Truong TTH, Dong HP, Le AH, Bach VQ (2020) Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River. Vietnam Environ Pollut 256:113412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113412
Nguyen TT (2013) Heavy metal contamination in water and sediment of To Lich River in inner city Hanoi. Kyoto University, Doctor of Engineering. 107 pages. Avalaible at: https://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/2433/180494/2/dkogk03790.pdf
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) (1999) Screening quick reference tables (SquiRTs). http://response.restoration.noaa.gov/cpr/sediment/squirt/squirt.html. Accessed 23 Feb 2019
Pan Y, Xie J, Yan W, Zhang TC, Chen C (2022) Response of microbial community to different land-use types, nutrients and heavy metals in urban river sediment. J Environ Manage 321:115855
Pandey M, Tripathi S, Pandey AK, Tripathi BD (2014) Risk assessment of metal species in sediments of the river Ganga. CATENA 122:140–149
Paul V, Sankar MS, Vattikuti S, Dash P, Arslan Z (2021) Pollution assessment and land use land cover influence on trace metal distribution in sediments from five aquatic systems in southern USA. Chemosphere 263:128243
Pham MH, Ngoc NT, Minh NH, Viet PH, Berg M, Alder AC, Giger W (2010) Recent levels of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the sewer system in Hanoi. Vietnam Environ Pollut 158:913–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.09.018
Pham HC (2017) Report on the result of collection and compilation of 10 suti index in Hanoi city. The economic and social commission for Asia and the Pacific. United Nation – ESCAPE (Economic and Social Commision for Asia and the Pacific). Hanoi, November 2017. p 53. Avalaible at: ESCAP-2017-PB-SUTI-mobility-assessmentreport-Hanoi.pdf
Ramesh R, Al R, Ramesh S, Purvaja R, Subramanian V (2000) Distribution of rare earth elements and heavy metals in the surficial sediments of the Himalayan river system. Geochem J 34:295–319
Reza R, Singh G (2010) Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. Int J Environ Sci Tech 7(4):785–792
Rong S, Wu J, Liu J, Li Q, Ren C, Cao X (2023) Environmental magnetic characteristics and heavy metal pollution assessment of sediments in the Le’an River. China Minerals 13:145. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020145
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland HD, Turekian KK (eds) Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043751-6/03016-4
Ruiz F, Borrego J, López-González N et al (2007) The geological record of a mid-Holocene marine storm in southwestern Spain. Geobios 40:689–699
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:11251131
Singh H, Pandey R, Singh SK, Shukla DN (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediment of the River Ghaghara, a major tributary of the River Ganga in Northern India. Appl Water Sci 7:4133–4149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0572-y
Strady E, Dang VBH, Némery J et al (2017) Baseline seasonal investigation of nutrients and trace metals in surface waters and sediments along the Saigon River basin impacted by the megacity of Ho Chi Minh (Vietnam). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3226–3243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7660-7
Sulistyowati L, Nurhasanah N, Riani E, Cordova MR (2023) Heavy metals concentration in the sediment of the aquatic environment caused by the leachate discharge from a landfill. Global J Environ Sci Manage 9(2):323–336
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241. https://doi.org/10.1029/95RG00262
Taylor KG, Owens PN (2009) Sediments in urban river basins: a review of sediment-contaminant dynamics in an environmental system conditioned by human activities. J Soils Sediments 9(4):281–303
Thuong NT, Yoneda M, Ikegami M et al (2013a) Source discrimination of heavy metals in sediment and water of To Lich River in Hanoi City using multivariate statistical approaches. Environ Monit Assess 185:8065–8075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3155-x
Thuong NT, Yoneda M, Matsui Y (2013) Does embankment improve quality of a river? A case study in To Lich River inner city Hanoi, with special reference to heavy metals. J Environ Prot 4(4):30711, 10. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2013.44043
Tran DH (2018) Analysis and evaluation of heavy metal contents in sediment of To Lich River and West Lake to propose suitable management solutions. Vietnam Magazine Enviroment 1:49–55 (in Vietnamese)
Trinh AD, Meysman F, Rochelle-Newall E, Bonnet MP (2012) Quantification of sediment-water interactions in a polluted tropical river through biogeochemical modeling. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 26:2010GB003963
Turner A, Millward GE (2002) Suspended particles: their role in estuarine biogeochemical cycles. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:857–883. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2002.1033
US EPA (2000). United States Geological Survey (USGS) final report for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), Great Lakes National Program Office (GLNPO). In: Ingersoll CG, MacDonald DD, Wang N, Crane JL, Field LJ, Haverland PS, Kemble NE, Lindskoog RA, Severn C, Smorong DE (eds) Prediction of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwater sediment quality guidelines EPA 905/R-00/007. p 33. Avalaible at: https://archive.epa.gov/reg5sfun/ecology/web/pdf/91126.pdf
Venkatesh M, Anshumali (2020) Appraisal of the carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio in the bed sediment of the Betwa River, Peninsular India. Int J Sedim Res 35:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.07.003
