Abstract
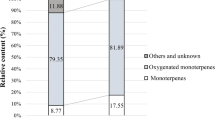
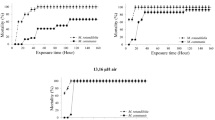
The adverse effects of relying solely on synthetic pesticides have become increasingly evident, leading many countries to explore alternatives sourced from plant-based green economies. Essential oil (EO) from stems and leaves of Adenosma buchneroides Bonati (A. buchneroides) was distilled by using hydrodistillation and subjected to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) for component identification. Subsequently, EO as well as its main constituents (thymol and p-cymene) were tested for their insecticidal activity against the red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum), the cigarette beetle (Lasioderma serricorne), and the booklouse (Liposcelis bostrychophila). The joint action of thymol and p-cymene produced an additive or synergistic effect. A. buchneroides essential oil (BHO) and the fixed ratio of the main compounds, thymol, and p-cymene both showed significant toxic activity against the target pests. This toxic effect is not simply the sum of individual effects, as it is influenced by various factors such as insect species and mode of action. These findings imply that the BHO and its phytoconstituents possess great potential to develop plant-derived biopesticides that will be safe for humans and the environment.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Campolo O, Giunti G, Russo A, Palmeri V, Zappalà L (2018) Essential oils in stored product insect pest control. J Food Qual 2018:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6906105
Don-Pedro KN (1996) Investigation of single and joint fumigant insecticidal action of citruspeel oil components. Pestic Sci 46:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199601)46:1%3c79::AID-PS319%3e3.0.CO;2-8
Ebadollahi A, Taghinezhad E, Setzer WN, Chen GN (2021) Susceptibility of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to the fumigation of two essential Satureja oils: optimization and modeling. Processes 9:12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071243
Enan EE (2005) Molecular and pharmacological analysis of an octopamine receptor from American cockroach and fruit fly in response to plant essential oils. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 59:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.20076
Feng YX, Wang Y, Chen ZY, Guo SS, You CX, Du SS (2019) Efficacy of bornyl acetate and camphene from Valeriana officinalis essential oil against two storage insects. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:16157–16165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05035-y
Feng Y-X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Chen Z-Y, Lu X-X, Du Y-S, Du S-S (2021) The potential contribution of cymene isomers to insecticidal and repellent activities of the essential oil from Alpinia zerumbet. Int Biodeter Biodegr 157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105138.
Gisi U, Binder H, Rimbach E (1985) Synergistic interactions of fungicides with different modes of action. Trans Br Mycol Soc 85:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(85)80192-3
Gou Y, Fan RY, Pei SJ, Wang YH (2018) Before it disappeared: ethnobotanical study of fleagrass (Adenosma buchneroides), a traditional aromatic plant used by the Akha people. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 14:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0277-9
Isman MB (2016) Pesticides based on plant essential oils: phytochemical and practical considerations, medicinal and aromatic crops: production, phytochemistry, and utilization. ACS Symposium Series, pp 13–26. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2016-1218.ch002
Isman MB (2019) Commercial development of plant essential oils and their constituents as active ingredients in bioinsecticides. Phytochem Rev 19:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09653-9
Isman MB (2020) Botanical insecticides in the twenty-first century-fulfilling their promise? Annu Rev Entomol 65:233–249. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-011019-025010
Jan R, Asaf S, Numan M, Lubna, Kim K-M (2021) Plant secondary metabolite biosynthesis and transcriptional regulation in response to biotic and abiotic stress conditions. Agronomy 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050968.
Jovanović Z, Kostić M, Popović Z (2007) Grain-protective properties of herbal extracts against the bean weevil Acanthoscelides obtectus Say. Ind Crops Prod 26:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.01.010
Junkum A, Intirach J, Chansang A, Champakaew D, Chaithong U, Jitpakdi A, Riyong D, Somboon P, Pitasawat B (2021) Enhancement of temephos and deltamethrin toxicity by Petroselinum crispum oil and its main constituents against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 58:1298–1315. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjab008
Kainat R, Mushtaq Z, Nadeem F (2019) Derivatization of essential oil of eucalyptus to obtain valuable market products. A comprehensive review. Int J Chem Biochem Sci 58–68. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335988153
La Pergola A, Restuccia C, Napoli E, Bella S, Brighina S, Russo A, Suma P (2017) Commercial and wild Sicilian Origanum vulgare essential oils: chemical composition, antimicrobial activity and repellent effects. J Essent Oil Res 29:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2017.1353448
Li S, Li H, Zhou Q, Zhang F, Desneux N, Wang S, Shi L (2022) Essential oils from two aromatic plants repel the tobacco whitefly Bemisia tabaci. J Pest Sci 95:971–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-021-01412-0
Li BY, Zhang JW, Zheng Y, Wang D, Wan CF, Du SS (2023) Insecticidal and repellent effects of the essential oils extract from Zanthoxylum myriacanthum against three storage pests. Chem Biodivers 20:e202200493. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202200493
Liu ZL, Ho SH (1999) Bioactivity of the essential oil extracted from Evodia rutaecarpa Hook f. et Thomas against the grain storage insects, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J Stored Prod Res 35:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-474X(99)00015-6
Lumjuan N, Rajatileka S, Changsom D, Wicheer J, Leelapat P, Prapanthadara LA, Somboon P, Lycett G, Ranson H (2011) The role of the Aedes aegypti Epsilon glutathione transferases in conferring resistance to DDT and pyrethroid insecticides. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.12.005
Mendy B, Wang’ombe MW, Radakovic ZS, Holbein J, Ilyas M, Chopra D, Holton N, Zipfel C, Grundler FM, Siddique S (2017) Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase NILR1 is required for induction of innate immunity to parasitic nematodes. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006284. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006284
Nayak MK, Daglish GJ, Byrne VS (2005) Effectiveness of spinosad as a grain protectant against resistant beetle and psocid pests of stored grain in Australia. J Stored Prod Res 41:455–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2004.07.002
Ouedrhiri W, Mechchate H, Moja S, Baudino S, Saleh A, Al Kamaly OM, Grafov A, Greche H (2022) Optimized antibacterial effects in a designed mixture of essential oils of Myrtus communis, Artemisia herba-alba and Thymus serpyllum for wide range of applications. Foods 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010132
Poudel DK, Rokaya A, Ojha PK, Timsina S, Satyal R, Dosoky NS, Satyal P, Setzer WN (2021) The chemical profiling of essential oils from different tissues of Cinnamomum camphora L. and their antimicrobial activities. Molecules 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175132.
