Abstract
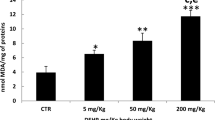
Acrylamide (ACR) is known to be a neurotoxic agent for humans and animals that has many applications in industry. Alpha-mangostin is a natural antioxidant that is extracted from mangosteen. This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of alpha-mangostin against ACR-induced neurotoxicity in rats and PC12 cells. Male Wistar rats were used in this investigation for 11 days, divided into 8 groups: 1. control group (normal saline), 2. ACR (50 mg/kg, i.p.), 3–6. ACR + alpha-mangostin (20, 40, 60 mg/kg, p.o.), 7. ACR + vitamin E (200 mg/kg, i.p., every other day) 8. alpha-mangostin (60 mg/kg, p.o.). On the last day of the study, the behavioral test was performed. The amounts of malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) were measured. Also, the effects of ACR and alpha-mangostin were assessed by MTT assay on PC12 cells, and the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), and cleaved caspase-3 proteins were measured by Western blotting. Receiving ACR caused motor disorders in animals, increased MDA, and decreased GSH levels of the cerebral cortex versus the control group. Alpha-mangostin (60 mg/kg) reduced ACR motility disorders, MDA amounts, and augmented GSH levels. The concurrent administration of vitamin E and ACR reduced gait score, MDA level, and amplified GSH content versus the ACR group. In the in vitro section, alpha-mangostin (1.25 µM, 24 h) increased cell viability, attenuated ROS, Bax/Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase-3 levels versus the ACR group. Alpha-mangostin reduced the toxicity of ACR by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Therefore, it could be a promising compound for managing ACR-induced neurotoxicity.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Ahmadian R, Heidari MR, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2022) Alpha-mangostin protects PC12 cells against neurotoxicity induced by cadmium and arsenic. Biol Trace Elem Reshttps://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03498-8
Ahrari Roodi P, Moosavi Z, Afkhami Goli A, Azizzadeh M, Hosseinzadeh H (2018) Histopathological study of protective effects of honey on subacute toxicity of acrylamide-induced tissue lesions in rats’ brain and liver. Iran J Toxicol 12:1–8. https://doi.org/10.32598/IJT.12.3.511.1
Ardakanian A, Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Omidkhoda F, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2022) Effect of alpha-mangostin on olanzapine-induced metabolic disorders in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 25:198–207. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2022.58734.13047
Eisvand F, Imenshahidi M, Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Tabatabaei Yazdi SA, Rameshrad M, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2022) Cardioprotective effects of alpha-mangostin on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Phytother Res 36:506–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7356
Esmaeelpanah E, Razavi BM, Vahdati Hasani F, Hosseinzadeh H (2018) Evaluation of epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin gallate effects on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in rats and cytotoxicity in PC 12 cells. Drug Chem Toxicol 41:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2017.1381108
Exon JH (2006) A review of the toxicology of acrylamide. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 9:397–412. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400600681430
Fang Y, Su T, Qiu X, Mao P, Xu Y, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Xie P, Liu Q (2016) Protective effect of alpha-mangostin against oxidative stress induced-retinal cell death. Sci Rep 6:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21018
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Hemadeh B, Razavi BM, Eisvand F, Hosseinzadeh H (2020a) Effect of carnosic acid on acrylamide induced neurotoxicity: in vivo and in vitro experiments. Drug Chem Toxicol 45:1528–1535. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2020.1845715
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Hosseinzadeh H (2020a) Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran J Basic Med Sci 23: 1100–1112. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Hosseinzadeh H (2020b) Effects of rosmarinic acid on nervous system disorders: an updated review. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:1779–1795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01935-w
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2020b) Investigating the ameliorative effect of alpha-mangostin on development and existing pain in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Phytother Res 34:3211–3225. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6768
Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Cheraghi Farmad H, Hosseinzadeh H, Mehri S (2021) Protective effects of selenium on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 24:1041–1049. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2021.55009.12331
Granda C, Moreira RG (2005) Kinetics of acrylamide formation during traditional and vacuum frying of potato chips. J Food Process Eng 28:478–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4530.2005.034.x
Ibrahim MY, Hashim NM, Mariod AA, Mohan S, Abdulla MA, Abdelwahab SI, Arbab IA (2016) α-Mangostin from Garcinia mangostana Linn: an updated review of its pharmacological properties. Arab J Chem 9:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.02.011
Janhom P, Dharmasaroja P (2015) Neuroprotective effects of alpha-mangostin on MPP+-induced apoptotic cell death in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Toxicol 2015:919058. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/919058
Jin C, Wu X, Zhang Y (2013) Relationship between antioxidants and acrylamide formation: A review. Food Res Int 51:611–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.047
Lai SM, Gu ZT, Zhao MM, Li XX, Ma YX, Luo L, Liu J (2017) Toxic effect of acrylamide on the development of hippocampal neurons of weaning rats. Neural Regen Res 12:1648–1654. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.217345
Li L, Sun H-y, Liu W, Zhao H-y, Shao M-l (2017) Silymarin protects against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity via Nrf2 signalling in PC12 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 102:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.01.021
Lingnert H, Grivas S, Jägerstad M, Skog K, Törnqvist M, Åman P (2002) Acrylamide in food: mechanisms of formation and influencing factors during heating of foods. Scand J Nutr 46:159–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/110264802762225273
