Abstract
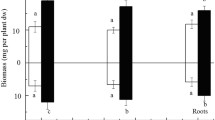
Root systems are sensitive to voltage and tend to improve the degradation of organic pollutants by promoting the root exudates and increasing microbial enzyme activity in the rhizosphere under the effect of electrokinetic. In this study, electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation (EKPR) was applied for the remediation of soil containing phenanthrene (PHE) and pyrene (PYR). Direct current (DC) voltage (1 V cm−1) was applied across the soils for 30 days following 3 treatment schedules (0 h, 4 h, and 12 h per day), referred to as treatments EK0, EK4, and EK12. Electrokinetic assistance improved phytoremediation. Compared to EK0, the removal of PHE and PYR increased by 51.79% and 45.07% for EK4 and by 43.18% and 38.75% for EK12. The applied voltage promoted root growth, stimulated the root exudate release, and increased accumulation of PHE and PYR by plants, and the effect was most pronounced in treatment EK4. Catalase and urease activities in rhizosphere soil also increased, by respective increments of 44.51% and 40.86% for EK4 and by 28.53% and 21.24% for EK12. In this study, we demonstrated that a low voltage applied for an appropriate duration (4 h per day) improves removal of PAHs by stimulating root growth, promoting the root exudate release and enhancing enzyme activity in the microbiome of rhizosphere soil.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on the manuscript.
References
Acar YB, Gale RJ, Alshawabkeh AN, Marks RE, Parker R (1995) Electrokinetic remediation: basics and technology status. J Hazard Mater 40(2):117–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3894(94)00066-P
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105159
Bandowe B, Leimer S, Meusel H, Velescu A, Wilcke W (2018) Plant diversity enhances the natural attenuation of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PAHs and oxygenated PAHs) in grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 129:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.10.017
Cameselle C, Chirakkara RA, Reddy KR (2013) Electrokinetic-enhanced phytoremediation of soils: status and opportunities. Chemosphere 93:626–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.029
Cang L, Zhou D, Wang Q, Fan G (2012) Impact of electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil on its physicochemical properties, enzymatic and microbial activities. Electrochim Acta 86:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.112
Chen Z, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Song B, Li H, Chen Z (2016) Effects of root organic exudates on rhizosphere microbes and nutrient removal in the constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 92:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.04.001
Chen L, Beiyuan J, Hu W, Zhang Z, Duan C, Cui Q, Zhu X, He H, Huang X, Fang L (2022) Phytoremediation of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) contaminated soils using alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 293:133577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133577
Deng X, Chen B, Chen Y, Lu L, Yuan X, Yang Y, Zeng Q (2021) Variations in root morphological indices of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by seedling establishment methods and their relation to arsenic accumulation in plant tissues. Environ Pollut 281:116999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116999
Fan R, Ma W, Zhang H (2020) Microbial community responses to soil parameters and their effects on petroleum degradation during bio-electrokinetic remediation. Sci Total Environ 748:142463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142463
Fan G, Zhou D, Zhang Z, Ai Y, Zhang W, Shi G, Tong F, Liu L, Chen W, Li J, Gao Y (2021) Effect of two-dimensional electric field on the growth and cadmium uptake of Sedum plumbizincicola. Sep Purif Technol 259:118121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118121
Gao P, Wang S, Cheng F, Guo S (2022) Improvement of the electrokinetic fluxes by tall fescue: alleviation of ion attenuation and maintainability of soil colloidal properties. Chemosphere 290:133128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133128
Guo S, Fan R, Li T, Hartog N, Li F, Yang X (2014) Synergistic effects of bioremediation and electrokinetics in the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 109:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.007
Guo M, Gong Z, Miao R, Su D, Li X, Jia C, Zhuang J (2017) The influence of root exudates of maize and soybean on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation and soil bacterial community structure. Ecol Eng 99:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.018
Houshani M, Salehi-Lisar SY, Motafakkerazad R, Movafeghi A (2019) Uptake and distribution of phenanthrene and pyrene in roots and shoots of maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:9938–9944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04371-3
Huang H, Tang J, Niu Z, Giesy JP (2019) Interactions between electrokinetics and rhizoremediation on the remediation of crude oil-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 229:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.150
Huang Y, Li K, Liu H, Yuan X, Li M, Xiong B, Du R, Johnson DM, Xi Y (2022) Distribution, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in soil from the water level fluctuation zone of Xiangxi Bay, Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Geochem Hlth 44:2615–2628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01047-1
