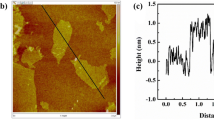
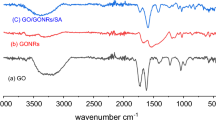
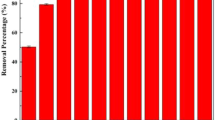
Abstract
A reinforced composite aerogel absorbent was synthesized using a green chemistry method and an environmentally friendly freeze-drying technique. The absorbent consisted of sodium alginate, polyethyleneimine (PEI), and graphene oxide (GO). The ability of the absorbent to remove Cr (VI) ions from aqueous solutions was studied. PEI was a nitrogen source for Cr (VI) removal and a cross-linking agent for GO sheets, while SA was a reinforcing material. The aerogel was investigated using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, texture analysis, Raman spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Batch studies were conducted to investigate the effect of pH and contact time on adsorption. The results indicated that the SA/PEI/GO aerogel had a maximum adsorption capacity of 174.05 mg·g−1 for Cr (VI) at pH 2. The adsorption mechanism was described using the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models. Thermodynamic studies revealed that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic. The aerogel demonstrated good regeneration ability and satisfactory recovery for Cr (VI) even after five cycles. These findings suggest that the composite aerogel could be a promising adsorbent for efficiently removing Cr (VI) from wastewater.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are provided in the manuscript.
References
Alvarez GS, Foglia ML, Camporotondi DE et al (2011) A functional material that combines the Cr(VI) reduction activity of Burkholderia sp. with the adsorbent capacity of sol–gel materials. J Mater Chem 21:6359–6364. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM04112B
Cai D, Song M (2007) Preparation of fully exfoliated graphite oxide nanoplatelets in organic solvents. J Mater Chem 17:3678–3680. https://doi.org/10.1039/B705906J
Cao N, Lyu Q, Li J et al (2017) Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chemical Engineering Journal 326:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2017.05.117
Chauke VP, Maity A, Chetty A (2015) High-performance towards removal of toxic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using graphene oxide-alpha cyclodextrin-polypyrrole nanocomposites. J Mol Liq 211:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2015.06.044
Daemi H, Barikani M (2012) Synthesis and characterization of calcium alginate nanoparticles, sodium homopolymannuronate salt and its calcium nanoparticles. Scientia Iranica 19:2023–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCIENT.2012.10.005
de Borja OF, Sammaraie H, Campano C et al (2022) Hexavalent chromium removal from industrial wastewater by adsorption and reduction onto cationic cellulose nanocrystals. Nanomaterials 12:4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO12234172
Ferrari A, Robertson J (2000) Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys Rev B 61:14095. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095
Ferrari AC, Meyer JC, Scardaci V et al (2006) Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys Rev Lett 97:187401. https://doi.org/10.1103/PHYSREVLETT.97.187401/FIGURES/3/MEDIUM
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2009.09.013
Ge H, Ma Z (2015) Microwave preparation of triethylenetetramine modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite for adsorption of Cr(VI). Carbohydr Polym 131:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2015.06.025
Gheju M, Balcu I, Mosoarca G (2016) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on MnO2. J Hazard Mater 310:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.042
Gherasim CV, Bourceanu G (2013) Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions using a polyvinyl-chloride inclusion membrane: experimental study and modelling. Chem Eng J 220:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2013.01.058
Hashim M, Mukhopadhyay S, … JS-J of environmental, 2011 undefined (2011) Remediation technologies for heavy metal contaminated groundwater. Elsevier https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.009
Ho YS, Ng JCY, McKay G (2011) Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents. Sep Purif Methods 29:189–232. https://doi.org/10.1081/SPM-100100009
Hozhabr Araghi S, Entezari MH, Chamsaz M (2015) Modification of mesoporous silica magnetite nanoparticles by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 218:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2015.07.008
Hsu LC, Wang SL, Lin YC et al (2010) Cr(VI) Removal on fungal biomass of Neurospora crassa: the importance of dissolved organic carbons derived from the biomass to Cr(VI) reduction. Environ Sci Technol 44:6202–6208. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES1017015/SUPPL_FILE/ES1017015_SI_001.PDF
Hummers WS, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339–1339
Jiao C, Xiong J, Tao J et al (2016) Sodium alginate/graphene oxide aerogel with enhanced strength–toughness and its heavy metal adsorption study. Int J Biol Macromol 83:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2015.11.061
Karthik R, Meenakshi S (2015) Removal of Cr(VI) ions by adsorption onto sodium alginate-polyaniline nanofibers. Int J Biol Macromol 72:711–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.09.023
Kong D, Zhang F, Wang K et al (2014) Fast removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using Cr(VI)-imprinted polymer particles. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:4434–4441. https://doi.org/10.1021/IE403484P
