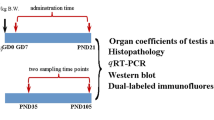
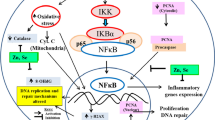
Abstract
Deca brominated diphenyl ether (BDE-209) is a widely used flame retardant with endocrine-disrupting activity which reportedly caused sperm quality decline and damaged blood-testis barrier (BTB). However, whether BDE-209 exposure led to BTB integrity dysfunction through affecting microtubule cytoskeletal organization and junctions was not well-elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the role of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in BDE-209-mediated perturbation of BTB integrity. Male rats and primary culture Sertoli cells were co-treated with BDE-209 and propylpyrazoletriol (PPT). The data demonstrated that BDE-209 impaired BTB integrity by reducing crucial tight junction-related proteins with ZO-1 and Occludin. Furthermore, the data suggested that BDE-209 diminished the apical ectoplasmic specialization markers with Eps8 and Formin1. In addition, BDE-209 damaged BTB ultrastructure including tight junctions and ectoplasmic specialization structures with broken tight junctions and the absence of actin microfilaments. Further experiments revealed that ERα was triggered in BDE-209-treated Sertoli cells. Unexpectedly, we found that PPT rescued BDE-209-mediated disruption of BTB integrity including tight junction and apical ectoplasmic specialization by activating ERα in Sertoli cells. Taken together, these findings indicated that intratesticular BDE-209 exposure perturbed BTB integrity and destroyed BTB structure by blocking ERα pathway. Our findings provide a new therapeutic target for male reproductive dysfunction.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Ahmad R, Haldar C (2010) Effect of intra-testicular melatonin injection on testicular functions, local and general immunity of a tropical rodent Funambulus pennanti. Endocrine 37:479–488
Aslam H, Rosiepen G, Krishnamurthy H, Arslan M, Clemen G, Nieschlag E, Weinbauer GF (1999) The cycle duration of the seminiferous epithelium remains unaltered during GnRH antagonist-induced testicular involution in rats and monkeys. J Endocrinol 161:281–288
Cao XN, Shen LJ, Wu SD, Yan C, Zhou Y, Xiong G, Wang YC, Liu Y, Liu B, Tang XL, Guo M, Liu DY, Long CL, Sun M, He DW, Lin T, Wei GH (2017) Urban fine particulate matter exposure causes male reproductive injury through destroying blood-testis barrier (BTB) integrity. Toxicol Lett 266:1–12
Clermont Y (1972) Kinetics of spermatogenesis in mammals: seminiferous epithelium cycle and spermatogonial renewal. Physiol Rev 52:198–236
Du Plessis SS, Cabler S, McAlister DA, Sabanegh E, Agarwal A (2010) The effect of obesity on sperm disorders and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol 7:153–161
Fang Y, Su Y, Xu J, Hu Z, Zhao K, Liu C, Zhang H (2021) Varicocele-mediated male infertility: from the perspective of testicular immunity and inflammation. Front Immunol 12:729539
Feng Y, Fang X, Shi Z, Xu M, Dai J (2010) Effects of PFNA exposure on expression of junction-associated molecules and secretory function in rat Sertoli cells. Reprod Toxicol 30:429–437
Fijak M, Pilatz A, Hedger MP, Nicolas N, Bhushan S, Michel V, Tung KSK, Schuppe HC, Meinhardt A (2018) Infectious, inflammatory and “autoimmune” male factor infertility: how do rodent models inform clinical practice? Hum Reprod Update 24:416–441
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Mohaqiq M, Haidar Abbas Raza S, Taheri M (2021) The role of different compounds on the integrity of blood-testis barrier: a concise review based on in vitro and in vivo studies. Gene 780:145531
Harris HA, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2002) Characterization of the biological roles of the estrogen receptors, ERalpha and ERbeta, in estrogen target tissues in vivo through the use of an ERalpha-selective ligand. Endocrinology 143:4172–4177
Holtmann N, Edimiris P, Andree M, Doehmen C, Baston-Buest D, Adams O, Kruessel JS, Bielfeld AP (2020) Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in human semen-a cohort study. Fertil Steril 114:233–238
Hooley RP, Paterson M, Brown P, Kerr K, Saunders PT (2009) Intra-testicular injection of adenoviral constructs results in Sertoli cell-specific gene expression and disruption of the seminiferous epithelium. Reproduction 137:361–370
