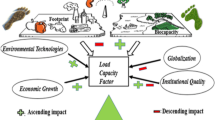
Abstract
In contemplating the prospects of advanced world countries, researchers stand divided among two groups: one group crying “melting of glaciers” and the group denying global warming as a significant concern while reaping the fruits of growth. One persistent concern for the other group is much desirable economic growth at the cost of environmental degradation, which is now reaching a scale where the global climate is become not only unsustainable but also causing a significant threat to our existence. In our opinion, environmental degradation should be taken very seriously now, particularly by pointing out the necessary variables causing it so that effective policy designs are formulated. The present study also gives a brief overview of the environmental repercussions with references to technology-led growth in developed countries. We have incorporated the direct composition effect captured by the capital-labor ratio (K/L), indicating that advanced countries use environmentally friendly technology for production processes. We propose that the most vulnerable impact of economic activities on environmental degradation (measured through carbon dioxide emissions) are urbanization, trade, and energy use. The latter is probably more policy-oriented, is undoubtedly more easily measured, and could be deeply analyzed for policy formulation. Whereas, in the urban areas, emissions of carbon dioxide particulate with an increase in population and development and serve as a significant concern for global environmental sustainability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
1996–2016
References
Ahmed Z, Adebayo TS, Udemba EN, Murshed M, Kirikkaleli D (2022a) Effects of economic complexity, economic growth, and renewable energy technology budgets on ecological footprint: the role of democratic accountability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(17):24925–24940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17673-2
Ahmed Z, Caglar AE, Murshed M (2022b) A path towards environmental sustainability: the role of clean energy and democracy in ecological footprint of Pakistan. J Clean Prod 358:132007
Ajmi AN, Inglesi-Lotz R (2021) Revisiting the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia: carbon dioxide vs. ecological footprint. Energ Source Part B: Econ Plan Policy 16(5):406–419
Alam MS, Duraisamy P, Siddik AB, Murshed M, Mahmood H, Palanisamy M, Kirikkaleli D (2023) The impacts of globalization, renewable energy, and agriculture on CO2 emissions in India: contextual evidence using a novel composite carbon emission-related atmospheric quality index. Gondwana Res 119(C):384–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2023.04.005
Antweiler W, Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2001) Is free trade good for the environment? Am Econ Rev 91(4):877–908
Anwar A, Sharif A, Fatima S, Ahmad P, Sinha A, Khan SAR, Jermsittiparsert K (2021b) The asymmetric effect of public private partnership investment on transport CO2 emission in China: evidence from quantile ARDL approach. J Clean Prod 288:125282
Anwar MA, Madni GR, Yasin I (2021a) Environmental quality, forestation, and health expenditure: a cross-country evidence. Environ Dev Sustain 23:16454–16480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01364-6
Arellano M, Bond S (1991) Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev Econ Stud 58(2):277–297
Aslam A (2020) The hotly debate of human capital and economic growth: why institutions may matter? Qual Quant 54(4):1351–1362
Aslam A, Naveed A, Shabbir G (2021) Is it an institution, digital or social inclusion that matters for inclusive growth? A panel data analysis. Qual Quant 55(1):333–355
Aslam A, Sultana N, Yasin I (2017) Bi-directional associations among educational quality, institutions and social inclusion. Pak Econ Soc Rev 55(2):473–490
Aziz N, Sharif A, Raza A, Jermsittiparsert K (2021) The role of natural resources, globalization, and renewable energy in testing the EKC hypothesis in MINT countries: new evidence from Method of Moments Quantile Regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:13454–13468
Baltagi BH, Feng Q, Kao C (2012) A Lagrange Multiplier test for cross-sectional dependence in a fixed effects panel data model. J Econ 170(1):164–177
Bélaïd F, Youssef M (2017) Environmental degradation, renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption, and economic growth: assessing the evidence from Algeria. Energy Policy 102:277–287
