Abstract
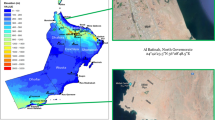
Today, increasing concerns about greenhouse gas emissions, climate change, and resource depletion from fossil fuels have drawn attention to wind energy. In this context, wind turbine technologies are constantly evolving to eliminate such concerns by using wind energy. The wind speed from the measurement mast at a height of 80 m was used in wind turbines of different capacities and was investigated. To assess the potential of the system that produces electricity from wind energy, it has been analyzed in terms of energy, exergy, and economic. The energy and exergy efficiencies of each wind turbine were analyzed with the wind speed and meteorological data. When the average monthly power calculated for each turbine is proportioned to the turbine capacity, the energy efficiency varies between 10 and 70%. Enercon_1500 and Enercon_3050 values are high, while Enercon_3500 and Enercon_2350 have low efficiency compared to other turbines. The annual total energy production is 12.19 GWh for the highest Enercon_4200 and 4.48 GWh for the lowest Enercon_1500. The exergy efficiencies range from 20 to 79% for selected wind turbines. In the last part of the study, monthly average electricity production costs were determined by using the turbines selected for the determined region. When compared in terms of unit electricity cost, the Enercon_1500 turbine is higher, while the Enercon_4200 is lower.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Adnan M, Ahmad J, Ali SF, Imran M (2021) A techno-economic analysis for power generation through wind energy: a case study of Pakistan. Energy Rep 7:1424–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.02.068
Akpinar A (2013) Evaluation of wind energy potentiality at coastal locations along the north eastern coasts of Turkey. Energy 50:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.11.019
Allouhi A (2019) Energetic, exergetic, economic and environmental (4 E) assessment process of wind power generation. J Clean Prod 235:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.299
Allouhi A, Zamzoum O, Islam MR et al (2017) Evaluation of wind energy potential in Morocco’s coastal regions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.047
Almutairi M, Harb K, Marey O, Almutairi K (2022) Evaluation of wind power generation projects to reduce air pollution using multi-criteria decision-making methods in Saudi Arabia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:88587–88605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21950-z
Argin M, Yerci V, Erdogan N et al (2019) Exploring the offshore wind energy potential of Turkey based on multi-criteria site selection. Energy Strateg Rev 23:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2018.12.005
Arslan O (2010) Technoeconomic analysis of electricity generation from wind energy in Kutahya, Turkey. Energy 35:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.09.002
Arslan H, Baltaci H, Akkoyunlu BO et al (2020) Wind speed variability and wind power potential over Turkey: case studies for çanakkale and İstanbul. Renew Energy 145:1020–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.128
Asgari E, Ehyaei MA (2015) Exergy analysis and optimisation of a wind turbine using genetic and searching algorithms. Int J Exergy 16:293–314. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEX.2015.068228
Baskut O, Ozgener L (2012) Exergoeconomic assessment of a wind turbine power plant (WTTP): Cesme, Izmir, example. Energy 47:577–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.09.014
Baskut O, Ozgener O, Ozgener L (2010) Effects of meteorological variables on exergetic efficiency of wind turbine power plants. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:3237–3241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.06.002
Baskut O, Ozgener O, Ozgener L (2011) Second law analysis of wind turbine power plants: Cesme, Izmir example. Energy 36:2535–2542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.01.047
Bejan A (2016) Advanced engineering thermodynamics. John Wiley & Sons
Belabes B, Youcefi A, Guerri O et al (2015) Evaluation of wind energy potential and estimation of cost using wind energy turbines for electricity generation in north of Algeria. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 51:1245–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.043
Bilir L, İmir M, Devrim Y, Albostan A (2015) An investigation on wind energy potential and small scale wind turbine performance at İncek region – Ankara, Turkey. Energy Convers Manag 103:910–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.017
Celik AN (2007) A techno-economic analysis of wind energy in southern Turkey. Int J Green Energy 4:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435070701338358
Chang TP (2011) Performance comparison of six numerical methods in estimating Weibull parameters for wind energy application. Appl Energy 88:272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.06.018
