Abstract
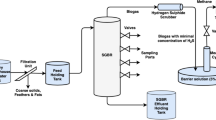
A lab-scale gravity-driven bioreactor (GDB) was designed and constructed to evaluate the simultaneous treatment of black liquor and domestic wastewater. The GDB was operated with a mixture of black liquor and domestic wastewater at a ratio of 1:1 and maintained at an average organic loading rate of 1235 mg-COD/L-Day. The wastewater was fed to the primary sedimentation tank at a flow rate of approximately 12 mL/min and subsequently passed through serially connected anaerobic and aerobic chambers with the same flow rate. Each wastewater sample was allowed to undergo a hydraulic retention time of approximately 72 h, ensuring effective treatment. The GDB was actively operated for nine samples (W1–W9) at a weekly frequency. The entire process was conducted within the workstation’s ambient temperature range of 30–35 °C to sustain microbial activity and treatment efficiency in an open environment. The performance of the GDB was evaluated in terms of various pollution indicators, including COD, BOD5, lignin removal, TDS, TSS, EC, PO43−, SO42−, microbial load (CFU/mL and MPN index), total nitrogen, and color reduction. The results showed that the GDB achieved promising treatment efficiencies: 84.5% for COD, 71.80% for BOD5, 82.8% for TDS, 100% for TSS, 74.71% for E.C., 67.25% for PO43−, 81% for SO42−, and 69.36% for TN. Additionally, about 80% reduction in lignin content and 57% color reduction were observed after the treatment. The GDB substantially reduced microbial load in CFU/mL (77.98%) and MPN (90%). This study marks the first to report on wastewater treatment from two different sources (black liquor and domestic wastewater) using a simple GDB design. Furthermore, it highlights the GDB’s potential as a cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and efficient solution for wastewater treatment, with no need for supplementary chemical or physical agents and zero operational costs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz OY, Brink DP, Prothmann J, Ravi K, Sun M, García-Hidalgo J, Sandahl M, Hulteberg CP, Turner C, Lidén G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2016) Biological valorization of low molecular weight lignin. Biotechnol Adv 34(8):1318–1346
American Public Health Association (1926) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, vol 6. American Public Health Association
Ashrafi O, Yerushalmi L, Haghighat F (2015) Wastewater treatment in the pulp-and-paper industry: a review of treatment processes and the associated greenhouse gas emission. J Environ Manag 158:146–157
Bajpai P (2016) Structure of lignocellulosic biomass. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuel production. Springer, Singapore, pp 7–12
Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1994) Biological colour removal of pulp and paper mill wastewaters. J Biotechnol 33(3):211–220
Bajpai P, Bajpai P (2018) Biological treatment of pulp and paper mill effluents. In: Biotechnology for Pulp and Paper Processing. Springer, Singapore, pp 313–369
Blumenthal UJ, Mara DD, Peasey A, Ruiz-Palacios G, Stott R (2000) Guidelines for the microbiological quality of treated wastewater used in agriculture: recommendations for revising WHO guidelines. Bull World Health Organ 78:1104–1116
Bottrell SH, Hatfield D, Bartlett R, Spence MJ, Bartle KD, Mortimer RJ (2010) Concentrations, sulfur isotopic compositions and origin of organosulfur compounds in pore waters of a highly polluted raised peatland. Organ Geochem 41(1):55–62
Castro FD, Bassin JP, Dezotti M (2017) Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater containing the Reactive Orange 16 azo dye by a combination of ozonation and moving-bed biofilm reactor: evaluating the performance, toxicity, and oxidation by-products. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6307–6316
Chandra R, Raj A, Purohit HJ, Kapley A (2007) Characterisation and optimisation of three potential aerobic bacterial strains for kraft lignin degradation from pulp paper waste. Chemosphere 67(4):839–846
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Biores Technol 99(10):4044–4064