Liu Z, Song G, Zou C, Liu G, Wu W, Yuan T, Liu X (2015) Acrylamide induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in BV-2 microglial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 84:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.03.013
Mehri S, Abnous K, Mousavi SH, Shariaty VM, Hosseinzadeh H (2012) Neuroprotective effect of crocin on acrylamide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9752-8
Mehri S, Shahi M, Razavi BM, Hassani FV, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone in acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17:1007–1011
Mehri S, Abnous K, Khooei A, Mousavi SH, Shariaty VM, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) Crocin reduced acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rat through inhibition of oxidative stress. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18:902–908
Mihara M, Uchiyama M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(78)90342-1
Mohammadzadeh L, Rahbardar MG, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2021) Crocin protects malathion-induced parkinson-like disease by inhibiting apoptosis and α-synuclein accumulation in rats’ striatum. J Mol Neurosci 72:983–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01990-3
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 582:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7
Nava Catorce M, Acero G, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Fragoso G, Govezensky T, Gevorkian G (2016) Alpha-mangostin attenuates brain inflammation induced by peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration in C57BL/6J mice. J Neuroimmunol 297:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.05.008
Oprea D, Sanz CG, Barsan MM, Enache TA (2022) PC-12 Cell line as a neuronal cell model for biosensing applications. Biosensors 12:500. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070500
Parekh P, Sharma N, Gadepalli A, Sharma M, Chatterjee S, Kate A, Khairnar A (2022) AMPK-dependent autophagy activation and alpha-Synuclein clearance: a putative mechanism behind alpha-mangostin’s neuroprotection in a rotenone-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Metab Brain Dis 37:2853–2870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01087-1
Pennisi M, Malaguarnera G, Puglisi V, Vinciguerra L, Vacante M, Malaguarnera M (2013) Neurotoxicity of acrylamide in exposed workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:3843–3854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10093843
Prasad SN, Muralidhara (2012) Evidence of acrylamide induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster - its amelioration with spice active enrichment: relevance to neuropathy. Neurotoxicology 33:1254–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2012.07.006
R Saboktakin M, A Tabar N, M Tabatabaie R, Maharramov A, A Ramazanov M (2012) Intelligent drug delivery systems based on modified chitosan nanoparticles. Lett Org Chem 9:56-70https://doi.org/10.2174/157017812799303999
Razavi BM, Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Hosseinzadeh H (2021) A review of therapeutic potentials of turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its active constituent, curcumin, on inflammatory disorders, pain, and their related patents. Phytother Res 35:6489–6513. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7224
Ruankham W, Suwanjang W, Phopin K, Songtawee N, Prachayasittikul V, Prachayasittikul S (2021) Modulatory effects of alpha-mangostin mediated by SIRT1/3-FOXO3a pathway in oxidative stress-induced neuronal cells. Front Nutr 8:714463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.714463
Schmid W (1855) Ueber Das Mangostin. Liebigs Ann Chem 93:83–88
Tandisepanah Z, Foroutanfar A, Aziminia A, Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2022) Protective effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Lippia citriodora Kunth. on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity. Avicenna J Phytomed 12:281–294. https://doi.org/10.22038/AJP.2021.19173
Tousian H, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2020) Alpha-mangostin decreased cellular senescence in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. DARU J Pharm Sci 28:45–55. https://doi.org/10.22038/AJP.2021.19173
Tousian Shandiz H, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Review of Garcinia mangostana and its xanthones in metabolic syndrome and related complications. Phytother Res 31:1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5862
Touzé S, Guerin V, Guezennec A-G, Binet S, Togola A (2015) Dissemination of acrylamide monomer from polyacrylamide-based flocculant use—sand and gravel quarry case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6423–6430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3177-0
Wang H, Joseph JA (1999) Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic Biol Med 27:612–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(99)00107-0
Wenzl T, De La Calle MB, Anklam E (2003) Analytical methods for the determination of acrylamide in food products: a review. Food Addit Contam 20:885–902. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030310001605051
Yousef MI, El-Demerdash FM (2006) Acrylamide-induced oxidative stress and biochemical perturbations in rats. Toxicology 219:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.11.008
Zamani E, Shokrzadeh M, Fallah M, Shaki F (2017) A review of acrylamide toxicity and its mechanism. Pharm Biomed Res 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.pbr.3.1.1
Zhu YJ, Zeng T, Zhu YB, Yu SF, Wang QS, Zhang LP, Guo X, Xie KQ (2008) Effects of acrylamide on the nervous tissue antioxidant system and sciatic nerve electrophysiology in the rat. Neurochem Res 33:2310–2317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9730-9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Pharmaceutical Research Center and the Vice-Chancellor of Research, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
This dissertation has been financially supported by the Vice Chancellor for Research of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Hossein Hosseinzadeh and Dr. Bibi Marjan Razavi supervised the whole project, conceived the original idea, verified the analytical methods, and checked the whole procedure and paper. Farivar Ghobakhlou did the experiments and analyzed the data. Farhad Eisvand helped in doing the experiments and analyzing the data. Mahboobeh Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All animal tests were carried out in accordance with the Mashhad School of Pharmacy's ethics committee (code 931569).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghobakhlou, F., Eisvand, F., Razavi, B.M. et al. Evaluating the effect of alpha-mangostin on neural toxicity induced by acrylamide in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 95789–95800 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29162-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29162-9