Abstract
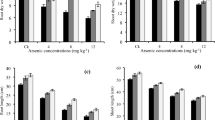
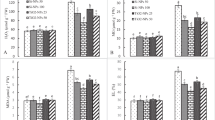
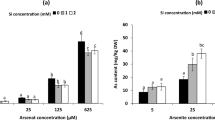
Soil contamination with toxic heavy metals (such as arsenic (As)) is becoming a serious global problem due to rapid development of social economy, although the use of silicon (Si) and sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) has been found effective in enhancing plant tolerance against biotic and abiotic stresses including the As toxicity. For this purpose, a pot experiment was conducted using the different levels of As toxicity in the soil, i.e., (0 mM (no As), 50, and 100 µM) which were also supplied with the different exogenous levels of Si, i.e., (0 (no Si), 1.5, and 3 mM) and also with the NaHS, i.e., (0 (no NaHS), 1, and 2 mM) on growth, photosynthetic pigments, gas exchange characteristics, oxidative stress biomarkers, antioxidant machinery (enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants), and their gene expression, ion uptake, organic acid exudation, and As uptake of maize (Zea mays L.). Results from the present study showed that the increasing levels of As in the soil significantly (P < 0.05) decreased plant growth and biomass, photosynthetic pigments, gas exchange attributes, sugars, and nutritional contents from the roots and shoots of the plants. In contrast, increasing levels of As in the soil significantly (P < 0.05) increased oxidative stress indicators in terms of malondialdehyde, hydrogen peroxide, and electrolyte leakage and also increased organic acid exudation patter in the roots of Z. mays, although the activities of enzymatic antioxidants and the response of their gene expressions in the roots and shoots of the plants and non-enzymatic such as phenolic, flavonoid, ascorbic acid, and anthocyanin contents were initially increased with the exposure of 50 µM As, but decreased by the increasing the As concentration 100 µM in the soil. The negative impact of As toxicity can overcome the application of Si and NaHS, which ultimately increased plant growth and biomass by capturing the reactive oxygen species and decreased oxidative stress in Z. mays by decreasing the As contents in the roots and shoots of the plants. Our results also showed that the Si was more sever and showed better results when we compared with NaHS under the same treatment of As in the soil. Research findings, therefore, suggest that the combined application of Si and NaHS can ameliorate As toxicity in Z. mays, resulting in improved plant growth and composition under metal stress, as depicted by balanced exudation of organic acids.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and material are available for research purpose and for reference.
References
Abbas S, Javed MT, Shahid M, Tanwir K, Saleem MH, Niazi NK (2023) Deciphering the impact of Acinetobacter sp. SG-5 strain on two contrasting Zea mays L. cultivars for root exudations and distinct physio-biochemical attributes under cadmium stress. J Plant Growth Regul 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-10987-0
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad MK (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Aebi H (1984): [13] Catalase in vitro, Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, pp 121–126
Afzal J, Saleem MH, Batool F, Elyamine AM, Rana MS, Shaheen A, El-Esawi MA, Tariq Javed M, Ali Q, Arslan Ashraf M, Hussain GS, Hu C (2020) Role of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) in resistance to cadmium stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Biomolecules 10:1693
Ahmad P, Ahanger MA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Alam P (2018) Exogenous application of nitric oxide modulates osmolyte metabolism, antioxidants, enzymes of ascorbate-glutathione cycle and promotes growth under cadmium stress in tomato. Protoplasma 255:79–93
Ahmad P, Ahanger MA, Alam P, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Ali S, Ashraf M (2019) Silicon (Si) supplementation alleviates NaCl toxicity in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] through the modifications of physio-biochemical attributes and key antioxidant enzymes. J Plant Growth Regul 38:70–82
