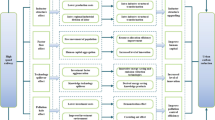
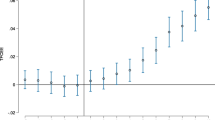
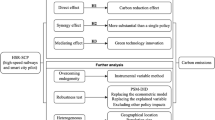
Abstract
Improving carbon productivity is an important measure to promote low-carbon development. Since high-speed rail (HSR) has both economic and environmental effects, it is particularly important to clarify the relationship between HSR development and carbon productivity. In this paper, 285 cities in China from 2007 to 2017 are used as a research sample, and the relationship between the opening of HSR and the city’s carbon productivity is studied using the spatial difference-in-difference method (SDID). The result shows that due to the intermediary effect of technological innovation and industrial structure, the opening of HSR significantly increases urban carbon productivity. At the same time, this influence has a significant positive spatial spillover effect. On average, when a city opens HSR, the local carbon productivity increases by 5.18%, and the carbon productivity of its neighboring cities increases by 13.52%. Overall, the positive effect of HSR on carbon productivity is more pronounced in the middle and western regions. However, the spatial spillover effect in the eastern region is significantly negative. These findings help to accurately assess the social benefits of HSR network expansion and provide important decision-making references for climate governance in the HSR era.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due the data comes from the undisclosed database of “Tongji University Regional Economic Research Institute Database,” but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acemoglu D, Aghion P, Bursztyn L, Hemous D (2012) The environment and directed technical change. Am Econ Rev 102(1):131–166. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.102.1.131
Anselin L, Griffith DA (1988) Do spatial effecfs really matter in regression analysis? Pap Reg Sci 65:11–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5597.1988.tb01155.x
Beck T, Levine R, Levkov A (2010) Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. The J Financ 65(5):1637–1667. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2010.01589.x
Bernard AB, Moxnes A, Saito YU (2019) Production networks, geography, and firm performance. J Polit Econ 127(2):639–688. https://doi.org/10.1086/700764
Chen Z, Haynes KE (2017) Impact of high-speed rail on regional economic disparity in China. J Transport Geogr 65:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.08.003
Chen Z, Xue J, Rose AZ, Haynes KE (2016) The impact of high-speed rail investment on economic and environmental change in China: a dynamic CGE analysis. Transp Res Pt A-Policy Pract 92:232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2016.08.006
Chen G, Hou F, Chang K (2018) Regional decomposition analysis of electric carbon productivity from the perspective of production and consumption in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1508–1518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0590-1
Cole MA, Elliott RJ (2003) Determining the trade–environment composition effect: the role of capital, labor and environmental regulations. J Environ Econ Manage 46(3): 363-383. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0095-0696(03)00021-4
Cole MA, Elliott RJ, Okubo T, Zhou Y (2013) The carbon dioxide emissions of firms: a spatial analysis. J Environ Econ Manage 65(2):290–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2012.07.002
Dong X (2018) High-speed railway and urban sectoral employment in China. Transp Res Pt A-Policy Pract 116:603–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2018.07.010
Dong B, Gong J, Zhao X (2012) FDI and environmental regulation: pollution haven or a race to the top? J Regul Econ 41(2):216–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11149-011-9162-3
Dong X, Zheng S, Kahn ME (2020) The role of transportation speed in facilitating high skilled teamwork across cities. J Urban Econ 115:103212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2019.103212
Dong K, Ren X, Zhao J (2021) How does low-carbon energy transition alleviate energy poverty in China? A nonparametric panel causality analysis. Energy Econ 103:105620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105620
Elhorst JP, Lacombe DJ, Piras G (2012) On model specification and parameter space definitions in higher order spatial econometric models. Reg Sci Urban Econ 42:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2011.09.003
Elhorst JP (2014) Dynamic spatial panels: models, methods and inferences. Spatial econometrics. Springer, Berlin:95–119. https://linkspringer.53yu.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-40340-8_4
Faber B (2014) Trade integration, market size, and industrialization: evidence from China’s National Trunk Highway System. Rev Econ Stud 81(3): 1046–1070. http://hdl.handle.net/10.1093/restud/rdu010. Accessed 10 January 2022
