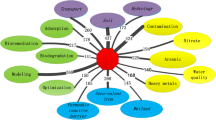
Abstract
Contaminant transport modeling (CTM) in the groundwater represents the complex bio-geo-chemical processes in the subsurface system and plays a vital role in designing remediation strategies for contaminated sites. Hence, this study evaluated 1955 articles on CTM-based studies published from 2010 to 2022 by utilizing the Scopus® database to provide a quantitative analysis of current trends and future directions. A systematic approach comprised of a bibliometric survey and visualization of various networks was conducted with the VOSviewer and Biblioshiny software for quantitative analysis of progress of CTM research field over the past decade. The hotspots and evolution of themes of CTM were found using Sankey diagrams, and thematic maps. It was observed that articles were published at an exponential rate over past 5 years. The analysis of Scopus® database revealed that the average citations per article and the average citations per year per article were 14.7 and 2.225. In the past decade, USA published 489 articles and emerged as the leading country based on mutual collaborations and cooperation with other top 9 most productive countries. Flinders University was ranked in the first position based on the number of articles, followed by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The findings obtained from this study can help researchers identify exploitation and core areas, to understand better the direction of research of mathematical model development, and to determine hotspots of CTM research field.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary files. The detailed excel sheet files used are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akbari M, Khodayari M, Danesh M et al (2020) A bibliometric study of sustainable technology research. Cogent Bus Manag 7:1751906. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2020.1751906
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr 11:959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Aria M, Misuraca M, Spano M (2020) Mapping the evolution of social research and data science on 30 years of social indicators research. Soc Indic Res 149:803–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-020-02281-3
Batagelj V, Mrvar A (2004) Pajek — analysis and visualization of large networks. In: Jünger M, Mutzel P (eds) Graph Drawing Software. Mathematics and Visualization. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18638-7_4
Bolster D, Roche KR, Morales VL (2019) Recent advances in anomalous transport models for predicting contaminants in natural groundwater systems. Curr Opin Chem Eng 26:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2019.09.006
Bonvicini S, Antonioni G, Morra P, Cozzani V (2015) Quantitative assessment of environmental risk due to accidental spills from onshore pipelines. Process Saf Environ Prot 93:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.04.007
Boraah N, Chakma S, Kaushal P (2022) Attributes of wood biochar as an efficient adsorbent for remediating heavy metals and emerging contaminants from water: A critical review and bibliometric analysis. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107825
Brantley SL, Yoxtheimer D, Arjmand S et al (2014) Water resource impacts during unconventional shale gas development: The Pennsylvania experience. Int J Coal Geol 126:140–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.12.017
Brusseau ML, Guo Z (2018) The integrated contaminant elution and tracer test toolkit, ICET3, for improved characterization of mass transfer, attenuation, and mass removal. J Contam Hydrol 208:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.11.005
Brusseau ML, Jessup RE, Rao PSC (1989) Modeling the transport of solutes influenced by multiprocess nonequilibrium. Water Resour Res 25:1971–1988. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR025i009p01971
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 57:359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen C, Ibekwe-SanJuan F, Hou J (2010) The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 61:1386–1409. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21309
Chiang WH, Kinzelbach W (1998) Processing modflow. A simulation program for modelling groundwater flow and pollution. User manual. https://ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/baug/ifu/ifu-dam/softwares/pmwin/pm5.pdf
Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2012) SciMAT: a new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 63:1609–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22688
Deb D, Chakma S (2022) Colloid and colloid-facilitated contaminant transport in subsurface ecosystem—a concise review. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04201-z
Dentz M, Berkowitz B (2003) Transport behavior of a passive solute in continuous time random walks and multirate mass transfer. Water Resour Res 39:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001WR001163
Dentz M, Kang PK, Le Borgne T (2015) Continuous time random walks for non-local radial solute transport. Adv Water Resour 82:16–26
