Abstract
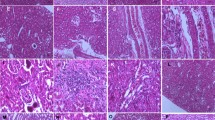
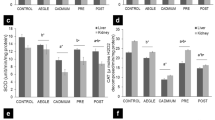
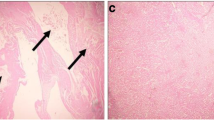
Exposure to cadmium has been related to liver and kidney diseases such as polycystic and nephrotic syndrome. It is still unclear how cadmium contributes to these diseases. It is believed that the induction of oxidative stress resulting from the inhibition of antioxidant enzyme activities and changes in drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver could explain the role of cadmium in the development of different diseases in the kidney and probably other organs. Changes in oxidative stress markers, antioxidant enzymes, and drug-metabolizing enzyme activities were assessed in the liver of male rats exposed to cadmium chloride. Additionally, the protective effects of silymarin and garlic extract against cadmium toxicosis were evaluated. Rats were randomly divided into eight groups as follows, groups 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, received orally saline, CdCl2 (1 mg/kg), garlic extract [800 mg/kg], silymarin (25 mg/kg) and silymarin plus garlic extract respectively for 28 consecutive days. Rats in groups 6, 7, and 8 were pretreated with the same doses of garlic, silymarin, and garlic plus silymarin, respectively for two hours before cadmium administration. The Western immunoblotting technique was used to investigate the protein expression of cytochrome P450 isozymes. Spectrophotometric methods were used to assess the activity of both antioxidant- and drug-metabolizing enzymes. Free radical levels [measured as thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS)], catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase activities increased whereas the levels of glutathione and the activities of glutathione S-transferase, glutathione reductase, and glutamyl transferase, cytochrome P450, aryl hydrocarbon dehydrogenase (AHH), dimethylnitrosamine-N-demethylase I (DMN-dI), 7-ethoxycoumarine-O-deethylase (ECOD), cytochrome b5 and NADPH-Cytochrome-c-reductase enzyme activities decreased after cadmium treatment. Furthermore, Western immunoblotting data revealed that glutathione peroxidase protein expression increased following cadmium exposure, but cytochrome P450 2E1 and 3A4 expressions were downregulated. However, pretreatment of rats with silymarin or garlic extract or both before cadmium administration was found to restore the protein expression of cytochrome P450 2E1 and 3A4, the level of free radicals, antioxidant enzymes, drug-metabolizing enzyme activities to their normal levels. Similarly, histological studies revealed that silymarin and/or garlic extract reduced the liver damage caused by cadmium. Silymarin and/or garlic extract reduced the adverse effects of cadmium on the activity of both drug-metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes activity. These antioxidants could be provided to those who work in cadmium-based sectors to help them cope with the adverse effects of cadmium on their kidneys. In addition, Inhibiting drug-metabolizing enzyme activity should be considered when administering therapeutic medications to persons exposed to cadmium because most therapeutic drugs and many endogenous substances are largely metabolized by these enzymes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AHH:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon dehydrogenase
- DMN-dI:
-
Dimethylnitrosamine-N-demethylase I
- ECOD:
-
7-Ethoxycoumarine-O-deethylase
- GSH:
-
Cytochrome b5, and NADPH-Cytochrome -c-reductase, glutathione
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- DAS:
-
Diallyl sulfide
- DMN:
-
Dimethylnitrosamine
- B(a)P:
-
Benzo(a)pyrene
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferases
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- γ-GT:
-
γ-Glutamyl transferase
References
Abdulmajeed AM, Alharbi BM, Alharby HF et al (2022) Simultaneous Action of Silymarin and Dopamine Enhances Defense Mechanisms Related to Antioxidants, Polyamine Metabolic Enzymes, and Tolerance to Cadmium Stress in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plants (Basel) 11(22):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223069
Allmann S, Mayer L, Olma J, Kaina B, Hofmann TG, Tomicic MT, Christmann M (2020) Benzo[a]pyrene represses DNA repair through altered E2F1/E2F4 function marking an early event in DNA damage-induced cellular senescence. Nucleic Acids Res 48(21):12085–12101. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa965
Altındağ F (2022) Silymarin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by downregulating TNF-α and NF-kB and by upregulating IL-10. J Exper Clin Med 39(1):216–220. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/omujecm/issue/66082/950894
Anderson ME, Meister A (1983) Transport and direct utilization of gamma-glutamylcysteine for glutathione synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80(3):707–711. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.80.3.707
