Abstract
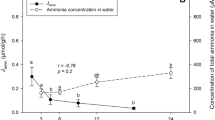
The inland saline waters were continuously observed to have low potassium concentrations compared to their seawater counterpart of the same salinity. We hypothesize that the toxic effect of sulfate may manifest in low potassium saline (LPSW) waters compared to brackish water of the same salinity. Thus, LC50 trials were performed in GIFT (genetically improved farmed tilapia) fry (0.5 ± 0.02 g) to determine the acute sulfate toxicity in freshwater (FW, 0.5 g L−1), artificial seawater (ASW, 10 g L−1), and LPSW (10 g L−1). The median lethal concentrations (96h LC50) of sulfate ion in FW, LPSW, and ASW for the GIFT were 5.30 g L−1, 2.56 g L−1, and 2.98 g L−1, respectively. A second experiment was conducted for 21 days, exposing fish to a sub-lethal level of sulfate ion (SO42−) concentration (1000 mg L−1, one-fifth of FW LC50) with different types of waters (FW, freshwater, 0.5 g L−1; ASW, artificial seawater, 10 g L−1; LPSW, low potassium saline water, 10 g L−1) with and without sulfate inclusion to constitute the treatments as follows, (FW, FW + SO4, ASW, ASW + SO4, LPSW, LPSW + SO4). The effect of sulfate on GIFT reared in sulfate-rich potassium-deficient medium saline water was evaluated by focusing on the hematological adjustments, stress-induced oxidative damage, and osmoregulatory imbalances. The survival was not altered due to the sulfate concentration and K+ deficiency; however, there were significant changes in branchial NKA (Na+/K+-ATPase) activity and osmolality. The increase in NKA was highest in LPSW treatment, suggesting that internal ionic imbalance was triggered due to an interactive effect of sulfate and K+ deficiency. The cortisol levels showed a pronounced increase due to sulfate inclusion irrespective of K+ deficiency. The antioxidant enzymes, i.e., SOD (superoxide dismutase), catalase, GST (glutathione-S-transferase), and GPX (glutathione peroxidase), reflected a similar pattern of increment in the gills and liver of the LPSW + SO4 groups, suggesting a poor antioxidant status of the exposed group. The hepatic peroxidation status, i.e. TBARS (thiobarbituric acid reactive substances), and the peroxide values were enhanced due to both K+ deficiency and sulfate inclusion, suggesting a possible lipid peroxidation in the liver due to handling the excess sulfate anion concentration. The hematological parameters, including haemoglobin, total erythrocyte count, and hematocrit level, reduced significantly in the LPSW + SO4 group, indicating a reduced blood oxygen capacity due to the sulfate exposure and water potassium deficiency. The hepatic acetylcholine esterase activity was suppressed in all the treatments with sulfate inclusion, while the highest suppression was observed in the LPSW + SO4 group. Thus, it is concluded that sulfate-induced physiological imbalances manifest more in potassium-deficient water, indicating that environmental sulfate is more detrimental to inland saline water than freshwater or brackish water of the same salinity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and other materials will be available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Abou Anni IS, Bianchini A, Barcarolli IF, Junior ASV, Robaldo RB, Tesser MB, Sampaio LA (2016) Salinity influence on growth, osmoregulation and energy turnover in juvenile pompano Trachinotus marginatus Cuvier 1832. Aquaculture 455:63–72
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, pp 673–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-091302-2.50032-3
Ahn TY, Park HJ, Kim JH, Kang JC (2020) Effects of antioxidant enzymes and bioaccumulation in eels (Anguilla japonica) by acute exposure of waterborne Cadmium. Fish Aquat Sci 23(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-020-00166-7
Allan GL, Banens B, Fielder S (2001) Developing commercial inland saline aquaculture in Australia: part 2. Resource inventory and assessment. NSW Fisheries Final Report Series 31:116. https://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/545615/FFRS-31_Allan-et-al-2001.pdf. Accessed Dec 2021
Amado LL, Robaldo RB, Geracitano L, Monserrat JM, Bianchini A (2006) Biomarkers of exposure and effect in the Brazilian flounder Paralichthys orbignyanus (Teleostei: Paralichthyidae) from the Patos Lagoon estuary (Southern Brazil). Mar Pollut Bull 52(2):207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.11.007
Ansari S, Ansari BA (2014) Temporal variations of CAT, GSH, and LPO in gills and livers of zebrafish, Danio rerio, exposed to dimethoate. Fish Aquat Life 22(2):101–109. https://doi.org/10.2478/aopf-2014-0009
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis, sixteenth. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC, pp 5–15
Atencio L, Moreno I, Jos A, Prieto AI, Moyano R, Blanco A, Camean AM (2009) Effects of dietary selenium on the oxidative stress and pathological changes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to a microcystin-producing cyanobacterial water bloom. Toxicon 53(2):269–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.11.011
Atli G, Canli M (2007) Enzymatic responses to metal exposures in a freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus. Comp Biochem Physiol c: Toxicol Pharmacol 145(2):282–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Barton BA, Morgan JD, Vijayan MM (2002) Physiological and condition-related indicators of environmental stress in fish. In: Adams SM (ed) Biological indicators of aquatic ecosystem stress. American Fisheries Society, New York, pp 111–148