Detty JM, McGuire KJ (2010) Topographic controls on shallow groundwater dynamics: implications of hydrologic connectivity between hillslopes and riparian zones in a till mantled catchment. Hydrol Process 24:2222–2236. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7656
Doherty JE, Hunt RJ (2010) Approaches to highly parameterized inversion — a guide to using PEST for groundwater-model calibration (Vol. 2010). Reston, VA, USA: US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey. https://doi.org/10.3133/sir20105169
Essaid HI, Bekins BA, Cozzarelli IM (2015) Organic contaminant transport and fate in the subsurface: evolution of knowledge and understanding. Water Resour Res 51:4861–4902. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017121
Giri S, Mahato MK, Singh PK, Singh AK (2021) Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment for fluoride and nitrate in the groundwater of the mica belt of Jharkhand, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess an Int J 27:1939–1953. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2021.1934814
Goh KH, See KF (2021) Twenty years of water utility benchmarking: a bibliometric analysis of emerging interest in water research and collaboration. J Clean Prod 284:124711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124711
Guleria A, Chakma S (2019) Probabilistic human health risk assessment of groundwater contamination due to metal leaching: a case study of Indian dumping sites. Hum Ecol Risk Assess An Int J 0:1–33.https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1695193
Guleria A, Singh R, Chakma S, Birke V (2022) Ecological and human health risk assessment of chromite ore processing residue (COPR) dumpsites in Northern India: a multi–pathways based probabilistic risk approach. Process Saf Environ Prot 163:405–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.05.051
Guo Z, Brusseau ML (2017) The impact of well-field configuration on contaminant mass removal and plume persistence for homogeneous versus layered systems. Hydrol Process 31:4748–4756. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11393
Guo Z, Brusseau ML, Fogg GE (2019) Determining the long-term operational performance of pump and treat and the possibility of closure for a large TCE plume. J Hazard Mater 365:796–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.057
Haghbin M, Sharafati A, Dixon B, Kumar V (2021) Application of soft computing models for simulating nitrate contamination in groundwater: comprehensive review, assessment and future opportunities. Arch Comput Methods Eng 28:3569–3591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09513-2
Hammond GE, Lichtner PC, Mills RT (2014) Evaluating the performance of parallel subsurface simulators: an illustrative example with PFLOTRAN. Water Resour Res 50:208–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/2012WR013483
Han Z, Ma H, Shi G et al (2016) A review of groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in China. Sci Total Environ 569–570:1255–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.201
Hasan MA, Ahmad S, Mohammed T (2021) Groundwater contamination by hazardous wastes. Arab J Sci Eng 46:4191–4212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05452-7
Hire S, Sandbhor S, Ruikar K (2022) Bibliometric survey for adoption of building information modeling (BIM) in construction industry — a safety perspective. Arch Comput Methods Eng 29:679–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09584-9
Hydrogeologic W (2015) Visual MODFLOW 2011.1 User’s manual: for professional applications in three-dimensional groundwater flow and contaminant transport modeling. https://www.swstechnology.com
Hyman JD, Karra S, Makedonska N et al (2015) dfnWorks: A discrete fracture network framework for modeling subsurface flow and transport. Comput Geosci 84:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.08.001
Kasavan S, Yusoff S, Rahmat Fakri MF, Siron R (2021) Plastic pollution in water ecosystems: a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2020. J Clean Prod 313:127946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127946
Kumar R, Goel P (2021) Exploring the domain of interpretive structural modelling (ISM) for sustainable future panorama: a bibliometric and content analysis. Arch Comput Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09675-7
Langevin CD, Hughes JD, Banta ER, Niswonger RG, Panday S, Provost AM (2017) Documentation for the MODFLOW 6 groundwater flow model (No. 6-A55). US Geological Survey. https://doi.org/10.3133/tm6A55
Lari KS, Davis GB, Rayner JL et al (2019) Natural source zone depletion of LNAPL: a critical review supporting modelling approaches. Water Res 157:630–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.001
Lei G, Liu F, Liu P et al (2019) A bibliometric analysis of forensic entomology trends and perspectives worldwide over the last two decades (1998–2017). Forensic Sci Int 295:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.12.002
Li P, Karunanidhi D, Subramani T, Srinivasamoorthy K (2021) Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 80:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00805-z
