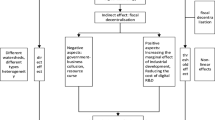
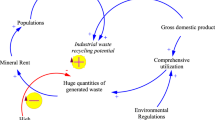
Abstract
The digital economy is playing a crucial effect in the field of environmental governance. Digital and intelligent management is an essential means to fully realize the “zero-waste city” construction. The present paper investigates the impact of digital economy on China’s provincial “zero-waste city” construction. The results indicate that digital economy can contribute to “zero-waste city” construction. The digital economy has a positive nonlinear effect on the construction of “zero-waste city,” but the marginal effect is diminishing. The digital economy can facilitate “zero-waste city” construction by improving industrial structure upgrading and green technology innovation. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that digital economy contributes to the construction of “zero-waste city” in the eastern and western regions and high-level environmental regulation regions, while this impact is insignificant in the central region and low-level environmental regulation regions. The digital economy exerts the most significant positive influence on waste resource recycling followed by waste final disposal and then waste reduction at the source. These findings underscore the effect of digital economy in fostering “zero-waste city” construction and promoting sustainable waste management. The present study provides new ideas for the “zero-waste city” construction in emerging developing countries such as China.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad RW, Salah K, Jayaraman R, Yaqoob I, Omar M (2021) Blockchain for waste management in smart cities: a survey. IEEE Access 9:131520–131541. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3113380
Aslam MS, Huang B, Cui L (2020) Review of construction and demolition waste management in China and USA. J Environ Manage 264:110445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110445
Bai L, Chen XH (2020) How does digital economy affect industrial SO2 emission? Theoretical interpretation and empirical test. J Dongbei Univ Finan Econ 73–81. https://doi.org/10.19653/j.cnki.dbcjdxxb.2020.05.008 (In Chinese)
Bai R, Lin B (2022) Are residents willing to pay for garbage recycling: evidence from a survey in Chinese first-tier cities. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:106789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106789
Borchard R, Zeiss R, Recker J (2022) Digitalization of waste management: insights from German private and public waste management firms. Waste Manage Res 40:775–792. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X211029173
Castigliego JR, Pollack A, Cleveland CJ, Walsh MJ (2021) Evaluating emissions reductions from zero waste strategies under dynamic conditions: a case study from Boston. Waste Manage 126:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.026
Castiglione A, Cimmino L, Di Nardo M, Murino T (2023) A framework for achieving a circular economy using the blockchain technology in a sustainable waste management system. Comput Ind Eng 180:109263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109263
Che S, Wang J (2022) Digital economy development and haze pollution: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:73210–73226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20957-w
Chen P (2022) Is the digital economy driving clean energy development? -New evidence from 276 cities in China. J Clean Prod 372:133783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133783
Cole C, Osmani M, Quddus M, Wheatley A, Kay K (2014) Towards a zero waste strategy for an English Local Authority. Resour Conserv Recycl 89:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2014.05.005
Cui Y, Cao Y, Ji Y, Chang I-S, Wu J (2022) Determinant factors and business strategy in a sustainable business model: an explorative analysis for the promotion of solid waste recycling technologies. Bus Strateg Environ 31:2533–2545. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3042
De Jaeger S, Eyckmans J, Rogge N, Van Puyenbroeck T (2011) Wasteful waste-reducing policies? The impact of waste reduction policy instruments on collection and processing costs of municipal solid waste. Waste Manage 31:1429–1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.02.021
Delgado-Antequera L, Gémar G, Molinos-Senante M, Gómez T, Caballero R, Sala-Garrido R (2021) Eco-efficiency assessment of municipal solid waste services: influence of exogenous variables. Waste Manage 130:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.05.022
Deus RM, Mele FD, Bezerra BS, Battistelle RAG (2020) A municipal solid waste indicator for environmental impact: assessment and identification of best management practices. J Clean Prod 242:118433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118433
Du WX (2022) Solid waste resource utilization is the key factor of high quality development. People’s Tribune 09:6–8 (In Chinese)
Duan HB, Zhou JJ, Zhao NN, Lan XF, Zheng RY, Fu XR, Chen Y, Sun JM (2023) A digital management platform for supporting the MSW classification: a case study of Huzhou City. Environ Eng 1–16. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2097.X.20230419.1749.016.html. (In Chinese)
Esmaeilian B, Wang B, Lewis K, Duarte F, Ratti C, Behdad S (2018) The future of waste management in smart and sustainable cities: a review and concept paper. Waste Manage 81:177–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.047
Fan W, Wang F, Liu S, Chen T, Bai X, Zhang Y (2023) How does financial and manufacturing co-agglomeration affect environmental pollution? Evidence from China. J Environ Manage 325:116544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116544