Azeez OM, Akhigbe RE, Anigbogu CN (2012) Exposure to petroleum hydrocarbon: implications in lung lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense system in rat. Toxicol Int 19(3):306–309. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6580.103678
Bakr S, Sayed MA, Salem KM, Morsi EM, Masoud M, Ezzat EM (2023) Lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) blood levels and potential hematological health risk among inhabitants of the claimed hazardous region around Qaroun Lake in Egypt. BMC Public Health 23(1):1071. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-16007-w
Boonpeng S, Siripongvutikorn S, Sae-Wong C, Sutthirak P (2014) The antioxidant and anti-cadmium toxicity properties of garlic extracts. Food Sci Nutr 2(6):792–801. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.164
Bowers LD, Wong ET (1980) Kinetic serum creatinine assays. II. A critical evaluation and review. Clin Chem 26(5):555–61 (PMID: 7020989)
Cao G, Sofic E, Prior RL (1996) Antioxidant capacity of tea and common vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 44:3426–3431 (S0021-8561(96)00253-1)
Chatha AMM, Naz S, Mansouri B, Nawaz A (2023) Accumulation and human healthrisk assessment of trace elements in two fish species, Cirrhinus mrigala and Oreochromis niloticus, at Tarukri Drain, District Rahimyar Khan, Punjab. Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30(19):56522–56533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26337-2
Cheng C, Ma H, Liu G, Fan S, Guo Z (2022) Mechanism of Cadmium Exposure Induced Hepatotoxicity in the Mud Crab (Scylla paramamosain): Activation of Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants (basel) 11(5):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050978
Chia MA, Lombardi AT, da Graça Gama Melão M, Parrish CC (2015) Combined nitrogen limitation and cadmium stress stimulate total carbohydrates, lipids, protein and amino acid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae). Aquat Toxicol. 160:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.002
Chiu DT, Stults FH, Tappel AL (1976) Purification and properties of rat lung soluble glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 445(3):558–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2744(76)90110-8
Cong Y, Chi Q, Teng X, Li S (2019) The Protection of Selenium Against Cadmium-Induced Mitochondrial Damage via the Cytochrome P450 in the Livers of Chicken. Biol Trace Elem Res 190(2):484–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1557-x
De Boer JG, Yang H, Holcroft J, Skov K (2004) Chemoprotection against N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced mutation in the rat esophagus. Nut Cancer 50(2):168–173
Dehn PF, White CM, Conners DE, Shipkey G, Cumbo TA (2004) Characterization of the human hepatocellular carcinoma (hepg2) cell line as an in vitro model for cadmium toxicity studies. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 40(5–6):172–182. https://doi.org/10.1290/1543-706X
Doğan D, Meydan İ, Kömüroğlu AU (2022) Protective Effect of Silymarin and Gallic Acid against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity. Int J Clin Pract 2022:6541026. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6541026
El-Sharaky AS, Newairy AA, Badreldeen MM, Eweda SM, Sheweita SA (2007) Protective role of selenium against renal toxicity induced by cadmium in rats. Toxicol 235(3):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.03.014
Gamble M (2008) The haematoxylin and eosin. In: Bancroft JD, Gamble M (eds) Theory and practice of histological techniques, vol 11, 6th edn. Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone, p 121–134
Greenlee W, Poland A (1978) An improved assay of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase activity: induction of hepatic enzyme activity in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice by phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 205:596–605 (PMID: 660532)
Horiguchi H (2012) Current status of cadmium exposure among Japanese, especiallyregarding the safety standard for cadmium concentration in rice and adverse effects on proximal renal tubular function observed in farmers exposed to cadmium through consumption of self-grown rice]. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 67(4):447–54 (Japanese). https://doi.org/10.1265/jjh.67.447
Hu G, Han C, Wild CP, Hall J, Chen J (1992) Lack of effects of selenium on N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced tumorigenesis, DNA methylation, and oncogene expression in rats and mice. Nutr Cancer 18(3):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635589209514229
Ip C, Lisk DJ, Stoewsand GS (1992) Mammary cancer prevention by regular garlic and selenium-enriched garlic. Nutr Cancer 17(3):279–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635589209514197
Iqbal T, Das D (2022) Biochemical Investigation of Membrane-Bound Cytochrome b5 and the Catalytic Domain of Cytochrome b5 Reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochemistry 61(10):909–921. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00002