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang W, Yao X, Wang B, Wang Z (2022) Spatiotemporal changes of eutrophication and heavy metal pollution in the inflow river system of Baiyangdian after the establishment of Xiongan New Area. Peer J 10:e13400. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13400
Wang M, Zhang W, Dong Z, Yang Z, Zhao J, Guo X (2023) Distinct mediating patterns between metal filtering and species coexistence of rare and abundant subcommunities in heavily polluted river sediments. Environ Int 172:107747
Wei J, Duan M, Li Y, Nwankwegu AS, Ji Y, Zhang J (2019) Concentration and pollution assessment of heavy metals within surface sediments of the Raohe Basin. China Sci Rep 9:13100. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49724-7
Wen KL, Lin CM, Kuo CH, Phuong NH, Hung NT (2013) Microzonation study in the Hanoi, Vietnam. Presentation at the 10th International Workshop of Seismic Microzoning and Risk Reduction September 25, 2013, Tokyo, Japan. Avalaible at: chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://iisee.kenken.go.jp/symposium/10thIWSMRR/11.pdf
Wenye L, Wenqiang Z, Baoqing S, Baoping S, Xiaoping G, Zhenhan L (2022) Risk assessment of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a typical urban river. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:46649–54666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18966-w
Wijesiri B, Liu A, Deilami K, He B, Hong N, Yang B, Zhao X, Ayoko G, Goonetilleke A (2019) Nutrients and metals interactions between water and sediment phases: an urban river case study. Environ Pollut 251:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.018
Wu D, Liu H, Wu J, Gao X (2022) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals pollution in urban lake sediments of Huaihe River basin. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:14653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214653
Xia F, Zhang C, Qu L, Song Q, Ji X, Mei K, Zhang M (2020) A comprehensive analysis and source apportionment of metals in riverine sediments of a rural-urban watershed. J Hazard Mater 381:121230
Xiao Q, Zong Y, Malik Z, Lu S (2019) Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning. Northeast China Hum Ecol Risk Assess 26(5):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1578946
Xie Y, Huo X, Hu C, Tao Y (2023) Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in the surface sediments in the Hailar River, the upper source of the Erguna River between China and Russia. Sustainability 15:3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043655
Xingyuan Z, Fawen L, Yong Z (2010) Impact of changes in river network structure on hydrological connectivity of watersheds. Ecol Indic 146:109848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109848
XLSTAT Addinsoft (2019) XLSTAT Statistical and Data Analysis Solution. Addinsoft, Boston, MA, USA
Yang L, Cheng S, Wang X, Nie X, Xu P, Gao X, Yuan C, Wang W (2013) Source identification and health impact of PM2.5 in a heavily polluted urban atmosphere in China. Atmos Environ 75:265–269
Yuan X, Zhang L, Li J, Wang C, Ji J (2014) Sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the river, estuary and lake environments of a fluvial plain, China. CATENA 119:52–60
Zhang C, Yu Z, Zeng G, Jiang M, Yang Z, Cui F, Zhu M, Shen L, Hu L (2014) Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ Int 73:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.08.010
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Bi Z, Yu Y, Shi P, Ren L, Shan Z (2020) The impact of land use changes and erosion process on heavy metal distribution in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau. China Sci Total Environ 718:137305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137305
Zhang L, Tan X, Chen H, Liu Y, Cui Z (2022) Effects of agriculture and animal husbandry on heavy metal contamination in the aquatic environment and human health in Huangshui River basin. Water 14:549. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040549
Zhao Y, Yang Y, Dai R, Leszek S, Wang X, Xiao L (2021) Adsorption and migration of heavy metals between sediments and overlying water in the Xinhe River in central China. Water Sci Technol 84(5):1257–1269. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.314
Zuchiewicz W, Nguyen QC, Jerzy Z, Nguyen TY (2013) Late Cenozoic tectonics of the Red River Fault Zone, Vietnam, in the light of geomorphic studies. J Geodyn 69:11
Funding
The study was funded by the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST) (for the project no. NCXS02.02/23–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Phung TXB, Le TPQ, Le ND, Hoang TTH, Nguyen TMH, Rochelle-Newall E, Nguyen TAH, Duong TT, Pham TMH, and Nguyen TD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Phung TXB and Le TPQ. All authors commented on previous manuscript versions and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have given consent for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Updated observations (2020–2022) on metal concentrations in river sediments in inner Hanoi city, Vietnam were reported.
• Fe, Zn, As, and Cr concentrations were higher than the permissible values of the Vietnam technical regulation.
• Igeo and EF values revealed that Mn, Ni, and Fe were from natural sources whereas other metals were from both anthropogenic and natural sources.
• RI values demonstrated the considerable ecological risk for Hanoi riverine sediment.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Phung, T.X.B., Le, T.P.Q., Da Le, N. et al. Metal contamination, their ecological risk, and relationship with other variables in surface sediments of urban rivers in a big city in Asia: case study of Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 22362–22379 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32549-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32549-x