Ahmad P, Alyemeni MN, Al-Huqail AA, Alqahtani MA, Wijaya L, Ashraf M, Kaya C, Bajguz A (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles application alleviates arsenic (As) toxicity in soybean plants by restricting the uptake of as and modulating key biochemical attributes, antioxidant enzymes, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. Plants 9:825
Ahmad S, Mfarrej MFB, El-Esawi MA, Waseem M, Alatawi A, Nafees M, Saleem MH, Rizwan M, Yasmeen T, Anayat A, Ali S (2022) Chromium-resistant Staphylococcus aureus alleviates chromium toxicity by developing synergistic relationships with zinc oxide nanoparticles in wheat. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 230:113142
Ahmad R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Dawood M, Farid M, Hussain A, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019b) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 168(2):289–300
Akram R, Turan V, Wahid A, Ijaz M, Shahid MA, Kaleem S, Hafeez A, Maqbool MM, Chaudhary HJ, Munis MFH (2018) Paddy land pollutants and their role in climate change. Environ Pollut Paddy Soils 113–124
Al Jabri H, Saleem MH, Rizwan M, Hussain I, Usman K, Alsafran M (2022) Zinc oxide nanoparticles and their biosynthesis: overview. Life 12:594
Alamri S, Hu Y, Mukherjee S, Aftab T, Fahad S, Raza A, Ahmad M, Siddiqui MH (2020) Silicon-induced postponement of leaf senescence is accompanied by modulation of antioxidative defense and ion homeostasis in mustard (Brassica juncea) seedlings exposed to salinity and drought stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 157:47–59
Alatawi A, Wang X, Maqbool A, Saleem MH, Usman K, Rizwan M, Yasmeen T, Arif MS, Noreen S, Hussain A, Ali S (2022) S-fertilizer (elemental sulfur) improves the phytoextraction of cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:1655
Ali B, Mwamba TM, Gill RA, Yang C, Ali S, Daud MK, Wu Y, Zhou W (2014) Improvement of element uptake and antioxidative defense in Brassica napus under lead stress by application of hydrogen sulfide. Plant Growth Regul 74:261–273
Ali U, Shaaban M, Bashir S, Fu Q, Zhu J, Islam MS, Hu H (2019) Effect of rice straw, biochar and calcite on maize plant and Ni bio-availability in acidic Ni contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 259:109674
Alsafran M, Usman K, Ahmed B, Rizwan M, Saleem MH, Al Jabri H (2022) Understanding the phytoremediation mechanisms of potentially toxic elements: a proteomic overview of recent advances. Front Plant Sci 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.881242
Anwaar SA, Ali S, Ali S, Ishaque W, Farid M, Farooq MA, Najeeb U, Abbas F, Sharif M (2015) Silicon (Si) alleviates cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) from zinc (Zn) toxicity stress by limiting Zn uptake and oxidative damage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3441–3450
Anwar S, Khan S, Ashraf MY, Noman A, Zafar S, Liu L, Ullah S, Fahad S (2017) Impact of chelator-induced phytoextraction of cadmium on yield and ionic uptake of maize. Int J Phytorem 19:505–513
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1
Austin RB (1990) Prospects for genetically increasing the photosynthetic capacity of crops. Plant Biology 10:395–409
Azuma K, Nakayama M, Koshioka M, Ippoushi K, Yamaguchi Y, Kohata K, Yamauchi Y, Ito H, Higashio H (1999) Phenolic antioxidants from the leaves of Corchorus olitorius L. J Agric Food Chem 47:3963–3966
Bashir A, Rizwan M, Ali S, urRehman MZ, Ishaque W, Riaz MA, Maqbool A (2018) Effect of foliar-applied iron complexed with lysine on growth and cadmium (Cd) uptake in rice under Cd stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20691–20699
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bhat JA, Faizan M, Bhat MA, Huang F, Yu D, Ahmad A, Bajguz A, Ahmad P (2022) Defense interplay of the zinc-oxide nanoparticles and melatonin in alleviating the arsenic stress in soybean (Glycine max L.). Chemosphere 288:132471
Bilen S, Bilen M, Turan V (2019) Relationships between cement dust emissions and soil properties. Polish J Environ Stud 28(5)
Bray H, Thorpe W (1954) Analysis of phenolic compounds of interest in metabolism. Methods Biochem Anal 27–52
Chen J, Wang W-H, Wu F-H, You C-Y, Liu T-W, Dong X-J, He J-X, Zheng H-L (2013) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Soil 362:301–318