Begg K, Pankhurst NW (2004) Endocrine and metabolic responses to stress in a laboratory population of the tropical damselfish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. J Fish Biol 64(1):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2004.00290.x
Blahova J, Plhalova L, Hostovsky M, Divisova L, Dobsikova R, Mikulikova I, Stepanova S, Svobodova Z (2013) Oxidative stress responses in zebrafish Danio rerio after subchronic exposure to atrazine. Food Chem Toxicol 61:82–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.041
Boeuf G, Payan P (2001) How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp Biochem Physiol c: Toxicol Pharmacol 130(4):411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(01)00268-X
Booth MA, Fielder DS (2016) Fortification of an aquafeed with potassium chloride does not improve survival of juvenile Australian snapper Pagrus auratus Reared in Potassium Deficient Saline Groundwater. Fishes 1(1):52–64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes1010052
Chandra S (2008) Toxic effect of Malathion on acetylcholinesterase activity of liver, brain and gills of freshwater catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. Environ Conserv J 9(3):47–52. https://doi.org/10.36953/ECJ.2008.090310
Dabas A, Nagpure NS, Kumar R, Kushwaha B, Kumar P, Lakra WS (2012) Assessment of tissue-specific effect of cadmium on antioxidant defense system and lipid peroxidation in freshwater murrel, Channa punctatus. Fish Physiol Biochem 38(2):469–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9527-7
Dalfo E, Portero-Otin M, Ayala V, Martinez A, Pamplona R, Ferrer I (2005) Evidence of oxidative stress in the neocortex in incidental Lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(9):816–830. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.jnen.0000179050.54522.5a
Dey MM (2000) The impact of genetically improved f armed Nile tilapia in Asia. Aquac Econ Manag 4(1–2):107–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/13657300009380263
Dorval J, Leblond VS, Hontela A (2003) Oxidative stress and loss of cortisol secretion in adrenocortical cells of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed in vitro to endosulfan, an organochlorine pesticide. Aquat Toxicol 63(3):229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00182-0
Dröge W (2003) Oxidative Stress and Aging. In: Roach RC, Wagner PD, Hackett PH (eds) Hypoxia. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 543. Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8997-0_14
Eknath AE, Acosta BO (1998) Genetic improvement of farmed tilapias (GIFT) project: final report, March 1988 to December 1997:1–33. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/2563. Accessed Nov 2021
El-Gendy KS, Aly NM, Mahmoud FH, Kenawy A, El-Sebae AKH (2010) The role of vitamin C as antioxidant in protection of oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid. Food Chem Toxicol 48(1):215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
El-Sayed AFM (2006) Tilapia culture in salt water: environmental requirements, nutritional implications and economic potentials. Avances En Nutricion Acuicola 8:95–105
Evans DH (2008) Teleost fish osmoregulation: what have we learned since August Krogh, Homer Smith, and Ancel Keys. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol I 295(2):704–713. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.90337.2008
Faheem M, Lone KP (2018) Oxidative stress and histopathologic biomarkers of exposure to bisphenol-A in the freshwater fish, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Braz J Pharm Sci 53(3):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902017000317003
FAO (2022) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. Rome, FAO. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc0461en
Fatima M, Ahmad I, Sayeed I, Athar M, Raisuddin S (2000) Pollutant-induced over-activation of phagocytes is concomitantly associated with peroxidative damage in fish tissues. Aquat Toxicol 49(4):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00086-7
Ferreira M, Moradas-Ferreira P, Reis-Henriques MA (2005) Oxidative stress biomarkers in two resident species, mullet (Mugil cephalus) and flounder (Platichthys flesus), from a polluted site in River Douro Estuary, Portugal. Aquat Toxicol 71:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.10.009
Foskett JK, Logsdon CD, Turner T, Machen TE, Bern HA (1981) Differentiation of the chloride extrusion mechanism during seawater adaptation of a teleost fish, the cichlid Sarotherodon mossambicus. J Exp Biol 93(1):209–224. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.93.1.209
Frasco MF, Guilhermino L (2002) Effects of dimethoate and beta- naphthoflavone on selected biomarkers of Poecilia reticulata. Fish Physiol Biochem 26:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025457831923
Gill TS, Epple A (1993) Stress-related changes in the hematological profile of the American eel (Anguilla rostrata). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 25(2):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1993.1021
Goldenfarb PB, Bowyer FP, Hall T, Brosious E (1971) Reproducibility in the hematology laboratory: the microhematocrit determination. Am J Clin Pathol 56:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/56.1.35
Greenwood NN, Earnshaw A (1984) Origin of the Elements. Isotopes and Atomic Weights Greenwood, NN and Earnshaw A (eds) Chemistry of the Elements, Pergamon, pp 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-030712-1.50004-1