Chong S, Sen TK, Kayaalp A, Ang HM (2012) The performance enhancements of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors for domestic sludge treatment–a state-of-the-art review. Water Res 46(11):3434–3470
Collivignarelli MC, Abbà A, Miino MC, Damiani S (2019) Treatments for colour removal from wastewater: state of the art. J Environ Manag 236:727–745
Costa S, Dedola DG, Pellizzari S, Blo R, Rugiero I, Pedrini P, Tamburini E (2017) Lignin biodegradation in pulp-and-paper mill wastewater by selected white rot fungi. Water 9(12):935
Daraz U, Li Y, Ahmad I, Iqbal R, Ditta A (2022) Remediation technologies for acid mine drainage: recent trends and future perspectives. Chemosphere 137089
Dick JG, Malvessi E (2022) Strategies for reuse and recycling of water and effluents in pulp and paper industries. Res Soc Dev 11(13):e568111335950–e568111335950
Duan J, Huo X, Du WJ, Liang JD, Wang DQ, Yang SC (2016) Biodegradation of kraft lignin by a newly isolated anaerobic bacterial strain, Acetoanaerobium sp. WJDL-Y2. Lett Appl Microbiol 62(1):55–62
EPA Environmental Protection Agency (2014) Sediments. In: Water: pollution prevention & control. Retrieved from http://water.epa.gov/polwaste/sediments. Accessed June–August 2023
Faubert P, Barnabé S, Bouchard S, Côté R, Villeneuve C (2016) Pulp and paper mill sludge management practices: what are the challenges to assessing the impacts on greenhouse gas emissions. Resour Conserv Recycl 108:107–133
Guo H, Yao HY, Huang QQ, Li T, Show DY, Ling M, ... Lee DJ (2023) Anaerobic–anoxic–oxic biological treatment of high-strength, highly recalcitrant polyphenylene sulfide wastewater. Bioresour Technol 371:128640
Hermosilla D, Merayo N, Gascó A, Blanco Á (2015) The application of advanced oxidation technologies to the treatment of effluents from the pulp and paper industry: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(1):168–191
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PH, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology 9th. William & Wilkins, Baltimor
Huang Y, Ding W, Zhou X, Jin W, Han W, Chi K, ... Jiang G (2022) Sub-pilot scale cultivation of Tetradesmus dimorphus in wastewater for biomass production and nutrients removal: effects of photoperiod, CO2 concentration and aeration intensity. J Water Process Eng 49:103003
Hubbe MA, Metts JR, Hermosilla D, Blanco MA, Yerushalmi L, Haghighat F, ... Elliott A (2016) Wastewater treatment and reclamation: a review of pulp and paper industry practices and opportunities. BioResources 11(3):7953–8091
Ju F, Beck K, Yin X, Maccagnan A, McArdell CS, Singer HP, ... Bürgmann H (2019) Wastewater treatment plant resistomes are shaped by bacterial composition, genetic exchange, and upregulated expression in the effluent microbiomes. ISME J 13(2):346–360
Kamali M, Khodaparast Z (2015) Review on recent developments on pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 114:326–342
Karadag D, Köroğlu OE, Ozkaya B, Cakmakci M (2015) A review on anaerobic biofilm reactors for the treatment of dairy industry wastewater. Process Biochem 50(2):262–271
Khan SI, Zada NS, Sahinkaya M, Colak DN, Ahmed S, Hasan F, Belduz AO, Çanakçi S, Khan S, Badshah M, Shah AA (2021) Cloning, expression and biochemical characterization of lignin-degrading DyP-type peroxidase from Bacillus sp. Strain BL5. Enzyme Microb Technol 151:109917
Khan SI, Zarin A, Ahmed S, Hasan F, Belduz AO, Çanakçi S, ... Shah AA (2022) Degradation of lignin by Bacillus altitudinis SL7 isolated from pulp and paper mill effluent. Water Sci Technol 85(1):420–432
Khanthong K, Jang H, Kadam R, Jo S, Lee J, Jungyu P (2023) Bioelectrochemical system for nitrogen removal: fundamentals, current status, trends, and challenges. Chemosphere 139776
Kinnarinen T, Golmaei M, Jernström E, Häkkinen A (2016) Separation, treatment and utilization of inorganic residues of chemical pulp mills. J Clean Prod 133:953–964
Lappalainen J, Baudouin D, Hornung U, Schuler J, Melin K, Bjelić S, Vogel F, Konttinen J, Joronen T (2020) Sub-and supercritical water liquefaction of kraft lignin and black liquor derived lignin. Energies 13(13):3309
Lin H, Gao W, Meng F, Liao BQ, Leung KT, Zhao L, ... Hong H (2012) Membrane bioreactors for industrial wastewater treatment: a critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(7):677–740
