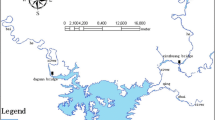
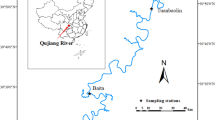
Abstract
Water quality plays an important role in river habitats. This study revealed the annual and seasonal variations and trend prediction of water quality in the middle Yangtze River after the third impoundment stage of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Multivariate statistical methods including principal component analysis/factor analysis (PCA/FA), Mann–Kendall (M–K) tests, discriminant analysis (DA), rescaled range (R/S) analysis, and the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME-WQI) were used. Herein, eight water quality constituents including pH, electrical conductivity (EC), chloride (Cl), dissolved oxygen (DO), ammonia nitrogen (NH3N), total phosphorus (TP), water temperature (T), and permanganate index (CODmn) were monthly monitored in the Jiujiang hydrological transaction during 2010–2019. The information of eight water quality constituents, related to salinity, nutrient status, and oxidation reactions efficiency, was extracted. Water quality status remained as fair-good during 2010–2019 based on the results of CCME-WQI, with the seasonal significance ranked as T > DO > Cl > pH > EC > TP > NH3N > CODmn. In the future decade, annual average T was predicted to continue to increase although it might decrease in the wet season. EC was predicted to continue increasing annually especially in the wet season while Cl might decrease. NH3N and TP might maintain a significant decreasing trend in the future wet and dry seasons. DO maintained significantly increasing especially in the future dry seasons, whereas CODmn will continue to decrease annually and seasonally. The continued alkalization trend of waterbody was predicted, which is more significant in the wet season. The results provide helpful references for the ecological protection of the middle Yangtze River.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bao Y, Gao P, He X (2015) The water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir - a unique geomorphological unit. Earth-Science Rev 150:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EARSCIREV.2015.07.005
Bilgin A (2018) Evaluation of surface water quality by using Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) method and discriminant analysis method: a case study Coruh River Basin. Environ Monit Assess 190.https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-018-6927-5
Bostanmaneshrad F, Partani S, Noori R et al (2018) Relationship between water quality and macro-scale parameters (land use, erosion, geology, and population density) in the Siminehrood River Basin. Sci Total Environ 639:1588–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.05.244
Canedo-Argueelles M, Kefford BJ, Piscart C et al (2013) Salinisation of rivers: an urgent ecological issue. Environ Pollut 173:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.011
Chang H (2008) Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res 42:3285–3304. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2008.04.006
Devic G, Djordjevic D, Sakan S (2014) Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in Serbia. Sci Total Environ 468–469:933–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.011
Farò D, Zolezzi G, Wolter C (2021) How much habitat does a river need? A spatially-explicit population dynamics model to assess ratios of ontogenetical habitat needs. J Environ Manage 286.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.112100
Feng L, Zhou J (2013) Trend predictions in water resources using rescaled range (R/S) analysis. Environ Earth Sci 68:2359–2363. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-012-1917-3
Fornaroli R, Ippolito A, Tolkkinen MJ et al (2018) Disentangling the effects of low pH and metal mixture toxicity on macroinvertebrate diversity. Environ Pollut 235:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2017.12.097
Gao Q, Li Y, Cheng Q et al (2016) Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res 92:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2015.12.055
Geng M, Wang K, Yang N, et al (2021) Spatiotemporal water quality variations and their relationship with hydrological conditions in Dongting Lake after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. J Clean Prod 283.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.124644
Guo H, Hu Q, Zhang Q, Feng S (2012) Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J Hydrol 416–417:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2011.11.027
Hayakawa A, Ikeda S, Tsushima R et al (2015) Spatial and temporal variations in nutrients in water and riverbed sediments at the mouths of rivers that enter Lake Hachiro, a shallow eutrophic lake in Japan. CATENA 133:486–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.04.009
Hurst HE (1951) Long-term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans Am Soc Civ Eng 116:770–799
Jowett IG (1997) Instream flow methods: a comparison of approaches. Ltd Regul Rivers 13:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1646(199703)13:2
Lever J, Krzywinski M, Altman N (2017) Points of significance: principal component analysis. Nat Methods 14:641–642. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4346
Lewis EL, Perkin RG (1978) Salinity: its definition and calculation. J Geophys Res 83:466. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC083IC01P00466
Liu CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6
Ma X, Li Y, Li B et al (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus losses by runoff erosion: field data monitored under natural rainfall in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. CATENA 147:797–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2016.09.004