Rees D (2007) Insects of stored grain: a pocket reference. Csiro, Australia. https://doi.org/10.1071/9780643094673
Regnault-Roger C, Vincent C, Arnason JT (2012) Essential oils in insect control: low-risk products in a high-stakes world. Annu Rev Entomol 57:405–424. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120710-100554
Restuccia C, Oliveri Conti G, Zuccarello P, Parafati L, Cristaldi A, Ferrante M (2019) Efficacy of different citrus essential oils to inhibit the growth and B1 aflatoxin biosynthesis of Aspergillus flavus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:31263–31272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06169-9
Saad MMG, El-Deeb DA, Abdelgaleil SAM (2019) Insecticidal potential and repellent and biochemical effects of phenylpropenes and monoterpenes on the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum Herbst. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:6801–6810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04151-z
Savary S, Willocquet L, Pethybridge SJ, Esker P, McRoberts N, Nelson A (2019) The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat Ecol Evol 3:430–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0793-y
Sohail M, Aqueel MA, Dai P, Ellis JD (2021) The larvicidal and adulticidal effects of selected plant essential oil constituents on greater wax moths. J Econ Entomol 114:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toaa249
Tak J-H, Isman MB (2017) Enhanced cuticular penetration as the mechanism of synergy for the major constituents of thyme essential oil in the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Ind Crops Prod 101:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.03.003
Teixeira B, Marques A, Ramos C, Neng NR, Nogueira JMF, Saraiva JA, Nunes ML (2013) Chemical composition and antibacterial and antioxidant properties of commercial essential oils. Ind Crops Prod 43:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.07.069
Tribolium Genome Sequencing C et al (2008) The genome of the model beetle and pest Tribolium castaneum. Nature 452:949–955. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06784
Vito R, Muggeo M (2008) Segmented: an R package to fit regression models with broken-line. R News 8:20–25. https://journal.r-project.org/articles/RN-2008-004/
Wang C, Zhang H, Liu Q, Qi J, Zhuang H, Gou Y, Wang H, Wang Y (2021) A review of the aromatic genus Adenosma: geographical distribution, traditional uses, phytochemistry and biological activities. J Ethnopharmacol 275:114075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114075
Wang C, Qi J, Liu Q, Wang Y, Wang H (2022) Allelopathic potential of aqueous extracts from fleagrass (Adenosma buchneroides Bonati) against two crop and three weed species. Agriculture 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081103.
Xie YJ, Jin H, Yang X, Gu QL, Zhang DY (2020) Toxicity of the essential oil fromThymus serpyllum and thymol to larvae and pupae of the houseflyMusca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:35330–35340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09633-z
Yong X, Biqiang C, Zheng Y, Jingkai D (2008) A preliminary study on the new perfume plant Adenosma buchneroides Bonati. In: Proceedings of the 7th China Symposium on Flavors and Flavors Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, pp 33–36
Yong-peng M, Hong-xia Z, Guo S, Zhi-zhi D (2018) Chemical constituents from Adenosma buchneroides. Nat Prod Res Dev 30:1376–1381+1398. https://doi.org/10.16333/j.1001-6880.2018.8.015
You CX, Yang K, Wu Y, Zhang WJ, Wang Y, Geng ZF, Chen HP, Jiang HY, Du SS, Deng ZW, Liu ZL (2014) Chemical composition and insecticidal activities of the essential oil of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. aerial parts against two stored product insects. Eur Food Res Technol 239:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2242-8
Zambonelli A, D’Aulerio AZ, Severi A, Benvenuti S, Maggi L, Bianchi A (2004) Chemical composition and fungicidal activity of commercial essential oils of Thymus vulgaris L. J Essent Oil Res 16:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2004.9698653
Zhao NN, Zhou L, Liu ZL, Du SS, Deng ZW (2012) Evaluation of the toxicity of the essential oils of some common Chinese spices against Liposcelis bostrychophila. Food Control 26:486–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.02.021
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (7202109) and the Graduate Research and Practice Projects of Minzu University of China (SZKY2022054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Thanks to all co-authors for completing this research. Q-HX designed and performed this research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. J-NY provided guidance on data analysis, and B-YL, T-L, and YZ checked this manuscript together. AB and S-SD gave support for the research and provided the materials.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Informed consent and consent to publish were obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Giovanni Benelli
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, QH., Tian-Liang, Li, BY. et al. Bioactivities of thymol and p-cymene from the essential oil of Adenosma buchneroides against three stored-product insects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110841–110850 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30068-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30068-9