Abstract
In terms of achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs), the developing economies are facing many issues, and one of the key issues is environmental degradation. Being a developing economy, Pakistan is also experiencing thought-provoking impacts of global warming and still far away from the ideal track of sustainable development. For addressing environment-related issue and achieving the targets of SDGs, a policy-level reorientation might be necessary. In this view, this study investigates the impact of economic growth, transport infrastructure, urbanization, financial development, and renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions by using the data of Pakistan during 1990–2020. For this purpose, we use novel wavelet quantile correlation approach. The empirical results of wavelet quantile correlation approach demonstrate that economic growth, transport infrastructure, urbanization, and financial development are responsible for environmental pollution. Whereas, result also claims that renewable energy consumption is a useful tool for reducing environmental pollution in Pakistan. Moreover, the results of FMOLS approach show that 1% increase in economic growth, transportation infrastructure, urbanization, and financial development increases CO2 emissions by 0.240, 0.010, 0.478, and 0.102%, respectively. However, 1% increase in renewable energy usage reduces CO2 emission by 1.083%. Based on the empirical outcomes, this study proposes comprehensive policy framework for achieving the targets of SDG 7 (clean energy), SDG 8 (economic growth), SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities), and SDG 13 (climate action).
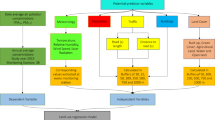
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available upon request.
References
Acheampong AO, Dzator J, Dzator M, Salim R (2022) Unveiling the effect of transport infrastructure and technological innovation on economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 182:121843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121843
Ağbulut Ü (2022) Forecasting of transportation-related energy demand and CO2 emissions in Turkey with different machine learning algorithms. Sustain Prod Consump 29:141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.10.001
Ahmed M, Azam M, Khan AM (2022) Testing stationarity of per capita energy consumption across the globe: a better picture using the wavelet framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(43):65334–65352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20416-6
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Majeed A, Raza MY (2020) Does financial development and foreign direct investment improve environmental quality? Evidence from belt and road countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:23586–23601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08748-7
Akadiri SS, Adebayo TS (2022) Asymmetric nexus among financial globalization, non-renewable energy, renewable energy use, economic growth, and carbon emissions: impact on environmental sustainability targets in India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):16311–16323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16849-0
Akhtar N, Syakir Ishak MI, Bhawani SA, Umar K (2021) Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: a review. Water 13(19):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192660
Andong RF, Sajor E (2017) Urban sprawl, public transport, and increasing CO 2 emissions: the case of Metro Manila, Philippines. Environ Dev Sustain 19:99–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9729-8
Arfanuzzaman M, Dahiya B (2019) Sustainable urbanization in Southeast Asia and beyond: challenges of population growth, land use change, and environmental health. Growth Chang 50(2):725–744. https://doi.org/10.1111/grow.12297
Asher S, Garg T, Novosad P (2020) The ecological impact of transportation infrastructure. Econ J 130(629):1173–1199. https://doi.org/10.1093/ej/ueaa013
Avotra AARN, Nawaz A (2023) Asymmetric impact of transportation on carbon emissions influencing SDGs of climate change. Chemosphere 324:138301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138301
Badulescu D, Simut R, Badulescu A, Badulescu AV (2019) The relative effects of economic growth, environmental pollution and non-communicable diseases on health expenditures in European Union countries. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(24):5115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245115
Bakr AR, Fu GY, Hedeen D (2020) Water quality impacts of bridge stormwater runoff from scupper drains on receiving waters: a review. Sci Total Environ 726:138068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138068
Baloch MA, Zhang J, Iqbal K, Iqbal Z (2019) The effect of financial development on ecological footprint in BRI countries: evidence from panel data estimation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6199–6208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3992-9
Chandran VGR, Tang CF (2013) The impacts of transport energy consumption, foreign direct investment and income on CO2 emissions in ASEAN-5 economies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 24:445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.03.054
Charfeddine L (2017) The impact of energy consumption and economic development on ecological footprint and CO2 emissions: evidence from a Markov switching equilibrium correction model. Energy Econ 65:355–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.05.009
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:138–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.031
Chatti W (2021) Moving towards environmental sustainability: information and communication technology (ICT), freight transport, and CO2 emissions. Heliyon 7(10):e08190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08190
Chaudhry SM, Ahmed R, Shafiullah M, Huynh TLD (2020) The impact of carbon emissions on country risk: evidence from the G7 economies. J Environ Manag 265:110533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110533
