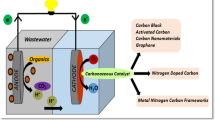
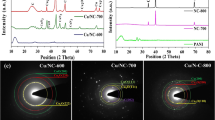
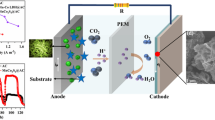
Abstract
With the rapid development of the economy, energy demand is more urgent. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) have the advantages of non-toxic, safety, and environmental protection, and are considered the ideal choice for the next generation of energy storage equipment. However, the slow kinetics of oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) on MFC air cathodes and the high cost of traditional platinum (Pt) catalysts hinder their practical application, so there is a need to develop efficient, low-cost, and stable electrocatalysts as alternatives. Recently, metal–organic framework (MOFs) has attracted wide attention in electrocatalysis. Electrocatalysts prepared by the nanocomposite of MOFs and carbon nanomaterials have multiple advantages, such as adjustable chemical properties, high specific surface area, and good electrical conductivity, which have been proven to be a promising electrocatalytic material. In this paper, the latest research progress of metal–organic frames (MOFs) and carbon nanocomposites is reviewed, and the preparation methods and modification of MOFs and carbon nanofibers, carbon nanotubes, and graphene composites are introduced, respectively, as well as their applications in MFC cathode. Finally, the main prospects of MOFs/carbon nanocomposite catalysts are put forward.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Allen MJ, Tung VC, Kaner RB (2010) Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chem Rev 110(1):132–145
Antolini E (2009) Carbon supports for low-temperature fuel cell catalysts. Appl Catal B 88(1–2):1–24
Armstrong MR, Shan B, Mu B (2017) Microscopy study of morphology of electrospun fiber-MOF composites with secondary growth. MRS Advances 2(46):2457–2463
Chen Z, Higgins D, Chen Z (2010) Nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes and their impact on the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells. Carbon 48(11):3057–3065
Chen C, Zhang X, Zhou ZY et al (2016a) Highly active Fe, N co-doped graphene nanoribbon/carbon nanotube composite catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim Acta 222:1922–1930
Chen D, Taylor KP, Hall Q et al (2016b) The neuropeptides FLP-2 and PDF-1 act in concert to arouse Caenorhabditis elegans locomotion. Genetics 204(3):1151–1159
Dai L (2013) Functionalization of graphene for efficient energy conversion and storage. Acc Chem Res 46(1):31–42
Ding W, Li L, Xiong K et al (2015) Shape fixing via salt recrystallization: a morphology-controlled approach to convert nanostructured polymer to carbon nanomaterial as a highly active catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc 137(16):5414–5420
Dou Y, Zhang W, Kaiser A (2020) Electrospinning of metal-organic frameworks for energy and environmental applications. Adv Sci (weinh) 7(3):1902590
Dwivedi KA, Huang SJ, Wang CT et al (2021) Fundamental understanding of microbial fuel cell technology: recent development and challenges. Chemosphere 288:132446
Falcaro P, Ricco R, Doherty CM et al (2014) MOF positioning technology and device fabrication. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5513–5560
Feng C, Guo Y, Xie Y et al (2020) Bamboo-like nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers encapsulated nickel-cobalt alloy nanoparticles composite material derived from the electrospun fiber of a bimetal-organic framework as efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts. Nanoscale 12(10):5942–5952
Fornero JJ, Rosenbaum M, Cotta MA et al (2008) Microbial fuel cell performance with a pressurized cathode chamber. Environ Sci Technol 42(22):8578–8584
Geng D, Liu H, Chen Y et al (2011) Non-noble metal oxygen reduction electrocatalysts based on carbon nanotubes with controlled nitrogen contents. J Power Sources 196(4):1795–1801
Ghasemi M, Shahgaldi S, Ismail M et al (2011) Activated carbon nanofibers as an alternative cathode catalyst to platinum in a two-chamber microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(21):13746–13752
Ghosh S, Das S, Meg M (2020) Conducting polymer-based nanohybrids for fuel cell application. Polymers (basel) 12(12):2993
Guo J, Gao M, Nie J et al (2019) ZIF-67/PAN-800 bifunctional electrocatalyst derived from electrospun fibers for efficient oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reaction. J Colloid Interface Sci 544:112–120
Guo Y, Dong A, Huang Q et al (2022) Hierarchical N-doped CNTs grafted onto MOF-derived porous carbon nanomaterials for efficient oxygen reduction. J Colloid Interface Sci 606:1833–1841
Han Z, Wang J, Liu S et al (2022) Electrospinning of neat graphene nanofibers. Adv Fiber Mater 4:268–279