Chen C-N, Pan S-M (1996) Assay of superoxide dismutase activity by combining electrophoresis and densitometry. Bot Bullet Acad Sinica 37
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Du H, Gao W, Li J, Shen S, Wang F, Fu L, Zhang K (2019) Effects of digested biogas slurry application mixed with irrigation water on nitrate leaching during wheat-maize rotation in the North China Plain. Agric Water Manag 213:882–893
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Pt R, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
El-Tohory S, Zeng W, Huang J, Moussa MG, Dong L, Mohamed A, Khalifa O, Saleem MH, Zhran M, Salama MA, Wu J (2023) Effect of intercropping and biochar application on cadmium removal capacity by corchorus olitorius and zea mays. Environ Technol Innov 29:103033
Faizan M, Sehar S, Rajput VD, Faraz A, Afzal S, Minkina T, Sushkova S, Adil MF, Yu F, Alatar AA, Akhter F, Faisal M (2021) Modulation of cellular redox status and antioxidant defense system after synergistic application of zinc oxide nanoparticles and salicylic acid in rice (Oryza sativa) plant under arsenic stress. Plants 10:2254
Fan X, Wen X, Huang F, Cai Y, Cai K (2016) Effects of silicon on morphology, ultrastructure and exudates of rice root under heavy metal stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38:197
Farooq MA, Gill RA, Ali B, Wang J, Islam F, Ali S, Zhou W (2016) Subcellular distribution, modulation of antioxidant and stress-related genes response to arsenic in Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicology 25:350–366
Greger M, Landberg T (2008) Role of rhizosphere mechanisms in Cd uptake by various wheat cultivars. Plant Soil 312:195–205
Hadi F, Bano A, Fuller MP (2010) The improved phytoextraction of lead (Pb) and the growth of maize (Zea mays L.): the role of plant growth regulators (GA3 and IAA) and EDTA alone and in combinations. Chemosphere 80:457–462
Hafeez A, Tipu MI, Saleem MH, Al-Ashkar I, Saneoka H, Sabagh AE (2022) Foliar application of moringa leaf extract (MLE) enhanced antioxidant system, growth, and biomass related attributes in safflower plants. S Afr J Bot 150:1087–1095
Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Nahar K, Mohsin SM, Bhuyan MB, Parvin K, Hawrylak-Nowak B, Fujita M (2019) Silicon-induced antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification works coordinately in alleviating nickel toxicity in Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicology 28:261–276
Hassan A, Parveen A, Hussain S, Hussain I, Rasheed R (2022) Investigating the role of different maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars by studying morpho-physiological attributes in chromium-stressed environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:72886–72897
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Heile AO, Zaman Qu, Aslam Z, Hussain A, Aslam M, Saleem MH, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A, Ali S (2021) Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity using silicon fertilization in wheat by altering antioxidant metabolism and osmotic adjustment. Sustainability 13:11317
Huq ME, Fahad S, Shao Z, Sarven MS, Al-Huqail AA, Siddiqui MH, ur Rahman MH, Khan IA, Alam M, Saeed M (2019) High arsenic contamination and presence of other trace metals in drinking water of Kushtia district, Bangladesh. J Environ Manage 242:199–209
Hussain I, Afzal S, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R, Saleem MH, Alatawi A, Ameen F, Fahad S (2022) Effect of metals or trace elements on wheat growth and its remediation in contaminated soil. J Plant Growth Regul 42(4(2023)):2258–2282
Imran M, Hussain S, Rana MS, Saleem MH, Rasul F, Ali KH, Potcho MP, Pan S, Duan M, Tang X (2021) Molybdenum improves 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, grain quality traits and yield attributes in fragrant rice through efficient nitrogen assimilation under cadmium toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111911
Iqbal MA, Khalid M, Zahir ZA, Ahmad R (2016) Auxin producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improve growth, physiology and yield of maize under saline field conditions. Int J Agric Biol 18:37–45
