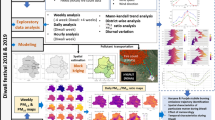
Abstract
Here, we present the results of a comprehensive study of air quality in two tunnels located in the city of Krakow, southern Poland. The study comprised three PM fractions of suspended particulate matter (PM1, PM2.5 and PM10) sampled during campaigns lasting from March 14 to April 24, 2016 and from June 28 to July 18, 2016, in the road tunnel and the tram tunnel, respectively. The collected samples had undergone comprehensive chemical, elemental and carbon isotope analyses. The results of these analyses gave the basis for better characterization of urban transport as a source of air pollution in the city. The concentrations of particulate matter varied, depending on the analysed PM fraction and the place of sampling. For the tram tunnel, the average concentrations were 53.2 µg·m−3 (PM1), 73.8 µg·m−3 (PM2.5), 96.5 µg·m−3 (PM10), to be compared with 44.2 µg·m−3, 137.7 µg·m−3, 221.5 µg·m−3, respectively, recorded in the road tunnel. The isotope-mass balance calculations carried out separately for the road and tram tunnel and for each PM fraction, revealed that 60 to 79% of carbon present in the samples collected in the road tunnel was associated with road transport, to be compared with 15–33% obtained in the tram tunnel. The second in importance were biogenic emissions (17–21% and 41–49% in the road and tram tunnel, respectively. Sixteen different polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) have been identified in the analysed samples. As expected, much higher concentrations of PAHs were detected in the road tunnel when compared to the tram tunnel. Based on the analysed PAHs concentrations, health risk assessment was determined using 3 different types of indicators: carcinogenic equivalent (CEQ), mutagenic equivalent (MEQ) and toxic equivalent (TEQ).






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004
Aguilera J, Whigham LD (2018) Using the 13C/12C carbon isotope ratio to characterise the emission sources of airborne particulate matter: a review of literature. Isot Environ Health Stud 54:573–587. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2018.1531854
Arditsoglou A, Samara C (2005) Levels of total suspended particulate matter and major trace elements in Kosovo: a source identification and apportionment study. Chemosphere 59:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.056
Assonov S, Groening M, Fajgelj A, Hélie J-F, Claude H-M (2020) Preparation and characterisation of IAEA-603, a new primary reference material aimed at the VPDB scale realisation for δ 13 C and δ 18 O determination. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 34:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.8867
Barbieri M (2016) The Importance of enrichment factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo ) to evaluate the soil contamination. J Geol Geophys 5:1–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2381-8719.1000237
Belis CA, Karagulian F, Larsen BR, Hopke PK (2013) Critical review and meta-analysis of ambient particulate matter source apportionment using receptor models in Europe. Atmos Environ 69:94–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.009
Cavalli F, Viana M, Yttri KE, Genberg J, Putaud JP (2010) Toward a standardised thermal-optical protocol for measuring atmospheric organic and elemental carbon: the EUSAAR protocol. Atmos Meas Tech 3:79–89. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-3-79-2010
Cesari D, Contini D, Genga A, Siciliano M, Elefante C, Baglivi F, Daniele L (2012) Analysis of raw soils and their resuspended PM10 fractions: characterisation of source profiles and enrichment factors. Appl Geochem 27:1238–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.02.029
Chow JC, Lowenthal DH, Chen LWA, Wang X, Watson JG (2015) Mass reconstruction methods for PM2.5: a review. Air Qual Atmos Health 8:243–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-015-0338-3
Colombi C, Angius S, Gianelle V, Lazzarini M (2013) Particulate matter concentrations, physical characteristics and elemental composition in the Milan underground transport system. Atmos Environ 70:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.01.035
Coplen TB, Brand WA, Gehre M, Grhning M, Meljer HAJ, Toman B, Verkouteren RM (2006) New guidelines for delta13C measurements. Anal Chem 78:2439–2441
Czernik J, Goslar T (2001) Preparation of graphite targets in the Gliwice Radiocarbon Laboratory for AMS 14C dating. Radiocarbon 43:283–291
