Abstract
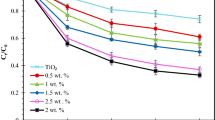
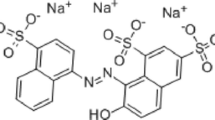
Chlorazol yellow (CY) is a commonly used anionic, toxic, mutagenic, and potentially carcinogenic azo dye, which is menacing to the environment, aquatic system, food chain, and human health as well. To remove CY dye molecules from an aqueous medium, a series of Ce, Bi, and N co-doped TiO2 photocatalysts were prepared by varying the composition of the dopants. Under sunlight irradiation, the resultant 5 wt% (Ce-Bi-N) co-doped TiO2 composite catalyst was found to show the best catalytic activity. Hence, the required characterization of this catalyst was performed systematically using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. From the thorough investigation, it is revealed that the CY molecules reached adsorption–desorption equilibrium onto the surface of the catalyst within 30 min following second-order kinetics. Herein, the catalyst attained 97% degradation when exposed to sunlight at neutral (pH ~ 7, [CY] = 5 mg L−1) medium. The developed catalyst can destruct CY molecules with a maximum rate of 23.1 µg CY g−1 min−1 and the photodegradation kinetics follows first-order kinetics below 23.5 mg L−1, a fractional order between 23.5 and 35.0 mg L−1, and a zeroth order above 35.0 mg L−1 of CY concentration. Finding from scavenging effect implies that \({\mathrm{O}}_{2}^{-}\) and \({\mathrm{OH}}^{\bullet }\) radicals have significant influence on the degradation. A suitable mechanism has been proposed with excellent stability and verified reusability of the proposed photocatalyst.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Abdullah EA, Abdullah AH, Zainal Z et al (2012) Synthesis and characterisation of Penta-bismuth Hepta-oxide nitrate, Bi5O7NO3, as a new adsorbent for methyl orange removal from an aqueous solution. E-Journal Chem 9:2429–2438. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/707853
Agrawal K, Bhatt A, Bhardwaj N et al (2020) Integrated approach for the treatment of industrial effluent by physico-chemical and microbiological process for sustainable environment. Combined Application of Physico-Chemical & Microbiological Processes for Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant. Springer, Singapore, pp 119–143
Akrami A, Niazi A (2016) Synthesis of maghemite nanoparticles and its application for removal of Titan yellow from aqueous solutions using full factorial design. Desalin Water Treat 57:22618–22631. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1136693
Akter N, Hossain MA, Hassan MJ et al (2016) Amine modified tannin gel for adsorptive removal of Brilliant Green dye. J Environ Chem Eng 4:1231–1241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.01.013
Alansi AM, Al-Qunaibit M, Alade IO et al (2018) Visible-light responsive BiOBr nanoparticles loaded on reduced graphene oxide for photocatalytic degradation of dye. J Mol Liq 253:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.034
Alderete BL, da Silva J, Godoi R et al (2021) Evaluation of toxicity and mutagenicity of a synthetic effluent containing azo dye after advanced oxidation process treatment. Chemosphere 263:128291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128291
Ali H, Guler AC, Masar M et al (2021) Solid-state synthesis of direct z-scheme Cu2O/WO3 nanocomposites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Catalysts 11:1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020293
Ani IJ, Akpan UG, Olutoye MA, Hameed BH (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater by TiO2- and ZnO-based photocatalysts: recent development. J Clean Prod 205:930–954
Ansari SA, Khan MM, Ansari MO, Cho MH (2016) Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide (N-doped TiO2) for visible light photocatalysis. New J Chem 40:3000–3009
Arifin MN, Tarek M, Rahman Khan MM (2022) Efficient treatment of organic pollutants by boron doped TiO2 photocatalysts under visible light radiation. Chem Eng Res Des 180:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.02.016
Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T et al (2001) Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science (80-) 293:269–271. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061051
Asl SK, Sadrnezhaad SK, Rad MK, Üner D (2012) Comparative photodecolorization of red dye by anatase, rutile (TiO2), and wurtzite (ZnO) using response surface methodology. Turkish J Chem 36:121–135. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1104-31
Astuti Y, Listyani BM, Suyati L, Darmawan A (2021) Bismuth oxide prepared by sol-gel method: variation of physicochemical characteristics and photocatalytic activity due to difference in calcination temperature. Indones J Chem 21:108–117. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.53144
Bazin I, Ibn Hadj Hassine A, Haj Hamouda Y et al (2012) Estrogenic and anti-estrogenic activity of 23 commercial textile dyes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.08.003
Benkhaya S, M’rabet S, El Harfi A (2020) Classifications, properties, recent synthesis and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 6:e03271
