Abstract
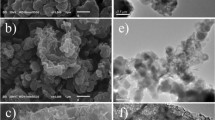
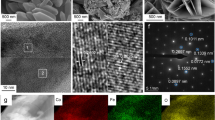
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a relatively new technique that uses electric double layer (EDL) effects, high-affinity chemical groups, redox-active materials, and membrane capacitive electrosorption principle for the desalination. In this paper, hydrothermal synthesis of cobalt ferric oxide (CFO) metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) coupled with the vacuum filtration method, or the freeze-drying method is used to fabricate high-performance nanocomposites: CFO-graphene, CFO-CNTs, and CFO-3DrGO. Two times of hydrothermal reaction methods were conducted to fabricate the CFO-3DrGO nanoengineered as a pseudocapacitive/EDL electrode. The results have demonstrated that the SAC of CFO-3DrGO/CFO (64.5 mg g−1) is greater than that of the CFO-graphene/CFO (55.16 mg g−1) and CFO-CNTs/CFO (21.5 mg g−1) due to the better surface area of the CFO-3DrGO nanocomposite (330 m2 g−1). The higher surface area of the CFO-3DrGO is due to the porous and interconnected 3D structure of the 3DrGO, and it provides a larger surface area to form EDL capacitance. In addition, the added porous 3DrGO entangled with the spinel crystals (CoFe2O4) in the composite allowed for a quick ion diffusion across the interconnected open macroporous structures.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Acharya J, Raj BGS, Ko TH, Khil M-S, Kim H-Y, Kim B-S (2020) Facile one pot sonochemical synthesis of CoFe2O4/MWCNTs hybrids with well-dispersed MWCNTs for asymmetric hybrid supercapacitor applications. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:3073–3085
Al Suwaidi F, Younes H, Sreepal V, Nair RR, Aubry C, Zou L (2019) Strategies for tuning hierarchical porosity of 3D rGO to optimize ion electrosorption. 2D Mater 6:045010
Anovitz LM, Cole DR (2015) Characterization and analysis of porosity and pore structures. Rev Mineral Geochem 80:61–164
Bharath G, Arora N, Hai A, Banat F, Savariraj D, Taher H, Mangalaraja RV (2020) Synthesis of hierarchical Mn3O4 nanowires on reduced graphene oxide nanoarchitecture as effective pseudocapacitive electrodes for capacitive desalination application. Electrochimica Acta 337:135668
Biesheuvel P, Van der Wal A (2010) Membrane capacitive deionization. J Membr Sci 346:256–262
Cao J, Wang Y, Chen C, Yu F, Ma J (2018) A comparison of graphene hydrogels modified with single-walled/multi-walled carbon nanotubes as electrode materials for capacitive deionization. J Colloid Interface Sci 518:69–75
Cao C, Wu X, Zheng Y, Chen Y (2020) Three-dimensional cubic ordered mesoporous carbon with chitosan for capacitive deionization disinfection of water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:15001–15010
Chen J, Yao B, Li C, Shi G (2013) An improved Hummers method for eco-friendly synthesis of graphene oxide. Carbon 64:225–229
Christensen G, Younes H, Hong H, Peterson GP (2013) Alignment of carbon nanotubes comprising magnetically sensitive metal oxides by nonionic chemical surfactants. Journal of Nanofluids 2(1):25–28
Conway BE (2013) Electrochemical supercapacitors: scientific fundamentals and technological applications. Springer Sci Bus Media
El-Deen AG, Barakat NA, Khalil KA, Motlak M, Kim HY (2014) Graphene/SnO2 nanocomposite as an effective electrode material for saline water desalination using capacitive deionization. Ceram Int 40:14627–14634
Elseman AM, Fayed MG, Mohamed SG, Rayan DA, Allam NK, Rashad MM, Song QL (2020) CoFe2O4@carbon spheres electrode: a one-step solvothermal method for enhancing the electrochemical performance of hybrid supercapacitors. ChemElectroChem 7:526–534
Fraggedakis D, McEldrew M, Smith RB, Krishnan Y, Zhang Y, Bai P, Chueh WC, Shao-Horn Y, Bazant MZ (2021) Theory of coupled ion-electron transfer kinetics. Electrochimica Acta 367:137432