Bergara ME, Henisz WJ, Spiller PT (1998) Political institutions and electric utility investment: A cross-nation analysis. Calif Manage Rev 40(2):18–35
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253
Carley S, Yahng L (2018) Willingness-to-pay for sustainable beer. PLoS One 13(10):e0204917
Cass D (1965) Optimum growth in an aggregative model of capital accumulation. Rev Econ Stud 32(3):233–240
Chen X, Rahaman MA, Murshed M, Mahmood H, Hossain MA (2023) Causality analysis of the impacts of petroleum use, economic growth, and technological innovation on carbon emissions in Bangladesh. Energy 267:126565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126565
Cole MA, Elliott RJ (2003) Determining the trade–environment composition effect: the role of capital, labor and environmental regulations. J Environ Econ Manage 46(3):363–383
Congleton RD (1992) Political institutions and pollution control. Rev Econ Stat:412–421
Dabachi UM, Mahmood S, Ahmad AU, Ismail S, Farouq IS, Jakada AH, Kabiru K (2020) Energy consumption, energy price, energy intensity environmental degradation, and economic growth nexus in African OPEC countries: evidence from simultaneous equations models. J Environ Treat Tech 8(1):403–409
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1(2):277–300
Ding Q, Khattak SI, Ahmad M (2021) Towards sustainable production and consumption: assessing the impact of energy productivity and eco-innovation on consumption-based carbon dioxide emissions (CCO2) in G-7 nations. Sustain Prod Consum 27:254–268
Dou G, Choi T-M (2021) Does implementing trade-in and green technology together benefit the environment? Eur J Oper Res 295(2):517–533
Ehrlich PR, Holdren JP (1971) Impact of Population Growth: complacency concerning this component of man’s predicament is unjustified and counterproductive. Science 171(3977):1212–1217
Farooq A, Hamid K, Aslam A, Shabbir G (2019) Triangular nexus between institutional quality, trade liberalization, and agricultural growth in Pakistan. Paradigms 13(2):10–17
Gielen D, Gorini R, Leme R, Prakash G, Wagner N, Janeiro L, Collins S, Kadir M, Asmelash E, Ferroukhi R (2021) World Energy Transitions Outlook: 1.5 °C Pathway. International Renewable Energy Agency
Glaeser EL, Resseger MG (2010) The complementarity between cities and skills. J Reg Sci 50(1):221–244
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Gyamfi BA, Ozturk I, Bein MA, Bekun FV (2021) An investigation into the anthropogenic effect of biomass energy utilization and economic sustainability on environmental degradation in E7 economies. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 15(3):840–851
Halkos GE, Gkampoura E-C (2021) Examining the linkages among carbon dioxide emissions, electricity production and economic growth in different income levels. Energies 14(6):1682
He X, Khan S, Ozturk I, Murshed M (2023) The role of renewable energy investment in tackling climate change concerns: environmental policies for achieving SDG-13. Sustain Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2491
Howarth RB (1997) Energy efficiency and economic growth. Contemp Econ Policy 15(4):1–9
Ibrahim RL, Ajide KB (2022) Trade facilitation and environmental quality: empirical evidence from some selected African countries. Environ Dev Sustain 24(1):1282–1312
IMF (2018) World economic outlook. IMF Washington, DC
Jacobson MZ, Delucchi MA (2011) Providing all global energy with wind, water, and solar power, Part I: Technologies, energy resources, quantities and areas of infrastructure, and materials. Energy Policy 39(3):1154–1169
Jahanger A, Usman M, Ahmad P (2022) Investigating the effects of natural resources and institutional quality on CO2 emissions during globalization mode in developing countries. Int J Environ Sci Technol:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04638-2
Jiang Q, Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Lin P (2021) Mitigation pathways to sustainable production and consumption: examining the impact of commercial policy on carbon dioxide emissions in Australia. Sustain Prod Consump 25:390–403
Jorgenson DW, Wilcoxen PJ (1998) Energy the environment, and economic growth. In Handbook of Natural Res Energy Econ 3:1267–1349
Kahuthu A (2006) Economic growth and environmental degradation in a global context. Environ Dev Sustain 8(1):55–68