Fan X, Xu Y, Nan Y, Li B, Cai H (2020) Impacts of high-speed railway on the industrial pollution emissions in China: evidence from multi-period difference-in-differences models. Kybernetes 49(11):2713–2735. https://doi.org/10.1108/K-07-2019-0499
Gao Y, Song S, Sun J, Zang L (2018) Does high-speed rail really promote economic growth? evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region. Available at SSRN: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3158554
Görg H, Strobl E (2007) The effect of R&D subsidies on private R&D. Economica 74(294):215–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0335.2006.00547.x
Guirao B, Campa JL, Casado-Sanz N (2018) Labour mobility between cities and metropolitan integration: the role of high speed rail commuting in Spain. Cities 78:140–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.02.008
He W, Wang B, Wang Z (2018) Will regional economic integration influence carbon dioxide marginal abatement costs? Evidence from Chinese panel data. Energy Econ 74:263–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.06.010
Hernández A, Jiménez JL (2014) Does high-speed rail generate spillovers on local budgets? Transport Pol 35:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2014.06.003
Heyman F, Sjöholm F, Tingvall PG (2007) Is there really a foreign ownership wage premium? Evidence from matched employer–employee data. J Int Econ 73(2):355–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinteco.2007.04.003
Hu X, Liu C (2016) Carbon productivity: a case study in the Australian construction industry. J Clean Prod 112:2354–2362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.10.042
Huang Y (2021) Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the impact of high-speed railway on urban economy: empirical study of Chinese cities. J Transp Geogr 91:102972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2021.102972
Iftikhar Y, He W, Wang Z (2016) Energy and CO2 emissions efficiency of major economies: a non-parametric analysis. J Clean Prod 139:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.072
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2018) Global Warming of 1.5°C: An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5°C Above Pre-industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. World Meteorological Organization Geneva, Switzerland.
Jaffe AB, Newell RG, Stavins RN (2002) Environmental policy and technological change. Environ Resour Econ 22(1):41–70. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015519401088
Jia R, Shao S, Yang L (2021) High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: a spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Econ 99:105271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105271
Kanwar S, Evenson R (2003) Does intellectual property protection spur technological change? Oxf Econ Pap 55(2):235–264. https://doi.org/10.1093/oep/55.2.235
Kaya Y, Yokobori K (1997) Environment, energy, and economy: strategies for sustainability. United Nations University Press, Tokyo
Kong Q, Shen C, Li R, Wong Z (2021) High-speed railway opening and urban green productivity in the post-COVID-19: evidence from green finance. Glob Financ J 49:100645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfj.2021.100645
Levinson A, Taylor MS (2008) Unmasking the pollution haven effect. Int Econ Rev 49(1):223–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2354.2008.00478.x
Li K, Lin B (2015) Impacts of urbanization and industrialization on energy consumption/CO2 emissions: does the level of development matter? Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:1107–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.185
Li Z, Xu H (2018) High-speed railroads and economic geography: evidence from Japan. J Reg Sci 58(4):705–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12384
Li P, Lu Y, Wang J (2016) Does flattening government improve economic performance? Evidence from China. J Dev Econ 123:18–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2016.07.002
Li Y, Luo E, Zhang H, Tian X, Liu T (2018) Measuring interregional spillover and feedback effects of economy and CO2 emissions: a case study of the capital city agglomeration in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 139:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.07.021
Li X, Cheng Z (2022) Does high-speed rail improve urban carbon emission efficiency in China? Socio-Econ Plan Sci 101308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2022.101308
Lin Y (2017) Travel costs and urban specialization patterns: evidence from China’s high speed railway system. J Urban Econ 98:98–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2016.11.002
Lin B, Jia H (2022) Does the development of China’s high-speed rail improve the total-factor carbon productivity of cities? Transport Res Part D-Transport Environ 105:103230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2022.103230