Hurter PN, Hatton TA (1992) Solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by poly(ethylene oxide-propylene oxide) block copolymer micelles: effects of polymer structure. Langmuir 8:1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00041a010
Hwang S, Cutright TJ (2002) Biodegradation of aged pyrene and phenanthrene in a natural soil. Chemosphere 47:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00016-4
Iannucci A, Canfora L, Nigro F, Vita PD, Beleggia R (2021) Relationships between root morphology, root exudate compounds and rhizosphere microbial community in durum wheat. Appl Soil Ecol 158:103781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103781
Jia H, Lu H, Liu J, Li J, Dai M, Yan C (2016) Effects of root exudates on the leachability, distribution, and bioavailability of phenanthrene and pyrene from mangrove sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:5566–5576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5772-0
Jiang O, Li L, Duan G, Gustave W, Zhai W, Zou L, An X, Tang X, Xu J (2023) Root exudates increased arsenic mobility and altered microbial community in paddy soils. J Environ Sci China 127:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2022.05.0361001-0742
Kumar M, Bolan NS, Hoang SA, Sawarkar AD, Rinklebe J (2021) Remediation of soils and sediments polluted with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: to immobilize, mobilize, or degrade? J Hazard Mater 420:126534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126534
Kumari B, Rajput S, Gaur P, Singh SN, Singh DP (2014) Biodegradation of pyrene and phenanthrene by bacterial consortium and evaluation of role of surfactant. Cell Mol Biol 60:22–28. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2014.60.5.5
Li F, Guo S, Wang S, Zhao M (2020) Changes of microbial community and activity under different electric fields during electro-bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 254:126880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126880
Lipińska A, Kucharski J, Wyszkowska J (2014) The effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the structure of organotrophic bacteria and dehydrogenase activity in soil. Polycycl Aromat Comp 34:35–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2013.844175
Liu YM, Cao WQ, Chen XX, Yu BG, Zou CQ (2020) The responses of soil enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure to nine years of varied zinc application rates. Sci Total Environ 737:140245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140245
Liu J, Yang Y, Zheng Q, Su X, Zhou Z (2022) Response of soil aggregate stability and rill erodibility to soil electric field. CATENA 215:106338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106338
Lu H, Wang W, Li F, Zhu L (2019) Mixed-surfactant-enhanced phytoremediation of PAHs in soil: Bioavailability of PAHs and responses of microbial community structure. Sci Total Environ 653:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.385
Mao X, Han FX, Shao X, Guo K, McComb J, Arslan Z, Zhang Z (2016) Electro-kinetic remediation coupled with phytoremediation to remove lead, arsenic and cesium from contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.021
Margesin R, Zimmerbauer A, Schinner F (2000) Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities. Chemosphere 40:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00218-0
Sánchez V, López-Bellido FJ, Cañizares P, Rodríguez L (2018) Can electrochemistry enhance the removal of organic pollutants by phytoremediation? J Environ Manage 225:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.086
Sánchez V, Francisco L-B, Rodrigo MA, Rodríguez L (2019a) Enhancing the removal of atrazine from soils by electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation using ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Chemosphere 232:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.216
Sánchez V, López-Bellido FJ, Rodrigo MA, Rodríguez L (2019b) Electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation of atrazine: differences between electrode and interelectrode soil sections. Sep Purif Technol 211:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.09.064
Saunders D, Carrillo JC, Gundlach ER, Iroakasi O, Visigah K, Zabbey N, Bonte M (2022) Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments and edible aquatic species in an oil-contaminated mangrove ecosystem in Bodo, Niger Delta, Nigeria: bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 832:154802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154802
Sivaram AK, Logeshwaran P, Lockington R, Naidu R, Megharaj M (2019) Phytoremediation efficacy assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soils using garden pea (Pisum sativum) and earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 229:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.005
Song L, Niu X, Tian Y, Xiao Y (2021) Assessment of PAH degradation potential of native species from a coking plant through identifying of the beneficial bacterial community within the rhizosphere soil. Chemosphere 264:128513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128513
Sun TR, Long C, Wang QY, Zhou DM, Cheng JM, Xu H (2010) Roles of abiotic losses, microbes, plant roots, and root exudates on phytoremediation of PAHs in a barren soil. J Hazard Mater 176:919–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.124