Li L, Fan L, Sun M et al (2013) Adsorbent for hydroquinone removal based on graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin–chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 58:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2013.03.058
Li LL, Feng XQ, Han RP et al (2017) Cr(VI) removal via anion exchange on a silver-triazolate MOF. J Hazard Mater 321:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2016.09.029
Li X, Zhou H, Wu W et al (2015) Studies of heavy metal ion adsorption on chitosan/sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide composites. J Colloid Interface Sci 448:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2015.02.039
Liu B, Huang Y (2011) Polyethyleneimine modified eggshell membrane as a novel biosorbent for adsorption and detoxification of Cr(VI) from water. J Mater Chem 21:17413–17418. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM12329G
Liu C, Jin RN, Ouyang X kun, Wang YG (2017) Adsorption behavior of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal—polyethyleneimine composite for removal of Cr(VI) ions. Appl Surf Sci 408:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.265
Lv X, Xue X, Jiang G et al (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) assembled on magnetic Fe3O4/graphene for chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 417:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2013.11.044
Ma HL, Zhang Y, Hu QH et al (2012) Chemical reduction and removal of Cr(VI) from acidic aqueous solution by ethylenediamine-reduced graphene oxide. J Mater Chem 22:5914–5916. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM00145D
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM et al (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4:4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/NN1006368/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/NN-2010-006368_0011.JPEG
Moussavi G, Khosravi R (2010) Removal of cyanide from wastewater by adsorption onto pistachio hull wastes: parametric experiments, kinetics and equilibrium analysis. J Hazard Mater 183:724–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.07.086
Ojembarrena FDB, ; Sánchez-Salvador JL;, Mateo S;, et al (2022) Modeling of hexavalent chromium removal with hydrophobically modified cellulose nanofibers. Polymers 14:3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14163425
Omer AM, Khalifa RE, Hu Z et al (2019) Fabrication of tetraethylenepentamine functionalized alginate beads for adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 125:1221–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2018.09.097
Pan C, Troyer LD, Catalano JG, Giammar DE (2016) Dynamics of chromium(VI)removal from drinking water by iron electrocoagulation. Environ Sci Technol 50:13502–13510. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.6B03637/SUPPL_FILE/ES6B03637_SI_001.PDF
Pan C, Troyer LD, Liao P et al (2017) Effect of humic acid on the removal of chromium(VI) and the production of solids in iron electrocoagulation. Environ Sci Technol 51:6308–6318. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.7B00371/SUPPL_FILE/ES7B00371_SI_001.PDF
Pang Y, Zeng GM, Tang L et al (2011) Cr(VI) reduction by Pseudomonas aeruginosa immobilized in a polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate matrix containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Bioresour Technol 102:10733–10736. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2011.08.078
Periyasamy S, Gopalakannan V, Viswanathan N (2018) Hydrothermal assisted magnetic nano-hydroxyapatite encapsulated alginate beads for efficient Cr(VI) uptake from water. J Environ Chem Eng 6:1443–1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.01.007
Saha B, Orvig C (2010) Biosorbents for hexavalent chromium elimination from industrial and municipal effluents. Coord Chem Rev 254:2959–2972. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCR.2010.06.005
Saha R, Nandi R, Saha B (2011) Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. https://doi.org/101080/009589722011583646 64:1782–1806. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2011.583646
Samuel MS, Shah SS, Subramaniyan V et al (2018) Preparation of graphene oxide/chitosan/ferrite nanocomposite for chromium(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 119:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2018.07.052
Saslow SA, Um W, Pearce CI et al (2017) Reduction and simultaneous removal of 99Tc and Cr by Fe(OH)2(s) mineral transformation. Environ Sci Technol 51:8635–8642. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.7B02278/SUPPL_FILE/ES7B02278_SI_001.PDF
Shakya A, Agarwal T (2019) Removal of Cr(VI) from water using pineapple peel derived biochars: adsorption potential and re-usability assessment. J Mol Liq 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111497
Sharma G, Naushad M, Al-Muhtaseb AH et al (2017) Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-crosslinked-poly(alginic acid) nanohydrogel for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) metal ion from aqueous medium. Int J Biol Macromol 95:484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.072
Singh DK, Kumar V, Mohan S, Hasan SH (2017) Polylysine functionalized graphene aerogel for the enhanced removal of Cr(VI) through adsorption: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic modeling of the process. J Chem Eng Data 62:1732–1742. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JCED.7B00188/SUPPL_FILE/JE7B00188_SI_001.PDF