Hassan MH, Soliman AB, Elmehelmey WA et al (2018) A Ni-loaded, metal-organic framework-graphene composite as a precursor for in situ electrochemical deposition of a highly active and durable water oxidation nanocatalyst. Chem Commun (camb) 55(1):31–34
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA et al (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43(8):3434–3441
Hou Y, Wen Z, Cui S et al (2015) An Advanced nitrogen-doped graphene/cobalt-embedded porous carbon polyhedron hybrid for efficient catalysis of oxygen reduction and water splitting. Adv Func Mater 25(6):872–882
Hou Y, Huang T, Wen Z et al (2014) Metal−organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped core-shell-structured porous Fe/Fe3C@C nanoboxes supported on graphene sheets for efficient oxygen reduction reactions. Adv Energy Mater 4(11):1400337
Huang Y, Tang K, Yuan F et al (2020) N-doped porous carbon nanofibers fabricated by bacterial cellulose-directed templating growth of MOF crystals for efficient oxygen reduction reaction and sodium-ion storage. Carbon 168:12–21
Jafari M, Parnian MJ, Gharibi H, Liang Z, Zou R (2021) Carbon-based nonprecious metal electrocatalysts derived from MOFs for oxygen-reduction reaction. Int J Energy Res 45(11):15676–15738
Ji D, Fan L, Li L et al (2019) Hierarchical catalytic electrodes of cobalt-embedded carbon nanotube/carbon flakes arrays for flexible solid-state zinc-air batteries. Carbon 142:379–387
Jiang N, Huang M, Li J et al (2021) Enhanced bioelectricity output of microbial fuel cells via electrospinning zeolitic imidazolate framework-67/polyacrylonitrile carbon nanofiber cathode. Bioresour Technol 337:125358
Jin S (2019) How to effectively utilize MOFs for electrocatalysis. ACS Energy Lett 4(6):1443–1445
Kamedulski P, Skorupska M, Binkowski P et al (2021) High surface area micro-mesoporous graphene for electrochemical applications. Sci Rep 11(1):22054
Kempahanumakkagari S, Vellingiri K, Deep A et al (2018) Metal–organic framework composites as electrocatalysts for electrochemical sensing applications. Coord Chem Rev 357:105–129
Kim J, Cote LJ, Huang J (2012) Two dimensional soft material: new faces of graphene oxide. Acc Chem Res 45(8):1356–1364
Leus K, Bogaerts T, De Decker J et al (2016) Systematic study of the chemical and hydrothermal stability of selected “stable” metal organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 226:110–116
Li H, Liu H, Jong Z et al (2011) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with high activity for oxygen reduction in alkaline media. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(3):2258–2265
Li D, Luo L, Pang Z et al (2014) Novel phenolic biosensor based on a magnetic polydopamine-laccase-nickel nanoparticle loaded carbon nanofiber composite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(7):5144–5151
Li Y, Zhu G, Huang H et al (2019) A N, S dual doping strategy via electrospinning to prepare hierarchically porous carbon polyhedra embedded carbon nanofibers for flexible supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 7(15):9040–9050
Li H, Zhang X, Qin Y et al (2021) Crafting controllable Fe-based hierarchically organic-frameworks from bacterial cellulose nanofibers for efficient electrocatalysts in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 512:230522
Li J, Qian J, Chen X et al (2022) Three-dimensional hierarchical graphitic carbon encapsulated CoNi alloy/N-doped CNTs/carbon nanofibers as an efficient multifunctional electrocatalyst for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Compos Part B: Eng 231:109573
Liang W, Wang B, Cheng J et al (2021) 3D, eco-friendly metal-organic frameworks@carbon nanotube aerogels composite materials for removal of pesticides in water. J Hazard Mater 401:123718
Liu S, Zhang H, Zhao Q et al (2016) Metal-organic framework derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon@graphene sandwich-like structured composites as bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Carbon 106:74–83
Liu Y, Ma Q, Yang M et al (2016) Flexible hollow nanofibers: Novel one-pot electrospinning construction, structure and tunable luminescence–electricity–magnetism trifunctionality. Chem Eng J 284:831–840
Liu C, Wang J, Li J et al (2017) Electrospun ZIF-based hierarchical carbon fiber as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J Mater Chem A 5(3):1211–1220
Liu T, Yang F, Cheng G et al. (2018) Reduced graphene oxide-wrapped Co9-x Fex S8/Co,Fe-N-C composite as bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution. Small 14:1703748
