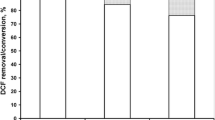
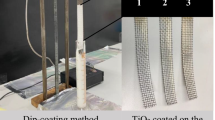
Abstract
Pollution of water sources by pathogens is a significant concern worldwide. In the present study, a pilot-scale once-through reactor was fabricated to investigate bacteria’s inactivation and the degradation of organic matter present in municipal wastewater using an iron-mediated TiO2 catalyst in fixed mode. The catalyst was fabricated (in a spherical shape) using waste material such as foundry sand and fly ash and coated with TiO2 for a combined hybrid effect. The influence of H2O2 concentration and the flow rate of the reactor were examined. 4.1 log reductions of bacteria with 52% and 39% of BOD and COD reductions in 45 min of treatment were observed. The catalyst was also found to be highly durable, with only a 12.5% of reduction in catalyst activity observed after 200 recycles. Therefore, this pilot-scale research indicates the ability of waste materials to be employed as a practical approach for water disinfection applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Acharya R, Naik B, Parida K (2018) Cr(VI) remediation from aqueous environment through modified-TiO2-mediated photocatalytic reduction. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:1448–1470. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.137
Acharya R, Pani P (2022) Visible light susceptible doped TiO2 photocatalytic systems: an overview. Mater Today Proc 67:1276–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.09.037
Amadi AA, Osu AS (2018) Effect of curing time on strength development in black cotton soil – quarry fines composite stabilized with cement kiln dust (CKD). J King Saud Univ - Eng Sci 30:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2016.04.001
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2017) Standard methods: For the examination of water and waste water, 23rd edn.
Bansal P, Verma A (2017a) Synergistic effect of dual process (photocatalysis and photo-Fenton) for the degradation of Cephalexin using TiO2 immobilized novel clay beads with waste fly ash/foundry sand. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 342:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.04.010
Bansal P, Verma A (2018a) Pilot-scale single-step reactor combining photocatalysis and photo-Fenton aiming at faster removal of Cephalexin. J Clean Prod 195:540–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.219
Bansal P, Verma A (2017b) Novel Fe-TiO2composite driven dual effect for reduction in treatment time of pentoxifylline: slurry to immobilized approach. Mater Des 125:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.083
Bansal P, Verma A (2018b) N, Ag co-doped TiO2 mediated modified in-situ dual process (modified photocatalysis and photo-Fenton) in fixed-mode for the degradation of Cephalexin under solar irradiations. Chemosphere 212:611–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.120
Bansal P, Verma A, Talwar S (2018) Detoxification of real pharmaceutical wastewater by integrating photocatalysis and photo-Fenton in fixed-mode. Chem Eng J 349:838–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.140
Bharti B, Kumar S, Lee HN, Kumar R (2016) Formation of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ state in TiO2 thin film and enhanced optical properties by air plasma treatment. Sci Rep 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32355
Chong MN, Jin B, Saint CP (2011) Bacterial inactivation kinetics of a photo-disinfection system using novel titania-impregnated kaolinite photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 171:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.024
Domínguez-Espíndola RB, Bruguera-Casamada C, Silva-Martínez S et al (2019) Photoelectrocatalytic inactivation of pseudomonas aeruginosa using an Ag-decorated TiO2 photoanode. Sep Purif Technol 208:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.005
Fang Q, Li B, Li YY et al (2019) 0D/2D Z-scheme heterojunctions of g-C3N4 quantum dots/ZnO nanosheets as a highly efficient visible-light photocatalyst. Adv Powder Technol 30:1576–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.05.004
Gamage J, Cui W, Zhang Z (2013) Degradative and disinfective properties of carbon-doped anatase – rutile TiO 2 mixtures under visible light irradiation. Catal Today 207:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.015
Giannakis S (2018) Analogies and differences among bacterial and viral disinfection by the photo-Fenton process at neutral pH: a mini review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27676–27692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0926-x
Ismail MA, Hedhili MN, Anjum DH et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of iron-doped tio2 nanoparticles using ferrocene from flame spray pyrolysis. Catalysts 11:438. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040438
Karunakaran C, Abiramasundari G, Gomathisankar P et al (2010) Cu-doped TiO 2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 352:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.08.012
Karunakaran C, Vijayabalan A, Manikandan G (2013) Photocatalytic bacteria inactivation by polyethylene glycol-assisted sol–gel synthesized Cd-doped TiO2 under visible light. Res Chem Intermed 39:1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0700-0
Karunakaran C, Vijayabalan A, Manikandan G, Gomathisankar P (2011) Visible light photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria by Cd – TiO2. Catal Commun 12:826–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.01.017
