Abstract
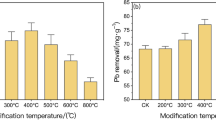
To solve the problems such as water eutrophication caused by excess phosphorus, the potential residual value of aluminum sludge was fully exploited and its phosphate adsorption capacity was further improved. In this study, twelve metal-modified aluminum sludge materials were prepared by co-precipitation method. Among them, Ce-WTR, La-WTR, Y-WTR, Zr-WTR, and Zn-WTR showed excellent adsorption capacity for phosphate. The adsorption performance of Ce-WTR on phosphate was twice that of the native sludge. The enhanced adsorption mechanism of metal modification on phosphate was investigated. The characterization results showed that the increase in specific surface area after metal modification was 9.64, 7.5, 7.29, 3, and 1.5 times, respectively. The adsorption of phosphate by WTR and Zn-WTR was in the accordance with Langmuir model, while the others were more following the Freundlich model (R2 > 0.991). The effects of dosage, pH, and anion on phosphate adsorption were investigated. The surface hydroxyl groups and metal (hydrogen) oxides played an important role in the adsorption process. The adsorption mechanism involves physical adsorption, electrostatic attraction, ligand exchange, and hydrogen bonding. This study provides new ideas for the resource utilization of aluminum sludge and theoretical support for preparing novel adsorbents for efficient phosphate removal.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cao X-q, Chen M, Wang Y, Shen S, Zhang Z, Li B, Sun B (2022) Al30 polycation pillared montmorillonite preparation and phosphate adsorption removal from water. Surf Interfaces 29:101780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101780
Du M, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Lv M, Tang A, Yu Y, Qu X, Chen Z, Wen Q, Li A (2022) Insight into the synthesis and adsorption mechanism of adsorbents for efficient phosphate removal: Exploration from synthesis to modification. Chem Eng J 442:136147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136147
Erol K (2016a) DNA adsorption via Co(II) immobilized cryogels. J Macromol Sci, Pure Appl Chem 53:629–635. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2016.1212310
Erol K (2016) The adsorption of calmoduline via nicotinamide immobilized poly(HEMA-GMA) cryogels. J Turkish Chem Soc Sect A: Chem 4:133–148. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.287321
Erol K, Uzun L (2017) Two-step polymerization approach for synthesis of macroporous surface ion-imprinted cryogels. J Macromol Sci, Part A 0, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2017.1342519
Erol B, Erol K, Gkmee E (2019a) The effect of the chelator characteristics on insulin adsorption in immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Process Biochem 83:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.05.009
Erol K, Yıldız E, Alacabey İ, Karabörk M, Uzun L (2019b) Magnetic diatomite for pesticide removal from aqueous solution via hydrophobic interactions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33631–33641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06423-0
Erol K, Bülter MB, Köse DA, Can HK (2021a) Water-soluble polymeric particle embedded cryogels: synthesis, characterisation and adsorption of haemoglobin. J Polym Eng 41:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0285
Erol K, Tatar D, Veyisolu A, Tokatl A (2021b) Antimicrobial magnetic poly(GMA) microparticles: synthesis, characterization and lysozyme immobilization. J Polym Eng 41:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0191
Everaert M, Bergmans J, Broos K, Hermans B, Michielsen B (2021) Granulation and calcination of alum sludge for the development of a phosphorus adsorbent: from lab scale to pilot scale. J Environ Manage 279:111525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111525
He J, Xu Y, Wang W, Hu B, Wang Z, Yang X, Wang Y, Yang L (2020) Ce(III) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range. Chem Eng J 379:122431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122431
Hong X, Zhu S, Xia M, Du P, Wang F (2022) Investigation of the efficient adsorption performance and adsorption mechanism of 3D composite structure La nanosphere-coated Mn/Fe layered double hydrotalcite on phosphate. J Colloid Interface Sci 614:478–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.01.149
Huang W, Chen J, He F, Tang J, Li D, Zhu Y, Zhang Y (2015) Effective phosphate adsorption by Zr/Al-pillared montmorillonite: insight into equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Appl Clay Sci 104:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.12.002
