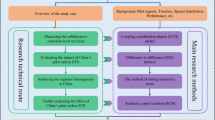
Abstract
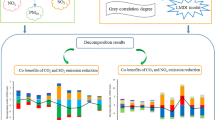
Synergizing the reduction of air pollutants and carbon emissions (APCE) has become a critical tactic alternative to address the issue of climate change. Taking the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region of China as a case study, this paper explores the spatial and temporal distribution pattern of the coupling coordination degree (CCD) of combating APCE from 2011 to 2022, analyzes the dynamic change in CCD using the convergence test, and investigates the key factors affecting CCD via the Tobit regression model. The results show that (1) from 2011 to 2022, the air pollutants (AP) and CO2 emission (CE) in the YRD region decrease at the annual rate of 10.32% and 0.85%, respectively; (2) the CCD of reducing APCE in the YRD presents a W-shaped fluctuation before 2016 and then steps into a steady increase status after 2016; (3) the order of CCD in four provincial-level units by 2022 is Shanghai > Zhejiang > Jiangsu > Anhui. The proportion of cities where the CCD of reducing APCE enters the high-coordination period has reached 87.8%; and (4) the Tobit regression results affirm that economic growth, industrial structure, and green technological innovation exacerbate the CCD of combating APCE, while opening-up level mitigates it. The findings offer policymakers valuable insights into the importance of pursuing collaborative governance over APCE and ensuring sustainable development.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in China Statistical Year Book, Shanghai Statistical Year Book, Zhejiang Statistical Year Book, Jiangsu Statistical Year Book and Anhui Statistical Year Book.
References
Ahakwa I, Xu Y, Tackie EA (2023) Greening human capital towards environmental quality in Ghana: insight from the novel dynamic ARDL simulation approach. Energy Policy 176:113514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113514
Akhmat G, Zaman K, Shukui T, Sajjad F, Khan MA, Khan MZ (2014) The challenges of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution through energy sources: evidence from a panel of developed countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(12):7425–7435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2693-2
Aksoyoglu S, Baltensperger U, Prévôt AS (2016) Contribution of ship emissions to the concentration and deposition of air pollutants in Europe. Atmos Chem Phys 16(4):1895–1906
Alimujiang A, Jiang P (2020) Synergy and co-benefits of reducing CO2 and air pollutant emissions by promoting electric vehicles—a case of Shanghai. Energy Sustain Dev 55:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2020.02.005
Bang Y-Y, Lee DS, Lim S-R (2019) Analysis of corporate CO2 and energy cost efficiency: the role of performance indicators and effective environmental reporting. Energy Policy 133:110897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110897
Bereitschaft B, Debbage K (2013) Urban form, air pollution, and CO2 emissions in large U.S. metropolitan area. Prof Geogr 65(4):612–635. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2013.799991
Cai Q, Qiu X, Peng L, Li Q, Zhang Y (2023) Significant co-benefits of air pollutant and CO2 emission reduction from biomass energy utilization in power plants in China. Sci Total Environ 887:164116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164116
Cerdeira Bento JP, Moutinho V (2016) CO2 emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and international trade in Italy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.151
Chatti W, Majeed MT (2022) Information communication technology (ICT), smart urbanization, and environmental quality: evidence from a panel of developing and developed economies. J Clean Prod 366:132925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132925
Chen H, Chen W (2019) Potential impacts of coal substitution policy on regional air pollutants and carbon emission reductions for China’s building sector during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. Energy Policy 131:281–294
Chen M-J, Leon Guo Y, Lin P, Chiang H-C, Chen P-C, Chen Y-C (2023) Air quality health index (AQHI) based on multiple air pollutants and mortality risks in Taiwan: construction and validation. Environ Res 231:116214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116214
Chen S, Ding D, Shi G, Chen G (2022a) Digital economy, industrial structure, and carbon emissions: an empirical study based on a provincial panel data set from China. Chinese Journal of Population, Resources and Environment 20(4):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjpre.2022.11.002
Chen Y, Xu Y, Zhou K (2022b) Cross-administrative and downscaling environmental spatial management and control system: a zoning experiment in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Environ Manage 323:116257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116257
Chengjing N, Yixuan L, Linsheng Y, Li W, Fengying Z (2023) Spatio-temporal characteristics and coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and atmospheric particulate pollutants in the Bohai Rim in China. Ecol Ind 153:110387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110387
Coelho S, Ferreira J, Rodrigues V, Lopes M (2022) Source apportionment of air pollution in European urban areas: lessons from the ClairCity project. J Environ Manage 320:115899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115899