Jastrzebski Z, Leontowicz H, Leontowicz M et al (2007) The bioactivity of processed garlic (Allium sativum L.) as shown in vitro and in vivo studies on rats. Food Chem Toxicol 45(9):1626–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.02.028
Kabler SL, Seidel A, Jacob J, Doehmer J, Morrow CS, Townsend AJ (2009) Differential protection by human glutathione S-transferase P1 against cytotoxicity of benzo[a]pyrene, dibenzo[a, l]pyrene, or their dihydrodiol metabolites, in bi-transgenic cell lines that co-express rat versus human cytochrome P4501A1. Chem Biol Interact 179(2–3):240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2009.01.010
Kong DY, Hao LR, Zhang L, Li QG, Zhou JH, Shi SZ, Zhu F, Geng YQ, Chen XM (2015) Comparison of two fluid solutions for resuscitation in a rabbit model of crush syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol 19(6):1015–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1114-2
Korkmaz Y, Gungor H, Demirbas A, Dik B (2023) Pomegranate peel extract, N-Acetylcysteine and their combination with Ornipural alleviate Cadmium-induced toxicity in rats. J Vet Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.22-0375. (Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37495528)
Lacorte LM, Seiva FR, Rinaldi JC et al (2013) Caffeine reduces cadmium accumulation in the organism and enhances the levels of antioxidant protein expression in the epididymis. Reprod Toxicol 35:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2012.10.009
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2142136
Lee CY, Johnson L, Cox RH, McKinney JD, Lee SM (1981) Mouse liver glutathione S-transferases. Biochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem 256(15):8110–8116 (PMID: 6790531)
Li LX, Chu JH, Chen XW et al (2022) Selenium ameliorates mercuric chloride-induced brain damage through activating BDNF/TrKB/PI3K/AKT and inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathways. J Inorg Biochem 229:111716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2022.111716. (Epub 2022 Jan 5 PMID: 35065321)
Luck H (1974) Methods in Enzymatic Analysis II, (ed.) Bergmeyer. (Publ.) Academic Press, New York. 885
Lv MW, Zhang C, Ge J, Sun XH, Li JY, Li JL (2023) Resveratrol protects against cadmium-induced cerebrum toxicity through modifications of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in microsomes. J Sci Food Agric 103(12):5883–5892. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12668. (Epub 2023 May 12 PMID: 37115015)
Marks HS, Anderson JL, Stoewsand GS (1992) Inhibition of benzo(a)pyrene-induced bone marrow micronuclei formation by diallyl thioesters in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health 37:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287399209531652
Marques DN, Mason C, Stolze SC, Harzen A, Nakagami H, Skirycz A, Piotto FA, Azevedo RA (2023) Grafting systems for plant cadmium research: Insights for basic plant physiology and applied mitigation. Sci Total Environ 892:164610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164610
Metwally MMM, Hashem MA (2009) Protective role of garlic against cadmium toxicity in rats: Clinicopathological and histopathological studies. Egypt J Comp Path Clinic Path 22:114–140. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710387633
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175
Mooney LA, Madsen AM, Tang D et al (2005) Antioxidant vitamin supplementation reduces benzo(a)pyrene-DNA adducts and potential cancer risk in female smokers. Cancer Epidemiol, Biomarkers Prev 14:237–242 (PMID: 15668500)
Mostafa M, Sheweita S (1992) Modification of the oxidative N-demethylation of dimethylnitrosamine by various anti-inflammatory drugs. Ramazzini Newslett 2:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(91)90688-2
Murugavel P, Pari L (2007) Effects of diallyl tetrasulfide on cadmium-induced oxidative damage in the liver of rats. Human Exper Toxicol 26:527–534. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327107073810
Nash T (1953) The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J 55(3):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0550416
Ogar GO, Minari JB, Bello AJ et al (2022) Influence of ethanolic extract of Allium sativum on TP53 gene and its anticancer potential in N-Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA)-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in male albino rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 25(4):497–505. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2022.62295.13787
Omar SH, Al-Wabel NA (2010) Organosulfur compounds and possible mechanism of garlic in cancer. Saudi Pharm J 18:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2009.12.007
Omar AR, Nour AA, Dakrory AE (2023) Amelioration of silymarin against cadmium-induced toxicity in pregnant rats and their fetuses. Birth Defects Res 13:1192–1207. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.2217. (Epub 2023 Jul 4 PMID: 37401502)