Sui ZY, Cui Y, Zhu JH, Han BH (2013) Preparation of three-dimensional graphene oxide-polyethylenimine porous materials as dye and gas adsorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:9172–9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/AM402661T/SUPPL_FILE/AM402661T_SI_001.PDF
Tonghuan L, Xiaojiang D, Guojian D et al (2013) Adsorption of UO22+ on poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide- co-acrylic acid): effects of pH, ionic strength, initial uranyl concentration, and temperature. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10967-013-2434-X/METRICS
Vilcinskas K, Zlopasa J, Jansen KMB et al (2016) Water sorption and diffusion in (reduced) graphene oxide-alginate biopolymer nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng 301:1049–1063. https://doi.org/10.1002/MAME.201600154
Wang XS, Chen LF, Li FY et al (2010) Removal of Cr (VI) with wheat-residue derived black carbon: reaction mechanism and adsorption performance. J Hazard Mater 175:816–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.10.082
Xu C, Wang X, Zhu J (2008) Graphene - metal particle nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 112:19841–19845. https://doi.org/10.1021/JP807989B/SUPPL_FILE/JP807989B_SI_001.PDF
Yang S, Li L, Pei Z et al (2014) Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics of Cr(III) on graphene oxide. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 457:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2014.05.062
Yang Z, Xing G, Hou P, Han D (2018) Amino acid-mediated N-doped graphene aerogels and its electrochemical properties. Mater Sci Eng B 228:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEB.2017.11.028
Zhang L, Luo H, Liu P et al (2016) A novel modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite used as an adsorbent for Cr(VI) in aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 87:586–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2016.03.027
Zhang Y, Yan L, Xu W et al (2014) Adsorption of Pb(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic CoFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 191:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2013.12.015
Zhao S, Chen Z, Shen J et al (2017) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal based on reduction-coagulation-precipitation by NaBH4 combined with fly ash leachate as a catalyst. Chem Eng J 322:646–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2017.04.057
Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu S et al (2016) Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 218:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2016.06.102
Zhou T, Li C, Jin H et al (2017) Effective adsorption/reduction of Cr(VI) oxyanion by halloysite@polyaniline hybrid nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:6030–6043. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.6B14079/SUPPL_FILE/AM6B14079_SI_001.PDF
Funding
We acknowledge the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0308500) for the financial support of our research. This project was supported by The Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities (22JP006). It was supported by the Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Auxiliary Chemistry and Technology for Chemical Industry, Ministry of Education, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (No. KFKT2022-13) and Shaanxi Collaborative Innovation Center of Industrial Auxiliary Chemistry and Technology, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (No. KFKT2022-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ji Li conceived the idea, designed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. Bo Gao designed the experiments with Ji Li, prepared the materials and performed the adsorption measurements, and analyzed the results with Ji Li. Bo Gao and Ji Li analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. Fei Wei carried out the FTIR, XRD, and XPS measurements. Hongwei Gao discussed the data with Bo Gao and performed TEM on the graphene oxide and aerogel. All the authors edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval is not involved in the manuscript.
Consent to participate
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception design, data interpretation, and all steps involved in this work.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the version to be published.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Environmental Implication: Hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) is a pollutant that not only harms the ecological environment of water but also poses a potential threat to aquatic organisms and human health through the food chain. This issue has gained global attention, and it is urgent to find effective methods to remove Cr (VI) from water. This project has successfully developed a graphene aerogel that can efficiently remove hexavalent chromium from water. This innovation is significant in improving the water environment.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 719 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, ., Wei, F., Yang, H. et al. Effective removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by reinforced sodium alginate/polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide composite aerogels. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 111008–111020 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30189-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30189-1