Cui L, Weng S, Nadeem AM, Rafique MZ, Shahzad U (2022) Exploring the role of renewable energy, urbanization and structural change for environmental sustainability: comparative analysis for practical implications. Renew Energy 184:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.11.075
Fang C, Liu H, Wang S (2021) The coupling curve between urbanization and the eco-environment: China’s urban agglomeration as a case study. Ecol Indic 130:108107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108107
Fang C, Wang S, Li G (2015) Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: a case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl Energy 158:519–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.08.095
Ganda F, Milondzo KS (2018) The impact of carbon emissions on corporate financial performance: evidence from the South African firms. Sustainability 10(7):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072398
Ge M, Kannaiah D, Li J, Khan N, Shabbir MS, Bilal K, Tabash MI (2022) Does foreign private investment affect the clean industrial environment? Nexus among foreign private investment, CO2 emissions, energy consumption, trade openness, and sustainable economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(18):26182–26189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18814-x
Godil DI, Sharif A, Agha H, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) The dynamic nonlinear influence of ICT, financial development, and institutional quality on CO2 emission in Pakistan: new insights from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:24190–24200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08619-1
Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Onifade ST, Ampomah AB (2022) Beyond the environmental Kuznets curve: do combined impacts of air transport and rail transport matter for environmental sustainability amidst energy use in E7 economies? Environ Dev Sustain 24:11852–11870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01944-6
Haini H (2021) Examining the impact of ICT, human capital and carbon emissions: evidence from the ASEAN economies. Int Econ 166:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inteco.2021.03.003
Huang Y, Xu F, Abbas A, Zhang Y, Kim E (2023) Empirical impact of China-Pak business cycle synchronization on environmental degradation in Pakistan. Front Environ Sci 10:1030408. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1030408
Hussain J, Zhou K (2022) Globalization, industrialization, and urbanization in Belt and Road Initiative countries: implications for environmental sustainability and energy demand. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(53):80549–80567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21520-3
IEA (2022) Energy Statistics Data Browser. IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/energy-statistics-data-browser
International Energy Agency (2016) World Energy Outlook 2016. Int Energy Agency:1–8 http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/WEB_WorldEnergyOutlook2015ExecutiveSummaryEnglishFinal.pdf.
Iqbal A, Tang X, Rasool SF (2023) Investigating the nexus between CO2 emissions, renewable energy consumption, FDI, exports and economic growth: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Dev Sustain 25(3):2234–2263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02128-6
Jahanger A, Awan A, Anwar A, Adebayo TS (2023) Greening the Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS) economies: assessing the impact of electricity consumption, natural resources, and renewable energy on environmental footprint. Nat Resour Forum 47(3):484–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-8947.12294
Jalal R, Gopinathan R (2023) Time-frequency relationship between energy imports, energy prices, exchange rate, and policy uncertainties in India: evidence from wavelet quantile correlation approach. Financ Res Lett 55:103980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.103980
Jiang Y, Zhou Z, Liu C (2019) The impact of public transportation on carbon emissions: a panel quantile analysis based on Chinese provincial data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(4):4000–4012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3921-y
Jiang Q, Rahman ZU, Zhang X, Guo Z, Xie Q (2022a) An assessment of the impact of natural resources, energy, institutional quality, and financial development on CO2 emissions: evidence from the B&R nations. Res Policy 76:102716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102716
Jiang T, Li S, Yu Y, Peng Y (2022b) Energy-related carbon emissions and structural emissions reduction of China’s construction industry: the perspective of input–output analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(26):39515–39527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17604-1
Jiang Y, Sharif A, Anwar A, Cong PT, Lelchumanan B, Yen VT, Vinh NTT (2023) Does green growth in E-7 countries depend on economic policy uncertainty, institutional quality, and renewable energy? Evidence from quantile-based regression. Geosci Front 14(6):101652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101652
Karthick L, Michel J, Jagadish CA (2022) Vehicle safety system for two wheeler—a critical review. Materials Today: Proceedings 52:1594–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.258
Katircioğlu S, Katircioğlu S (2018) Testing the role of urban development in the conventional environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from Turkey. Appl Econ Lett 25(11):741–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2017.1361004
Khan H, Weili L, Khan I, Zhang J (2023) The nexus between natural resources, renewable energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission in BRI countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(13):36692–36709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24193-0
Khan SAR, Sharif A, Golpîra H, Kumar A (2019a) A green ideology in Asian emerging economies: from environmental policy and sustainable development. Sustain Dev 27(6):1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1958
Khan SAR, Zhang Y, Anees M, Golpîra H, Lahmar A, Qianli D (2018) Green supply chain management, economic growth and environment: a GMM based evidence. J Clean Prod 185:588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.226