Griffith MB, Lazorchak JM, Haring H (2020) Uptake of sulfate from ambient water by freshwater animals. Water 12(5):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051496
Guerriero G, Di Finizio A, Ciarcia G (2002) Stress-induced changes of plasma antioxidants in aquacultured sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Comp Biochem Physiol a: Mol Integr Physiol 132(1):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(01)00549-9
Gundersen DT, Bustaman S, Seim WK, Curtis LR (1994) pH, hardness, and humic acid influence aluminum toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in weakly alkaline waters. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51(6):1345–1355. https://doi.org/10.1139/f94-134
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jaoby W (1974) Glutatione-S-transferases—first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hopkins J, Tudhope GR (1973) Glutathione peroxidase in human red cells in health and disease. Br J Haematol 25(5):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01768.x
Hvas M, Nilsen TO, Oppedal F (2018) Oxygen uptake and osmotic balance of Atlantic salmon in relation to exercise and salinity acclimation. Front Mar Sci 5:368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00368
Hwang PP, Sun CM, Wu SM (1989) Changes of plasma osmolality, chloride concentration and gill Na−K-ATPase activity in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus during seawater acclimation. Mar Biol 100(3):295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391142
Iraz M, Erdogan H, Ozyurt B, Ozugurlu F, Ozgocmen S, Fadillioglu E (2005) Omega-3 essential fatty acid supplementation and erythrocyte oxidant/antioxidant status in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci 35(2):169–173
Ishikawa NM, Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Lombardi JV, Ferreira CM (2007) Hematological parameters in Nile Tilápia, Oreochromis niloticus exposed to sub-letal concentrations of mercury. Braz Arch Biol Technol 50:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Jones SB, Beauvais SL, Brewer SK, Little EE (1999) Physiological and behavioural measures of neurotoxicity in rainbow trout. In: Kennedy C, MacKinlay D (eds) Fish response to toxic environments. Towson University, Baltimore MD, pp 27–28
Kammerer BD, Kultz D (2009) Prolonged apoptosis in mitochondria-rich cells of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) exposed to elevated salinity. J Comp Physiol B 179(4):535–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-008-0333-1
Kateregga JN, Babu M, Abuine R, Ndukui JG (2014) Hematological and histopathological effects of cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae) from lake Victoria shores of Uganda in Swiss mice. Int J Appl Sci Technol 4(4):128–133
Kester DR, Duedall IW, Connors DN, Pytkowicz RM (1967) Preparation of artificial seawater 1. Limnol Oceanogr 12(1):176–179. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1967.12.1.0176
Kim HS, Manevich Y, Feinstein SI, Pak JH, Ho YS, Fisher AB (2003) Induction of 1-cys peroxiredoxin expression by oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285(2):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00078.2003
Kirk RG (1972) A review of recent developments in tilapia culture, with special reference to fish farming in the heated effluents of power stations. Aquaculture 1:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(72)90007-5
Leaver MJ, Scott K, George SG (1993) Cloning and characterisation of the major hepatic glutathione S-transferase from a marine teleost flatfish, the plaice (Pleuronectes platessa), with structural similarities to plant, insect and mammalian Theta class isoenzymes. Biochem J 292(1):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2920189
Lihong Li, Huilan Yi (2012) Effect of sulfur dioxide on ROS production, gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 58:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.06.009
Litwack G, Ketterer B, Arias IM (1971) Ligandin: a hepatic protein which binds steroids, bilirubin, carcinogens and a number of exogenous organic anions. Nature 234:466–467
Livingstone DR (1998) The fate of organic xenobiotics in aquatic ecosystems: quantitative and qualitative differences in biotransformation by invertebrates and fish. Comp Biochem Physiol a: Mol Integr Physiol 120(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(98)10008-9
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42(8):656–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00060-1
Lotan R (1960) Adaptability of Tilapia nilotica to various saline conditions. Bamidgeh 12:96–100
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006
McCormick SD (1993) Methods for nonlethal gill biopsy and measurement of Na+, K+ -ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50(3):656–658
Maheswaran R, Devapaul A, Muralidharan S, Velmurugan B, Ignacimuthu S (2008) Haematological studies of fresh water fish, Clarias batrachus (L.) exposed to mercuric chloride. Int J Integr Biol 2(1):49–54
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45228-9
Morris C and O'Donnell MJ (2021) Vacuolar H+-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase energize Na+ uptake mechanisms in the nuchal organ of the hyperregulating freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. J Exp Biol 224(12), p.jeb242205.