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econ 90(1):1–44
Karl TL (1997) The paradox of plenty. University of California Press
Kennedy G (2003) Food security in the context of urban sub-Saharan Africa. In: Food Africa Internet Forum 31
Khan Z, Murshed M, Dong K, Yang S (2021) The roles of export diversification and composite country risks in carbon emissions abatement: evidence from the signatories of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership agreement. Appl Econ 53(41):4769–4787
Komal R, Abbas F (2015) Linking financial development, economic growth and energy consumption in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:211–220
Koopmans TC (1969) Objectives, constraints, and outcomes in optimal growth models. In: Economic Models, Estimation and Risk Programming: Essays in Honor of Gerhard Tintner. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 110–132
Kovandzic T, Schaffer ME, Kleck G (2012) Gun prevalence, homicide rates and causality: a GMM approach to endogeneity bias. In: The Sage handbook of criminological research methods. Sage Publications Ltd., pp 76–92
Kuznets S (2019) Economic growth and income inequality. Routledge
Latan H, Jabbour CJC, de Sousa Jabbour ABL, Wamba SF, Shahbaz M (2018) Effects of environmental strategy, environmental uncertainty and top management’s commitment on corporate environmental performance: the role of environmental management accounting. J Clean Prod 180:297–306
Lei L, Ozturk I, Murshed M, Abrorov S, Alvarado R, Mahmood H (2023) Environmental innovations, energy innovations, governance, and environmental sustainability: evidence from South and Southeast Asian countries. Res Policy 82:103556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103556
Levin K, Cashore B, Bernstein S, Auld G (2012) Overcoming the tragedy of super wicked problems: constraining our future selves to ameliorate global climate change. Policy Sci 45(2):123–152
Lin B, Ahmad I (2017) Analysis of energy related carbon dioxide emission and reduction potential in Pakistan. J Clean Prod 143:278–287
Lorde T, Waithe K, Francis B (2010) The importance of electrical energy for economic growth in Barbados. Energy Econ 32(6):1411–1420
Lv T, Hu H, Xie H, Zhang X, Wang L, Shen X (2022) An empirical relationship between urbanization and carbon emissions in an ecological civilization demonstration area of China based on the STIRPAT model. Environ Dev Sustain 25(3):2465–2486
MacDiarmid SA, Peters KM, Shobeiri SA, Wooldridge LS, Rovner ES, Leong FC, Siegel SW, Tate SB, Feagins BA (2010) Long-term durability of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation for the treatment of overactive bladder. J Urol 183(1):234–240
Mahalik MK, Babu MS, Loganathan N, Shahbaz M (2017) Does financial development intensify energy consumption in Saudi Arabia? Renew Sust Energ Rev 75:1022–1034
Maller C, Townsend M, Pryor A, Brown P, St Leger L (2006) Healthy nature healthy people: ‘contact with nature’ as an upstream health promotion intervention for populations. Health Promot Int 21(1):45–54
McCarthy JF (2004) Changing to gray: decentralization and the emergence of volatile socio-legal configurations in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. World Development 32(7):1199–1223
Medhaug I, Stolpe MB, Fischer EM, Knutti R (2017) Reconciling controversies about the ‘global warming hiatus’. Nature 545(7652):41–47
Moore M, Gould P, Keary BS (2003) Global urbanization and impact on health. Int J Hyg Environ Health 206(4-5):269–278
Murshed M, Rashid S, Ulucak R, Dagar V, Rehman A, Alvarado R, Nathaniel SP (2021) Mitigating energy production-based carbon dioxide emissions in Argentina: the roles of renewable energy and economic globalization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:16939–16958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16867-y
Murshed M, Apergis N, Alam MS, Khan U, Mahmud S (2022) The impacts of renewable energy, financial inclusivity, globalization, economic growth, and urbanization on carbon productivity: Evidence from net moderation and mediation effects of energy efficiency gains. Renew Energy 196:824–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.012
Nordhaus WD (2017) Revisiting the social cost of carbon. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(7):1518–1523
Nzimande NP, Ngalawa H (2017) The endogeneity of business cycle synchronisation in SADC: a GMM approach. Cogent Econ Finance 5(1):1358914