Duan LF, Hu W, Deng D, Fang WK, Xiong M, Lu P L, Li ZL, Zhai CZ (2021) Impacts of reducing air pollutants and CO2 emissions in urban road transport through 2035 in Chongqing. Environ. Sci Ecotechnology 8:100125
Du K, Yu Y, Li J (2020) Does international trade promote CO2 emission performance? An empirical analysis based on a partially linear functional-coefficient panel data model. Energy Econ 92:104983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104983
Duan X, Li X, Tan W, Xiao R (2022) Decoupling relationship analysis between urbanization and carbon emissions in 33 African countries. Heliyon 8(9):e10423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10423
Essandoh OK, Islam M, Kakinaka M (2020) Linking international trade and foreign direct investment to CO2 emissions: any differences between developed and developing countries? Sci Total Environ 712:136437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136437
Fang G, Gao Z, Wang L, Tian L (2022) How does green innovation drive urban carbon emission efficiency? —evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J Clean Prod 375:134196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134196
Fayyazbakhsh A, Bell ML, Zhu X, Mei X, Koutný M, Hajinajaf N, Zhang Y (2022) Engine emissions with air pollutants and greenhouse gases and their control technologies. J Clean Prod 376:134260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134260
Fuller R, Landrigan PJ, Balakrishnan K, Bathan G, Bose-O’Reilly S, Brauer M, Yan C (2022) Pollution and health: a progress update. Lancet Planet Health 6(6):e535–e547. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00090-0
Gao Y, Zhang L, Huang A, Kou W, Bo X, Cai B, Qu J (2022) Unveiling the spatial and sectoral characteristics of a high-resolution emission inventory of CO2 and air pollutants in China. Sci Total Environ 847:157623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157623
He N, Zeng S, Jin G (2023) Achieving synergy between carbon mitigation and pollution reduction: does green finance matter? J Environ Manage 342:118356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118356
Hou Y, Zhang K, Zhu Y, Liu W (2021) Spatial and temporal differentiation and influencing factors of environmental governance performance in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 801:149699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149699
Howden-Chapman P, Keall M, Whitwell K, Chapman R (2020) Evaluating natural experiments to measure the co-benefits of urban policy interventions to reduce carbon emissions in New Zealand. Sci Total Environ 700:134408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134408
Howarth C, Viner D (2022) Integrating adaptation practice in assessments of climate change science: the case of IPCC Working Group II reports. Environ Sci Policy 135:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2022.04.009
Jamei E, Jamei Y, Seyedmahmoudian M, Horan B, Mekhilef S, Stojcevski A (2022) Investigating the impacts of COVID-19 lockdown on air quality, surface Urban Heat Island, air temperature and lighting energy consumption in City of Melbourne. Energ Strat Rev 44:100963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2022.100963
Jiang J, Ye B, Sun Z, Zeng Z, Yang X (2023) Low-carbon energy policies benefit climate change mitigation and air pollutant reduction in megacities: an empirical examination of Shenzhen, China. Sci Total Environ 892:164644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164644
Jiang P, Khishgee S, Alimujiang A, Dong H (2020) Cost-effective approaches for reducing carbon and air pollution emissions in the power industry in China. J Environ Manage 264:110452
Jephcote C, Hansell AL, Adams K, Gulliver J (2021) Changes in air quality during COVID-19 ‘lockdown’in the United Kingdom. Environ Pollut 272:116011
Korkut Pata U, Yilanci V, Hussain B, Naqvi SAA (2022) Analyzing the role of income inequality and political stability in environmental degradation: evidence from South Asia. Gondwana Res 107:13–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2022.02.009
Lei Y, Zhang Q, Nielsen C, He K (2011) An inventory of primary air pollutants and CO2 emissions from cement production in China, 1990–2020. Atmos Environ 45(1):147–154
Li J, Lin B (2017) Does energy and CO2 emissions performance of China benefit from regional integration? Energy Policy 101:366–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.036
Li L, Zhang Y, Zhou T, Wang K, Wang C, Wang T, Lü G (2022) Mitigation of China’s carbon neutrality to global warming. Nat Commun 13(1):5315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33047-9
Li W, Cai Z, Jin L (2022b) Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of the coupling coordinated development of production-living-ecology system in China. Ecol Ind 145:109738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109738
Li Z, Sun L, Geng Y, Dong H, Ren J, Liu Z, Higano Y (2017) Examining industrial structure changes and corresponding carbon emission reduction effect by combining input-output analysis and social network analysis: a comparison study of China and Japan. J Clean Prod 162:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.200
Lin H, Zhu J, Jiang P, Cai Z, Yang X, Yang X, Wei J (2022) Assessing drivers of coordinated control of ozone and fine particulate pollution: evidence from Yangtze River Delta in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 96:106840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106840