Mount DR, Gulley DD, Hockett JR, Garrison TD, Evans JM (1997) Statistical models to predict the toxicity of major ions to Ceriodaphnia dubia, Daphnia magna and Pimephales promelas (fathead minnows). Environ Toxicol Chem : An Int J 16(10):2009–2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Munari M, Marin MG, Matozzo V (2014) Effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine on the immune parameters and acetylcholinesterase activity of the clam Venerupis philippinarum. Mar Environ Res 94:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.11.007
Murthy VK, Reddy YD, Reddy RM, Bhaskar RM, Govindappa S (1984) Changes in brain acetylcholinesterase activity and behavior of freshwater fish in acid polluted environment. Environ Ecol 2(2):79–82
Nimmo IA (1987) The glutathione S-transferases of fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 3(4):163–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02180277
Nriagu JO (1978) Sulfur in the environment: Ecological impacts. New York, USA
Patriche T (2009) The importance of glucose determination in the blood of the cyprinids. Sci Pap Anim Sci Biotechnol 42(2):102–106
Pretto A, Loro VL, Morsch VM, Moraes BS, Menezes C, Clasen B, Hoehne L, Dressler V (2010) Acetylcholinesterase activity, lipid peroxidation, and bioaccumulation in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to Cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:1008–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9419-3
Purnamawati NK, Affandi R, Dewantoro E, Utami DAS (2019) Survival and growth response of snakehead fish Channa striata juvenile on various salinity levels of acid sulfate water. AACL Bioflux 12(4):1467–1479
Raju NJ, Ram P, Dey S (2009) Groundwater quality in the lower Varuna river basin, Varanasi district, Uttar Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 73(2):178–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0074-0
Rastgoo L, Alemzadeh A (2011) Biochemical responses of Gouan (Aeluropus littoralis) to heavy metals stress. Aust J Crop Sci 5(4):375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Rath S, Misra BN (1981) Toxicological effects of dichlorvos (DDVP) on brain and liver acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity of Tilapia mossambica, Peters. Toxicology 19(3):9–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Romani R, Antognelli C, Baldracchini F, De Santis A, Isani G, Giovannini E, Rosi G (2003) Increased acetylcholinesterase activities in specimens of Sparus auratus exposed to sublethal copper concentrations. Chem Biol Interact 145(3):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2797(03)00058-9
Roy LA, Davis DA, Saoud IP, Boyd CA, Pine HJ, Boyd CE (2010) Shrimp culture in inland low salinity waters. Rev Aquac 2(4):191–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-5131.2010.01036.x
Safari R (2016) Toxic effects of Cadmium on antioxidant defense systems and lipid peroxidation in Acipenser persicus (Borodin, 1897). Int J Aquat Biol 3(6):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Satoh K (1978) Estimation of lipid peroxides by thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). Clin Chim Acta 90:37–43
Schaperclaus W, Kulow H, Schreckenbach K (1991) Haematological and serological technique. In: Kothekar VS (ed) Fish disease, Vol 1, 2nd edn. Oxonian Press, Gulab Primlani, New Delhi, pp 71–108
Senger MR, Rico EP, de Bem AM, Frazzon APG, Dias RD, Bogo MR, Bonan CD (2006) Exposure to Hg2+ and Pb2+ changes NTPDase and ecto-5′-nucleotidase activities in central nervous system of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicology 226(2–3):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2006.07.012
Shah SL, Altindag A (2004) Hematological parameters of tench (Tinca tinca L.) after acute and chronic exposure to lethal and sublethal mercury treatments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73(5):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-004-0513-y
Shakoori AR, Iqbal MJ, Mughal AL, Ali SS (1994) Biochemical changes induced by inorganic mercury on the blood, liver and muscles of freshwater Chinese grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. J Ecotoxicol Environ Monit 4(2):81–92
Stewart HA, Noakes DL, Cogliati KM, Peterson JT, Iversen MH, Schreck CB (2016) Salinity effects on plasma ion levels, cortisol, and osmolality in Chinook salmon following lethal sampling. Comp Biochem Physiol a: Mol Integr Physiol 192:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.11.011