Li Y, Zhang X, Yang M et al (2017) Three-step effluent chlorination increases disinfection efficiency and reduces DBP formation and toxicity. Chemosphere 168:1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.137
Li YY, Zhou BX, Zhang HW et al (2019) Doping-induced enhancement of crystallinity in polymeric carbon nitride nanosheets to improve their visible-light photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 11:6876–6885. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr00229d
Lin T, Chen W, Cai B (2016) Inactivation mechanism of chlorination in Escherichia coli internalized in Limnoithona sinensis and Daphnia magna. Water Res 89:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.015
Nasralla NHS, Yeganeh M, Astuti Y et al (2018) Systematic study of electronic properties of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:17956–17966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9911-5
Nyangaresi PO, Qin Y, Chen G et al (2019) Comparison of UV-LED photolytic and UV-LED/TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection for Escherichia coli in water. Catal Today 335:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.015
Rizzo L, Sannino D, Vaiano V et al (2014) Environmental Effect of solar simulated N-doped TiO2 photocatalysis on the inactivation and antibiotic resistance of an E. coli strain in biologically treated urban wastewater. “Applied Catal B. Environ 144:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.033
Rodríguez-Chueca J, Ormad MP, Mosteo R et al (2016) Escherichia coli inactivation in fresh water through photocatalysis with TiO2-effect of H2O2 on disinfection kinetics. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 44:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500083
Sreeja S, Shetty V (2016) Microbial disinfection of water with endotoxin degradation by photocatalysis using Ag@TiO2 core shell nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:18154–18164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6841-8
Talwar S, Sangal VK, Verma AK (2019) In-situ dual effect of novel Fe-TiO2 composite for the degradation of phenazone. Sep Purif Technol 211:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.10.007
Taylor P, Suri RPS, Thornton HM, Muruganandham M (2012) Disinfection of water using Pt- and Ag-doped TiO2 photocatalysts. Environ Technol 1651–1659. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.641590
Thakur I, Verma A, Örmeci B (2021) Visibly active Fe-TiO2 composite: A stable and efficient catalyst for the catalytic disinfection of water using a once-through reactor. J Environ Chem Eng 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106322
Venieri D, Fraggedaki A, Kostadima M et al (2014) Solar light and metal-doped TiO2 to eliminate water-transmitted bacterial pathogens: photocatalyst characterization and disinfection performance. Appl Catal B Environ 154–155:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.02.007
Venieri D, Panagiotopoulou P, Makropoulou T (2018) N-doped TiO2 photocatalysts for bacterial inactivation in water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:2518–2526. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5639
Veréb G, Manczinger L, Bozsó G et al (2013) Environmental comparison of the photocatalytic efficiencies of bare and doped rutile and anatase TiO2 photocatalysts under visible light for phenol degradation and E. coli inactivation. Appl Catal b, Environ 129:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.045
Vijay M, Ramachandran K, Ananthapadmanabhan PV et al (2013) Photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by reactive plasma processed nanocrystalline TiO 2 powder. Curr Appl Phys 13:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.09.014
Wang CP, Chang CS, Lin WC (2020) Efficiency improvement of a flow-through water disinfection reactor using UV-C light emitting diodes. J Water Process Eng 40:101819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101819
Wong M, Chu W, Sun D et al (2006) Visible-light-induced bactericidal activity of a nitrogen-doped titanium photocatalyst against human pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6111–6116. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02580-05
Yen CC, Wang DY, Chang LS, Shih HC (2011) Characterization and photocatalytic activity of Fe- and N-co-deposited TiO2 and first-principles study for electronic structure. J Solid State Chem 184:2053–2060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.05.036
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the sophisticated analytical instrumentation facility, Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Punjab, India, for providing their facilities for the characterization of samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to this study. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Ina Thakur and Dr. Anoop Verma. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ina Thakur. Final paper corrections were done by Dr. Anoop Verma and Dr. Banu Örmeci. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, I., Verma, A. & Örmeci, B. Solar photocatalytic disinfection of real municipal wastewater using highly durable TiO2-coated composite in a pilot scale once through reactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43654–43664 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25331-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25331-y