Lindholm-Lehto PC, Knuutinen JS, Ahkola HS, Herve SH (2015) Refractory organic pollutants and toxicity in pulp and paper mill wastewaters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(9):6473–6499
Liu X, Shen F, Smith RL Jr, Qi X (2019) Black liquor-derived calcium-activated biochar for recovery of phosphate from aqueous solutions. Biores Technol 294:122198
Lu JJ, Zhang H, Li W, Yi JB, Sun FY, Zhao YW, ... Dong WY (2022) Biofilm stratification in counter-diffused membrane biofilm bioreactors (MBfRs) for aerobic methane oxidation coupled to aerobic/anoxic denitrification: effect of oxygen pressure. Water Res 226:119243
Luan YN, Yin Y, An Y, Zhang F, Wang X, Zhao F, ... Liu C (2022) Investigation of an intermittently-aerated moving bed biofilm reactor in rural wastewater treatment under low dissolved oxygen and C/N condition. Bioresour Technol 358:127405
Mahto KU, Das S (2022) Bacterial biofilm and extracellular polymeric substances in the moving bed biofilm reactor for wastewater treatment: a review. Biores Technol 345:126476
Majumdar S, Priyadarshinee R, Kumar A, Mandal T, Mandal DD (2019) Exploring Planococcus sp. TRC1, a bacterial isolate, for carotenoid pigment production and detoxification of paper mill effluent in immobilized fluidized bed reactor. J Clean Prod 211:1389–1402
Naz I, Seher S, Perveen I, Saroj DP, Ahmed S (2015) Physiological activities associated with biofilm growth in attached and suspended growth bioreactors under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Environ Technol 36(13):1657–1671
Naz I, Ullah W, Sehar S, Rehman A, Khan ZU, Ali N, Ahmed S (2016) Performance evaluation of stone-media pro-type pilot-scale trickling biofilter system for municipal wastewater treatment. Desalin Water Treat 57(34):15792–15805
Ni M, Chen Y, Pan Y, Huang Y, Li DP, Li L, ... Song Z (2022) Study on community structure and metabolic mechanism of dominant polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) and glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs) in suspended biofilm based on phosphate recovery. Sci Total Environ 815:152678
Paliwal R, Uniyal S, Rai JPN (2015) Evaluating the potential of immobilized bacterial consortium for black liquor biodegradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(9):6842–6853
Patel K, Patel N, Vaghamshi N, Shah K, Duggirala SM, Dudhagara P (2021) Trends and strategies in the effluent treatment of pulp and paper industries: a review highlighting reactor options. Curr Res Microb Sci 2:100077
Pathak C, Chopra AK, Srivastava S (2013) Accumulation of heavy metals in Spinacia oleracea irrigated with paper mill effluent and sewage. Environ Monit Assess 185(9):7343–7352
Pritchard M, Mkandawire T, O’neill JG (2007) Biological, chemical and physical drinking water quality from shallow wells in Malawi: case study of Blantyre, Chiradzulu and Mulanje. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 32(15–18):1167–1177
Rasool T, Rehman A, Naz I, Ullah R, Ahmed S (2018) Efficiency of a locally designed pilot-scale trickling biofilter (TBF) system in natural environment for the treatment of domestic wastewater. Environ Technol 39(10):1295–1306
Rehman A, Naz I, Khan ZU, Rafiq M, Naeem A, Ahmad S (2012) Sequential application of plastic media-trickling filter and sand filter for domestic wastewater treatment at low temperature condition. Br Biotechnol J 2(4):179
Rehman A, Anees M, Sehar S, Alhewairini SS, Saroj DP, Ahmed S (2021) Simulated modelling, design, and performance evaluation of a pilot-scale trickling filter system for removal of carbonaceous pollutants from domestic wastewater. Water 13(22):3210
Rehman A, Zakir B, Anees M, Naz I, Alhewairini SS, Sehar S (2022) Bio-purification of domestic wastewater through constructed wetland planted with Paspalidiumflavidum. Water Environ Res 94(1):e1685
Rice EW (ed) (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, vol 10. American public health association, Washington DC
Rinaldi R, Jastrzebski R, Clough MT, Ralph J, Kennema M, Bruijnincx PC, Weckhuysen BM (2016) Paving the way for lignin valorisation: recent advances in bioengineering, biorefining and catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(29):8164–8215
