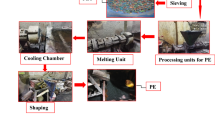
Abstract
While several research studies considered the utilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) aggregates for asphalt and concrete pavements, very few attempted its possible utilization for precast concrete applications like concrete paver blocks (CPBs). Moreover, few attempts made in the recent past to improve the strength properties of RAP inclusive concrete mixes by incorporating certain supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) have reported an insignificant or marginal effect. The present study attempts to comprehensively investigate the utilization potential of some locally and abundantly available materials having suitable physicochemical properties to improve the performance of a zero-slump CPB mix containing 50% RAP aggregates. The studied filler materials, namely, wollastonite (naturally occurring calcium metasilicate mineral) and jarosite (hazardous zinc industry waste), were used to replace 5–15% and 10–20% by volume of Portland cement in the 50% RAP CPB mix. Apart from their individual effects, the efficacy of wollastonite-jarosite blends was also investigated. Considering the lack of indoor storage facilities and economic aspects of CPBs, the influence of water spray curing regime on the performance of the RAP CPB mixes was studied and compared to that of continuous water curing regime. Inclusion of the considered fillers was found to statistically and significantly enhance the flexural strength, tensile splitting strength, and abrasion resistance of the 50% RAP CPB mix; however, the compressive strength (in most cases), permeable voids, water absorption, and water permeability properties showed an insignificant improvement. Results of thermogravimetric analysis confirmed the occurrence of pozzolanic reactivity, and microstructure analysis revealed improvements in packing of concrete matrix and ITZ with filler inclusion qualitatively substantiating the improvements in strength and durability characteristics. The toxicity characteristics of heavy metals that may leach from the hazardous jarosite-based RAP CPB mixes were found to be within permissible limits. Based on the performance requirements specified by IS, IRC, and ASTM standards, all the RAP CPB mixes with filler inclusions fulfilled the acceptance criteria for heavy traffic applications, and water spray curing can enact as an alternate method for curing these mixes. However, to avail maximum performance benefits, it is recommended to use 5% wollastonite, 15% jarosite, and a combination of 10% wollastonite and 10% jarosite as a Portland cement substitute to produce sustainable eco-friendly RAP CPB mixes.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelbary A, Mohamed AR (2018) Investigating abrasion resistance of interlocking blocks incorporating steel slag aggregate. ACI Mater J 115(1):47–54
Abraham SM, Ransinchung GD (2019) Effects of reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates and mineral admixtures on pore structure, mechanical and durability properties of cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 216:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.011
Alarcon-Ruiz L, Platret G, Massieu E, Ehrlacher A (2005) The use of thermal analysis in assessing the effect of temperature on a cement paste. Cem Concr Res 35(3):609–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.06.015
Arulrajah A, Piratheepan J, Disfani MM (2014) Reclaimed asphalt pavement and recycled concrete aggregate blends in pavement subbases: laboratory and field evaluation. J Mater Civ Eng 26(2):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000850
Asokan P, Saxena M, Asolekar SR (2006) Hazardous jarosite use in developing non-hazardous product for engineering application. J Hazard Mater 137(3):1589–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.04.054
Asphalt Pavement Alliance (2010) Carbon footprint: how does asphalt stack up. http://www.onasphalt.org/files/factsheets/Carbon%20Footprint_How%20Does%20Asphalt%20Stack%20Up.pdf. Accessed 10 August 2022
Asselanis JG, Aitcin PC, Mehta PK (1989) Effect of curing conditions on the compressive strength and elastic modulus of very high-strength concrete. J Cem Concr Aggregates 11(1):80–83