Fang B, Yu J, Chen Z, Osman AI, Farghali M, Ihara I, Hamza EH, Rooney DW, Yap P-S (2023) Artificial intelligence for waste management in smart cities: a review. Environ Chem Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01604-3
Gong P, Wang L, Liu X, Wei Y (2022) The value of social media tool for monitoring and evaluating environment policy communication: a case study of the ‘zero-waste city’ initiative in China. Energy Ecol Environ 7:614–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-022-00251-8
Gu B, Liu J, Ji Q (2022) The effect of social sphere digitalization on green total factor productivity in China: evidence from a dynamic spatial Durbin model. J Environ Manage 320:115946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115946
Guan Y, Huang G, Liu L, Huang CZ, Zhai M (2019) Ecological network analysis for an industrial solid waste metabolism system. Environ Pollut 244:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.052
Guo LJ, Liu GF (2021) Empirical study on the relationship between industrial structure optimization, financial development and solid waste emission: empirical study based on spatial spillover effect. Soft Sci 35:1–5+38. https://doi.org/10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2021.01.01 (In Chinese)
Guo Q, Ma X, Zhao J (2023) Can the digital economy development achieve the effect of pollution reduction? Evidence from Chinese Cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27584-z
Han Y, Liu J, Xu H (2022) A comprehensive assessment of the performance of China’s provincial zero-waste cities and impact factor diagnosis. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:106778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106778
Hansen BE (1999) Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: estimation, testing, and inference. J Econ 93:345–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(99)00025-1
Hao M, Xu S (2023) The impact of penalty on residents’ waste separation behavior: a moderated mediation model. Pol J Environ Stud 32:1145–1158. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/156789
Huang XY, Cha Y (2022) Impact of environmental policy innovation on urban green competitiveness in China. China Soft Sci 08:140–150 (In Chinese)
Huang X, Zhang S, Zhang J, Yang K (2023) Research on the impact of digital economy on regional green technology innovation: moderating effect of digital talent aggregation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(29):74409–74425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27279-5
Jian H, Xu M, Zhou L (2019) Collaborative collection effort strategies based on the “Internet + recycling” business model. J Clean Prod 241:118120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118120
Jiang P, Fan YV, Zhou J, Zheng M, Liu X, Klemeš JJ (2020) Data-driven analytical framework for waste-dumping behaviour analysis to facilitate policy regulations. Waste Manage 103:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.12.041
Jiang T (2022) Mediating effects and moderating effects in causal inference. China Ind Econ 100–120. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2022.05.005 (In Chinese)
Jiang LL, Liu XL, Cui LL, Du WX (2021) Research on the cooperative promotion strategy of the pilot construction of “no-waste cities”. Environ Protect 49:57–60. https://doi.org/10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2021.05.012 (In Chinese)
Kerdlap P, Low JSC, Ramakrishna S (2019) Zero waste manufacturing: a framework and review of technology, research, and implementation barriers for enabling a circular economy transition in Singapore. Resour Conserv Recycl 151:104438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104438
Khan SAR, Tabish M, Yu Z (2023) Investigating recycling decisions of internet recyclers: a step towards zero waste economy. J Environ Manage 340:117968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117968
Kinnunen PH-M, Kaksonen AH (2019) Towards circular economy in mining: opportunities and bottlenecks for tailings valorization. J Clean Prod 228:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.171
Kou P, Han Y (2021) Vertical environmental protection pressure, fiscal pressure, and local environmental regulations: evidence from China’s industrial sulfur dioxide treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:60095–60110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14947-7
Kurniawan TA, Meidiana C, Dzarfan Othman MH, Goh HH, Chew KW (2023) Strengthening waste recycling industry in Malang (Indonesia): lessons from waste management in the era of Industry 4.0. J Clean Prod 382:135296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135296
Li Z, Wang J (2022) The dynamic impact of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: evidence city-level empirical data in China. J Clean Prod 351:131570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131570
Lin H, Long CX (2021) Do discretion criteria for patent administrative law enforcement encourage innovation among firms? China Econ Q Int 1:160–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceqi.2021.05.001
Lin B, Ma R (2022) Green technology innovations, urban innovation environment and CO2 emission reduction in China: fresh evidence from a partially linear functional-coefficient panel model. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 176:121434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121434
Liu C, Liu Y (2021) Related theories, evaluation methods and practical experience of overseas research on “zero waste city.” Modern Urban Res 03:55–61 (In Chinese)
Llanquileo-Melgarejo P, Molinos-Senante M (2021) Evaluation of economies of scale in eco-efficiency of municipal waste management: an empirical approach for Chile. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:28337–28348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12529-1