Lin SL, Zhang ZX, Liu GP (2013) Technological innovation, spatial agglomeration and regional carbon productivity. China Popul Resour Environ 23:36–45 (in Chinese)
Lindmark M (2002) An Ekc–pattern in historical perspective: carbon dioxide emissions, technology, fuel prices and growth in Sweden 1870–1997. Ecol Econ 42(1):333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00108-8
Liu X, Bae J (2018) Urbanization and industrialization impact of CO2 emissions in China. J Clean Prod 172:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.156
Ma L, Long H, Chen K, Tu S, Zhang Y, Liao L (2019a) Green growth efficiency of Chinese cities and its spatio-temporal pattern. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.049
Ma M, Ma X, Cai W, Cai W (2019b) Carbon-dioxide mitigation in the residential building sector: a household scale-based assessment. Energ Convers Manage 198:111915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.111915
Meng X, Lin S, Zhu X (2018) The resource redistribution effect of high-speed rail stations on the economic growth of neighbouring regions: evidence from China. Transp Policy 68:178–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2018.05.006
Meng S, Sun R, Guo F, Deng Y (2022) The mechanism of renewable energy consumption, technological innovation and carbon productivity—an empirical study of Chinese data. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23557-w
Nie Y, Li Q, Wang E, Zhang T (2019) Study of the nonlinear relations between economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions in the eastern, central and Western regions of China. J Clean Prod 219:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.164
Pan J, Zhang L (2011) Research on the regional variation of carbon productivity in China. China Indus Econ 5:47–57. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2011.05.005. (in Chinese)
Pasche M (2002) Technical progress, structural change, and the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 42(3):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00135-0
Peng XH, Wang JY (2019) High-speed rail construction and green total factor productivity: based on factor allocation distortion, China Pop Resour Environ 29(11):11–19. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ZGRZ201911002&DbName=CJFQ2019 (in Chinese). Accessed 10 January 2022
Qin Y (2017) No county left behind? The distributional impact of high-speed rail upgrades in China. J Econ Geogr 17(3):489–520. https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbw013
Quiroga M, Sterner T, Persson M (2009) Have countries with lax environmental regulations a comparative advantage in polluting industries? Working Paper in Economics, 412, Goteborg University, Department of Economics
Shao S, Tian Z, Yang L (2017) High speed rail and urban service industry agglomeration: evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta region. J Transp Geogr 64:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.08.019
Shaw SL, Fang Z, Lu S, Tao R (2014) Impacts of high speed rail on railroad network accessibility in China. J Transp Geogr 40:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2014.03.010
Shi K, Chen Y, Li L, Huang C (2018) Spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China: a multiscale perspective. Appl Energy 211:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.042
Sims R, Schaeffer R, Creutzig F, Cruz-Núñez X, D’Agosto M, Dimitriu D, Figueroa Meza MJ, Fulton L, Kobayashi S, Lah O, McKinnon A, Newman P, Ouyang M, Schauer JJ, Sperling D, Tiwari G (2014) Transport. In: Edenhofer O, Pichs-Madruga R, Sokona Y, Farahani E, Kadner S, Seyboth K, Adler A, Baum I, Brunner S, Eickemeier P, Kriemann B, Savolainen J, Schlömer S, von Stechow C, Zwickel T, Minx JC (ed) Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of working group III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York. pp 599–670. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/ipcc_wg3_ar5_chapter8.pdf. Accessed 10 January 2022
Sun X, Yan S, Liu T, Wu J (2020) High-speed rail development and urban environmental efficiency in China: a city-level examination. Transport Res Part D-Transport Environ 86:102456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102456
Tobler WR (1970) A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ Geogr 46:234–240. https://doi.org/10.2307/143141
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) (2015) Report of the conference of the parties on its twenty-first session, held in Paris from 30 November to 13 December 2015 addendum part two: action taken by the conference of the parties at its twenty-first session. http://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/10a01.pdf. Accessed 10 January 2022