Jang J, Lee DS (2019) Effective phosphorus removal using chitosan/Ca-organically modified montmorillonite beads in batch and fixed-bed column studies. J Hazard Mater 375:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.070
Jiang S, Wang J, Qiao S, Zhou J (2021) Phosphate recovery from aqueous solution through adsorption by magnesium modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sci Total Environ 796:148907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148907
Jiang D, Wang X, Feng L, Yu Y, Hu J, Liu X, Wu H (2022) Structural insight into the alginate derived nano-La(OH)3/porous carbon composites for highly selective adsorption of phosphate. Int J Biol Macromol 200:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.076
Jiao G-J, Ma J, Li Y, Jin D, Guo Y, Zhou J, Sun R (2021) Enhanced adsorption activity for phosphate removal by functional lignin-derived carbon-based adsorbent: Optimization, performance and evaluation. Sci Total Environ 761:143217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143217
Jo J-Y, Kim J-G, Tsang YF, Baek K (2021) Removal of ammonium, phosphate, and sulfonamide antibiotics using alum sludge and low-grade charcoal pellets. Chemosphere 281:130960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130960
Kireç O, Alacabey İ, Erol K, Alkan H (2021) Removal of 17β-estradiol from aqueous systems with hydrophobic microspheres. J Polym Eng 41:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0150
Kong L, Tian Y, Wang Y, Li N, Liu Y, Pang Z, Huang X, Li M, Zhang J, Zuo W (2019) Periclase-induced generation of flowerlike clay-based layered double hydroxides: a highly efficient phosphate scavenger and solid-phase fertilizer. Chem Eng J 359:902–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.007
Li X, Kuang Y, Chen J, Wu D (2020) Competitive adsorption of phosphate and dissolved organic carbon on lanthanum modified zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 574:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.050
Liu R, Chi L, Wang X, Sui Y, Wang Y, Arandiyan H (2018) Review of metal (hydr)oxide and other adsorptive materials for phosphate removal from water. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5269–5286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.008
Liu B, Lou S, Zeng Y, Qin Y, Zhang W, Zhang L, Liu X (2021) High-efficiency adsorption of phosphate by Fe-Zr-La tri-metal oxide composite from aqueous media: performance and mechanism. Adv Powder Technol 32:4587–4598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.10.011
Maqbool N, Khan Z, Asghar A (2016) Reuse of alum sludge for phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 57:13246–13254. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1055806
Nazarian R, Desch RJ, Thiel SW (2021) Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption of phosphate on lanthanum oxide supported on activated carbon. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 624:126813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126813
Özçelik G, Çavuşoğlu FC, Özkara-Aydınoğlu Ş, Bayazit ŞS (2022) Enhanced & effective phosphate recovery from water by indium fumarate & zirconium fumarate metal-organic frameworks: synthesis, characterization, adsorption, kinetic and isotherm studies. Surf Interfaces 29:101719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101719
Qing Z, Wang L, Liu X, Song Z, Qian F, Song Y (2022) Simply synthesized sodium alginate/zirconium hydrogel as adsorbent for phosphate adsorption from aqueous solution: performance and mechanisms. Chemosphere 291:133103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133103
Razali M, Zhao YQ, Bruen M (2007) Effectiveness of a drinking-water treatment sludge in removing different phosphorus species from aqueous solution. Sep Purif Technol 55:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.12.004
Satir LT, Erol K (2020) Calcined eggshell for removal of Victoria blue R dye from wastewater medium by adsorption. J Turkish Chem Soc, Sect A: Chem 8:47–56. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.760083
Sudhakaran S, Abraham EV, Mahadevan H, Krishnan KA (2021) Crosslinked chitosan-montmorillonite biocomposite with Fe intercalation: enhancing surface chemistry for improved phosphate adsorption. Surf Interfaces 27:101468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101468
Wang Y, Li J, Yuan Y, Si Y, Xu J, Li M, Peng X (2021) La(OH)3 loaded magnetic nanocomposites derived from sugarcane bagasse cellulose for phosphate adsorption: characterization, performance and mechanism. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 626:127060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127060