Luo S, Yimamu N, Li Y, Wu H, Irfan M, Hao Y (2023) Digitalization and sustainable development: how could digital economy development improve green innovation in China? Bus Strateg Environ 32:1847–1871. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3223
Lyu Y, Wang W, Wu Y, Zhang J (2023) How does digital economy affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 857:159428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159428
Ma D, Zhu Q (2022) Innovation in emerging economies: research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J Bus Res 145:801–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.03.041
Maiurova A, Kurniawan TA, Kustikova M, Bykovskaia E, Othman MHD, Singh D, Goh HH (2022) Promoting digital transformation in waste collection service and waste recycling in Moscow (Russia): applying a circular economy paradigm to mitigate climate change impacts on the environment. J Clean Prod 354:131604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131604
Meng X-N, Xu S-C, Hao M-G (2023) Can digital-real integration promote industrial green transformation: fresh evidence from China’s industrial sector. J Clean Prod 426:139116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139116
Nassani AA, Hussain H, Condrea E, Grigorescu A, Yousaf Z, Haffar M (2023) Zero waste management: investigation of green technology, the green supply chain, and the moderating role of CSR intentions. Sustainability 15:4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054169
Nunn N, Qian N (2014) US food aid and civil conflict. Am Econ Rev 104:1630–1666. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.104.6.1630
Peng B, Zhao Y, Elahi E, Wan A (2022) Investment in environmental protection, green innovation, and solid waste governance capacity: empirical evidence based on panel data from China. J Environ Plann Manage 66:1229–1252. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2021.2017866
Pietzsch N, Ribeiro JLD, de Medeiros JF (2017) Benefits, challenges and critical factors of success for Zero Waste: a systematic literature review. Waste Manage 67:324–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.004
Ran Q, Yang X, Yan H, Xu Y, Cao J (2023) Natural resource consumption and industrial green transformation: does the digital economy matter? Resour Policy 81:103396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103396
Rena Yadav S, Patel S, Killedar DJ, Kumar S, Kumar R (2022) Eco-innovations and sustainability in solid waste management: an Indian upfront in technological, organizational, start-ups and financial framework. J Environ Manag 302:113953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113953
Ríos A-M, Picazo-Tadeo AJ (2021) Measuring environmental performance in the treatment of municipal solid waste: the case of the European Union-28. Ecol Ind 123:107328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107328
Shen Y, Zhang X (2023) Intelligent manufacturing, green technological innovation and environmental pollution. J Innov Knowl 8:100384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2023.100384
Shi Y, Lin Y, Wang S, Wen H, Lim MK, Tseng M-L (2023) Resource saving and carbon footprint reduction potential of urban symbiosis strategy in express packaging waste recycling network. Waste Manage 161:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2023.02.023
Silva A, Stocker L, Mercieca P, Rosano M (2016) The role of policy labels, keywords and framing in transitioning waste policy. J Clean Prod 115:224–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.069
Singh AP, Devi AS, Sahoo UK (2023) Quantifying plastic waste generation in Aizawl city, India: waste management and its impact on human and environmental health. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27513-0
Song Q, Li J, Zeng X (2015) Minimizing the increasing solid waste through zero waste strategy. J Clean Prod 104:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.027
Teng Y, Lin P-W, Chen X-L, Wang J-L (2022) An analysis of the behavioral decisions of governments, village collectives, and farmers under rural waste sorting. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:106780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106780
Wang R (2023) Is the development of digital finance conducive to reducing haze pollution? Empirical evidence from 284 cities in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:53478–53491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25652-y
Wang P, Xie LW (2014) Pollution control investment, enterprise technical innovation and pollution control efficiency. China Popul Resour Environ 24:51–58 (In Chinese)
Wang H, Han H, Liu T, Tian X, Xu M, Wu Y, Gu Y, Liu Y, Zuo T (2018) “Internet +” recyclable resources: a new recycling mode in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 134:44–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.03.006
Wang B, Farooque M, Zhong RY, Zhang A, Liu Y (2021) Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled accountability in source separation of household waste for a circular economy in China. J Clean Prod 300:126773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126773
Wang L, Chen L, Li Y (2022) Digital economy and urban low-carbon sustainable development: the role of innovation factor mobility in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:48539–48557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19182-2
Wen HW, Lv F, Cao ZK (2020) Research on the development level and influencing factors of provincial zero-waste cities in China. Environ Pollut Control 42:628–633. https://doi.org/10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.05.021 (In Chinese)