Wang Z, Sun Y, Wang B (2019) How does the new-type urbanisation affect CO2 emissions in China? An empirical analysis from the perspective of technological progress. Energy Econ 80:917–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.02.017
Wang C, Guo Y, Shao S, Fan M, Chen S (2020) Regional carbon imbalance within China: an application of the Kaya-Zenga index. J Environ Manage 262:110378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110378
Wu L, Sun L, Qi P, Ren X, Sun X (2021) Energy endowment, industrial structure upgrading, and CO2 emissions in China: revisiting resource curse in the context of carbon emissions. Res Policy 74:102329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102329
Xu H, Cao S, Xu X (2022) The development of highway infrastructure and CO2 emissions: the mediating role of agglomeration. J Clean Prod 337:130501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130501
Yang L, Li Z (2017) Technology advance and the carbon dioxide emission in China – empirical research based on the rebound effect. Energy Policy 101:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.11.020
Yang X, Lin S, Li Y, He M (2019) Can high-speed rail reduce environmental pollution? Evidence from China. J Clean Prod 239:118135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118135
Yang H, Shahzadi I, Hussain M (2021) USA carbon neutrality target: evaluating the role of environmentally adjusted multifactor productivity growth in limiting carbon emissions. J Environ Manage 298:113385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113385
Yao S, Zhang F, Wang F, Ou J (2019) Regional economic growth and the role of high-speed rail in China. Appl Econ 51(32):3465–3479. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2019.1581910
Yin J, Zheng M, Chen J (2015) The effects of environmental regulation and technical progress on CO2 Kuznets curve: an evidence from China. Energy Policy 77:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.11.008
You W, Lv Z (2018) Spillover effects of economic globalization on CO2 emissions: a spatial panel approach. Energy Econ 73:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.05.016
Yu N, Jong MD, Storm S, Mi J (2013) Spatial spillover effects of transport infrastructure: evidence from Chinese regions. J Transp Geogr 28:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2012.10.009
Yu Y, Yang X, Li K (2019) Effects of the terms and characteristics of cadres on environmental pollution: evidence from 230 cities in China. J Environ Manage 232:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.002
Yu Y, Han L, Wu J, Zhao W, Zhang Y (2022) Green growth effects of high-speed rail in China: the role of industrial transformation. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 58(3):668–680. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496X.2020.1833856
Yuan H, Feng Y, Lee CC, Cen Y (2020) How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ 92:104944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104944
Zhang F, Deng X, Phillips F, Fang C, Wang C (2020) Impacts of industrial structure and technical progress on carbon emission intensity: evidence from 281 cities in China. Technol Forecast Soc 154:119949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119949
Zhao J, Jiang Q, Dong X, Dong K, Jiang H (2022) How does industrial structure adjustment reduce CO2 emissions? Spatial and mediation effects analysis for China. Energy Econ 105:105704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105704
Zheng L, Long F, Chang Z, Ye J (2019) Ghost town or city of hope? The spatial spillover effects of high-speed railway stations in China. Transp Policy 81:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2019.07.005
Zhou P, Ang BW, Han JY (2010) Total factor carbon emission performance: a Malmquist index analysis. Energy Econ 2(1):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.10.003
Zhu B, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Wang P, Sheng J, He K, Wei YM, Xie R (2019) Exploring the effect of industrial structure adjustment on interprovincial green development efficiency in China: a novel integrated approach. Energy Policy 134:110946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Tuolei Wu and Shanlang Lin contributed equally to this manuscript. Methodology, data curation, and writing (original draft preparation) were performed by Tuolei Wu. Conceptualization, supervisor, and data curation were performed by Shanlang Lin. Visualization and writing (original draft preparation) were performed by Jingxian Wang. Software, validation, and writing (review and editing) were performed by Na Yan. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Lin, S., Wang, J. et al. High-speed rail and city’s carbon productivity in China: a spatial difference-in-differences approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 56284–56302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26297-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26297-7