Bharti B, Kumar S, Lee HN, Kumar R (2016) Formation of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ state in TiO2 thin film and enhanced optical properties by air plasma treatment. Sci Rep 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32355
Bilgin Simsek E (2017) Solvothermal synthesized boron doped TiO2 catalysts: photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 200:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.016
Breault TM, Bartlett BM (2012) Lowering the band gap of anatase-structured TiO2 by coalloying with Nb and N: Electronic structure and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J Phys Chem C 116:5986–5994. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2078456
Caner N, Kiran I, Ilhan S, Iscen CF (2009) Isotherm and kinetic studies of Burazol Blue ED dye biosorption by dried anaerobic sludge. J Hazard Mater 165:279–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.108
Chen L, Guo W, Yang Y et al (2013) Morphology-controlled preparation and enhanced simulated sunlight and visible-light photocatalytic activity of Pt/Bi5Nb3O15 heterostructures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:8342–8351. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp00084b
Chu L, Duo F, Zhang M et al (2020) Doping induced enhanced photocatalytic performance of SnO2:Bi3+ quantum dots toward organic pollutants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 589:124416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124416
Çiçek F, Özer D, Özer A, Özer A (2007) Low cost removal of reactive dyes using wheat bran. J Hazard Mater 146:408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.037
Cravanzola S, Cesano F, Gaziano F, Scarano D (2017) Sulfur-doped TiO2: structure and surface properties. Catalysts 7:214. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7070214
Danmaliki GI, Saleh TA (2017) Effects of bimetallic Ce/Fe nanoparticles on the desulfurization of thiophenes using activated carbon. Chem Eng J 307:914–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.143
DeVito SC (1993) Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 23:249–324. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389309388453
Ferreira FV, Souza LP, Martins TMM et al (2019) Nanocellulose/bioactive glass cryogels as scaffolds for bone regeneration. Nanoscale 11:19842–19849. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr05383b
Fried R, Oprea I, Fleck K, Rudroff F (2022) Biogenic colourants in the textile industry – a promising and sustainable alternative to synthetic dyes. Green Chem 24:13–35
Gičević A, Hindija L, Karačić A (2020) Toxicity of azo dyes in pharmaceutical industry. IFMBE Proceedings. Springer, Cham, pp 581–587
GilPavas E, Dobrosz-Gómez I, Gómez-García MÁ (2020) Efficient treatment for textile wastewater through sequential electrocoagulation, electrochemical oxidation and adsorption processes: optimization and toxicity assessment. J Electroanal Chem 878:114578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114578
Gürses A, Açıkyıldız M, Güneş K, Gürses MS (2016) Classification of dye and pigments. Springer, Cham, pp 31–45
Hamdi D, Mansouri L, Srivastava V et al (2021) Enhancement of Eu and Ce doped TiO2 thin films photoactivity: application on amido black photodegradation. Inorg Chem Commun 133:108912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108912
Hasani K, Moradi M, Mokhtari SA et al (2021) Degradation of basic violet 16 dye by electro-activated persulfate process from aqueous solutions and toxicity assessment using microorganisms: determination of by-products, reaction kinetic and optimization using Box-Behnken design. Int J Chem React Eng 19:261–275. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2020-0226
Hasnat MA, Uddin MM, Samed AJF et al (2007) Adsorption and photocatalytic decolorization of a synthetic dye erythrosine on anatase TiO2 and ZnO surfaces. J Hazard Mater 147:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.040
Hassani A, Eghbali P (2018) Metin Ö (2018) Sonocatalytic removal of methylene blue from water solution by cobalt ferrite/mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (CoFe2O4/mpg-C3N4) nanocomposites: response surface methodology approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2532(25):32140–32155. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-018-3151-3
Hassani A, Faraji M, Eghbali P (2020) Facile fabrication of mpg-C3N4/Ag/ZnO nanowires/Zn photocatalyst plates for photodegradation of dye pollutant. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 400:112665. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOCHEM.2020.112665
Helmy ET, Nemr AE, Mousa M, Arafa E, Eldafrawy S (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes pollutants in the industrial textile wastewater by using synthesized TiO2, C-doped TiO2, S-doped TiO2 and C,S co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Water Environ Nanotechnol 3:116–127. https://doi.org/10.22090/jwent.2018.02.003
