Abstract
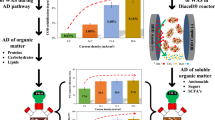
Despite its great potential to recover energy from waste sludge, anaerobic digestion (AD) still needs to solve issues such as slow hydrolysis and H2 inhibition. This study investigated the effects of coupling microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) with AD on the CH4 yield. Results and analysis show that the CH4 yield was significantly improved in MEC-AD reactors by two factors, i.e., enhanced and accelerated hydrolysis and acidogenesis, and enrichment of hydrogenotrophic methanogens in suspended culture. Compared with graphite rod and carbon fiber brush, carbon felt (CF) as an electrode showed the best performance in terms of net energy output. The CH4 yield of MEC-AD-CF was 40.2 L CH4/kg VS, 92.3% higher than in the control group, and the VS removal rate was also increased by 47.2%. Acetoclastic methanogens were dominant in the control AD reactor, while the relative abundance of Methanobacterium, which is electroactive and known as hydrogenotrophic methanogen, increased to 24.6% in MEC-AD with CF as electrodes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be sent on request.
References
Arenas C, Sotres A, Alonso RM, Gonzalez-Arias J, Moran A, Gomez X (2020) Pyrolysed almond shells used as electrodes in microbial electrolysis cell. Biomass Convers Biorefin 12(2):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00664-7
Baek G, Saikaly PE, Logan BE (2021) Addition of a carbon fiber brush improves anaerobic digestion compared to external voltage application. Water Res 188:116575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116575
Bao HX, Yang H, Zhang H, Liu YC, Su HZ, Shen ML (2020) Improving methane productivity of waste activated sludge by ultrasound and alkali pretreatment in microbial electrolysis cell and anaerobic digestion coupled system. Environ Res 180:108863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108863
Beegle JR, Borole AP (2017) An integrated microbial electrolysis-anaerobic digestion process combined with pretreatment of wastewater solids to improve hydrogen production. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 3(6):1073–1085. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00189D
Blasco-Gomez R, Batlle-Vilanova P, Villano M, Balaguer MD, Colprim J, Puig S (2017) On the edge of research and technological application: a critical review of electromethanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 18(4):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040874
Buitrón G, Cardeña R, Arcila JS (2019) Bioelectrosynthesis of methane integrated with anaerobic digestion. In: Mohan SV, Varjani S, Pandey A (eds) Microbial electrochemical technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 899–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64052-9.00037-6
Cheng KY, Kaksonen AH (2017) Integrating microbial electrochemical technologies with anaerobic digestion for waste treatment. In: Wong JW-C, Tyagi RD, Pandey A (eds) Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering: solid waste management. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 191–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63664-5.00009-5
Cheon J, Hidaka T, Mori S, Koshikawa H, Tsuno H (2008) Applicability of random cloning method to analyze microbial community in full-scale anaerobic digesters. J Biosci Bioeng 106:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.106.134
Desmond-Le Quemener E, Bridier A, Tian JH, Madigou C, Bureau C, Qi YJ, Bouchez T (2019) Biorefinery for heterogeneous organic waste using microbial electrochemical technology. Bioresour Technol 292:121943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121943
Feng YH, Zhang YB, Quan X, Chen S (2014) Enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge digestion by the addition of zero valent iron. Water Res 52:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.072
Fukuzaki S, Nishio N, Shobayashi M, Nagai S (1990) Inhibition of the fermentation of propionate to methane by hydrogen, acetate, and propionate. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:719–723. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.56.3.719-723.1990
Holmes DE, Shrestha PM, Walker DJF, Dang Y, Nevin KP, Woodard TL, Lovley DR (2017) Metatranscriptomic evidence for direct interspecies electron transfer between geobacter and methanothrix species in methanogenic rice paddy soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(9):e00223. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00223-17
Hua T, Li S, Li F, Zhou Q, Ondon BS (2019) Microbial electrolysis cell as an emerging versatile technology: a review on its potential application, advance and challenge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(6):1697–1711. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5898
Kafle GK, Kim SH (2013) Anaerobic treatment of apple waste with swine manure for biogas production: batch and continuous operation. Appl Energy 103:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.018
Kjeang E, McKechnie J, Sinton D, Djilali N (2007) Planar and three-dimensional microfluidic fuel cell architectures based on graphite rod electrodes. J Power Sources 168(2):379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.02.087
Kumar SS, Kumar V, Kumar R, Malyan SK, Bishnoi NR (2019) Ferrous sulfate as an in-situ anodic coagulant for enhanced bioelectricity generation and COD removal from landfill leachate. Energy 176:570–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.04.014
LaBarge N, Yilmazel YD, Hong P-Y, Logan BE (2017) Effect of pre-acclimation of granular activated carbon on microbial electrolysis cell startup and performance. Bioelectrochemistry 113:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2016.08.003
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG et al (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676
Lay JJ, Li YY, Noike T (1998) Interaction between homoacetogens and methanogens in lake sediments. J Ferment Bioeng 86:467–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0922-338X(98)80153-0
Logan BE, Call D, Cheng S, Hamelers HVM, Sleutels THJA, Jeremiasse AW, Rozendal RA (2008) Microbial electrolysis cells for high yield hydrogen gas production from organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8630–8640. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801553z
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal RA, Schrorder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5181–5192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0605016
Molina F, Castellano M, Garcia C, Roca E, Lema JM (2009) Selection of variables for on-line monitoring, diagnosis, and control of anaerobic digestion processes. Water Sci Technol 60(3):615–622. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.379