Sehar S, Naeem S, Perveen I, Ali N, Ahmed S (2015) A comparative study of macrophytes influence on wastewater treatment through subsurface flow hybrid constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 81:62–69
Sehar S, Naz I, Das T, Ahmed S (2016a) Evidence of microscopic correlation between biofilm kinetics and divalent cations for enhanced wastewater treatment efficiency. RSC Adv 6(18):15112–15120
Sehar S, Naz I, Khan S, Naeem S, Perveen I, Ali N, Ahmed S (2016b) Performance evaluation of integrated constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 88(3):280–7
Singh AK, Chandra R (2019) Pollutants released from the pulp paper industry: aquatic toxicity and their health hazards. Aquat Toxicol 211:202–216
Singh SP, Bansal MC, Singh SP, Singh AM, Dixit AK (2015) Rheological properties and statistical analysis of wheat straw soda black liquor. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Util Environ Eff 37(24):2639–2646
Solana ADJM, Nájera MJ (2016) Cost-effective advantages due to clean technologies: water compliance scenarios for a Mexican paper mill. J Cleaner Prod 112:4701–4709
Soo PL, Bashir MJ, Wong LP (2022) Recent advancements in the treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using anaerobic biofilm reactors: challenges and future perspectives. J Environ Manag 320:115750
Stein OR, Borden-Stewart DJ, Hook PB, Jones WL (2007) Seasonal influence on sulfate reduction and zinc sequestration in subsurface treatment wetlands. Water Res 41(15):3440–3448
Stillger L, Müller D (2022) Peptide-coating combating antimicrobial contaminations: a review of covalent immobilization strategies for industrial applications. J Mater Sci 57(24):10863–10885
Stokke DD, Wu Q, Han G (2013) Introduction to wood and natural fiber composites. John Wiley & Sons
Toczyłowska-Mamińska R (2017) Limits and perspectives of pulp and paper industry wastewater treatment–A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 78:764–772
US-EPA (2007) Bureau of Water Supply and Wastewater Management: Department of Environmental Protection Agency, Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator Training (Module 20: Trickling filters
Virkutyte J (2017) Aerobic treatment of effluents from pulp and paper industries. In: Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering, pp. 103–130
World Health Organization (2006) WHO guidelines for the safe use of wasterwater excreta and greywater (Vol. 1). World Health Organization
Xu Z, Qin L, Cai M, Hua W, Jin M (2018) Biodegradation of kraft lignin by newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas putida, and Ochrobactrum tritici strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14171–14181
Zhang C, Chen J, Wen Z (2012) Alternative policy assessment for water pollution control in China’s pulp and paper industry. Resour Conserv Recycl 66:15–26
Zhang S, Xiao J, Wang G, Chen G (2020) Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignin by ligninolytic enzymes and analysis of the hydrolyzed lignin products. Biores Technol 304:122975
Funding
This research work was part of a project entitled “Development of biological treatment system for pulp and paper industry waste water”. It was sponsored by the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan, (NRPU) Grant Number 6871.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, concept, data collection, and analysis were performed by TR, AJ, MIA, MB, MA, IA, ZH, and MU. The first draft of the manuscript was written by TR and AJ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The manuscript is submitted after the approval of all coauthors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors have read the final manuscript and agreed to submit.
Consent for publication
All authors have carefully read the final manuscript and agreed to publish it in “Environmental Science and Pollution Research.”
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rasool, T., Ansar, M., Ali, I. et al. Performance evaluation of gravity-driven bioreactor (GDB) for simultaneous treatment of black liquor and domestic wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 7043–7057 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31576-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31576-4