Abstract
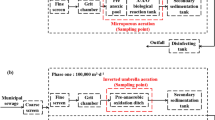
A large number of pathogenic bioaerosols are generated during the treatment process of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), and they can pose potential risks to human health. Therefore, this study systematically analyzed the emission characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus bioaerosols released from an inverted umbrella aeration tank, a microporous aeration tank, and a residual sludge storage yard in a WWTP, and quantitatively evaluated the health risks of four kinds of exposed populations with nasal/oral breathing patterns under optimistic and conservative estimations. The results displayed that the bioaerosol concentration in inverted umbrella aeration tank was higher than that in microporous aeration tank and residual sludge storage yard. Aerosolization ratio in residual sludge storage yard was an order of magnitude lower than that in aeration tanks. Sludge workers were at higher health risks than the other three exposed populations. The health risks of nasal breathers (infection risk: 1.62 × 10−5–2.56 × 10−3 pppy; disease burden: 4.24 × 10−8–6.72 × 10−6 DALYs pppy) were 0.61–0.63 times higher than those of oral breathers (infection risk: 9.95 × 10−6–1.59 × 10−3 pppy; disease burden: 2.61 × 10−8–4.18 × 10−6 DALYs pppy). For female field engineers using oral breathing, laboratory technicians, and researchers without personal protective equipment (PPE), infection risk and disease burden had the opposite results, which indicated that satisfying one certain benchmark did not mean absolute safety. In addition, health risks of exposed populations were reduced by an order of magnitude after wearing PPE. This study can provide a reliable theoretical basis for the risk prevention of bioaerosols and supply data support for the strategies of health risk control perspectives for local sewage utilities.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bauer H, Fuerhacker M, Zibuschka F, Schmid H, Puxbaum H (2002) Bacteria and fungi in aerosols generated by two different types of wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 36(16):3965–3970
Beijing Institute of Medical Device Testing (2011) Technical requirements for medical surgical masks: Section 2.6. National Medical Products Administration, Beijing, p 3
Benami M, Busgang A, Gillor O, Gross A (2016) Quantification and risks associated with bacterial aerosols near domestic greywater-treatment systems. Sci Total Environ 562:344–352
Blanky M, Sharaby Y, Rodriguez-Martinez S, Halpern M, Friedler E (2017) Greywater reuse-assessment of the health risk induced by Legionella pneumophila. Water Res 125:410–417
Bos ME, Verstappen KM, van Cleef BAGL, Dohmen W, Dorado-Garcia A, Graveland H, Duim B, Wagenaar JA, Kluytmans JAJW, Heederik DJJ (2016) Transmission through air as a possible route of exposure for MRSA. J Exposure Sci Environ Epidemiol 26(3):263–269
Bragoszewska E, Biedron I (2018) Indoor air quality and potential health risk impacts of exposure to antibiotic resistant bacteria in an office rooms in southern Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(11):2604
Brooks JR, McLaughlin MR, Gerba CP, Pepper IL (2012) Land application of manure and class B biosolids: an occupational and public quantitative microbial risk assessment. J Environ Qual 41(6):2009–2023
Burdsall AC, Xing Y, Cooper CW, Harper WF (2021) Bioaerosol emissions from activated sludge basins: characterization, release, and attenuation. Sci Total Environ 753:1–7
Busgang A, Friedler E, Gilboa Y, Gross A (2018) Quantitative microbial risk analysis for various bacterial exposure scenarios involving greywater reuse for irrigation. Water 10(4):1–15
Carducci A, Donzelli G, Cioni L, Verani M (2016) Quantitative microbial risk assessment in occupational settings applied to the airborne human adenovirus infection. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(7):1–10
Carducci A, Donzelli G, Cioni L, Federigi I, Lombardi R, Verani M (2018) Quantitative microbial risk assessment for workers exposed to bioaerosol in wastewater treatment plants aimed at the choice and setup of safety measures. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(7):1–12
Courault D, Albert I, Perelle S, Fraisse A, Renault P, Salemkour A, Amato P (2017) Assessment and risk modeling of airborne enteric viruses emitted from wastewater reused for irrigation. Sci Total Environ 592:512–526
De Gannes V, Eudoxie G, Hickey WJ (2013) Prokaryotic successions and diversity in composts as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing. Bioresour Technol 133:573–580
De Giudici P, Guillam MT, Segala C, Keck G (2013) Microbiological risk assessment of waste management activities: composting and sewage sludge application. Environ Risques Sante 12(5):422–433
Dehghani M, Sorooshian A, Ghorbani M, Fazlzadeh M, Miri M, Badiee P, Parvizi A, Ansari M, Baghani AN, Delikhoon M (2018) Seasonal variation in culturable bioaerosols in a wastewater treatment plant. Aerosol Air Qual Res 18(11):2826–2839
Devleesschauwer B, Havelaar AH, de Noordhout CM, Haagsma JA, Praet N, Dorny P, Duchateau L, Torgerson PR, Van Oyen H, Speybroeck N (2014) Calculating disability-adjusted life years to quantify burden of disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health 59(3):565–569
Esfahanian E, Adhikari U, Dolan K, Mitchell J (2019) Construction of a new dose-response model for Staphylococcus aureus considering growth and decay kinetics on skin. Pathog 8(4):1–12
Fathi S, Hajizadeh Y, Nikaeen M, Gorbani M (2017) Assessment of microbial aerosol emissions in an urban wastewater treatment plant operated with activated sludge process. Aerobiologia 33(4):507–515