Iannuzzi C, Borriello M, D’Agostino A, Cimini D, Schiraldi C, Sirangelo I (2019) Protective effect of extractive and biotechnological chondroitin in insulin amyloid and advanced glycation end product-induced toxicity. J Cell Physiol 234:3814–3828
Jensen CFS, Ostergren P, Dupree JM, Ohl DA, Sonksen J, Fode M (2017) Varicocele and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol 14:523–533
Jia X, Xu Y, Wu W, Fan Y, Wang G, Zhang T, Su W (2017) Aroclor1254 disrupts the blood-testis barrier by promoting endocytosis and degradation of junction proteins via p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Death Dis 8:e2823
Leblond CP, Clermont Y (1952) Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci 55:548–573
Li S, Wang Q, Yu H, Yang L, Sun Y, Xu N, Wang N, Lei Z, Hou J, Jin Y, Zhang H, Li L, Xu F, Zhang L (2021a) Polystyrene microplastics induce blood-testis barrier disruption regulated by the MAPK-Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:47921–47931
Li X, Liu J, Zhou G, Sang Y, Zhang Y, Jing L, Shi Z, Zhou X, Sun Z (2021b) BDE-209 and DBDPE induce male reproductive toxicity through telomere-related cell senescence and apoptosis in SD rat. Environ Int 146:106307
Liu PY, Zhao YX, Zhu YY, Qin ZF, Ruan XL, Zhang YC, Chen BJ, Li Y, Yan SS, Qin XF, Fu S, Xu XB (2012) Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human semen. Environ Int 42:132–137
Liu L, Zhang Y, Chang X, Li R, Wu C, Tang L, Zhou Z (2018) Fluorochloridone perturbs blood-testis barrier/Sertoli cell barrier function through Arp3-mediated F-actin disruption. Toxicol Lett 295:277–287
Liu B, Shen LJ, Zhao TX, Sun M, Wang JK, Long CL, He DW, Lin T, Wu SD, Wei GH (2020) Automobile exhaust-derived PM2.5 induces blood-testis barrier damage through ROS-MAPK-Nrf2 pathway in sertoli cells of rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:110053
Liu H, Zeng X, Ma Y, Chen X, Losiewicz MD, Du X, Tian Z, Zhang S, Shi L, Zhang H, Yang F (2022a) Long-term exposure to low concentrations of MC-LR induces blood-testis barrier damage through the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 236:113454
Liu JB, Li ZF, Lu L, Wang ZY, Wang L (2022b) Glyphosate damages blood-testis barrier via NOX1-triggered oxidative stress in rats: long-term exposure as a potential risk for male reproductive health. Environ Int 159:107038
Lundholm L, Bryzgalova G, Gao H, Portwood N, Fält S, Berndt KD, Dicker A, Galuska D, Zierath JR, Gustafsson J, Efendic S, Dahlman-Wright K, Khan A (2008) The estrogen receptor {alpha}-selective agonist propyl pyrazole triol improves glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice; potential molecular mechanisms. J Endocrinol 199:X1
Mruk DD, Cheng CY (2015) The mammalian blood-testis barrier: its biology and regulation. Endocr Rev 36:564–591
Mustafa S, Wei Q, Ennab W, Lv Z, Nazar K, Siyal FA, Rodeni S, Kavita N, Shi F (2019) Resveratrol ameliorates testicular histopathology of mice exposed to restraint stress. Animals (Basel) 9(10):743
Ni Z, Sun W, Li R, Yang M, Zhang F, Chang X, Li W, Zhou Z (2021a) Fluorochloridone induces autophagy in TM4 Sertoli cells: involvement of ROS-mediated AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 19:64
Ni DQ, Ma DD, Hao SL, Yang WX, Kovacs T, Tan FQ (2021b) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles perturb the blood-testis barrier via disruption of actin-based cell adhesive function. Aging 13:25440–25452
Pena-Corona SI, Vasquez Aguire WS, Vargas D, Juarez I, Mendoza-Rodriguez CA (2021) Effects of bisphenols on blood-testis barrier protein expression in vitro: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Toxicol 103:139–148
Sarkar D, Singh SK (2021) Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) exposure to lactating mice perturbs steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in adult male offspring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111783
Sharkey M, Harrad S, Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Drage DS, Berresheim H (2020) Phasing-out of legacy brominated flame retardants: the UNEP Stockholm Convention and other legislative action worldwide. Environ Int 144:106041
Sharma A, Minhas S, Dhillo WS, Jayasena CN (2021) Male infertility due to testicular disorders. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106:e442–e459