Sukenik A, Reisner M, Carmeli S, Werman M (2006) Oral toxicity of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in mice: Long-term exposure to low doses. Environ Toxicol: An Int J 21(6):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20220
Takei Y, Hwang (2016) Homeostatic responses to osmotic stress. Fish Physiol 35:207–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802728-8.00006-0
Tsakiris S, Angelogianni P, Schulpis KH, Stavridis JC (2000) Protective effect of L-phenylalanine on rat brain acetylcholinesterase inhibition induced by free radicals. Clin Biochem 33(2):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Tseng YC, Hwang PP (2008) Some insights into energy metabolism for osmoregulation in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 148(4):419–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.04.009
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(2):178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Wang N, Dorman RA, Ingersoll CG, Hardesty DK, Brumbaugh WG, Hammer EJ, Bauer CR, Mount DR (2016) Acute and chronic toxicity of sodium sulfate to four freshwater organisms in water-only exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(1):115–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3148
Watson TA, Beamish FWH (1980) Effects of zinc on branchial ATPase activity in vivo in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Comp Pharmacol 66(1):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4492(80)90075-1
Whitefield AK, Blaber SJM (1979) The distribution of the freshwater cichlid Sarotherodon mossambicus in estuarine systems. Environ Biol Fishes 4:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005931
Zaffar I, Varghese T, Dasgupta, Sahu NP, Srivastava PP, Harikrishna V, Mushtaq Z, Dar SA, Prakash S, Krishna G (2021) Dietary potassium partially compensates the requirement of aqueous potassium of P. vannamei reared in medium saline inland groundwater. Aquac Res 52(9):4094–4104. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15248
Zak D, Hupfer M, Cabezas A, Jurasinski G, Audet J, Kleeberg A, McInnes R, Kristiansen SM, Petersen RJ, Liu H, Goldhammer T (2021) Sulfate in freshwater ecosystems: a review of sources, biogeochemical cycles, ecotoxicological effects and bioremediation. Earth Sci Rev 212:1–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103446
Zhang X, Wen H, Wang H, Ren Y, Zhao J, Li Y (2017) RNA-Seq analysis of salinity stress–responsive transcriptome in the liver of spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). PLoS One 12(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173238
Zielinski S, Portner HO (2000) Oxidative stress and antioxidative defense in cephalopods: a function of metabolic rate or age. Comp Biochem Physiol b: Biochem Mol Biol 125(2):147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-0491(99)00162-5
Funding
The research is partially funded by the National Agricultural Higher Education Project (NAHEP- World Bank and Indian Council of Agricultural Research) with grant number [1010041].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Tincy Varghese conceptualized the research; experimental designing was performed by Subrata Dasgupta, Subodh Gupta, and Narottam Prasad Sahu. Data analysis, data curation, original drafting, writing review, and revision were performed by Shivangi Bhatt, Vattiringal Jayadradhan Rejish Kumar, and Tincy Varghese. Shivangi Bhatt wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
The study protocol was performed in the Fish Nutrition, Biochemistry, and Physiology Division of the Central Institute of Fisheries Education Mumbai following the approved guidelines of CPCSEA Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) intended for the care and use of animals in scientific research.
Consent for publication
All the authors have granted permission to publish this article in environment science and pollution research.
Consent to participate
It is not applicable as no trials with human subjects are involved.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatt, S., Dasgupta, S., Gupta, S. et al. Effect of sulfate on the osmoregulatory and physio-biochemical responses of GIFT (Oreochromis niloticus) juveniles reared in potassium-deficient medium saline waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 18636–18655 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32219-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32219-y