Charabi Y, Abdul-Wahab S, Al-Mahruqi AM et al (2022) The potential estimation and cost analysis of wind energy production in Oman. Environ Dev Sustain 24:5917–5937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01692-7
Cunden TSM, Abdel Hassan NBR, Lollchund MR (2021) Analysis of wind energy resources for the ısland of Mauritius using concepts of thermodynamics. In Progress in Advanced Computing and Intelligent Engineering: Adv Intell Syst Comput 1299 AISC:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4299-6_60
Dabbaghiyan A, Fazelpour F, Abnavi MD, Rosen MA (2016) Evaluation of wind energy potential in province of Bushehr, Iran. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:455–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.148
Demiroren A, Yilmaz U (2010) Analysis of change in electric energy cost with using renewable energy sources in Gökceada, Turkey: an island example. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.06.030
Diyoke C (2019) A new approximate capacity factor method for matching wind turbines to a site: case study of Humber region, UK. Int J Energy Environ Eng 10:451–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-019-00320-5
Ehyaei MA, Ahmadi A, Rosen MA (2019) Energy, exergy, economic and advanced and extended exergy analyses of a wind turbine. Energy Convers Manag 183:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.008
Ehyaei MA, El Haj Assad M (2021) Chapter 13 - Energy and exergy analyses of wind turbines. In: Assad MEH, Rosen MABT-D and PO of RES (eds). Academic Press, pp 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821602-6.00015-8
Fazelpour F, Markarian E, Soltani N (2017) Wind energy potential and economic assessment of four locations in Sistan and Balouchestan province in Iran. Renew Energy 109:646–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.03.072
Frangopoulos CA (1987) Thermo-economic functional analysis and optimization. Energy 12:563–571
Gökçek M, Genç MS (2009) Evaluation of electricity generation and energy cost of wind energy conversion systems (WECSs) in Central Turkey. Appl Energy 86:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.03.025
Gölçek M, Erdem HH, Bayülken A (2007) A techno-economical evaluation for ınstallation of suitable wind energy plants in western Marmara, Turkey. Energy Explor Exploit 25:407–427. https://doi.org/10.1260/014459807783791791
Gönül Ö, Duman AC, Deveci K, Güler Ö (2021) An assessment of wind energy status, incentive mechanisms and market in Turkey. Eng Sci Technol an Int J 24:1383–1395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.03.016
IRENA (2022a) World energy transitions outlook 2022: 1.5°C pathway, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi.
IRENA (2022b) Renewable power generation costs in 2021, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi
IRENA (2023) Renewable capacity statistics 2023, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi
Jahromi S, Moosavian SF, Yaghoubirad M et al (2022) 4E analysis of the horizontal axis wind turbine with LCA consideration for different climate conditions. Energy Sci Eng 4085–4111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.1272
Johnson GL (2006) Wind energy systems electronic edition. 449
Jung C, Schindler D (2020) Introducing a new approach for wind energy potential assessment under climate change at the wind turbine scale. Energy Convers Manag 225:113425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113425
Kahatapitiya C, Jayasooriya VM, Muthukumaran S (2022) GIS-based weighted overlay model for wind and solar farm locating in Sri Lanka. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24595-0
Kantar YM, Usta I (2015) Analysis of the upper-truncated Weibull distribution for wind speed. Energy Convers Manag 96:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.02.063
Kassem Y, Abdalla MHA (2022) Modeling predictive suitability to identify the potential of wind and solar energy as a driver of sustainable development in the Red Sea state, Sudan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:44233–44254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19062-9
Keyhani A, Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti M, Khanali M, Abbaszadeh R (2010) An assessment of wind energy potential as a power generation source in the capital of Iran, Tehran. Energy 35:188–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.09.009
Krohn, S, Morthorst PE, Awerbuch S (2009) The economics of wind energy A Report by the European Wind Energy Association
Lamas W de W (2017) Exergo-economic analysis of a typical wind power system. Energy 140:1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.020
Li Y, Wu XP, Li QS, Tee KF (2018) Assessment of onshore wind energy potential under different geographical climate conditions in China. Energy 152:498–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.172
Lu L, Yang H, Burnett J (2002) Investigation on wind power potential on Hong Kong islands—an analysis of wind power and wind turbine characteristics. Renew Energy 27:1–12