ASTM C1585 – 13 (2013b) Standard test method for measurement of rate of absorption of water by hydraulic cement concretes. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM C267 – 01 (2012c) Standard test methods for chemical resistance of mortars, grouts, and monolithic surfacings and polymer concretes. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM C642 – 13 (2013a) Standard test method for density, absorption, and voids in hardened concrete. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM C779/C779M – 12 (2012b) Standard test methods for abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete surfaces. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM C936/C936M – 16 (2016) Standard specification for solid concrete interlocking paving units. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM D1557 – 12 (2012a) Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using modified effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft3 (2,700 kN-m/m3)). ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM D2172/D2172M – 17 (2017) Standard test methods for quantitative extraction of asphalt binder from asphalt mixtures. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
Berry M, Kappes B, Kappes L (2015) Optimization of concrete mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. ACI Mater J 112(6):723–734
Brand AS, Roesler JR (2015) Ternary concrete with fractionated reclaimed asphalt pavement. ACI Mater J 112(1):155–164
Brand AS, Roesler JR (2016) Expansive and concrete properties of SFS–FRAP aggregates. J Mater Civ Eng 28(2):04015126. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001403
Brand AS, Roesler JR (2017a) Bonding in cementitious materials with asphalt-coated particles: Part I-The interfacial transition zone. Constr Build Mater 130:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.019
Brand AS, Roesler JR (2017b) Bonding in cementitious materials with asphalt-coated particles: part II–cement-asphalt chemical interactions. Constr Build Mater 130:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.013
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 15658 (2006) Precast concrete blocks for paving – specification. BIS, New Delhi, India
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 2386 (Part III) (2002a) Methods of test for aggregates for concrete – specific gravity, density, voids, absorption and bulking. BIS, New Delhi, India
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 3085 (2002b) Method of test for permeability of cement mortar and concrete. BIS, New Delhi, India
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 383 (1997) Specification for coarse and fine aggregates from natural sources for concrete. BIS, New Delhi, India
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 8112 (2013) Ordinary Portland cement, 43 grade – specification. BIS, New Delhi, India
Chandra S, Choudhary R (2013) Performance characteristics of bituminous concrete with industrial wastes as filler. J Mater Civ Eng 25(11):1666–1673. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000730
Cocke DL (1990) The binding chemistry and leaching mechanisms of hazardous substances in cementitious solidification/stabilization systems. J Hazard Mater 24(2–3):231–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3894(90)87013-8
Copeland A (2011) Reclaimed asphalt pavement in asphalt mixtures: state of the practice. Rep. No. FHWA-HRT-11–021. Washington, DC: Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center, Federal Highway Administration. https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/publications/research/infrastructure/pavements/11021/11021.pdf. Accessed 10 August 2022
De Lira RR, Cortes DD, Pasten C (2015) Reclaimed asphalt binder aging and its implications in the management of RAP stockpiles. Constr Build Mater 101:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.125
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD (2021) Effect of natrojarosite as replacement to Portland cement in roller-compacted concrete pavement mixtures. ACI Mater J 118(1):1–12
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD, Singh S (2019) Feasibility of roller compacted concrete pavement containing different fractions of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr Build Mater 199:508–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.047
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD, Singh S, Sahdeo SK (2020a) Utilization of industrial and agricultural wastes for productions of sustainable roller compacted concrete pavement mixes containing reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. Resour Conserv Recycl 152:104504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104504
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD, Singh S (2020b) Improving the properties of RAP-RCCP mixes by incorporating supplementary cementitious materials as part addition of portland cement. J Mater Civ Eng 32(8):04020229. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003283
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD, Singh S (2020c) Zinc waste as a substitute for portland cement in roller-compacted concrete pavement mixes containing RAP aggregates. J Mater Civ Eng 32(8):04020207. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003278