Østergaard PA, Duic N, Noorollahi Y, Mikulcic H, Kalogirou S (2020) Sustainable development using renewable energy technology. In: In, vol 146. Elsevier, pp 2430–2437
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:639–647
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Mimeo, University of Cambridge
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22(2):265–312
Peters KM, Carrico DJ, Perez-Marrero RA, Khan AU, Wooldridge LS, Davis GL, MacDiarmid SA (2010) Randomized trial of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus Sham efficacy in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome: results from the SUmiT trial. J Urol 183(4):1438–1443
Rahman MM (2020) Environmental degradation: the role of electricity consumption, economic growth and globalisation. J Environ Manag 253:109742
Razzaq A, Sharif A, Najmi A, Tseng ML, Lim MK (2021) Dynamic and causality interrelationships from municipal solid waste recycling to economic growth, carbon emissions and energy efficiency using a novel bootstrapping autoregressive distributed lag. Resour Conserv Recycl 166:105372
Richardson M (2009) Principal component analysis. http://people.maths.ox.ac.uk/richardsonm/SignalProcPCA.pdf (last access: 3.5. 2013)
Ringnér M (2008) What is principal component analysis? Nat Biotechnol 26(3):303–304
Safdar N, Chaudhry IS, Chaudhry MO (2019) Energy consumption, environmental degradation and economic growth in developing countries. Pak J Life Soc Sci 39(2)
Saqib N, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Usman M (2023) Integration of renewable energy and technological innovation in realizing environmental sustainability: the role of human capital in EKC framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):16372–16385
Sekrafi H, Sghaier A (2018) Examining the relationship between corruption, economic growth, environmental degradation, and energy consumption: a panel analysis in MENA region. J Knowl Econ 9(3):963–979
Selden TM, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development: is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27(2):147–162
Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S (1992) Economic growth and environmental quality: time-series and cross-country evidence, vol 904. World Bank Publications
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Indic 52:379–393
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew Energy 133:685–691
Sharma SS (2011) Determinants of carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from 69 countries. Appl Energy 88(1):376–382
Shlens J (2014) A tutorial on principal component analysis https://arxiv.org/abs/1404.1100
Siddiqui R (2004) Energy and economic growth in Pakistan. Pak Dev Rev:175–200
Sohag K, Begum RA, Abdullah SMS, Jaafar M (2015) Dynamics of energy use, technological innovation, economic growth and trade openness in Malaysia. Energy 90:1497–1507
Solow RM (1956) A contribution to the theory of economic growth. Q J Econ 70(1):65–94
Solow RM (2005) Reflections on growth theory. Handb Econ Growth 1:3–10
Solow RM (2007) The last 50 years in growth theory and the next 10. Oxf Rev Econ Policy 23(1):3–14
Spilker G (2013) Globalization, political institutions and the environment in developing countries. Routledge
Stern DI (2011) The role of energy in economic growth. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1219(1):26–51
Suki NM, Suki NM, Afshan S, Sharif A, Meo MS (2022a) The paradigms of technological innovation and renewables as a panacea for sustainable development: a pathway of going green. Renew Energy 181:1431–1439
Suki NM, Suki NM, Sharif A, Afshan S (2021) The role of logistics performance for sustainable development in top Asian countries: evidence from advance panel estimations. Sustain Dev 29(4):595–606
Suki NM, Suki NM, Sharif A, Afshan S, Jermsittiparsert K (2022b) The role of technology innovation and renewable energy in reducing environmental degradation in Malaysia: a step towards sustainable environment. Renew Energy 182:245–253
Syrquin M (1988) Patterns of structural change. Handb Dev Econ 1:203–273
Tipping ME, Bishop CM (1999) Probabilistic principal component analysis. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol 61(3):611–622
Turok I, McGranahan G (2013) Urbanization and economic growth: the arguments and evidence for Africa and Asia. Environ Urban 25(2):465–482