Irshad S, Xie Z, Kamran M, Nawaz A, Faheem MS, Gulzar H, Saleem MH, Rizwan M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Ali S (2021) Biochar composite with microbes enhanced arsenic biosorption and phytoextraction by Typha latifolia in hybrid vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. Environ Pollut 291:118269
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms: effect of heavy metals. Aquat Bot 11:67–77
Javed MT, Stoltz E, Lindberg S, Greger M (2013) Changes in pH and organic acids in mucilage of Eriophorum angustifolium roots after exposure to elevated concentrations of toxic elements. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1876–1880
Javed MT, Akram MS, Tanwir K, Chaudhary HJ, Ali Q, Stoltz E, Lindberg S (2017) Cadmium spiked soil modulates root organic acids exudation and ionic contents of two differentially Cd tolerant maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:216–225
Javed MT, Akram MS, Habib N, Tanwir K, Ali Q, Niazi NK, Gul H, Iqbal N (2018) Deciphering the growth, organic acid exudations, and ionic homeostasis of Amaranthus viridis L. and Portulaca oleracea L. under lead chloride stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2958–2971
Javed MT, Saleem MH, Aslam S, Rehman M, Iqbal N, Begum R, Ali S, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2020) Elucidating silicon-mediated distinct morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and organic acid exudation patterns of cadmium stressed Ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 157:23–37
Jia-Wen W, Yu S, Yong-Xing Z, Yi-Chao W, Hai-Jun G (2013) Mechanisms of enhanced heavy metal tolerance in plants by silicon: a review. Pedosphere 23:815–825
Kamran M, Danish M, Saleem MH, Malik Z, Parveen A, Abbasi GH, Jamil M, Ali S, Afzal S, Riaz M (2020) Application of abscisic acid and 6-benzylaminopurine modulated morpho-physiological and antioxidative defense responses of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by minimizing cobalt uptake. Chemosphere 263:128169
Kaya C, Higgs D, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol Plant 168:256–277
Kaya C, Şenbayram M, Akram NA, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Sulfur-enriched leonardite and humic acid soil amendments enhance tolerance to drought and phosphorus deficiency stress in maize (Zea mays L.). Sci Rep 10:1–13
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Al-Huqail AA, Alqahtani MA, Ahmad P (2020a) Silicon is dependent on hydrogen sulphide to improve boron toxicity tolerance in pepper plants by regulating the AsA-GSH cycle and glyoxalase system. Chemosphere 257:127241
Kaya C, Sarıoğlu A, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Gibberellic acid-induced generation of hydrogen sulfide alleviates boron toxicity in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 153:53–63
Khan E, Gupta M (2018) Arsenic–silicon priming of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds influence mineral nutrient uptake and biochemical responses through modulation of Lsi-1, Lsi-2, Lsi-6 and nutrient transporter genes. Sci Rep 8:1–16
Kong M, Liang J, Ali Q, Wen W, Wu H, Gao X, Gu Q (2021) 5-Methoxyindole, a chemical homolog of melatonin, adversely affects the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Int J Mol Sci 22:10991
Lessl JT, Guan DX, Sessa E, Rathinasabapathi B, Ma LQ (2015) Transfer of arsenic and phosphorus from soils to the fronds and spores of arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata and three non-hyperaccumulators. Plant Soil 390:49–60
Lewis CE, Walker JR, Lancaster JE, Sutton KH (1998) Determination of anthocyanins, flavonoids and phenolic acids in potatoes. I: Coloured cultivars of Solanum tuberosum L. J Sci Food Agric 77:45–57
Liang Y, Sun W, Zhu Y-G, Christie P (2007) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environ Pollut 147:422–428
Ma J, Li Y, Chen F, Sun Y, Zhu Y, Wang L (2023) Bacillus mycoides PM35 in combination with titanium dioxide (TiO2)⎯ nanoparticles enhanced morpho-physio-biochemical attributes in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under cadmium stress. Chemosphere 323:138224