Tang Y, Junaid M, Niu A, Deng S, Pei D (2017) Diverse toxicological risks of PAHs in surface water with an impounding level of 175m in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Sci Total Environ 580:1085–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.064
Tian W, Zhao J, Zhou Y, Qiao K, Jin X, Liu Q (2017) Effects of root exudates on gel-beads/reeds combination remediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.09.021
Trivedi P, Leach JE, Tringe SG, Sa T, Singh BK (2020) Plant–microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:607–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0412-1
Tsbam A, Tkb C, Wan H, Sb E, Sq F, Zsk G, Nlmk E, As H, Hj I, Sy C (2021) Ecological and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sungai Perak, Malaysia. J Clean Prod 294:126124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126124
Virkutyte J, Sillanpää M, Latostenmaa P (2002) Electrokinetic soil remediation — critical overview. Sci Total Environ 289:97–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01027-0
Wang J, Farooq TH, Aslam A, Shakoor A, Chen X, Yan W (2021) Non-targeted metabolomics reveal the impact of phenanthrene stress on root exudates of ten urban greening tree species. Environ Res 196:110370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110370
Wu Y, Wang S, Cheng F, Guo P, Guo S (2020) Enhancement of electrokinetic-bioremediation by ryegrass: sustainability of electrokinetic effect and improvement of n-hexadecane degradation. Environ Res 188:109717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109717
Xu CY, Yu ZH, Li H (2015) The coupling effects of electric field and clay mineralogy on clay aggregate stability. J Soils Sediments 15:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1063-0
Xu L, Dai H, Skuza L, Wei S (2020) Optimal voltage and treatment time of electric field with assistant Solanum nigrum L. cadmium hyperaccumulation in soil. Chemosphere 253:126575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126575
Xu J, Huang X, Luo P, Zhang M, Li H, Gong D, Liu F, Xiao R, Wu J (2022) Root exudates release from Myriophyllum aquaticum and effects on nitrogen removal by constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 375:134095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134095
Yang GCC, Huang S, Jen Y, Tsai P (2016) Remediation of phthalates in river sediment by integrated enhanced bioremediation and electrokinetic process. Chemosphere 150:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.044
Yu Z, Li H, Liu X, Xu C, Xiong H (2016) Influence of soil electric field on water movement in soil. Soil till Res 155:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.08.020
Yu X, Kang X, Li Y, Cui Y, Tu W, Shen T, Yan M, Gu Y, Zou L, Ma M, Xiang Q, Zhao K, Liang Y, Zhang X, Chen Q (2019) Rhizobia population was favoured during in situ phytoremediation of vanadium-titanium magnetite mine tailings dam using Pongamia pinnata. Environ Pollut 255:113167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113167
Yuan L, Guo P, Guo S, Wang J, Huang Y (2021) Influence of electrical fields enhanced phytoremediation of multi-metal contaminated soil on soil parameters and plants uptake in different soil sections. Environ Res 198:111290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111290
Zhan X, Wu W, Zhou L, Liang J, Jiang T (2010) Interactive effect of dissolved organic matter and phenanthrene on soil enzymatic activities. J Environ Sci China 22:607–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60139-X
Zhang LQ, Zhu MT, Peng Y, Song LS, Liu Y (2022) Removal rate of benzo[a]pyrene from soil and characteristics of leaf physiological response by Ophiopogon japonicus and Carex breviculmis. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 42(7):1198–1207. https://doi.org/10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2022.07.1198
Zhou Y, Zou Q, Fan M, Xu Y, Chen Y (2020) Highly efficient anaerobic co-degradation of complex persistent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a bioelectrochemical system. J Hazard Mater 381:120945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120945
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42107441, 22136003, 42177397), the 111 Project (D20015), the Research Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Q20211205), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2020CFB153), and Open Fund of Engineering Research Center of Eco-environment in Three Gorges Reservoir Region (No: KF2022-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ming Li: formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft. Yingping Huang: writing, review and editing; resources; funding acquisition. Kun Li: conceptualization, methodology. Xi Yuan: supervision, funding acquisition. Huigang Liu: conceptualization. Meng Li: methodology. Tao Xu: formal analysis, funding acquisition. Zhaonian Zhang: funding acquisition. David M Johnson: writing—review and editing. Ying Xi: conceptualization; formal analysis; writing, original draft; funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Huang, Y., Li, K. et al. Enhancement of electrokinetic-phytoremediation by Ophiopogon japonicus: stimulation of electrokinetic on root system and improvement of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 97591–97600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29342-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29342-7