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection P.R. China) (2002) Environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838–2002) (in Chinese). https://www.mee.gov.cn/
Nilsson C, Reidy CA, Dynesius M, Revenga C (2005) Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science (80- ) 308:405–408. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1107887
Noges P, Kagu M, Noges T (2007) Role of climate and agricultural practice in determining matter discharge into large, shallow Lake Vortsjarv, Estonia. Hydrobiologia 581:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0504-6
Pak HY, Chuah CJ, Yong EL, Snyder SA (2021) Effects of land use configuration, seasonality and point source on water quality in a tropical watershed: a case study of the Johor River Basin. Sci Total Environ 780.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.146661
Shi P, Zhang Y, Li Z et al (2017) Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. CATENA 151:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2016.12.017
Shi S, Cheng H, Xuan X et al (2018) Fluctuations in the tidal limit of the Yangtze River estuary in the last decade. Sci China Earth Sci 61:1136–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11430-017-9200-4
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVSOFT.2006.02.001
Sun J, Xiao Z, Lin B, et al (2021) Longitudinal transport timescales in a large dammed river - the Changjiang River. Sci Total Environ 771.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.144886
Sun JL, Zhao LL, Liao L et al (2020) Interactive effect of thermal and hypoxia on largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) gill and liver: aggravation of oxidative stress, inhibition of immunity and promotion of cell apoptosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 98:923–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FSI.2019.11.056
Sun Z, Chong L, Meng X et al (2022) Multivariate relations of river habitat to water–sediment indexes in the Yangtze Estuary. CATENA 216:106416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106416
Tang Q, Bao Y, He X et al (2014) Sedimentation and associated trace metal enrichment in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 479–480:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2014.01.122
Tian Q, Xu KH, Dong CM, et al (2021) Declining sediment discharge in the Yangtze River from 1956 to 2017: spatial and temporal changes and their causes. Water Resour Res 57.https://doi.org/10.1029/2020WR028645
Varol M, Gökot B, Bekleyen A, Şen B (2012) Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. CATENA 92:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2011.11.013
Varol M, Şen B (2009) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 159:543–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-008-0650-6
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Debán L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00138-9
Villarini G, Serinaldi F, Smith JA, Krajewski WF (2009) On the stationarity of annual flood peaks in the continental United States during the 20th century. Water Resour Res 45.https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007645
Wang H, Sun F, Liu W (2020) Characteristics of streamflow in the main stream of Changjiang River and the impact of the Three Gorges Dam. CATENA 189:104498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104498
Wang J, Fu Z, Qiao H, Liu F (2019) Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 650:1392–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.09.137
Wang Y, Xu H, Li M (2021) Long-term changes in phytoplankton communities in China’s Yangtze Estuary driven by altered riverine fluxes and rising sea surface temperature. Geomorphology 376.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOMORPH.2020.107566
Winner RW, Strecker RL, Ingersoll EM (1962) Some physical and chemical characteristics of Acton Lake, Ohio. Ohio J Sci 62:55–61 (http://hdl.handle.net/1811/4839)
Xiang R, Wang L, Li H, et al (2021) Temporal and spatial variation in water quality in the Three Gorges Reservoir from 1998 to 2018. Sci Total Environ 768.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.144866
Yang SL, Milliman JD, Li P, Xu K (2011) 50,000 dams later: erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Glob Planet Change 75:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GLOPLACHA.2010.09.006
Zhang L, Liu J, Zhang D et al (2018) Seasonal and spatial variations of microcystins in Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:6300–6307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0967-1
Zhou Y, Ma J, Zhang Y et al (2019) Influence of the three Gorges Reservoir on the shrinkage of China’s two largest freshwater lakes. Glob Planet Change 177:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.03.014
Funding
This study is financially supported by the National Major Hydraulic Engineering Construction Funds “Research Program on Key Sediment Problems of the Three Gorges Project” (No. 12610100000018J129-06) and Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91647209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lin Chong: investigation, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing — original draft. Jiwen Zhong: resources, visualization, writing — review and editing. Zhilin Sun: investigation, supervision. Chunhong Hu: project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to publish
Not applicable. This manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, L., Zhong, J., Sun, Z. et al. Temporal variations and trends prediction of water quality during 2010–2019 in the middle Yangtze River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 28745–28758 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23968-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23968-9