Lu AX, Ploskonka AM, Tovar TM et al (2017) Direct surface growth of uio-66-nh2 on polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for efficient toxic chemical removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(49):14502–14506
Mahalingam S, Ayyaru S, Ahn YH (2021) Facile one-pot microwave assisted synthesis of rGO-CuS-ZnS hybrid nanocomposite cathode catalysts for microbial fuel cell application. Chemosphere 278:130426
Meng Xu, Ling W, Mei Z et al (2022) Self-supporting nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide@carbon nanofiber hybrid membranes as high-performance integrated air cathodes in microbial fuel cells. Carbon 193:242–257
Molco M, Laye F, Samperio E et al (2021) Performance Fabrics Obtained by In Situ Growth of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Electrospun Fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(10):12491–12500
Nagaiah TC, Kundu S, Bron M et al (2010) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as a cathode catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline medium. Electrochem Commun 12(3):338–341
Noor T, Pervaiz S, Iqbal N et al (2020) Nanocomposites of NiO/CuO Based MOF with rGO: an efficient and robust electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation reaction in DMFC. Nanomaterials (basel) 11:17192
Pääkkö M, Vapaavuori J, Silvennoinen R et al (2008) Long and entangled native cellulose I nanofibers allow flexible aerogels and hierarchically porous templates for functionalities. Soft Matter 4:2492–2499
Pandey RK, Chen L, Teraji S et al (2019) Eco-friendly, direct deposition of metal nanoparticles on graphite for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(40):36525–36534
Peng L, Zhang X, Sun Y et al (2021) (2021) Electrospun ZIF-derived cavity porous carbon nanofibers as a freestanding cathode for lithium-oxygen batteries with ultralow overpotential. Nanoscale 13(39):16477–16486
Peterson GW, Lee DT, Barton HF et al (2021) Fibre-based composites from the integration of metal–organic frameworks and polymers. Nat Rev Mater 6(7):605–621
Rani S, Sharma B, Malhotra R et al (2020) Sn-MOF@CNT nanocomposite: an efficient electrochemical sensor for detection of hydrogen peroxide. Environ Res 191:110005
Rathinavel S, Priyadharshini K, Panda D (2021) A review on carbon nanotube: an overview of synthesis, properties, functionalization, characterization, and the application. Mater Sci Eng, B 268:115095
Ren J, Huang Y, Zhu H et al (2020) Recent progress on MOF-derived carbon materials for energy storage. Carbon Energy 2(2):176–202
Rubin HN, Neufeld BH, Reynolds MM (2018) Surface-anchored metal-organic framework-cotton material for tunable antibacterial copper delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(17):15189–15199
Sawant SY, Han TH, Cho MH (2016) Metal-free carbon-based materials: promising electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. Int J Mol Sci 18(1):25
Syed SAS, Tayyaba N, Costas M, Muhammad AN, Angeliki B, Muhammad SJ, Aziz R, Panagiotis T (2021) Nanostructure engineering of metal-organic derived frameworks: cobalt phosphide embedded in carbon nanotubes as an efficient ORR catalyst. Molecules 26(21):6672
Tang H, Cai S, Xie S et al (2016) Metal-organic-framework-derived dual metal- and nitrogen-doped carbon as efficient and robust oxygen reduction reaction catalysts for microbial fuel cells. Adv Sci (weinh) 3(2):1500265
Trapero JR, Horcajada L, Linares JJ et al (2017) Is microbial fuel cell technology ready? An economic answer towards industrial commercialization. Appl Energy 185:698–707
Twisk F (2013) Rebuttal to Ickmans et al. association between cognitive performance, physical fitness, and physical activity level in women with chronic fatigue syndrome. J Rehabil Res Dev 50(6):795–810
Wang Y, Zhang W, Deng D et al (2017) Two-dimensional materials confining single atoms for catalysis. Chin J Catal 38(9):1443–1453
Wang C, Kaneti YV, Bando Y et al (2018) Metal–organic framework-derived one-dimensional porous or hollow carbon-based nanofibers for energy storage and conversion. Mater Horiz 5(3):394–407
Wang Q, Yan S, Han G et al (2020) Facile production of natural silk nanofibers for electronic device applications. Comp Sci Technol 187:107950
Wang Y, Zhong K, Li H et al (2021) Bimetallic hybrids modified with carbon nanotubes as cathode catalysts for microbial fuel cell: effective oxygen reduction catalysis and inhibition of biofilm formation. J Power Sour 485:229273
Wen B, Yang H, Lin Y et al (2022) Novel bimetallic MOF derived hierarchical Co@C composites modified with carbon nanotubes and its excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 605:657–666
Wong CH, Chua CK, Khezri B et al (2013) Graphene oxide nanoribbons from the oxidative opening of carbon nanotubes retain electrochemically active metallic impurities. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(33):8685–8688