Lin T-Y, Chiu Y-H, Lin Y-N, Chang T-H, Lin P-Y (2023a) Greenhouse gas emission indicators, energy consumption efficiency, and optimal carbon emission allowance allocation of the EU countries in 2030. Gas Sci Eng 110:204902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgsce.2023.204902
Lin W, Lin K, Du L, Du J (2023b) Can regional joint prevention and control of atmospheric reduce border pollution? Evidence from China’s 12th Five-Year Plan on air pollution. J Environ Manage 342:118342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118342
Liu F, Khan Y, Marie M (2023) Carbon neutrality challenges in Belt and Road countries: what factors can contribute to CO2 emissions mitigation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):14884–14901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22983-0
Liu F, Qiu SB (2020) Relations between factor-market distortion and environmental pollution—analysis of intermediate effect based on technological innovation. Desalination Water Treat 188:303–308
Lovett GM, Tear TH, Evers DC, Findlay SE, Cosby BJ, Dunscomb JK, Weathers KC (2009) Effects of air pollution on ecosystems and biological diversity in the eastern United States. Ann NY Acad Sci 1162(1):99–135
Ma M, Tang J (2022) Interactive coercive relationship and spatio-temporal coupling coordination degree between tourism urbanization and eco-environment: a case study in Western China. Ecol Ind 142:109149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109149
Milando CW, Martenies SE, Batterman SA (2016) Assessing concentrations and health impacts of air quality management strategies: Framework for Rapid Emissions Scenario and Health impact ESTimation (FRESH-EST). Environ Int 94:473–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.005
Monforti-Ferrario F, Blanco MP (2021) The impact of power network congestion, its consequences and mitigation measures on air pollutants and greenhouse gases emissions. A case from Germany. Renew Sust Energ Rev 150:111501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111501
Nam K-M, Waugh CJ, Paltsev S, Reilly JM, Karplus VJ (2014) Synergy between pollution and carbon emissions control: comparing China and the United States. Energy Econ 46:186–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2014.08.013
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theor 20(3):597–625. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266466604203073
Raihan A (2023) The dynamic nexus between economic growth, renewable energy use, urbanization, industrialization, tourism, agricultural productivity, forest area, and carbon dioxide emissions in the Philippines. Energy Nexus 9:100180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nexus.2023.100180
Rontard B, Reyes Hernández H (2022) Political construction of carbon pricing: experience from New Zealand emissions trading scheme. Environmental Development 43:100727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2022.100727
Shan Y, Guan D, Liu J, Mi Z, Liu Z, Liu J, Zhang Q (2017) Methodology and applications of city level CO2 emission accounts in China. J Clean Prod 161:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.075
Shan Y, Guan Y, Hang Y, Zheng H, Li Y, Guan D, Hubacek K (2022) City-level emission peak and drivers in China. Sci Bull 67(18):1910–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.08.024
Shen J, Cai W, Chen X, Chen X, Zhao Z, Ma Z, Zhang S (2022) Synergies of carbon neutrality, air pollution control, and health improvement — a case study of China energy interconnection scenario. Glob Energy Intercon 5(5):531–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloei.2022.10.007
Sicard P, Agathokleous E, De Marco A, Paoletti E, Calatayud V (2021) Urban population exposure to air pollution in Europe over the last decades. Environ Sci Eur 33(1):1–12
Skjærseth JB, Wettestad J (2009) The origin, evolution and consequences of the EU Emissions Trading System. Glob Environ Polit 9(2):101–122. https://doi.org/10.1162/glep.2009.9.2.101
Song P, Mao X, Li Z, Tan Z (2023) Study on the optimal policy options for improving energy efficiency and co-controlling carbon emission and local air pollutants in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 175:113167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113167
Sun X, Lian W, Gao T, Chen Z, Duan H (2023) Spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emission intensity in electricity generation and spatial spillover effects of driving factors across China’s provinces. J Clean Prod 405:136908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136908
Takeshita T (2012) Assessing the co-benefits of CO2 mitigation on air pollutants emissions from road vehicles. Appl Energy 97:225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.12.029
Turnock S, Butt E, Richardson T, Mann G, Reddington C, Forster P, Johnson C (2016) The impact of European legislative and technology measures to reduce air pollutants on air quality, human health and climate. Environ Res Lett 11(2):024010
Wakamatsu S, Morikawa T, Ito A (2013) Air pollution trends in Japan between 1970 and 2012 and impact of urban air pollution countermeasures. Asian J Atmospheric Environ 7(4):177–190