Durant JL, Busby WF, Lafleur AL, Penman BW, Crespi CL (1996) Human cell mutagenicity of oxygenated, nitrated and unsubstituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with urban aerosols. Mutat Res - Genet Toxicol 371:123–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1218(96)90103-2
Furman P, Styszko K, Skiba A, Zięba D, Zimnoch M, Kistler M, Kasper-Giebl A, Gilardoni S (2021) Seasonal variability of PM10 chemical composition including 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene, marker of plastic combustion and toxicity in wadowice, south poland. Aerosol Air Qual Res 21:1–12. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2020.05.0223
Genga A, Ielpo P, Siciliano T, Siciliano M (2017) Carbonaceous particles and aerosol mass closure in PM2.5 collected in a port city. Atmos Res 183:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.08.022
Górka M, Jȩdrysek MO (2008) δ13C of organic atmospheric dust deposited in Wrocław (SW Poland): critical remarks on the passive method. Geol Quarterly 52:115–126
Hampel R, Peters A, Beelen R, Brunekreef B, Cyrys J, Faire UD, Hoogh KD, Fuks K, Hoffmann B, Hüls A, Imboden M, Jedynska A, Kooter I, Koenig W, Künzli N, Leander K, Magnusson P, Männistö S, Penell J, Pershagen G, Phuleria H, Probst-hensch N, Pundt N, Schaffner E, Schikowski T, Sugiri D, Tiittanen P, Tsai M, Wang M, Wolf K, Lanki T (2015) Long-term effects of elemental composition of particulate matter on in fl ammatory blood markers in European cohorts. Environ Int 82:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.05.008
Harrison RM, Jones AM, Lawrence RG (2003) A pragmatic mass closure model for airborne particulate matter at urban background and roadside sites. Atmos Environ 37:4927–4933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.08.025
Ho KF, Lee SC, Cao JJ, Chow JC, Watson JG, Chan CK (2006) Seasonal variations and mass closure analysis of particulate matter in Hong Kong. Sci Total Environ 355:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.03.013
Hueglin C, Gehrig R, Baltensperger U, Gysel M, Monn C, Vonmont H (2005) Chemical characterisation of PM2.5, PM10 and coarse particles at urban, near-city and rural sites in Switzerland. Atmos Environ 39:637–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.027
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00478-5
Jakovljević I, Pehnec G, Vađić V, Čačković M, Tomašić V, Jelinić JD (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 particle fractions in an urban area. Air Qual Atmos Health 11:843–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0603-3
Jandacka D, Durcanska D, Bujdos M (2017) The contribution of road traffic to particulate matter and metals in air pollution in the vicinity of an urban road. Transp Res Part D 50:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2016.11.024
Jandacka D, Durcanska D, Cibula R (2022) Concentration and inorganic elemental analysis of particulate matter in a road tunnel environment (Žilina, Slovakia): contribution of non-exhaust sources. Front Environ Sci 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.952577
Kozielska B, Rogula-Kozłowska W, Klejnowski K (2015) Seasonal variations in health hazards from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bound to submicrometer particles at three characteristic sites in the heavily polluted polish region. Atmosphere 6:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6010001
Krakow City Hall (2017). eng. Krakow in numbers 2016; ISSN 2450-968X; Kraków, pp. 1–28. https://www.bip.krakow.pl/zalaczniki/dokumenty/n/186447/karta
Krakow City Hall (2020). eng. Krakow in numbers 2019; ISSN 2450-968X; Kraków, pp. 1–28. https://www.bip.krakow.pl/plik.php?zid=283921&wer=0&new=t&mode=shw
Krakow City Hall (2021). eng. Krakow in numbers 2020; ISSN 2450-968X; Kraków, pp. 1–32. https://www.bip.krakow.pl/zalaczniki/dokumenty/n/316550/karta
Křůmal K, MikuŠka P, Večeřa Z (2013) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hopanes in PM1 aerosols in urban areas. Atmos Environ 67:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.10.033
Lammel G, Röhrl A, Schreiber H (2002) Atmospheric lead and bromine in Germany: post-abatement levels, variabilities and trends. Environ Sci Pollut Res 9:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987589