Hemalatha P, Karthick SN, Hemalatha KV et al (2016) La-doped ZnO nanoflower as photocatalyst for methylene blue dye degradation under UV irradiation. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:2367–2378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4034-8
Hiremath S, Antony Raj MAL, Chandra Prabha MN, Vidya C (2018) Tamarindus indica mediated biosynthesis of nano TiO2 and its application in photocatalytic degradation of Titan yellow. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7338–7346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.052
Hu Y, Li D, Zheng Y et al (2011) BiVO4/TiO2 nanocrystalline heterostructure: a wide spectrum responsive photocatalyst towards the highly efficient decomposition of gaseous benzene. Appl Catal B Environ 104:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.02.031
Huang M, Xu C, Wu Z et al (2008) Photocatalytic discolorization of methyl orange solution by Pt modified TiO2 loaded on natural zeolite. Dye Pigment 77:327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2007.01.026
Huang W, Cheng H, Feng J et al (2018) Synthesis of highly water-dispersible N-doped anatase titania based on low temperature solvent-thermal method. Arab J Chem 11:871–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.12.028
Hübner K (2006) 150 jahre mauvein. Chemie Unserer Zeit 40:274–275
Jamee R, Siddique R (2019) Biodegradation of synthetic dyes of textile effluent by microorganisms: an environmentally and economically sustainable approach. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 9:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1556/1886.2019.00018
Jang MH, Hwang YS (2018) Effects of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes on toxicity and bioaccumulation of lead in Daphnia magna. PLoS One 13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194935
Kalantary RR, Dadban Shahamat Y, Farzadkia M et al (2015) Photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of diazinon in aqueous solution using nano-TiO2(Degussa, P25): kinetic and statistical analysis. Desalin Water Treat 55:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.928795
Karim AV, Hassani A, Eghbali P, Nidheesh PV (2022) Nanostructured modified layered double hydroxides (LDHs)-based catalysts: a review on synthesis, characterization, and applications in water remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 26:100965. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COSSMS.2021.100965
Khan MM, Ansari SA, Pradhan D et al (2014) Band gap engineered TiO2 nanoparticles for visible light induced photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic studies. J Mater Chem A 2:637–644. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta14052k
Khan R, Bhawana P, Fulekar MH (2013) Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12:75–97
Kishor R, Purchase D, Saratale GD et al (2021) Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.105012
Kovalevskiy N, Selishchev D, Svintsitskiy D et al (2020) Synergistic effect of polychromatic radiation on visible light activity of N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Catal Commun 134:105841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2019.105841
Li H, Liu J, Qian J et al (2014) Preparation of Bi-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their visible light photocatalytic performance. Cuihua Xuebao/chinese J Catal 35:1578–1589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60124-8
Li Y, Yang Z, Wang Y et al (2017) A mesoporous cationic thorium-organic framework that rapidly traps anionic persistent organic pollutants. Nat Commun 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01208-w
Liu G, Feng M, Tayyab M et al (2021) Direct and efficient reduction of perfluorooctanoic acid using bimetallic catalyst supported on carbon. J Hazard Mater 412:125224. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.125224
Liu T, Wang L, Lu X et al (2017) Comparative study of the photocatalytic performance for the degradation of different dyes by ZnIn2S4: adsorption, active species, and pathways. RSC Adv 7:12292–12300. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA00199A
Liu Y, Yu H, Lv Z et al (2012) Simulated-sunlight-activated photocatalysis of Methylene Blue using cerium-doped SiO2/TiO2 nanostructured fibers. J Environ Sci (china) 24:1867–1875. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61008-5
Luo L, Sun L, Long Y et al (2019) Multiferroic properties of aurivillius structure Bi4SmFeTi3O15 thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:9945–9954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01334-9
Milosevic I, Jayaprakash A, Greenwood B et al (2017) Synergistic effect of fluorinated and N doped TiO2 nanoparticles leading to different microstructure and enhanced photocatalytic bacterial inactivation. Nanomater 7:391. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO7110391
Milošević I, Rtimi S, Jayaprakash A et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of fluorinated anatase nanoparticles and subsequent N-doping for efficient visible light activated photocatalysis. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 171:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.035