Liu W, Li X, Wang M, Liu L (2021) Research trend and dynamical development of focusing on the global critical metals: a bibliometric analysis during 1991–2020. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17816-5
McDonald MG, Harbaugh AW (1988) A modular three-dimensional finite-difference ground-water flow model. Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations 06-A1, US Geological Survey. https://doi.org/10.3133/twri06A1
Mrvar A, Batagelj V (2016) Analysis and visualization of large networks with program package Pajek. Complex Adapt Syst Model 4:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40294-016-0017-8
Municchi F, Di Pasquale N, Dentz M, Icardi M (2021) Heterogeneous multi-rate mass transfer models in OpenFOAM®. Comput Phys Commun 261:107763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2020.107763
Myers T (2012) Potential contaminant pathways from hydraulically fractured shale to aquifers. Groundwater 50:872–882. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2012.00933.x
Oude Essink GHP, van Baaren ES, de Louw PGB (2010) Effects of climate change on coastal groundwater systems: a modeling study in the Netherlands. Water Resour Res 46:2009WR008719. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008719
Owen SJ, Jones NL, Holland JP (1996) A comprehensive modeling environment for the simulation of groundwater flow and transport. Eng Comput 12:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198737
Paniconi C, Putti M (2015) Physically based modeling in catchment hydrology at 50: Survey and outlook. Water Resour Res 51:7090–7129. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017780
Parker JC, van Genuchten MT (1984) Determinng transport parameters from laboratory and field tracer experiments. http://hdl.handle.net/10919/56284
Parvin F, Tareq SM (2021) Impact of landfill leachate contamination on surface and groundwater of Bangladesh: a systematic review and possible public health risks assessment. Appl Water Sci 11:100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01431-3
Pietrzak D (2021) Modeling migration of organic pollutants in groundwater — review of available software. Environ Model Softw 144:105145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105145
Poonoosamy J, Wanner C, Alt Epping P et al (2021) Benchmarking of reactive transport codes for 2D simulations with mineral dissolution–precipitation reactions and feedback on transport parameters. Comput Geosci 25:1337–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-018-9793-x
Ramírez-Malule H, Quiñones-Murillo DH, Manotas-Duque D (2020) Emerging contaminants as global environmental hazards. Bibliometric Anal Emerg Contam 6:179–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2020.05.001
Ranjbari M, Saidani M, Shams Esfandabadi Z et al (2021) Two decades of research on waste management in the circular economy: insights from bibliometric, text mining, and content analyses. J Clean Prod 314:128009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128009
Riehmann P, Hanfler M, Froehlich B (2005) Interactive Sankey diagrams. In IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization. INFOVIS. (pp. 233–240). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/INFVIS.2005.1532152
Rumbaugh DB, Rumbaugh JO (2017) Guide to using groundwater vistas: Version 7. Leesport, PA. https://www.groundwatermodels.com/Groundwater_Vistas.php
Salim HK, Padfield R, Hansen SB et al (2018) Global trends in environmental management system and ISO14001 research. J Clean Prod 170:645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.017
Salomon MJ, Cavagnaro TR (2022) Healthy soils: the backbone of productive, safe and sustainable urban agriculture. J Clean Prod 341:130808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130808
Sharma S, Nagpal AK, Kaur I (2019) Appraisal of heavy metal contents in groundwater and associated health hazards posed to human population of Ropar wetland, Punjab, India and its environs. Chemosphere 227:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.009
Shen C, Phanikumar MS (2010) A process-based, distributed hydrologic model based on a large-scale method for surface–subsurface coupling. Adv Water Resour 33:1524–1541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.09.002
Šimůnek J, Genuchten MT, Šejna M (2008) Development and applications of the HYDRUS and STANMOD software packages and related codes. Vadose Zo J 7:587–600. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2007.0077
Šimůnek J, van Genuchten MT (2008) Modeling nonequilibrium flow and transport processes using HYDRUS. Vadose Zo J 7:782. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2007.0074
Simunek J, van Genuchten MT, Sejna M (2005) The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. University of California-Riverside Research Reports 3:1–240. https://www.ars.usda.gov/arsuserfiles/20360500/pdf_pubs/P2119.pdf
Šimůnek J, van Genuchten MT, Šejna M (2006) The HYDRUS software package for simulating the two- and three-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Czech Republic, Prague