Ma J, Ali S, Saleem MH, Mumtaz S, Yasin G, Ali B, Al-Ghamdi AA, Elshikh MS, Vodnar DC, Marc RA, Rehman A, Khan MN, Chen F, Ali S (2022a) Short-term responses of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) to the individual and combinatorial effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and silicon in the soil contaminated by boron. Front Plant Sci 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.983156
Ma J, Saleem MH, Yasin G, Mumtaz S, Qureshi FF, Ali B, Ercisli S, Alhag SK, Ahmed AE, Vodnar DC, Hussain I, Marc RA, Chen F (2022b) Individual and combinatorial effects of SNP and NaHS on morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and phytoextraction of chromium through Cr-stressed spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Front Plant Sci 13:973740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.973740
Madhu PM, Sadagopan RS (2020) Effect of heavy metals on growth and development of cultivated plants with reference to cadmium, chromium and lead–a review. J Stress Physiol Biochem 16:84–102
Marmiroli M, Pigoni V, Savo-Sardaro ML, Marmiroli N (2014) The effect of silicon on the uptake and translocation of arsenic in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Environ Exp Bot 99:9–17
Mfarrej M, Wang X, Hamzah Saleem M, Hussain I, Rasheed R, Arslan Ashraf M, Iqbal M, Sohaib Chattha M, Nasser Alyemeni M (2021) Hydrogen sulphide and nitric oxide mitigate the negative impacts of waterlogging stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Biol 24(4):670–683
Mondal S, Pramanik K, Ghosh SK, Pal P, Mondal T, Soren T, Maiti TK (2021) Unraveling the role of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in the alleviation of arsenic phytotoxicity: a review. Microbiol Res 250:126809
Mumtaz S, Hameed M, Ahmad F, Ahmad MSA, Ahmad I, Ashraf M, Saleem MH (2021) Structural and functional determinants of physiological pliability in Kyllinga brevifolia Rottb. for Survival in Hyper-Saline Saltmarshes. Water Air Soil Pollut 232:424
Mushtaq T, Shah AA, Akram W, Yasin NA (2020) Synergistic ameliorative effect of iron oxide nanoparticles and Bacillus subtilis S4 against arsenic toxicity in Cucurbita moschata: polyamines, antioxidants, and physiochemical studies. Int J Phytorem 22:1408–1419
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Ozfidan-Konakci C, Yildiztugay E, Elbasan F, Kucukoduk M, Turkan I (2020) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO) alleviate cobalt toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by modulating photosynthesis, chloroplastic redox and antioxidant capacity. J Hazard Mater 388:122061
Panda P, Nath S, Chanu TT, Sharma GD, Panda SK (2011) Cadmium stress-induced oxidative stress and role of nitric oxide in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Physiol Plant 33:1737–1747
Pękal A, Pyrzynska K (2014) Evaluation of aluminium complexation reaction for flavonoid content assay. Food Anal Methods 7:1776–1782
Pirooz P, Amooaghaie R, Ahadi A, Sharififar F (2021) Silicon-induced nitric oxide burst modulates systemic defensive responses of Salvia officinalis under copper toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:752–761
Ranum P, Peña-Rosas JP, Garcia-Casal MN (2014) Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1312:105–112
Rehman M, Liu L, Bashir S, Saleem MH, Chen C, Peng D, Siddique KH (2019) Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as forage in aged copper-contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:121–129
Rehman M, Fahad S, Saleem Mh, Hafeez M, Rahman Mh, Liu F, Deng G (2020) Red light optimized physiological traits and enhanced the growth of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.). Photosynthetica 58(4):922–931
Rehman M, Saleem MH, Fahad S, Bashir S, Peng D, Deng G, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH, Khan SM, Shah RA (2021) Effects of rice straw biochar and nitrogen fertilizer on ramie (Boehmeria nivea L) morpho-physiological traits, copper uptake and post-harvest soil characteristics, grown in an aged-copper contaminated soil. J Plant Nutr 45(1):11–24
Rizwan M, Meunier J-D, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209:326–334