Debbarma S, Ransinchung GD, Singh S (2021) Suitability of various supplementary cementitious admixtures for RAP inclusive RCCP mixes. Int J Pavement Eng 22(12):1568–1581. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2019.1703981
Demidenko NI, Podzorova LI, Rozanova VS, Skorokhodov VA, Shevchenko VY (2001) Wollastonite as a new kind of natural material (a review). Glass Ceram 58(9):308–311. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013931009149
Dey V, Kachala R, Bonakdar A, Mobasher B (2015) Mechanical properties of micro and sub-micron wollastonite fibers in cementitious composites. Constr Build Mater 82:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.02.084
Dubey P, Paswan S, Sukhija M, Saboo N (2020) Assessing the effect of reclaimed asphalt pavement on mechanical properties of dry-lean concrete. J Mater Civ Eng 32(11):04020348. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003434
El Euch Ben Said S, El Euch Khay S, Loulizi A (2018) Experimental investigation of PCC incorporating RAP. Int J Concr Struct Mater 12(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40069-018-0227-x
Erdem S, Blankson MA (2014) Environmental performance and mechanical analysis of concrete containing recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) and waste precast concrete as aggregate. J Hazard Mater 264:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.040
Gencel O, Ozel C, Koksal F, Erdogmus E, Martínez-Barrera G, Brostow W (2012) Properties of concrete paving blocks made with waste marble. J Cleaner Prod 21(1):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.08.023
Ghabchi R, Singh D, Zaman M (2014) Evaluation of moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixes containing RAP and different types of aggregates and asphalt binders using the surface free energy method. Constr Build Mater 73:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.042
Ghafoori N, Mathis R (1997a) Sulfate resistance of concrete pavers. J Mater Civ Eng 9(1):35–40. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(1997)9:1(35)
Ghafoori N, Mathis R (1997b) A comparison of freezing and thawing durability of non-air entrained concrete pavers under ASTM C 67 and ASTM C 666. ACI Mater J 94(4):311–331
Ghafoori N, Sukandar BM (1995) Abrasion resistance of concrete block pavers. ACI Mater J 92(1):25–36
Gupta T, Sachdeva SN (2019) Investigations on jarosite mixed cement concrete pavements. Arab J Sci Eng 44(10):8787–8797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03801-1
Huang B, Shu X, Li G (2005) Laboratory investigation of portland cement concrete containing recycled asphalt pavements. Cem Concr Res 35(10):2008–2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.05.002
Indian Bureau of Mines (2018) Indian minerals yearbook 2016. Ministry of Mines, Government of India
Indian Roads Congress (IRC), IRC SP 63 (2018) Guidelines for the use of interlocking concrete block pavement. IRC, New Delhi, India
British Standards Institution (BSI), BS EN 1338 (2003) Concrete paving blocks – requirements and test methods. BSI, London, UK
Kalla P, Misra A, Gupta RC, Csetenyi L, Gahlot V, Arora A (2013) Mechanical and durability studies on concrete containing wollastonite–fly ash combination. Constr Build Mater 40:1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.102
Kalla P, Rana A, Chad YB, Misra A, Csetenyi L (2015) Durability studies on concrete containing wollastonite. J Cleaner Prod 87:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.038
Khan RI, Ashraf W (2019) Effects of ground wollastonite on cement hydration kinetics and strength development. Constr Build Mater 218:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.061
Low NM, Beaudoin JJ (1992) Mechanical properties of high performance cement binders reinforced with wollastonite micro-fibres. Cem Concr Res 22(5):981–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(92)90122-C
Low NM, Beaudoin JJ (1994) The flexural toughness and ductility of portland cement-based binders reinforced with wollastonite micro-fibres. Cem Concr Res 24(2):250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(94)90050-7
Maddalena R, Roberts JJ, Hamilton A (2018) Can Portland cement be replaced by low-carbon alternative materials? A study on the thermal properties and carbon emissions of innovative cements. J Cleaner Prod 186:933–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.138
Martys NS, Ferraris CF (1997) Capillary transport in mortars and concrete. Cem Concr Res 27(5):747–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(97)00052-5
Mathur R, Misra AK, Goel P (2007) Influence of wollastonite on mechanical properties of concrete. J Sci Ind Res 66:1029–1034