Xia W, Zou R, An L, Xia D, Guo S (2015) A metal–organic framework route to in situ encapsulation of Co@Co3O4@C core@bishell nanoparticles into a highly ordered porous carbon matrix for oxygen reduction. Energy Environ Sci 8(2):568–576
Xiao Y, Guo B, Zhang J et al (2020) A bimetallic MOF@graphene oxide composite as an efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Dalton Trans 49(17):5730–5735
Xiong W, Du F, Liu Y et al (2010) 3-D carbon nanotube structures used as high performance catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc 132(45):15839–15841
Xu Y, Wen Y, Zhu W et al (2012) Electrospun nanofibrous mats as skeletons to produce MOF membranes for the detection of explosives. Mater Lett 87:20–23
Xue F, Miao X, Liu W et al (2023) Resolving molecular size and homologues with a self assembled metal organic framework photonic crystal detector. ACS Mater Lett 5:1703–1709
Yang L, Bai Y, Zhang H, Geng J, Shao Z, Yi B (2017) Nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from Fe-MIL nanocrystals as an electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen reduction. RSC Adv 7(36):22610–22618
Yang CH, Hsiao YC, Lin LY (2021) Novel in situ synthesis of freestanding carbonized ZIF67/polymer nanofiber electrodes for supercapacitors via electrospinning and pyrolysis techniques. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(35):41637–41648
Zhang B, Wen Z, Ci S et al (2014) Synthesizing nitrogen-doped activated carbon and probing its active sites for oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(10):7464–7470
Zhang Y, Yuan S, Feng X et al (2016) Preparation of nanofibrous metal-organic framework filters for efficient air pollution control. J Am Chem Soc 138(18):5785–5788
Zhang S, Su W, Wang X et al (2019) Bimetallic metal-organic frameworks derived cobalt nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube nanopolyhedra as advanced electrocatalyst for high-performance of activated carbon air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 127:181–187
Zhang Z, Huang Y, Gao X et al (2020) Rational design of hierarchically structured CoS2@NCNTs from metal–organic frameworks for efficient lithium/sodium storage performance. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3(7):6205–6214
Zhao Y, Watanabe K, Hashimoto K (2012) Self-supporting oxygen reduction electrocatalysts made from a nitrogen-rich network polymer. J Am Chem Soc 134(48):19528–19531
Zhao C, Qiu Z, Yang J et al (2020) Metal–organic frameworks-derived core/shell porous carbon materials interconnected by reduced graphene oxide as effective cathode catalysts for microbial fuel cells. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(37):13964–13972
Zhao R, Wu X, Gao Y et al (2020b) A unique bimetallic MOF derived carbon–MWCNTs hybrid structure for selective electrochemical determination of lead ion in aqueous solution. Microchem J 158:105271
Zheng X, Cao Y, Liu D et al (2019) Bimetallic metal-organic-framework/reduced graphene oxide composites as bifunctional electrocatalysts for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(17):15662–15669
Zheng L, Lin X, Liu Y, Li HY, Sun YX, Li CJ (2021) Synergistically enhanced oxygen reduction reaction and oxytetracycline mineralization by FeCoO/GO modified cathode in microbial fuel cell. Sci Total Environ 808:151837
Zhong HX, Wang J, Zhang YW et al (2014) ZIF-8 derived graphene-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon sheets as highly efficient and durable oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53(51):14235–14239
Zhu Q-L, Xia W, Zheng L-R, Zou R, Liu Z, Xu Q (2017) Atomically dispersed Fe/N-doped hierarchical carbon architectures derived from a metal–organic framework composite for extremely efficient electrocatalysis. ACS Energy Lett 2(2):504–511
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 52103070), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-TP-20-057A1, FRF-IDRY-22-019, 06500100), the “Ten thousand plan” —national high-level personnel of special support program, and the National Environmental and Energy Science and Technology International Cooperation Base.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuyan: Formal analysis; Date Curation; Writing—Original Draft; Zhen: Date Curation; Yan: Writing—Review and Editing; Congju: Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, S., Guo, Z., Zhou, Y. et al. Research progress of MOFs/carbon nanocomposites on promoting ORR in microbial fuel cell cathodes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 93422–93434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29169-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29169-2