Rizwan M, Meunier J-D, Davidian J-C, Pokrovsky O, Bovet N, Keller C (2016) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Sakharov IY, Ardila GB (1999) Variations of peroxidase activity in cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) beans during their ripening, fermentation and drying. Food Chem 65:51–54
Sakya A, Prahasto D (2020) The application of phosphorus and potassium to increase drought tolerance in Pereskia bleo (Kunt) DC with proline and antioxidant indicators, IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing, pp 012055
Saleem MH, Ali S, Seleiman MF, Rizwan M, Rehman M, Akram NA, Liu L, Alotaibi M, Al-Ashkar I, Mubushar M (2019) Assessing the correlations between different traits in copper-sensitive and copper-resistant varieties of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.). Plants 8:545
Saleem MH, Ali S, Hussain S, Kamran M, Chattha MS, Ahmad S, Aqeel M, Rizwan M, Aljarba NH, Alkahtani S (2020) Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): a potential candidate for phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants 9:496
Saleem MH, Ali S, Irshad S, Hussaan M, Rizwan M, Rana MS, Hashem A, Abd-Allah EF, Ahmad P (2020) Copper uptake and accumulation, ultra-structural alteration, and bast fibre yield and quality of fibrous jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) plants grown under two different soils of China. Plants 9:404
Saleem MH, Ali S, Rehman M, Rana MS, Rizwan M, Kamran M, Imran M, Riaz M, Soliman MH, Elkelish A (2020) Influence of phosphorus on copper phytoextraction via modulating cellular organelles in two jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) varieties grown in a copper mining soil of Hubei Province, China. Chemosphere 248:126032
Saleem MH, Fahad S, Khan SU, Ahmar S, Khan MHU, Rehman M, Maqbool Z, Liu L (2020) Morpho-physiological traits, gaseous exchange attributes, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) grown in different concentrations of copper-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 189:109915
Saleem MH, Parveen A, Khan SU, Hussain I, Wang X, Alshaya H, El-Sheikh MA, Ali S (2022) Silicon fertigation regimes attenuates cadmium toxicity and phytoremediation potential in two maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars by minimizing its uptake and oxidative stress. Sustainability 14:1462
Saleem MH, Mfarrej MFB, Alatawi A, Mumtaz S, Imran M, Ashraf MA, Rizwan M, Usman K, Ahmad P, Ali S (2023) Silicon enhances morpho–physio–biochemical responses in arsenic stressed spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by minimizing its uptake. J Plant Growth Regul 42(3):2053–72
Shafigh M, Ghasemi-Fasaei R, Ronaghi A (2016) Influence of plant growth regulators and humic acid on the phytoremediation of lead by maize in a Pb-polluted calcareous soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:1733–1740
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Rabbani F, Farooq ABU, Amjad M, Abbas G, Niazi NK (2019) Foliar uptake of arsenic nanoparticles by spinach: an assessment of physiological and human health risk implications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20121–20131
Siddiqui MH, Mukherjee S, Al-Munqedhi BMA, Kumar R, Kalaji HM (2022) Salicylic acid and silicon impart resilience to lanthanum toxicity in Brassica juncea L. seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 20:1–4
Sun Y, Ma L, Ma J, Li B, Zhu Y, Chen F (2022) Combined application of plant growth promoting bacteria and iron oxide nano-particles ameliorates the toxic effects of arsenic in Ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Front Plant Sci 13:5264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1098755
Sun Y, Mfarrej MFB, Song X, Ma J, Min B, Chen F (2023) New insights in to the ameliorative effects of zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles to arsenic stressed spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 107715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107715
Tanveer Y, Yasmin H, Nosheen A, Ali S, Ahmad A (2022) Ameliorative effects of plant growth promoting bacteria, zinc oxide nanoparticles and oxalic acid on Luffa acutangula grown on arsenic enriched soil. Environ Pollut 300:118889
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Kumar D, Chauhan DK (2012) Rice seedlings under cadmium stress: effect of silicon on growth, cadmium uptake, oxidative stress, antioxidant capacity and root and leaf structures. Chem Ecol 28:281–291