Lewan MD, Kotarba MJ (2014) Thermal-maturity limit for primary thermogenic-gas generation from humic coals as determined by hydrous pyrolysis. AAPG Bull 98:2581–2610. https://doi.org/10.1306/06021413204
Major I, Furu E, Jonovics R, Hajdas I, Kertesz Z, Molnar M (2012) Method development for the 14C measurement of atmospheric aerosols. Acta Phys Debrecina 83:83–95
Masiol M, Squizzato S, Formenton G, Badiuzzaman K, Hopke PK, Nenes A, Pandis SN, Tositti L, Benetello F, Visin F, Pavoni B (2020) Hybrid multiple-site mass closure and source apportionment of PM 2. 5 and aerosol acidity at major cities in the Po Valley. Sci Total Environ 704:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135287
Matuszko D (2007) Climate of Krakow in the 20th century. Institute of Geography and Spatial Management of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow
Mirante F, Alves C, Pio C, Pindado O, Perez R, Revuelta MA, Artiñano B (2013) Organic composition of size segregated atmospheric particulate matter, during summer and winter sampling campaigns at representative sites in Madrid, Spain. Atmos Res 132–133:345–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.07.005
Mook WG, Van Der Plicht J (1999) Reporting 14C activities and concentrations. Radiocarbon 41:227–239
Nisbet ICT, LaGoy PK (1992) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-2300(92)90009-X
Pacura W, Szramowiat-Sala K, Macherzyński M, Gołaś J, Bielaczyc P (2022) Analysis of micro-contaminants in solid particles from direct injection gasoline vehicles. Energies 15:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155732
Parliament of the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (2016). Public Law No. XVIII/243/16; eng. Resolution on the introduction of restrictions on the operation of installations in which fuels are burned in the area of the Krakow Municipality; Krakow,Poland, p.1–7. http://edziennik.malopolska.uw.gov.pl/ActDetails.aspx?year=2016&poz=812
Querol X, Viana M, Alastuey A, Amato F, Moreno T, Castillo S, Pey J, Rosa JD, Campa ASDL, Artíñano B, Salvador P, Santos SGD, Fernández-Patier R, Moreno-Grau S, Negral L, Minguillón M, Monfort E, Gil J, Inza A, Ortega L, Santamaría J, Zabalza J (2007) Source origin of trace elements in PM from regional background, urban and industrial sites of Spain. Atmos Environ 41:7219–7231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.05.022
Rogula-Kozłowska W, Klejnowski K, Rogula-Kopiec P, Mathews B, Szopa S (2012) A study on the seasonal mass closure of ambient fine and coarse dusts in Zabrze, Poland. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0533-y
Rogula-Kozłowska W, Klejnowski K, Rogula-Kopiec P, Ośródka L, Krajny E, Błaszczak B, Mathews B (2014) Spatial and seasonal variability of the mass concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Poland. Air Qual Atmos Health 7:41–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-013-0222-y
Rosiek, K. (2017). eng. Report on measurements of vehicular traffic volume at the entrances to the city of Krakow; Warszawa, pp. 1–92. https://www.Bip.Krakow.Pl/Zalaczniki/Dokumenty/n/202228/Karta
Ryż A, Ryż K (2009). eng. Krakows Fast Tram. eng. Geoengineering: roads, bridges, tunnels// pl. Geoinżynieria: drogi mosty tunele 1, 20 pp. 12–23. http://inzynieria.com/czasopisma/wydania/gdmt
Samek L, Stegowski Z, Styszko K, Furman L, Fiedor J (2018) Seasonal contribution of assessed sources to submicron and fine particulate matter in a Central European urban area. Environ Pollut 241:406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.082
Samek L, Styszko K, Stegowski Z, Zimnoch M, Skiba A, Turek-Fijak A, Gorczyca Z, Furman P, Kasper-Giebl A, Rozanski K (2021) Comparison of PM10 sources at traffic and urban background sites based on elemental, chemical and isotopic composition: case study from Krakow, Southern Poland. Atmosphere 12:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101364
Samek L, Stegowski Z, Furman L, Styszko K, Szramowiat K, Fiedor J (2017) Quantitative assessment of PM2.5 sources and their seasonal variation in Krakow. Water Air Soil Pollut 228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3483-5
Samek L, Stegowski Z, Styszko K, Furman L, Zimnoch M, Skiba A, Kistler M, Kasper-Giebl A, Rozanski K, Konduracka E (2020a) Seasonal variations of chemical composition of PM2.5 fraction in the urban area of Krakow, Poland: PMF source attribution. Air Qual Atmos Health 13:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00773-x