Ullah S, Akhtar P, Zaefarian G (2018) Dealing with endogeneity bias: the generalized method of moments (GMM) for panel data. Ind Mark Manag 71:69–78
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Energy Policy 162:112780
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P (2023) Are Mercosur economies going green or going away? An empirical investigation of the association between technological innovations, energy use, natural resources and GHG emissions. Gondwana Res 113:53–70
Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
Usman M, Radulescu M (2022) Examining the role of nuclear and renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint: does the role of technological innovation really create some difference? Sci Total Environ 841:156662
Véron R (2006) Remaking urban environments: the political ecology of air pollution in Delhi. Environ Plan A 38(11):2093–2109
Vidal R, Ma Y, Sastry SS (2016) Principal component analysis. In: Generalized principal component analysis. Springer, pp 25–62
Wen J, Mughal N, Zhao J, Shabbir MS, Niedbała G, Jain V, Anwar A (2021) Does globalization matter for environmental degradation? Nexus among energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy Policy 153:112230
Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P (1987) Principal component analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 2(1-3):37–52
Yan C, Murshed M, Ozturk I, Siddik AB, Ghardallou W, Khudoykulov K (2023) Decarbonization blueprints for developing countries: the role of energy productivity improvement, renewable energy, and financial development in environmental improvement. Resour Policy 83:103674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103674
Yasin I, Ahmad N, Chaudhary MA (2020) Catechizing the environmental-impression of urbanization, financial development, and political institutions: a circumstance of ecological footprints in 110 developed and less-developed countries. Soc Indic Res 147(2):621–649
Yasin I, Ahmad N, Chaudhary MA (2021) The impact of financial development, political institutions, and urbanization on environmental degradation: evidence from 59 less-developed economies. Environ Dev Sustain 23(5):6698–6721
Yasmeen R, Li Y, Hafeez M, Ahmad H (2018) The trade-environment nexus in light of governance: a global potential. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(34):34360–34379
Yilanci V, Gorus MS, Aydin M (2019) Are shocks to ecological footprint in OECD countries permanent or temporary? J Clean Prod 212:270–301
Zandi G, Haseeb M, Malaysia J (2019) The role of trade liberalization in carbon dioxide emission: evidence from heterogeneous panel estimations. Int J Financial Res 10(5):228–240
Zeraibi A, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Murshed M (2021) The influences of renewable electricity generation, technological innovation, financial development, and economic growth on ecological footprints in ASEAN-5 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(37):51003–51021
Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does structural transformation in economy impact inequality in renewable energy productivity? implications for sustainable development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050
Żuk P, Żuk P, Pluciński P (2021) Coal basin in Upper Silesia and energy transition in Poland in the context of pandemic: the socio-political diversity of preferences in energy and environmental policy. Res Policy 71:101987
Abdi H, Williams LJ (2010) Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev 2(4):433–459
Adams S, Klobodu EKM (2017) Urbanization, democracy, bureaucratic quality, and environmental degradation. J Policy Model 39(6):1035–1051
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I. Y. and A. A. conceptualized and wrote the original draft; A. B. S. and M. M. compiled the literature review and generated the graphical illustrations, reviewed and edited, conducted the econometric analysis, and analyzed the findings; and K. A. wrote the Introduction and supervised and reviewed the whole work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yasin, I., Aslam, A., Siddik, A.B. et al. Offshoring the scarring causes and effects of environmental challenges faced by the advanced world: an empirical evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 79335–79345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27918-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27918-x