Getirana A, Kumar S, Girotto M, Rodell M (2017) Rivers and floodplains as key components of global terrestrial water storage variability. Geophys Res Lett 44:10359–10368
Hassanvand A, Chen GQ, Webley PA, Kentish SE (2018) A comparison of multicomponent electrosorption in capacitive deionization and membrane capacitive deionization. Water Res 131:100–109
He D, Wong CE, Tang W, Kovalsky P, Waite TD (2016) Faradaic reactions in water desalination by batch-mode capacitive deionization. Environ Sci Technol Lett 3:222–226
Jaoude MA, Alhseinat E, Polychronopoulou K, Bharath G, Darawsheh IFF, Anwer S, Baker MA, Hinder SJ, Banat F (2020) Morphology-dependent electrochemical performance of MnO2 nanostructures on graphene towards efficient capacitive deionization. Electrochimica Acta 330:135202
Khan D, Qiu L, Liang C, Mirza K, Kashif M, Yang B, Kra KL, Wang Y, Li X (2022) Formation and distribution of different pore types in the lacustrine calcareous shale: insights from XRD, FE-SEM, and low-pressure nitrogen adsorption analyses. ACS Omega 7:10820–10839
Kuo S-L, Wu N-L (2005) Electrochemical capacitor of MnFe2O4 with NaCl electrolyte. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8:A495–A499
Li H, Zou L, Pan L, Sun Z (2010) Novel graphene-like electrodes for capacitive deionization. Environ Sci Technol 44:8692–8697
Li Z, Song B, Wu Z, Lin Z, Yao Y, Moon K-S, Wong C (2015) 3D porous graphene with ultrahigh surface area for microscale capacitive deionization. Nano Energy 11:711–718
Li G, Cai W, Zhao R, Hao L (2019) Electrosorptive removal of salt ions from water by membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI): characterization, adsorption equilibrium, and kinetics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17787–17796
Li Y, Song C, Chen J, Shang X, Chen J, Li Y, Huang M, Meng F (2020) Sulfur and nitrogen Co-doped activated CoFe2O4@C nanotubes as an efficient material for supercapacitor applications. Carbon 162:124–135
Li G, Cao Y, Zhang Z, Hao L (2021) Removal of ammonia nitrogen from water by mesoporous carbon electrode–based membrane capacitance deionization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:7945–7954
Liu X, Wang J (2021) Adsorptive removal of Sr2+ and Cs+ from aqueous solution by capacitive deionization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:3182–3195
McGuinness NB, Garvey M, Whelan A, John H, Zhao C, Zhang G, Dionysiou DD, Byrne JA, Pillai SC (2015) Nanotechnology solutions for global water challenges. In Water challenges and solutions on a global scale. American Chemical Society, pp 375–411
Moronshing M, Subramaniam C (2017) Scalable approach to highly efficient and rapid capacitive deionization with CNT-thread as electrodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:39907–39915
Moustafa HM, Obaid M, Nassar MM, Abdelkareem MA, Mahmoud MS (2020) Titanium dioxide-decorated rGO as an effective electrode for ultrahigh-performance capacitive deionization. Sep Purif Technol 235:116178
World Water Assessment Programme (United Nations), and UN-Water (2009) Water in a changing world
Qu Y, Yang H, Yang N, Fan Y, Zhu H, Zou G (2006) The effect of reaction temperature on the particle size, structure and magnetic properties of coprecipitated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 60:3548–3552
Ren C, Jia X, Zhang W, Hou D, Xia Z, Huang D, Hu J, Chen S, Gao S (2020) Hierarchical porous integrated Co1−xS/CoFe2O4@rGO nanoflowers fabricated via temperature‐controlled in situ calcining sulfurization of multivariate CoFe‐MOF‐74@rGO for high‐performance supercapacitor. Adv Funct Mater 30(45):2004519
Sami SK, Seo JY, Hyeon S-E, Shershah MSA, Yoo P-J, Chung C-H (2018) Enhanced capacitive deionization performance by an rGO–SnO2 nanocomposite modified carbon felt electrode. RSC Adv 8:4182–4190
Secretariat UNWWAP (2016) Water and jobs.