Moreno R, Martinez EJ, Escapa A, Martinez O, Diez-Antolinez R, Gomez X (2018) Mitigation of volatile fatty acid build-up by the use of soft carbon felt electrodes: evaluation of anaerobic digestion in acidic conditions. Fermentation 4(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4010002
Park J, Lee B, Tian D, Jun H (2018) Bioelectrochemical enhancement of methane production from highly concentrated food waste in a combined anaerobic digester and microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 247:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.021
Park SG, Rajesh PP, Sim YU, Jadhav DA, Noori T, Kim DHY, Al-Qaradawi SY, Yang E, Jang JK, Chae KJ (2022) Addressing scale-up challenges and enhancement in performance of hydrogen-producing microbial electrolysis cell through electrode modifications. Energy Rep 8:2726–2746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.198
Qin X, Lu XQ, Cai T, Niu CX, Han YL, Zhang ZY, Zhu XF, Zhen GY (2021) Magnetite-enhanced bioelectrochemical stimulation for biodegradation and biomethane production of waste actived sludge. Sci Total Environ 789:147859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147859
Ren GP, Hu AD, Huang SF, Ye J, Tang JH, Zhou SH (2018) Graphite-assisted electro-fermentation methanogenesis: spectroelectrochemical and microbial community analyses of cathode biofilms. Bioresour Technol 269:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.078
Rice EW, Baird R, Eaton AD, Clesceri LS (eds) (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Sanaye S, Mohammadi MH, Yazdani M, Rashvanlou RB (2022) Bio-gas augmentation and waste minimization by co-digestion process in anaerobic digestion system of a municipal waste water treatment plant. Energ Conver Manage 268:115989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.115989
Wang K, Yin J, Shen DS, Li N (2014) Anaerobic digestion of food waste for volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production with different types of inoculum: effect of pH. Bioresour Technol 161:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.088
Wang SN, Fang F, Li KY, Yue YR, Xu RZ, Luo JY, Ni BJ, Cao JS (2022a) Sludge reduction and microbial community evolution of activated sludge induced by metabolic uncoupler o-chlorophenol in long-term anaerobic-oxic process. J Environ Manage 316:115230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115230
Wang W, Lee DJ, Lei ZF (2022b) Integrating anaerobic digestion with microbial electrolysis cell for performance enhancement: a review. Bioresour Technol 344(B):126321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126321
Wang XT, Zhang YF, Wang B, Wang S, Xing X, Xu XJ, Liu WZ, Ren NQ, Lee DJ, Chen C (2022c) Enhancement of methane production from waste activated sludge using hybrid microbial electrolysis cells-anaerobic digestion (MEC-AD) process - a review. Bioresour Technol 346:126641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126641
Wang XT, Zhao L, Chen C, Chen KY, Yang H, Xu XJ, Zhou X, Liu WZ, Xing DF, Ren NQ, Lee DJ (2021) Microbial electrolysis cells (MEC) accelerated methane production from the enhanced hydrolysis and acidogenesis of raw waste activated sludge. Chem Eng J 413:127472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127472
Wei J, Liang P, Huang X (2011) Recent progress in electrodes for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:9335–9344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.019
Wong MT, Zhang D, Li J, Hui RKH, Tun HM, Brar MS, Park T-J, Chen Y, Leung FC (2013) Towards a metagenomic understanding on enhanced biomethane production from waste activated sludge after pH 10 pretreatment. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-38
Xu Y, Geng H, Chen RJ, Liu R, Dai XH (2021) Enhancing methanogenic fermentation of waste activated sludge via isoelectric-point pretreatment: insights from interfacial thermodynamics, electron transfer and microbial community. Water Res 197:117072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117072
Yu Y, Lee C, Hwang S (2005) Analysis of community structures in anaerobic processes using a quantitative real-time PCR method. Water Sci Technol 52(1-2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0502
Zhang QQ, Wu LY, Huang JH, Qu YT, Pan Y, Liu L, Zhu HT (2022) Recovering short-chain fatty acids from waste sludge via biocarriers and microfiltration enhanced anaerobic fermentation. Resour Conserv Recycl 182:106342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106342
Zhang S, Zhang P, Zhang G, Fan J, Zhang Y (2012) Enhancement of anaerobic sludge digestion by high-pressure homogenization. Bioresour Technol 118:496–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.089
Zhang YB, Feng YH, Yu QL, Xu ZB, Quan X (2014) Enhanced high-solids anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by the addition of scrap iron. Bioresour Technol 159:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.114
Zhao ZS, Zhang YB, Quan X, Zhao HM (2016) Evaluation on direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic sludge digestion of microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour Technol 200:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.021
Zhen G, Lu X, Kobayashi T, Kumar G, Xu K (2016) Promoted electromethanosynthesis in a two-chamber microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) containing a hybrid biocathode covered with graphite felt (GF). Chem Eng J 284:1146–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.071
Zheng XM, Lin RJ, Xu J, He YY, Zhang XY, Xie L (2022) Enhanced methane production by bimetallic metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as cathode in an anaerobic digestion microbial electrolysis cell. Chem Eng J 440:135799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135799
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52270117 & 51878046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lisha Yang: methodology, validation, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, writing (original draft), and visualization. Long Chen: visualization. Kai Chen: visualization. Hongtao Zhu: conceptualization, supervision, writing (review and editing), and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, ., Chen, L., Chen, K. et al. Improved net energy recovery in a sludge anaerobic digestion process by coupling an electrochemical system: electrode material and its impact on suspended microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 99473–99483 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29335-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29335-6