Wang B, Zhang H, Xu Z, Xu Y, Hu X, Wang H, Wang C, Chen L (2022) La/Al engineered bentonite composite for efficient phosphate separation from aqueous media: Preparation optimization, adsorptive behavior and mechanism insight. Sep Purif Technol 290:120894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120894
Wu H-f, Wang J-p, Duan E-g, Hu W-h, Dong Y-b, Zhang G-q (2020) Phosphorus removal by adsorbent based on poly-aluminum chloride sludge. Water Sci Eng 13:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2020.09.006
Xiong H, Peng S, Zhang D (2022) Phosphate adsorption removal by (La-doping) Mn–Al bimetal oxide composites. Mater Chem Phys 285:126195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126195
Xu Q, Chen Z, Wu Z, Xu F, Yang D, He Q, Li G, Chen Y (2019) Novel lanthanum doped biochars derived from lignocellulosic wastes for efficient phosphate removal and regeneration. Bioresour Technol 289:121600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121600
Yang Q, Wang X, Luo W, Sun J, Xu Q, Chen F, Zhao J, Wang S, Yao F, Wang D, Li X, Zeng G (2018) Effectiveness and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption on iron-modified biochars derived from waste activated sludge. Biores Technol 247:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.136
Yu J, Li X, Wu M, Lin K, Xu L, Zeng T, Shi H, Zhang M (2022) Synergistic role of inherent calcium and iron minerals in paper mill sludge biochar for phosphate adsorption. Sci Total Environ 834:155193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155193
Zhan Y, Zhang H, Lin J, Zhang Z, Gao J (2017) Role of zeolite’s exchangeable cations in phosphate adsorption onto zirconium-modified zeolite. J Mol Liq 243:624–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.091
Zhang B, Xu L, Zhao Z, Peng S, Yu C, Zhang X, Zong Y, Wu D (2022a) Enhanced phosphate removal by nano-lanthanum hydroxide embedded silica aerogel composites: superior performance and insights into specific adsorption mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 285:120365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120365
Zhang C, Wang X, Wang X, Liu B (2022b) Characterization of La–Mg-modified palygorskite and its adsorption of phosphate. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107658
Zhang Y, Kang X, Guo P, Tan H, Zhang S-H (2022c) Studies on the removal of phosphate in water through adsorption using a novel Zn-MOF and its derived materials. Arab J Chem 103955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103955.
Zhao X, Zhang Y, Pan S, Zhang X, Zhang W, Pan B (2021) Utilization of gel-type polystyrene host for immobilization of nano-sized hydrated zirconium oxides: a new strategy for enhanced phosphate removal. Chemosphere 263:127938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127938
Zubair M, Manzar MS, Suleiman MA, Fernandes DP, Meili L, Essa WAB, Al-Adam H, AlGhamdi JM, Mu’azu ND, Haladu SA, Khan G (2022) Production of magnetic biochar-steel dust composites for enhanced phosphate adsorption. J Water Process Eng 47:102793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102793
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Innovation Practice Project of Postgraduates of Chang’an University (300103722010) and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Innovation Training Project of College Students (G202210710067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aixia Chen: writing—reviewing and editing. Juanjuan Guan: writing—original draft preparation, conceptualization. Ruirui Hu: methodology. Xiao Wei: software. Yixuan Zhang: data curation. Luxue Lv: visualization. Xinyuan Wang: investigation, supervision. Lei Zhang: investigation, supervision. Luqian Ji: investigation, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors confirm that the final version of the manuscript has been reviewed, approved, and consented for publication by all authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Aluminum sludge disposal was combined with phosphorus pollution control.
• Five metal-modified aluminum sludge has enhanced phosphate adsorption effect.
• Ce-WTR adsorbed twice as much phosphate as the original aluminum sludge.
• The metal cations in the higher valence state are more strongly bound to phosphate.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, A., Guan, J., Hu, R. et al. Enhanced phosphate adsorption studies on several metal-modified aluminum sludge: preparation optimization, adsorption behavior, and mechanistic insight. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 54628–54643 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26212-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26212-0