Shi W, Li H, Cao X, Leong ZY, Zhang J, Chen T, Zhang H, Yang HY (2016) Ultrahigh performance of novel capacitive deionization electrodes based on a three-dimensional graphene architecture with nanopores. Sci Rep 6:18966
Shi M, Qiang H, Chen C, Bano Z, Wang F, Xia M, Lei W (2021) Construction and evaluation of a novel three-electrode capacitive deionization system with high desalination performance. Sep Purif Technol 273:118976
Shi M, Ji G, Cui X, Liu C, Hong X, Ding Z, Qiang H, Wang F, Xia M (2022) Simple control of carbon mass loading in capacitive deionization for efficient deionized water production. Sep Purif Technol 301:121962
Si W, Li H (2021) Understanding the enhanced capacitive desalination performance of spherical ZnCo2O4 electrode. Adv Mater Interfaces 8:2100125
Singh PP (2021) Functionalized magnetic carbon nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Environ Appl Carbon Nanomater‐Based Devices 227–249
Tang W, He D, Zhang C, Kovalsky P, Waite TD (2017) Comparison of Faradaic reactions in capacitive deionization (CDI) and membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI) water treatment processes. Water Res 120:229–237
Tapley BD, Bettadpur S, Ries JC, Thompson PF, Watkins MM (2004) GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 305:503–505
Wang J, Chen Q, Hou B, Peng Z (2004) Synthesis and magnetic properties of single-crystals of MnFe2O4 nanorods. Eur J Inorg Chem 2004:1165–1168
Wang H, Zhang D, Yan T, Wen X, Shi L, Zhang J (2012) Graphene prepared via a novel pyridine–thermal strategy for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem 22:23745–23748
Wang Z, Dou B, Zheng L, Zhang G, Liu Z, Hao Z (2012b) Effective desalination by capacitive deionization with functional graphene nanocomposite as novel electrode material. Desalination 299:96–102
Wang Y, Han X, Wang R, Xu S, Wang J (2015) Preparation optimization on the coating-type polypyrrole/carbon nanotube composite electrode for capacitive deionization. Electrochim Acta 182:81–88
Wimalasiri Y, Zou L (2013) Carbon nanotube/graphene composite for enhanced capacitive deionization performance. Carbon 59:464–471
Xu Y, Xiang S, Zhou H, Wang G, Zhang H, Zhao H (2021) Intrinsic pseudocapacitive affinity in manganese spinel ferrite nanospheres for high-performance selective capacitive removal of Ca2+ and Mg2+. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:38886–38896
Yan W, Kim JY, Xing W, Donavan KC, Ayvazian T, Penner RM (2012) Lithographically patterned gold/manganese dioxide core/shell nanowires for high capacity, high rate, and high cyclability hybrid electrical energy storage. Chem Mater 24:2382–2390
Yan C, Kanaththage YW, Short R, Gibson CT, Zou L (2014) Graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite as electrode material for membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 344:274–279
Yao Q, Shi Z, Liu Q, Gu Z, Ning R (2018) The influences of separators on capacitive deionization systems in the cycle of adsorption and desorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3313–3319
Younes H, Zou L (2020) Asymmetric configuration of pseudocapacitive composite and rGO electrodes for enhanced capacitive deionization. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 6:392–403
Younes H, Ravaux F, El Hadri N, Zou L (2019) Nanostructuring of pseudocapacitive MnFe2O4/porous rGO electrodes in capacitive deionization. Electrochim Acta 306:1–8
Younes H, Ravaux F, El Hadri N, Zou L (2019) Nanostructuring of pseudocapacitive MnFe2O4/porous rGO electrodes in capacitive deionization. Electrochim Acta 306:1–8
Younes H, Hong H, Peterson GP (2021) A Novel Approach to Fabricate Carbon Nanomaterials–Nanoparticle Solids through Aqueous Solutions and Their Applications. Nanomanuf Metrol 4(4):226–236
Younes H, Kuang X, Lou D, DeVries B, Rahman MM, Hong H (2022) Magnetic-field-assisted DLP stereolithography for controlled production of highly aligned 3D printed polymer-Fe3O4@ graphene nanocomposites. Mater Res Bull 154:111938
Zhang D, Wen X, Shi L, Yan T, Zhang J (2012) Enhanced capacitive deionization of graphene/mesoporous carbon composites. Nanoscale 4:5440–5446
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Ding Luo for preparing the CNTs-CFO and graphene-CFO samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY: conceptualization, investigation, supervision, writing—original draft, reviewing, and editing. MMR: writing—original draft. HH: review of the original draft. MA: review of the original draft. FR: TEM, SEM, and STA measurements.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Younes, H., Rahman, M.M., Hong, H. et al. Capacitive deionization performance of asymmetric nanoengineered CoFe2O4 carbon nanomaterials composite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 32539–32549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24516-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24516-1