Khan S, Majeed MT (2023) Toward economic growth without emissions growth: the role of urbanization & industrialization in Pakistan. J Environ Stud Sci 13(1):43–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13412-022-00797-3
Khan S, Peng Z, Li Y (2019b) Energy consumption, environmental degradation, economic growth and financial development in globe: dynamic simultaneous equations panel analysis. Energy Rep 5:1089–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.08.004
Kumar AS, Padakandla SR (2022) Testing the safe-haven properties of gold and bitcoin in the backdrop of COVID-19: a wavelet quantile correlation approach. Financ Res Lett 47:102707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2022.102707
Li G, Li Y, Tsai CL (2015) Quantile correlations and quantile autoregressive modeling. J Am Stat Assoc 110(509):246–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2014.892007
Lin B, Omoju OE (2017) Does private investment in the transport sector mitigate the environmental impact of urbanisation? Evidence from Asia. J Clean Prod 153:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.064
Luo W, Bai H, Jing Q, Liu T, Xu H (2018) Urbanization-induced ecological degradation in Midwestern China: an analysis based on an improved ecological footprint model. Resour Conserv Recycl 137:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.05.015
Luo Z, Lam SK, Fu H, Hu S, Chen D (2019) Temporal and spatial evolution of nitrous oxide emissions in China: assessment, strategy and recommendation. J Clean Prod 223:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.134
Ma S, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang LJ, Jiang J, Zhang J (2022) Distinguishing the relative contributions of climate and land use/cover changes to ecosystem services from a geospatial perspective. Ecol Indic 136:108645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108645
Maddala GS, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 61(S1):631–652
Mahmood H, Alkhateeb TTY, Furqan M (2020) Industrialization, urbanization and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: asymmetry analysis. Energy Rep 6:1553–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.06.004
Marques A, Martins IS, Kastner T, Plutzar C, Theurl MC, Eisenmenger N, Pereira HM (2019) Increasing impacts of land use on biodiversity and carbon sequestration driven by population and economic growth. Nat Ecol Evol 3(4):628–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-019-0824-3
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2017) Testing the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:1366–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.039
Murshed M, Ahmed R, Kumpamool C, Bassim M, Elheddad M (2021) The effects of regional trade integration and renewable energy transition on environmental quality: evidence from South Asian neighbors. Bus Strateg Environ 30(8):4154–4170. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2862
Nathaniel S, Anyanwu O, Shah M (2020) Renewable energy, urbanization, and ecological footprint in the Middle East and North Africa region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:14601–14613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08017-7
Nguyen TT, Pham TAT, Tram HTX (2020) Role of information and communication technologies and innovation in driving carbon emissions and economic growth in selected G-20 countries. J Environ Manag 261:110162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110162
Okunolа AM, Nathaniel SP, Festus VB (2018) Revisiting population growth and food production nexus in Nigeria: an ARDL approach to cointegration. Agricult Resour Econ Int Sci E-J 4:41–51. https://doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.281759
PBS (2023) Retrieved from Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, Government of Pakistan. https://www.pbs.gov.pk/
PEC (2022) Pakistan economic survey, finance division, ministry of finance, Government of Pakistan. https://www.finance.gov.pk/survey_2022.html
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Prus P, Sikora M (2021) The impact of transport infrastructure on the sustainable development of the region—Case study. Agriculture 11(4):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040279
Ramzan M, Raza SA, Usman M, Sharma GD, Iqbal HA (2022) Environmental cost of non-renewable energy and economic progress: do ICT and financial development mitigate some burden? J Clean Prod 333:130066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130066
Rehman A, Alam MM, Ozturk I, Alvarado R, Murshed M, Işık C, Ma H (2023a) Globalization and renewable energy use: how are they contributing to upsurge the CO2 emissions? A global perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(4):9699–9712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22775-6
Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Işık C, Ozturk I (2023b) Estimating interlinks of carbon emissions from transportation, industrialization, and solid/liquid fuels with economic progress: evidence from Pakistan. Int J Environ Sci Technol 20(2):1981–1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04111-0
Ritchie H (2020) Cars, planes, trains: where do CO2 emissions from transport come from? Our World in Data. (Available at https://ourworldindata.org/co2-emissions-from-transport)
Rosqvist LS, Hiselius LW (2016) Online shopping habits and the potential for reductions in carbon dioxide emissions from passenger transport. J Clean Prod 131:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.054
Saboori B, Sapri M, bin Baba, M. (2014) Economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development)‘s transport sector: a fully modified bi-directional relationship approach. Energy 66:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.12.048
Saxe S, Kasraian D (2020) Rethinking environmental LCA life stages for transport infrastructure to facilitate holistic assessment. J Ind Ecol 24(5):1031–1046. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.13010