She J, Feng N, Zheng W, Zheng H, Cai P, Zou H, Yuan Y, Gu J, Liu Z, Bian J (2021) Zearalenone exposure disrupts blood-testis barrier integrity through excessive Ca(2+)-mediated autophagy. Toxins 13:875
Tao S, Wang L, Zhu Z, Liu Y, Wu L, Yuan C, Zhang G, Wang Z (2019) Adverse effects of bisphenol A on Sertoli cell blood-testis barrier in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:475–483
Wan HT, Lai KP, Wong CKC (2020) Comparative analysis of PFOS and PFOA toxicity on Sertoli cells. Environ Sci Technol 54:3465–3475
Wei Y, Zhou Y, Long C, Wu H, Hong Y, Fu Y, Wang J, Wu Y, Shen L, Wei G (2021) Polystyrene microplastics disrupt the blood-testis barrier integrity through ROS-mediated imbalance of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 289:117904
Wu D, Huang CJ, Jiao XF, Ding ZM, Zhang SX, Miao YL, Huo LJ (2019) Bisphenol AF compromises blood-testis barrier integrity and sperm quality in mice. Chemosphere 237:124410
Wu H, Wei Y, Zhou Y, Long C, Hong Y, Fu Y, Zhao T, Wang J, Wu Y, Wu S, Shen L, Wei G (2021) Bisphenol S perturbs Sertoli cell junctions in male rats via alterations in cytoskeletal organization mediated by an imbalance between mTORC1 and mTORC2. Sci Total Environ 762:144059
Xiao X, Mruk DD, Lee WM, Cheng CY (2011) c-Yes regulates cell adhesion at the blood-testis barrier and the apical ectoplasmic specialization in the seminiferous epithelium of rat testes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:651–665
Yuan B, Gu H, Xu B, Tang Q, Wu W, Ji X, Xia Y, Hu L, Chen D, Wang X (2016) Effects of gold nanorods on imprinted genes expression in TM-4 Sertoli cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:271
Yuan J, Sun X, Che S, Zhang L, Ruan Z, Li X, Yang J (2021) AhR-mediated CYP1A1 and ROS overexpression are involved in hepatotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Toxicol Lett 352:26–33
Zhai J, Geng X, Ding T, Li J, Tang J, Chen D, Cui L, Wang Q (2019) An increase of estrogen receptor alpha protein level regulates BDE-209-mediated blood-testis barrier disruption during spermatogenesis in F1 mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:4801–4820
Zhai J, Geng W, Zhang T, Wei Y, He H, Chen W (2022) BDE-209 induce spermatocytes arrest at early-pachytene stage during meiotic prophase I in mice. Toxicology 467:153061
Zhou GX, Liu WB, Dai LM, Zhu HL, Xiong YW, Li DX, Xu DX, Wang H (2022) Environmental cadmium impairs blood-testis barrier via activating HRI-responsive mitochondrial stress in mice. Sci Total Environ 810:152247
Zhou Y, Geng X, Chen Y, Shi H, Yang Y, Zhu C, Yu G, Tang Z (2018) Essential roles of Akt/snail pathway in microcystin-LR-induced tight junction toxicity in Sertoli cell. Food Chem Toxicol 112:290–298
Zhu L, Guan Y, Li X, Xiong X, Liu J, Wang Z (2022) BPA disrupts the SC barrier integrity by activating the cytokines/JNK signaling pathway in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Aquat Toxicol 245:106124
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82273598) and by the Nature Science Research Project of Anhui Province (No. 2108085MH305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinxia Zhai and Xiya Geng had the idea for the article. Xiya Geng, Yu Wei, and Wenfeng Geng conducted the experiment. Xiya Geng, Taifa Zhang, and Wenfeng Geng checked and managed the data. Xiya Geng, Yu Wei, and Tao Ding performed data analysis. Xiya Geng and Yu Wei drafted the manuscript. Jinxia Zhai, Huan He, Xin Gao, and Jixiang Xu provided expert review of the manuscript and reviewed and approved the manuscript. All authors contributed to the research article and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• BDE-209 exposure caused a decline in sperm quality.
• BDE-209 impaired blood-testis barrier integrity including tight junction and apical ectoplasmic specialization damage.
• BDE-209 induced elongated spermatid embedded in spermatogenic epithelium.
• BDE-209 induced blood-testis barrier dysfunction via estrogen receptor α.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, X., Wei, Y., Geng, W. et al. BDE-209 disrupted the blood-testis barrier integrity by inhibiting estrogen receptor α signaling pathway in Sprague–Dawley rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 47349–47365 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25476-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25476-w