Mishra G, Mukhopadhyay M (2019) TiO2 decorated functionalized halloysite nanotubes (TiO2@HNTs) and photocatalytic PVC membranes synthesis, characterization and its application in water treatment. Sci Rep 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40775-4
Modwi A, Ghanem MA, Al-Mayouf AM, Houas A (2018) Lowering energy band gap and enhancing photocatalytic properties of Cu/ZnO composite decorated by transition metals. J Mol Struct 1173:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.06.082
Murcia-López S, Hidalgo MC, Navío JA (2011) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Bi-doped TiO2 photocatalysts under simulated solar irradiation. Appl Catal A Gen 404:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.07.008
Nawaz MS, Ahsan M (2014) Comparison of physico-chemical, advanced oxidation and biological techniques for the textile wastewater treatment. Alexandria Eng J 53:717–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2014.06.007
Niu P, Wu G, Chen P et al (2020) Optimization of boron doped TiO2 as an efficient visible light-driven photocatalyst for organic dye degradation with high reusability. Front Chem 8:172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00172
Ozensoy E, Peden CHF, Szanyi J (2005) NO2 adsorption on ultrathin θ-Al2O3 films: formation of nitrite and nitrate species. J Phys Chem B 109:15977–15984. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp052053e
Pan D, Chen J, Yao S et al (2005) An amperometric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized in electropolymerized poly(o-aminophenol) and carbon nanotubes composite film on a gold electrode. Anal Sci 21:367–371. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.367
Qi D, Xing M, Zhang J (2014) Hydrophobic carbon-doped TiO2/MCF-F composite as a high performance photocatalyst. J Phys Chem C 118:7329–7336. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4123979
Radoičić MB, Janković IA, Despotović VN et al (2013) The role of surface defect sites of titania nanoparticles in the photocatalysis: aging and modification. Appl Catal B Environ 138–139:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.032
Saadati F, Keramati N, Ghazi MM (2016) Influence of parameters on the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:757–782
Sakr F, Alahiane S, Sennaoui A et al (2020) Removal of cationic dye (Methylene Blue) from aqueous solution by adsorption on two type of biomaterial of South Morocco. Materialstoday: Proceedings 22:93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.101
Sarker DR, Uddin MN, Elias M et al (2022) P-doped TiO2-MWCNTs nanocomposite thin films with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light exposure. Clean Eng Technol 6:100364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100364
Shi Z, Liu F, Yao S (2010) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of B, y co-doped nanosized TiO2 catalyst. J Rare Earths 28:737–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(09)60191-5
Sinha K, Chowdhury S, Das SP, Datta S (2013) Modeling of microwave-assisted extraction of natural dye from seeds of Bixa orellana (Annatto) using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Ind Crops Prod 41:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.04.004
Ben SH, Bouket AC, Pourhassan Z et al (2021) Diversity of synthetic dyes from textile industries, discharge impacts and treatment methods. Appl Sci 11:6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146255
Tang WZ, An H (1995) UV/TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of commercial dyes in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 31:4157–4170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(95)80015-D
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi 15:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
Teo SH, Ng CH, Islam A et al (2022) Sustainable toxic dyes removal with advanced materials for clean water production: a comprehensive review. J Clean Prod 332:130039
Uddin MM, Hasnat MA, Samed AJF, Majumdar RK (2007) Influence of TiO2 and ZnO photocatalysts on adsorption and degradation behaviour of Erythrosine. Dye Pigment 75:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.04.023
Varnagiris S, Medvids A, Lelis M et al (2019) Black carbon-doped TiO2 films: synthesis, characterization and photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 382:111941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111941
Vidya C, Manjunatha C, Sudeep M et al (2020) Photo-assisted mineralisation of titan yellow dye using ZnO nanorods synthesised via environmental benign route. SN Appl Sci 2:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42452-020-2537-2/FIGURES/11
Vidya C, Prabha MNC, Raj MALA (2016) Green mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for the photocatalytic degradation of Rose Bengal dye. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 6:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.09.004