Omotosho IO (2019) Oxidative stress indices as markers of lead and cadmium exposure toxicity in auto technicians in Ibadan, Nigeria. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:3030614. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3030614
Omura J, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
Padalko VI, Kozlova E, Leonova I (2012) Protective efficacy of garlic on cadmium induced oxidative stress in young and adult rats. Oxid Antioxid Med Sci 1:101–109 (PMID: 14209971)
Pakmanesh F, Mahjoub S, Neamati N, Moslemi D (2023) Chromium and lead levels and alteration in DDPH inhibition in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Caspian J Intern Med 14(3):553–559. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.14.3.533
Persijn JP, Van der Slike W (1982) A new method for the determination of γ glutamyletrans-peptidase in serum. J Clin Chem Clin, Biochem 14:421–427 (PMID: 9466)
Popoola AB, Ademilusi EO, Adedeji TG, Fasanmade AA (2022) Effect of silymarin on blood coagulation profile and osmotic fragility in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep 9:1325–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.06.005.PMID:36518474;PMCID:PMC9743456
Rinaldi M, Micali A, Marini H, Adamo EB, Puzzolo D, Pisani A et al (2017) Cadmium, Organ Toxicity and Therapeutic Approaches: A Review on Brain, Kidney and Testis Damage. Curr Med Chem 24(35):3879–3893. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170801101448
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hofeman DG, Hoekstra WG (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Said L, Banni M, Kerkeni A, Said K, Messaoudi I (2010) Influence of combined treatment with zinc and selenium on cadmium-induced testicular pathophysiology in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol 48:2759–2765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.003
Saxena P, Selvaraj K, Khare SK, Chaudhary N (2022) Superoxide dismutase as multipotent therapeutic antioxidant enzyme: Role in human diseases. Biotechnol Lett 44(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03200-3
Shang S, He Z, Hou W, Chen X, Zhao X, Han H, Chen S, Yang S, Tai F (2023) Molecular cloning, expression analysis and functional characterization of chicken cytochrome P450 27A1: A novel mitochondrial vitamin D3 25- hydroxylase. Poult Sci 102(8):102747
Shangguan X, Mao Y, Wang X, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang G, Li J (2022) Cyp17a affected by endocrine disruptors and its function in gonadal development of Hyriopsis cumingii. Gen Comp Endocrinol 323–324:114028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2022.114028
Sheweita SA (2000) Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes: Mechanisms and Functions. Current Drug Metab 1:107–132. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200003339117
Sheweita SA, Abd El-Gabar M, Bastawy M (2001) Carbon tetrachloride-induced changes in the activity of phase II drugmetabolizing enzyme in the liver of male rats: role of antioxidants. Toxicology 165(2–3):217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(01)00429-2
Sheweita SA, Mousa N, Newairy AA (2007) N-nitrosodimethylamine induced changes in the activities of carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes in the liver of male mice: role of glutathione and gossypol as antioxidants. African J Biochem Res 1:78–82
Sheweita SA, El-Hosseiny LS, Nashashibi MA (2016a) Protective Effects of Essential Oils as Natural Antioxidants against Hepatotoxicity Induced by Cyclophosphamide in Mice. PLoS One 11(11):e0165667. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165667
Sheweita SA, Al-Shora S, Hassan M (2016b) Effects of benzo[a]pyrene as an environmental pollutant and two natural antioxidants on biomarkers of reproductive dysfunction in male rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(17):17226–17235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6934-4
Sheweita SA, ElHady SA, Hammoda HM (2020) Trigonella stellata reduced the deleterious effects of diabetes mellitus through alleviation of oxidative stress, antioxidant- and drug-metabolizing enzymes activities. J Ethnopharmacol 256:112821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112821
Sheweita SA, El-Dafrawi YA, El-Ghalid OA, Ghoneim AA, Wahid A (2022) Antioxidants (selenium and garlic) alleviated the adverse effects of tramadol on the reproductive system and oxidative stress markers in male rabbits. Sci Rep 12(1):13958. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16862-4
Siewit CL, Gengler B, Vegas E, Puckett R, Louie MC (2010) Cadmium promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by potentiating the interaction between ERalpha and c-Jun. Mol Endocrinol 24(5):981–992. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2009-0410