Mehra P, Gupta RC, Thomas BS (2016a) Properties of concrete containing jarosite as a partial substitute for fine aggregate. J Cleaner Prod 120:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.015
Mehra P, Gupta RC, Thomas BS (2016b) Assessment of durability characteristics of cement concrete containing jarosite. J Cleaner Prod 119:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.055
Modarres A, Hosseini Z (2014) Mechanical properties of roller compacted concrete containing rice husk ash with original and recycled asphalt pavement material. Mater Des 64:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.07.072
MoEF (2008) Hazardous wastes (management, handling and transboundary movement) rules. Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi, India
MoEF (2010) India: greenhouse gas emissions 2007. Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi, India
Monu K, Ransinchung GD, Singh S (2019) Effect of long-term ageing on properties of RAP inclusive WMA mixes. Constr Build Mater 206:483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.087
Nandi S, Ransinchung GDRN (2021) Performance evaluation and sustainability assessment of precast concrete paver blocks containing coarse and fine RAP fractions: a comprehensive comparative study. Constr Build Mater 300:124042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124042
Nandi S, Ransinchung GDRN (2022) Laboratory investigation of Portland cement concrete paver blocks made with reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. Road Mater Pavement Des 23(3):546–564. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2020.1830153
Nandi S, Ransinchung GD, Rana GB (2022) A sustainable approach towards reducing cement consumption in the road sector using zinc industry waste. Int J Pavement Res Technol 15(6):1463–1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-021-00101-6
NTC 2017 (2004) Concrete paving blocks. NTC, Colombian Institute for Technical Standards and Certification (ICONTEC), Colombian Technical Standard, Bogotá, Columbia
Pappu A, Saxena M, Asolekar SR (2006) Jarosite characteristics and its utilisation potentials. Sci Total Environ 359(1–3):232–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.024
Ransinchung GD, Kumar B (2010) Investigations on pastes and mortars of ordinary portland cement admixed with wollastonite and microsilica. J Mater Civ Eng 22(4):305
Ransinchung GD, Kumar B, Kumar V (2009) Assessment of water absorption and chloride ion penetration of pavement quality concrete admixed with wollastonite and microsilica. Constr Build Mater 23(2):1168–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.06.011
Ray S, Daudi L, Yadav H, Ransinchung GD (2020) Utilization of jarosite waste for the development of sustainable concrete by reducing the cement content. J Cleaner Prod 272:122546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122546
Romero M, Rincón JM (1997) Microstructural characterization of a goethite waste from zinc hydrometallurgical process. Mater Lett 31(1–2):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(96)00235-2
Sahdeo SK, Ransinchung GD, Rahul KL, Debbarma S (2021) Reclaimed asphalt pavement as a substitution to natural coarse aggregate for the production of sustainable pervious concrete pavement mixes. J Mater Civ Eng 33(2):04020469. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003555
Sahdeo SK, Ransinchung GD, Nandi S (2023) Investigating the suitability of agricultural and industrial wastes for production of RAP inclusive pervious concrete pavement mixes: a sustainable approach. Int J Pavement Res Technol 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-023-00303-0
Settari C, Debieb F, Kadri EH, Boukendakdji O (2015) Assessing the effects of recycled asphalt pavement materials on the performance of roller compacted concrete. Constr Build Mater 101:617–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.039
Shi X, Mukhopadhyay A, Liu KW (2017) Mix design formulation and evaluation of portland cement concrete paving mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr Build Mater 152:756–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.174
Shi X, Mukhopadhyay A, Zollinger D (2018) Sustainability assessment for portland cement concrete pavement containing reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. J Cleaner Prod 192:569–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.004
Shi X, Grasley Z, Hogancamp J, Brescia-Norambuena L, Mukhopadhyay A, Zollinger D (2020) Microstructural, mechanical, and shrinkage characteristics of cement mortar containing fine reclaimed asphalt pavement. J Mater Civ Eng 32(4):04020050. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003110