Wahi RK, Yu WW, Liu Y et al (2005) Photodegradation of Congo Red catalyzed by nanosized TiO2. J Mol Catal A Chem 242:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.07.034
Wang HY, Li B, Teng JX et al (2017) N-doped carbon-coated TiN exhibiting excellent electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 257:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.10.066
Wei X, Zhu G, Fang J, Chen J (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of well-dispersible phase-pure anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Int J Photoenergy 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/726872
Worayingyong A, Sang-urai S, Smith MF et al (2014) Effects of cerium dopant concentration on structural properties and photocatalytic activity of electrospun Ce-doped TiO2 nanofibers. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 117:1191–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8501-5
Xiong Z, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zheng C (2015) Efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into liquid products over cerium doped titania nanoparticles synthesized by a sol-gel auto-ignited method. Fuel Process Technol 135:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.09.017
Xue W, Zhang G, Xu X et al (2011) Preparation of titania nanotubes doped with cerium and their photocatalytic activity for glyphosate. Chem Eng J 167:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.007
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184
Yan X, Yuan K, Lu N et al (2017) The interplay of sulfur doping and surface hydroxyl in band gap engineering: mesoporous sulfur-doped TiO2 coupled with magnetite as a recyclable, efficient, visible light active photocatalyst for water purification. Appl Catal B Environ 218:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.022
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2019) Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1193–1226
Yim S-D, Chung HT, Chlistunoff J et al (2015) A microelectrode study of interfacial reactions at the platinum-alkaline polymer interface. J Electrochem Soc 162:F499–F506. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0151506jes
Yu L, Shao Y, Li D (2017) Direct combination of hydrogen evolution from water and methane conversion in a photocatalytic system over Pt/TiO2. Appl Catal B Environ 204:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.11.039
Zeghioud H, Assadi AA, Khellaf N et al (2019) Photocatalytic performance of CuxO/TiO2 deposited by HiPIMS on polyester under visible light LEDs: oxidants, ions effect, and reactive oxygen species investigation. Mater 12:412. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA12030412
Zhu SR, Wu MK, Zhao WN et al (2017) Fabrication of heterostructured BiOBr/Bi24O31Br10/TiO2 photocatalyst by pyrolysis of MOF composite for dye degradation. J Solid State Chem 255:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2017.07.038
Funding
The authors received financial supports from the Ministry of Education, Bangladesh (Grant No. PS 20201512) and Shahjalal University of Science and Technology (PS/2022/1/01) to Mohammad A. Hasnat. Yuki Nagao appreciated the support by JSPS KAKENHI (JP21H00020) and JST CREST (JPMJCR21B3), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zannatul Mumtarin Moushumy: writing original draft, investigation, Mohammad Jobaer Hassan: data curation, investigation, formal analysis, Mohebul Ahsan: investigation, visualization, validation, Md. Mahmudul Hasan: characterization, Md Nizam Uddin: conceptualization, Yuki Nagao: characterization, Mohammad A. Hasnat: investigation, validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Disclaimer
The result presented here is honest and clear without data manipulation.
Additional information
Communicated by Sami Rtimi.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors can declare that the research is original and have not been published anywhere in any languages.
Highlights
• The TiO2-5 wt% (Ce-Bi-N) catalyst exhibited photocatalytic degradation of ca. 97% for chlorazol yellow (CY) dye in neutral medium.
• The developed catalyst can destruct CY molecules with a maximum rate of 23.1 µg CY g−1 min−1.
• A total of − 25.5 kJ mol−1 free energy (\(\Delta {G}^{o}=-RT\mathrm{ln}K\)) was liberated while the catalyst was employed for CY degradation.
• The photodegradation kinetics followed first-order kinetics bellow 23.5 mg L−1, fractional order between 23.5 and 35.0 mg L−1, and zeroth order above 35.0 mg L−1 of CY concentration.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moushumy, Z.M., Hassan, M.J., Ahsan, M. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of chlorazol yellow dye under sunlight irradiation using Ce, Bi, and N co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst in neutral medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 35153–35169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24220-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24220-0