Samek L, Turek-Fijak A, Skiba A, Furman P, Styszko K, Furman L, Stegowski Z (2020b) Complex characterization of fine fraction and source contribution to PM2.5 mass at an urban area in Central Europe. Atmosphere 11(10):1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00773-x
Sillanpää M, Hillamo R, Saarikoski S, Frey A, Pennanen A, Makkonen U, Spolnik Z, Van Grieken R, Braniš M, Brunekreef B, Chalbot MC, Kuhlbusch T, Sunyer J, Kerminen VM, Kulmala M, Salonen RO (2006) Chemical composition and mass closure of particulate matter at six urban sites in Europe. Atmos Environ 40:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.01.063
Stenström KE, Skog G, Georgiadou E, Genberg J, Mellström A (2011) A guide to radiocarbon units and calculations. (LUNFD6(NFFR-3111)/1-17/(2011)). Lund University, Nuclear Physics
Sternbeck J, Sjödin Å, Andréasson K (2002) Metal emissions from road traffic and the influence of resuspension - results from two tunnel studies. Atmos Environ 36:4735–4744. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00561-7
Szramowiat K, Woodburn J, Pacura W, Berent K, Bielaczyc P, Gołaś J (2018) Engine-generated solid particles – a case study. Combust Engines 174:33–39. https://doi.org/10.19206/ce-2018-304
Szramowiat-Sala K, Korzeniewska A, Sornek K, Marczak M, Wierońska F, Berent K, Gołaś J, Filipowicz M (2019) The properties of particulate matter generated during wood combustion in in-use stoves. Fuel 253:792–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.05.026
Van Der Plicht J, Hogg A (2006) Short communication A note on reporting radiocarbon. Quat Geochronol 1:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quageo.2006.07.001
Wedepohl KH (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1217–1232
Willett KL, Gardinali PR, Sericano JL, Wade TL, Safe SH (1997) Characterization of the H4IIE rat hepatoma cell bioassay for evaluation of environmental samples containing polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900211
Yatkin S, Bayram A (2007) Elemental composition and sources of particulate matter in the ambient air of a metropolitan city. Atmos Res 85:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.12.002
Yin J, Harrison RM (2008) Pragmatic mass closure study for PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10 at roadside, urban background and rural sites. Atmos Environ 42:980–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.005
Zimnoch M, Morawski F, Kuc T, Samek L, Bartyzel J, Gorczyca Z, Skiba A, Rozanski K (2020a) Summer-winter contrast in carbon isotope and elemental composition of total suspended particulate matter in the urban atmosphere of Krakow, Southern Poland. Nukleonika 65:181–191. https://doi.org/10.2478/nuka-2020-0029
Zimnoch M, Samek L, Furman L, Styszko K, Skiba A, Gorczyca Z, Galkowski M, Rozanski K, Konduracka E (2020b) Application of natural carbon isotopes for emission source apportionment of carbonaceous particulate matter in urban atmosphere: A case study from Krakow, Southern Poland. Sustainability 12:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145777
Funding
The project was financed by the Polish National Science Centre (grant no. 2019/33/N/ST10/02925). Contribution of KS was partly supported by program “Excellence initiative—research university” for the AGH University of Science and Technology No. 42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AS, KS, KR; methodology: AS, KS, PF, KSS, LS, ZG, DW, AKG, KR; validation: AS, KS, PF, KSS, LS, ZG, DW, AKG, KR; formal analysis: AS; investigation: AS, PF, KSS, LS, ZG, DW; resources: AS, KS, LS, ZG, DW, AKG; data curation: AS, KS, KSS; writing — original draft: AS, KR; writing — review and editing: KS, PF, KSS, LS, DW, ZG, AKG; visualization: AS, KS; supervision: KS, KR; project administration: AS, KS; funding acquisition: AS, KS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors and participants of the funding consortium have approved publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerhard Lammel
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Skiba, A., Styszko, K., Furman, P. et al. Source apportionment of suspended particulate matter (PM1, PM2.5 and PM10) collected in road and tram tunnels in Krakow, Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 14690–14703 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32000-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32000-1