Turan V (2019) Confident performance of chitosan and pistachio shell biochar on reducing Ni bioavailability in soil and plant plus improved the soil enzymatic activities, antioxidant defense system and nutritional quality of lettuce. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109594
Turan V (2020) Potential of pistachio shell biochar and dicalcium phosphate combination to reduce Pb speciation in spinach, improved soil enzymatic activities, plant nutritional quality, and antioxidant defense system. Chemosphere 245:125611
Turan V, Schröder P, Bilen S, Insam H, Juárez MF-D (2019) Co-inoculation effect of Rhizobium and Achillea millefolium L. oil extracts on growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and soil microbial-chemical properties. Sci Rep 9:1–10
UdDin I, Bano A, Masood S (2015) Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:271–278
Ulhassan Z, Bhat JA, Zhou W, Senan AM, Alam P, Ahmad P (2022) Attenuation mechanisms of arsenic induced toxicity and its accumulation in plants by engineered nanoparticles: a review. Environ Pollut 302:119038
Ulhassan Z, Khan I, Hussain M, Khan AR, Hamid Y, Hussain S, Allakhverdiev SI, Zhou W (2022) Efficacy of metallic nanoparticles in attenuating the accumulation and toxicity of chromium in plants: current knowledge and future perspectives. Environ Pollut 315:120390
Wen E, Yang X, Chen H, Shaheen SM, Sarkar B, Xu S, Song H, Liang Y, Rinklebe J, Hou D (2020) Iron-modified biochar and water management regime-induced changes in plant growth, enzyme activities, and phytoavailability of arsenic, cadmium and lead in a paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 407:124344.
Wu J, Geilfus C-M, Pitann B, Mühling K-H (2016) Silicon-enhanced oxalate exudation contributes to alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat. Environ Exp Bot 131:10–18
Yaseen R, Aziz O, Saleem MH, Riaz M, Zafar-ul-Hye M, Rehman M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Nasser Alyemeni M, El-Serehy HA (2020) Ameliorating the drought stress for wheat growth through application of ACC-deaminase containing rhizobacteria along with biogas slurry. Sustainability 12:6022
Zafar-ul-Hye M, Naeem M, Danish S, Khan MJ, Fahad S, Datta R, Brtnicky M, Kintl A, Hussain GS, El-Esawi MA (2020) Effect of cadmium-tolerant rhizobacteria on growth attributes and chlorophyll contents of bitter gourd under cadmium toxicity. Plants 9:1386
Zhang H, Hu L-Y, Li P, Hu K-D, Jiang C-X, Luo J-P (2010) Hydrogen sulfide alleviated chromium toxicity in wheat. Biol Plant 54:743–747
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan. The Teaching & Research Practice Field for School of Public Administration provided the pot experiment site.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51974313, 41907405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Formal analysis: Sadia Javed, Sahar Mumtaz, Muhammad Ahsan Asghar, Aishah Alatawi, Romina Alina Marc. Funding acquisition: Shafaqat Ali, Sadia Javed, Sahar Mumtaz. Methodology: Sadia Javed, Mohsen Mohamed Elsharkawy, Romina Alina Marc, Ghulam Yasin, Sahar Mumtaz. Software: Manar Fawzi Bani Mfarrej, Sadia Javed, Shah Fahad, Aishah Alatawi, Sahar Mumtaz, Ghulam Yasin Mohsen Mohamed Elsharkawy, Romina Alina Marc, Javeed Lone. Supervision: Javeed Lone, Romina Alina Marc, Shafaqat Ali. Writing—original draft: Mohsen Mohamed Elsharkawy, Aishah Alatawi, Shah Fahad, Muhammad Ahsan Asghar, Rana M. Alshegaihi, Manar Fawzi Bani Mfarrej, Shafaqat Ali. Writing—review and editing: Shah Fahad, Aishah Alatawi, Rana M. Alshegaihi, Ghulam Yasin, Manar Fawzi Bani Mfarrej. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Written consent was sought from each author to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alatawi, A., Mfarrej, M.F.B., Alshegaihi, R.M. et al. Application of silicon and sodium hydrosulfide alleviates arsenic toxicity by regulating the physio-biochemical and molecular mechanisms of Zea mays. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 76555–76574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27739-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27739-y