Sparnins VL, Barany G, Wattenberg LW (1988) Effects of organosulfur compounds from garlic and onions on benzo[a]pyrene-induced neoplasia and glutathione S-transferase activity in the mouse. Carcinogenesis 9(1):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/9.1.131
SPSS 2007. SPSS for Windows, Version 16.0. Chicago, SPSS Inc
Srinivasan R, Ramprasath C (2012) The beneficial role of silibinin in monitoring the cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in Albino Wistar rats. Recent Res Sci Technol 4:46–52
Surai PF (2015) Silymarin as a natural antioxidant: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel) 4(1):204–247. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox4010204
Szumiło J (2009) Srodki pochodzenia naturalnego w chemoprewencji raka płaskonabłonkowego przełyku–badania doświadczalne [Natural compounds in chemoprevention of esophageal squamous cell tumors–experimental studies]. Pol Merkur Lekarski 26(152):156–61. https://doi.org/10.17772/gp/59268
Tappel AL, Zalkin H (1959) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation in mitochondria by vitamin E. Arch Biochem Biophys 80:333–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605617
Tiran B, Karpf E, Tiran A (1995) Age dependency of selenium and cadmium content in human liver, kidney, and thyroid. Arch Environ Health 50(3):242–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1995.9940394. (PMID: 7618958)
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Nat Acad Sci 76:4350–4354. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12:1161–1208. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867053764635
Valko M, Rhodes C, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Varrà MO, Husáková L, Patočka J, Ianieri A, Ghidini S, Zanardi E (2023) Cadmium, lead, and mercury in two commercial squid species from the north Adriatic Sea (central Mediterranean):= contamination levels and health risk assessment. Ital J Food Saf 12(2):11037. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijfs.2023.11037
Venkatesan N, Arcos JC, Argus MF (1968) Differential effect of polycyclic hydrocarbons on the demethylation of the carcinogen dimethylnitrosamine by rat tissues. Life Sci 7(19):1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(68)90217-8
Wang SF, Zhou T, Du MR, Sheng J (2022) Identification of vitamin D-dependent rickets type IA caused by a mutation of the CYP27B1 using whole exome sequencing. Asian J Surg 45(5):1160–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.01.085
Wargovich M (1987) Diallyl sulfide, a flavor component of garlic (Allium sactivum), inhibits dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 8:487–489. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/8.3.487
Wargovich M, Woods C, Eng V, Stephens L, Grey K (1988) Chemoprevention of N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine induced esophageal cancer in rats by the naturally occurring thioether, diallyl sulfide. Cancer Res 48:6872–6875 (PMID: 3180095)
Wargovich M, Lmada O, Stephens L (1992) Initiation and post-initiation chemopreventive effects of diallyl sulfide in esophageal carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 64:39–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3835(92)90019-r
Wiebel FJ, Gelboin HV (1975) Aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylases in liver from rats of different age, sex and nutritional status. Distinction of two types by 7,8-benzoflavone. Biochem Pharmacol. 24(16):1511–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(75)90028-3
Williams CH, Kamin H (1962) Microsomal triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase of liver. J Biol Chem 237:587–595 (PMID: 14007123)
Funding
The authors confirm that the submitted work was not funded by any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Salah A. Sheweita was in charge of the research concept and writing the draft and the final versions of the manuscript.
Ahmed Abd El Rafea carried out the experimental work.
Sabah G. Elbana shared in the statistical analysis and writing the draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The local committee of animal care at Graduate Studies and Research, Alexandria University, Egypt, approved the experimental design and methodology, which adhere to the standards of the National Institute of Health, USA.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish the current study in Environmental Science & Pollution Research.
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that there are no known conflicts of interest that could influence the findings of this study.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheweita, S.A., Rafea, A.A.E. & Elbana, S.G. The deleterious effects of cadmium on oxidative stress markers, drug-metabolizing, and antioxidant enzyme activities: Role of Silymarin and Garlic as Antioxidants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 112490–112502 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30197-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30197-1