Shahbaz M, Van Hoang TH, Mahalik MK, Roubaud D (2017) Energy consumption, financial development and economic growth in India: new evidence from a nonlinear and asymmetric analysis. Energy Econ 63:199–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.01.023
Sharma D, Singh S (2016) Instituting environmental sustainability and climate resilience into the governance process: exploring the potential of new urban development schemes in India. Int Area Stud Rev 19(1):90–103. https://doi.org/10.1177/2233865916632942
Shayesteh K, Darani KM, Ildoromi A (2014) Estimating the ecological footprint of transportation in the City of Isphahan (Iran). Curr World Environ 9(3):760. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.3.24
Sikder M, Wang C, Yao X, Huai X, Wu L, KwameYeboah F et al (2022) The integrated impact of GDP growth, industrialization, energy use, and urbanization on CO2 emissions in developing countries: evidence from the panel ARDL approach. Sci Total Environ 837:155795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155795
Sufyanullah K, Ahmad KA, Ali MAS (2022a) Does emission of carbon dioxide is impacted by urbanization? An empirical study of urbanization, energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions-Using ARDL bound testing approach. Energy Policy 164:112908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112908
Sufyanullah K, Ahmad KA, Ali MAS (2022b) Does emission of carbon dioxide is impacted by urbanization? An empirical study of urbanization, energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions-Using ARDL bound testing approach. Energy Policy 164:112908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112908
Sun H, Hu L, Geng Y, Yang G (2020) Uncovering impact factors of carbon emissions from transportation sector: evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Area. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Chang 25:1423–1437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-020-09934-1
Tarigan AK (2019) Expectations, attitudes, and preferences regarding support and purchase of eco-friendly fuel vehicles. J Clean Prod 227:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.190
Voumik LC, Sultana T (2022) Impact of urbanization, industrialization, electrification and renewable energy on the environment in BRICS: fresh evidence from novel CS-ARDL model. Heliyon 8(11):e11457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11457
Wang WZ, Liu LC, Liao H, Wei YM (2021) Impacts of urbanization on carbon emissions: An empirical analysis from OECD countries. Energy Policy 151:112171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112171
Wei G, Bi M, Liu X, Zhang Z, He BJ (2023) Investigating the impact of multi-dimensional urbanization and FDI on carbon emissions in the belt and road initiative region: direct and spillover effects. J Clean Prod 384:135608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135608
World Bank (2023) The World Bank open Data. https://data.worldbank.org/. Accessed 07 Feb 2023
World Energy Council (2016) World Energy Resources 2016. World Energy Resour 2016 4–37. (Available at http://www.worldenergy.org/wpcontent/uploads/2013/09/Complete_WER_2013_Survey.pdf).
Wu Y, Shen J, Zhang X, Skitmore M, Lu W (2016) The impact of urbanization on carbon emissions in developing countries: a Chinese study based on the U-Kaya method. J Clean Prod 135:589–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.121
Xu X, Xu H (2021) The driving factors of carbon emissions in China’s transportation sector: a spatial analysis. Front Energ Res 9:664046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.664046
Yuan H, Feng Y, Lee J, Liu H (2020) The spatio-temporal heterogeneity of financial agglomeration on green development in China cities using GTWR model. Sustainability 12(16):6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166660
Zameer H, Shahbaz M, Vo XV (2020) Reinforcing poverty alleviation efficiency through technological innovation, globalization, and financial development. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 161:120326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120326
Zhang C, Liu C (2015) The impact of ICT industry on CO2 emissions: a regional analysis in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.011
Zhang X, Song X, Lu J, Liu F (2022) How financial development and digital trade affect ecological sustainability: the role of renewable energy using an advanced panel in G-7 Countries. Renew Energy 199:1005–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.09.028
Zhang YJ (2011) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 39(4):2197–2203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.02.026
Zhang YJ, Liu Z, Zhang H, Tan TD (2014) The impact of economic growth, industrial structure and urbanization on carbon emission intensity in China. Nat Hazards 73:579–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1091-x
Zhang Y, Zhang S (2018) The impacts of GDP, trade structure, exchange rate and FDI inflows on China's carbon emissions. Energy Policy 120:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.05.056
Zhao C, Wang K, Dong X, Dong K (2022) Is smart transportation associated with reduced carbon emissions? The case of China. Energy Econ 105:105715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105715
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the participatory contribution of all respondents to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Usman Malik: conceptualization, writing—original draft, data curation, methodology, formal estimations, result interpretation, concluding the study, and policy implications. Zia-ur-Rehman: supervision, editing, writing—original draft, methodology, and validation. Ahsan Anwar: literature review. Arshian Sharif: supervision and editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, M.U., Rehman, Z.u., Sharif, A. et al. Impact of transportation infrastructure and urbanization on environmental pollution: evidence from novel wavelet quantile correlation approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 3014–3030 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31197-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31197-x