Wu D, Xie Y, Lyu S (2023) Disentangling the complex impacts of urban digital transformation and environmental pollution: evidence from smart city pilots in China. Sustain Cities Soc 88:104266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.104266
Xiong B, Wang R (2020) Effect of environmental regulation on industrial solid waste pollution in China: from the perspective of formal environmental regulation and informal environmental regulation. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:7798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217798
Xu B, Lin B (2018) Investigating the role of high-tech industry in reducing China’s CO2 emissions: a regional perspective. J Clean Prod 177:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.174
Xu M, Lin B (2023) Accessing people’s attitudes towards garbage incineration power plants: evidence from models correcting sample selection bias. Environ Impact Assess Rev 99:107034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.107034
Yang G, Zhang Q, Zhao Z, Zhou C (2023) How does the “zero-waste city” strategy contribute to carbon footprint reduction in China? Waste Manage 156:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.11.032
Zaman AU (2014a) Measuring waste management performance using the ‘zero waste index’: the case of Adelaide, Australia. J Clean Prod 66:407–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.032
Zaman AU (2014b) Identification of key assessment indicators of the zero waste management systems. Ecol Ind 36:682–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.09.024
Zaman AU (2015) A comprehensive review of the development of zero waste management: lessons learned and guidelines. J Clean Prod 91:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.12.013
Zaman AU, Lehmann S (2011) Urban growth and waste management optimization towards ‘zero waste city.’ City Cult Soc 2:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccs.2011.11.007
Zaman AU, Lehmann S (2013) The zero waste index: a performance measurement tool for waste management systems in a “zero waste city.” J Clean Prod 50:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.11.041
Zambrano-Monserrate MA, Ruano MA, Ormeño-Candelario V (2021) Determinants of municipal solid waste: a global analysis by countries’ income level. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:62421–62430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15167-9
Zhang Z, Teng J (2023) Role of government in the construction of zero-waste cities: a case study of China’s Pearl River Delta city cluster. Sustainability 15:1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021258
Zhang A, Venkatesh VG, Liu Y, Wan M, Qu T, Huisingh D (2019) Barriers to smart waste management for a circular economy in China. J Clean Prod 240:118198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118198
Zhang P, Xie Y, Wang Y, Li B, Li Bo, Jia Q, Yang Z, Cai Y (2021) Water-energy-food system in typical cities of the world and China under zero-waste: commonalities and asynchronous experiences support sustainable development. Ecol Ind 132:108221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108221
Zhang J, Lyu Y, Li Y, Geng Y (2022a) Digital economy: an innovation driving factor for low-carbon development. Environ Impact Assess Rev 96:106821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106821
Zhang S, Tan Q, Xu G, Li J (2022b) Unveiling characteristics and trend of zero waste research: a scientometric perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:44391–44403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18048-3
Zhang Q, Xiang T, Zhang W, Wang H, An J, Li X, Xue B (2022c) Co-benefits analysis of industrial symbiosis in China’s key industries: case of steel, cement, and power industries. J Ind Ecol 26:1714–1727. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.13320
Zhao W, Yang D, Duan Y (2022) Measuring zero-waste city performance of a coal resource-based area in China with MCDM approach. Math Probl Eng 2022:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8479760
Zhao T, Zhang Z, Liang SK (2020) Digital economy, entrepreneurship, and high-quality economic development: empirical evidence from urban China. J Manag World 36:65–76. https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2020.0154 (In Chinese)
Zhou X, Song M, Cui L (2020) Driving force for China’s economic development under Industry 4.0 and circular economy: technological innovation or structural change? J Clean Production 271:122680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122680
Zuo KF, Kang MY, Lu JX (2022) The impact of social interaction and Internet use on rural residents’ willingness to sort domestic waste. Resour Sci 44:47–58. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2022.01.04 (In Chinese)
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. 2020ZDPYMS44), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (grant no. KYCX23_2604), and the Graduate Innovation Program of China University of Mining and Technology (grant no. 2023WLKXJ107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Meng-Ge Hao: formal analysis and writing—original draft; Shi-Chun Xu: investigation, supervision, conceptualization, and writing—review and editing; Xiao-Na Meng: data curation; Xiao-Fei Xue: software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, MG., Xu, SC., Meng, XN. et al. How does the digital economy affect the provincial “zero-waste city” construction? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 18448–18464 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32304-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32304-2