Wan G, Wang C, Wang J, Zhang X (2022) The income inequality-CO2 emissions nexus: transmission mechanisms. Ecol Econ 195:107360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2022.107360
Wang W-Z, Liu L-C, Liao H, Wei Y-M (2021) Impacts of urbanization on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis from OECD countries. Energy Policy 151:112171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112171
Wang Y, Duan X, Liang T, Wang L, Wang L (2022a) Analysis of spatio-temporal distribution characteristics and socioeconomic drivers of urban air quality in China. Chemosphere 291:132799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132799
Wang Z, Pham TLH, Sun K, Wang B, Bui Q, Hashemizadeh A (2022b) The moderating role of financial development in the renewable energy consumption - CO2 emissions linkage: the case study of Next-11 countries. Energy 254:124386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124386
Wu Q, Hong S, Yang L, Mu H, Huang C, Niu X, He C (2023) Coupling coordination relationships between air pollutant concentrations and emissions in China. Atmos Pollut Res 14(3):101678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2023.101678
Wu Q, Wang J, He Y, Liu Y, Jiang Q (2023b) Quantitative assessment and mitigation strategies of greenhouse gas emissions from rice fields in China: a data-driven approach based on machine learning and statistical modeling. Comput Electron Agric 210:107929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.107929
Wyche K, Nichols M, Parfitt H, Beckett P, Gregg D, Smallbone K, Monks P (2021) Changes in ambient air quality and atmospheric composition and reactivity in the South East of the UK as a result of the COVID-19 lockdown. Sci Total Environ 755:142526
Xia D, Zhang L (2022) Coupling coordination degree between coal production reduction and CO2 emission reduction in coal industry. Energy 258:124902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124902
Xiao K, Li F, Dong C, Cai Y, Li Y, Ye P, Zhang J (2020) Unraveling effects of coal output cut policy on air pollution abatement in China using a CGE model. J Clean Prod 269:122369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122369
Xu K, Mei R, Liang L, Sun W (2023) Regional convergence analysis of sustainable innovation efficiency in European Union countries. J Environ Manage 325:116636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116636
Yang F, Choi Y, Lee H (2021) Life-cycle data envelopment analysis to measure efficiency and cost-effectiveness of environmental regulation in China’s transport sector. Ecol Ind 126:107717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107717
Yang XL, Feng ZW, Chen YY (2023) Study on the Spatio-temporal patterns of urban air pollution and its spatial mismatch with air pollutant emissions in the Yellow River Basin. China. Environmental Research Communications 5(5):055008. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7620/acd0f4
Yawale SK, Hanaoka T, Kapshe M, Deshpande A (2023) Direct and indirect air pollutant reductions as co-benefits of the energy transition toward carbon-neutrality in India’s residential sector. Energ Strat Rev 49:101143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2023.101143
Yi M, Guan Y, Wu T, Wen L, Sheng MS (2023) Assessing China’s synergistic governance of emission reduction between pollutants and CO2. Environ Impact Assess Rev 102:107196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107196
Zhang Q-Y, Cai B-F, Wang M-D, Wang J-X, Xing Y-K, Dong G-X, Mao X-Q (2022) City level CO2 and local air pollutants co-control performance evaluation: a case study of 113 key environmental protection cities in China. Adv Clim Chang Res 13(1):118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2021.10.002
Zhang X, Ma Q, Chu W, Ning M, Liu X, Xiao F, Yan G (2023) Identify the key emission sources for mitigating ozone pollution: a case study of urban area in the Yangtze River Delta region. Sci Total Environ 164703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164703
Zhu B, Zhang T (2021) The impact of cross-region industrial structure optimization on economy, carbon emissions and energy consumption: a case of the Yangtze River Delta. Sci Total Environ 778:146089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146089
Zimmer A, Koch N (2017) Fuel consumption dynamics in Europe: tax reform implications for air pollution and carbon emissions. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 106:22–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2017.08.006
Funding
This work was supported by the Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 23BGL221).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fang Liu: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization, and funding acquisition. Anqi Li: data collection, visualization, and software. Yuwei Yang: data collection. Muhammad Bilal: writing—review, editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
We acknowledge that this paper has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal. Ethical approval and informed consent do not apply to this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Li, A., Bilal, M. et al. Synergistic effect of combating air pollutants and carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Delta of China: spatial and temporal divergence analysis and key influencing factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32197-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32197-1