Singh S, Ransinchung GD, Debbarma S, Kumar P (2018a) Utilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates containing waste from Sugarcane Mill Constr Build Mater for production of concrete mixes. J Cleaner Prod 174:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.179
Singh S, Ransinchung GD, Monu K, Kumar P (2018b) Laboratory investigation of RAP aggregates for dry lean concrete mixes. Constr Build Mater 166:808–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.131
Singh S, Shintre D, Ransinchung GD, Kumar P (2018c) Performance of fine RAP concrete containing flyash, silica fume, and bagasse ash. J Mater Civ Eng 30(10):04018233. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002408
Singh S, Ransinchung GD, Kumar P (2019a) Feasibility study of RAP aggregates in cement concrete pavements. Road Mater Pavement Des 20(1):151–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2017.1380071
Singh S, Ransinchung GD, Monu K (2019b) Sustainable lean concrete mixes containing wastes originating from roads and industries. Constr Build Mater 209:619–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.122
Singh S, Ransinchung GD, Kumar P (2017) Effect of mineral admixtures on fresh, mechanical and durability properties of RAP inclusive concrete. 156:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.144
Smith DR (1987) Mechanized installation of concrete block paving. Concr Int 9(7):37–40
Soliman AM, Nehdi ML (2012) Effect of natural wollastonite microfibers on early-age behavior of UHPC. J Mater Civ Eng 24(7):816–824. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000473
Soutsos MN, Tang K, Millard SG (2011) Use of recycled demolition aggregate in precast products, phase II: concrete paving blocks. Constr Build Mater 25(7):3131–3143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.12.024
Tan K, Gjorv OE (1996) Performance of concrete under different curing conditions. Cem Concr Res 26(3):355–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(96)85023-X
USEPA (1992) Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Method 1311, United States Environmental Protection Agency, USA
Wang D, Cannone Falchetto A, Moon KH, Riccardi C, Pei J, Wen Y (2019) Artificially prepared Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP)—an experimental investigation on re-recycling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:35620–35628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05970-w
Yoshitake I, Komure H, Nassif AY, Fukumoto S (2013) Tensile properties of high volume fly-ash (HVFA) concrete with limestone aggregate. Constr Build Mater 49:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.08.020
Zareei SA, Ameri F, Shoaei P, Bahrami N (2019) Recycled ceramic waste high strength concrete containing wollastonite particles and micro-silica: a comprehensive experimental study. Constr Build Mater 201:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.161
Zaumanis M, Mallick RB, Frank R (2013) Evaluation of rejuvenator’s effectiveness with conventional mix testing for 100% reclaimed Asphalt pavement mixtures. Transp Res Rec 2370(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.3141/2F2370-03
Zhang Z, Olek J, Diamond S (2002) Studies on delayed ettringite formation in heat-cured mortars: II. Characteristics of cement that may be susceptible to DEF. Cem Concr Res 32(11):1737–1742. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)00894-3
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Wolkem India Limited and Hindustan Zinc Limited located in Sirohi and Udaipur districts of Rajasthan, India, for providing wollastonite and jarosite material, respectively, to execute this laboratory study. Graduate student Mr. Jyotiraditya Garg, from Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, is gratefully acknowledged for assisting the authors in some of the experimental works presented in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sumit Nandi: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; Gondaimei Ransinchung Rongmei Naga: supervision, resources, writing—review and editing; Surya Kant Sahdeo: investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authors remained loyal to ethical rules during the data collection process.
Consent to participate
All authors have consented to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented to the publication of this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: José Dinis Silvestre
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nandi, S., Naga, G.R.R. & Sahdeo, S.K. Utilization of wollastonite, jarosite, and their blends for the sustainable development of concrete paver block mixes containing reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 20048–20072 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32338-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32338-6