Mahmoodi K, Ghassemi H, Razminia A (2020) Wind energy potential assessment in the Persian Gulf: a spatial and temporal analysis. Ocean Eng 216:107674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107674
Martin S, Jung S, Vanli A (2020) Impact of near-future turbine technology on the wind power potential of low wind regions. Appl Energy 272:115251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115251
MENR (2022) Republic of Turkey Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources. https://enerji.gov.tr/homepage
Nelson CA, Tew M, Phetteplace G et al (2000) Review of the federal ınteragency process used to select the new wind chill temperature (Wct) Index. 2000–2002
Ozgener O, Ozgener L (2007) Exergy and reliability analysis of wind turbine systems: a case study. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11:1811–1826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2006.03.004
Potić I, Joksimović T, Milinčić U et al (2021) Wind energy potential for the electricity production - Knjaževac Municipality case study (Serbia). Energy Strateg Rev 33:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2020.100589
Powell WR (1981) An analytical expression for the average output power of a wind machine. Sol Energy 26:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(81)90114-6
Redha AM, Dincer I, Gadalla M (2011) Thermodynamic performance assessment of wind energy systems: an application. Energy 36:4002–4010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.05.001
Rehman S, Natarajan N, Mohandes MA et al (2022) Wind and wind power characteristics of the eastern and southern coastal and northern inland regions, South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:85842–85854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14276-9
Rousset P, Petithuguenin T, Rodrigues T, Azevedo AC (2012) The fluidization behaviour of torrefied biomass in a cold model. Fuel 102:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.07.007
Saeed MA, Ahmed Z, Zhang W (2020) Wind energy potential and economic analysis with a comparison of different methods for determining the optimal distribution parameters. Renew Energy 161:1092–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.07.064
Taner T (2018) Economic analysis of a wind power plant: a case study for the Cappadocia region. J Mech Sci Technol 32:1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0241-6
Tiam Kapen P, Jeutho Gouajio M, Yemélé D (2020) Analysis and efficient comparison of ten numerical methods in estimating Weibull parameters for wind energy potential: application to the city of Bafoussam, Cameroon. Renew Energy 159:1188–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.185
Topographic-map_Turkey Topographic-map_Turkey (2022) https://en-gb.topographic-map.com/map-j5gt/Turkey/?center=39.11301%2C 36.47461. Accessed 22 Nov 2022
Ucar A, Balo F (2010) Assessment of wind power potential for turbine installation in coastal areas of Turkey. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:1901–1912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.03.021
Vardar A, Çet [idot] n B (2009) Economic assessment of the possibility of using different types of wind turbine in Turkey. Energy Sources Part B Econ Plan Policy 4:2 190–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567240701620465
Wind-turbine-models 2022 (2022) Wind-turbine-models, https://en.wind-turbine-models.com/turbines. Accessed 22 Nov 2022
Yaniktepe B, Savrun MM, Koroglu T (2013) Current status of wind energy and wind energy policy in Turkey. Energy Convers Manag 72:103–110
Yaniktepe B, Kara O, Aladag I, Ozturk C (2023) Comparison of eight methods of Weibull distribution for determining the best-fit distribution parameters with wind data measured from the met-mast. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:9576–9590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22777-4
Yildirim A, Bilgili M, Akgün H, Ünal Ş (2023) Techno-economic analysis of an offshore wind farm on the eastern Mediterranean Sea coast. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:35281–35293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24580-7
Yousuf MU, Abbasi MA, Kashif M, Umair M (2022) Energy, exergy, economic, environmental, energoeconomic, exergoeconomic, and enviroeconomic (7E) analyses of wind farms: a case study of Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:67301–67324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20576-5
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Iltek Energy Investment Industry and Trade Inc., who most kindly and generously allowed me to use the wind power plant data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OK contributed to the first draft of the manuscript; OK performed the analysis and preparation of tables and figures; the author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kara, O. Assessment of economic, energy, and exergy efficiencies using wind measurement mast data for different wind turbines. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 97447–97462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29344-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29344-5