Šimůnek J, van Genuchten MT, Šejna M (2016) Recent developments and applications of the HYDRUS computer software packages. Vadose Zo J 15:vzj2016.04.0033. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2016.04.0033
Šimůnek JŠM, Van Genuchten MT (1999) The HYDRUS-2D software package for simulating the twodimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media: Version 2.0. US Salinity Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture. https://www.pcprogress.com/Downloads/Pgm_Hydrus2D/HYDRUS2D.PDF
Song J, Huang G, Han D et al (2021) A review of reactive media within permeable reactive barriers for the removal of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater: current status and future prospects. J Clean Prod 319:128644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128644
Steefel CI, Appelo CAJ, Arora B et al (2015) Reactive transport codes for subsurface environmental simulation. Comput Geosci 19:445–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-014-9443-x
Toride N, Leij FJ, Van Genuchten MT (1995) The CXTFIT code for estimating transport parameters from laboratory or filed tracer experiments 2. Riverside, CA: US Salinity Laboratory
Tosco T, Petrangeli Papini M, Cruz Viggi C, Sethi R (2014) Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation: a review. J Clean Prod 77:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.026
Trefry MG, Muffels C (2007) FEFLOW: A finite-element ground water flow and transport m odeling tool. Ground Water 45:525–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00358.x
Tsay M, Li C (2017) Bibliometric analysis of the journal literature on women’s studies. Scientometrics 113:705–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2493-9
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2014) CitNetExplorer: a new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J Informetr 8:802–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2014.07.006
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84:523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2021) VOSviewer Manual. In Univeristeit Leiden (Issue July). https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.17.pdf
Venable GT, Shepherd BA, Loftis CM et al (2016) Bradford’s law: identification of the core journals for neurosurgery and its subspecialties. J Neurosurg 124:569–579. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.3.JNS15149
Wakida FT, Lerner DN (2005) Non-agricultural sources of groundwater nitrate: a review and case study. Water Res 39:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.07.026
Wang K, Wang H (2011) A fast characteristic finite difference method for fractional advection–diffusion equations. Adv Water Resour 34:810–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.11.003
White JT, Hunt RJ, Fienen MN, et al (2020) Approaches to highly parameterized inversion: PEST++ Version 5, a software suite for parameter estimation, uncertainty analysis, management optimization and sensitivity analysis (No. 7-C26). US Geological Survey. https://doi.org/10.3133/tm7C26
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, Mid-west China. Expo Heal 8:311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Xiao Z, Qin Y, Xu Z et al (2022) The journal buildings: a bibliometric analysis (2011–2021). Buildings 12:37. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12010037
Yadav B, Mathur S, Ch S, Yadav BK (2018) Simulation-optimization approach for the consideration of well clogging during cost estimation of in situ bioremediation system. J Hydrol Eng 23:04018001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001622
Zare F, Elsawah S, Iwanaga T et al (2017) Integrated water assessment and modelling: a bibliometric analysis of trends in the water resource sector. J Hydrol 552:765–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.031
Zhang S, Mao G, Crittenden J et al (2017a) Groundwater remediation from the past to the future: a bibliometric analysis. Water Res 119:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.029
Zhang Y, Huang K, Yu Y, Yang B (2017b) Mapping of water footprint research: a bibliometric analysis during 2006–2015. J Clean Prod 149:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.067
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77:273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zheng C, Wang PP (1999) MT3DMS: a modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion, and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems; documentation and user’s guide. http://hdl.handle.net/11681/4734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abhay Guleria: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, software, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Sumedha Chakma: conceptualization, supervision, writing — review and editing. All the authors read and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guleria, A., Chakma, S. A bibliometric and visual analysis of contaminant transport modeling in the groundwater system: current trends, hotspots, and future directions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 32032–32051 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24370-1