Fracchia L, Pietronave S, Rinaldi M, Martinotti MG (2006) Site-related airborne biological hazard and seasonal variations in two wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 40:1985–1994
Franchitti E, Pascale E, Fea E, Anedda E, Traversi D (2020) Methods for bioaerosol characterization: limits and perspectives for human health risk assessment in organic waste treatment. Atmosphere 11(5):1–19
Gao CX, Li YG, Wei JJ, Cotton S, Hamilton M, Wang L, Cowling BJ (2021) Multi-route respiratory infection: when a transmission route may dominate. Sci Total Environ 752:1–10
Garcia-Alcega S, Nasir ZA, Ferguson R, Noel C, Cravo-Laureau C, Whitby C, Dumbrell AJ, Colbeck I, Tyrrel S, Coulon F (2018) Can chemical and molecular biomarkers help discriminate between industrial, rural and urban environments? Sci Total Environ 631–632:1059–1069
Gholipour S, Mohammadi F, Nikaeen M, Shamsizadeh Z, Khazeni A, Sahbaei Z , Mousavi SM, Ghobadian M, Mirhendi H (2021) COVID-19 infection risk from exposure to aerosols of wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 273:1–9
Gibney K, Sinclair M, O’Toole J, Leder K (2013) Using disability-adjusted life years to set health-based targets: a novel use of an established burden of disease metric. J Public Health Pol 34:439–446
Gorny R (2020) Microbial aerosols: sources, properties, health effects, exposure assessment—a review. Kona Powder Part J 37:64–84
Grzyb J, Lenart-Boron A (2019) Bacterial bioaerosol concentration and size distribution in the selected animal premises in a zoological garden. Aerobiologia 35:253–268
Haas CN, Rose JB, Gerba CP (1999) Quantitative microbial risk assessment. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York
Haas CN, Rose JB, Gerba CP (2014) Quantitative microbial risk assessment. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York
Haas CN (2015) Microbial dose response modeling: past, present, and future. Environ Sci Technol 49:1245–1259
Han Y, Wang Y, Li L, Xu G, Liu J, Yang K (2018) Bacterial population and chemicals in bioaerosols from indoor environment: sludge dewatering houses in nine municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 618:469–478
Han YP, Yang KX, Yang T, Zhang MZ, Li L (2019) Bioaerosols emission and exposure risk of a wastewater treatment plant with A2O treatment process. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 169:161–168
Han YP, Yang T, Han C, Li L, Liu JX (2020) Study of the generation and diffusion of bioaerosol under two aeration conditions. Environ Pollut 267:1–11
Harb M, Hong PY (2016) Molecular-based detection of potentially pathogenic bacteria in membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems treating municipal wastewater: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:5370–5380
Hajare R, Labhasetwar P, Nagarnaik P (2021) A critical review of applications of QMRA for healthy and safe reclaimed water management. Environ Model Assess 26(3):339–354
Heinonen-Tanski H, Reponen T, Koivunen J (2009) Airborne enteric coliphages and bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Res 43(9):2558–2566
Heyder J, Gebhart J, Rudolf G, Schiller CF, Stahlhofen W (1986) Deposition of particles in the human respiratory-tract in the size range 0.005-15-Mu-M. J Aerosol Sci 17:811–825
Hsiao TC, Lin AYC, Lien WC, Lin YC (2020) Size distribution, biological characteristics and emerging contaminants of aerosols emitted from an urban wastewater treatment plant. J Hazard Mater 388:1–9
Jahne MA, Rogers SW, Holsen TM, Grimberg SJ (2015) Quantitative microbial risk assessment of bioaerosols from a manure application site. Aerobiologia 31(1):73–87
Jones AM, Harrison RM (2004) The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations-a review. Sci Total Environ 326:151–180
Karra S, Katsivela E (2007) Microorganisms in bioaerosol emissions from wastewater treatment plants during summer at a Mediterranean site. Water Res 41:1355–1365
Kouamé PK, Nguyen-Viet H, Dongo K, Zurbrügg C, Biémi J, Bonfoh B (2017) Microbiological risk infection assessment using QMRA in agriculture systems in Côte d’Ivoire, West Africa. Environ Monit Assess 189:1–11
Korzeniewska E (2011) Emission of bacteria and fungi in the air from wastewater treatment plants-a review. Front Biosci 3:393–407
Kozajda A, Jezak K (2020) Occupational exposure to Staphylococcus aureus in the wastewater treatment plants environment. Med Pr 71(3):265–278
Kozajda A, Jezak K, Kapsa A (2019) Airborne Staphylococcus aureus in different environments-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(34):34741–34753
Kowalski M, Wolany J, Pastuszka JS, Plaza G, Wlazlo A, Ulfig K, Malina A (2017) Characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in some Polish wastewater treatment plants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(10):2181–2192
Kumar SN, Gaurav S, Manish Y, Hirendrasinh P, Arti T (2020) A state-of-the-art review on WWTP associated bioaerosols: microbial diversity, potential emission stages, dispersion factors, and control strategies. J Hazard Mater 26:1–15
Li L, Gao M, Liu JX (2011) Distribution characterization of microbial aerosols emitted from a wastewater treatment plant using the Orbal oxidation ditch process. Process Biochem 46:910–915
Li J, Zhou L, Zhang X, Xu C, Dong L (2016) Bioaerosol emissions and detection of airborne antibiotic resistance genes from a wastewater treatment plant. Atmos Environ 124:404–412
Lim KY, Hamilton AJ, Jiang SC (2015) Assessment of public health risk associated with viral contamination in harvested urban stormwater for domestic applications. Sci Total Environ 523:95–108
Liu MM, Nobu MK, Ren J, Jin XW, Hong G, Yao H (2020) Bacterial compositions in inhalable particulate matters from indoor and outdoor wastewater treatment processes. J Hazard Mater 385:1–9
Lu F, Hu TY, Wei SY, Shao LM, He PJ (2021) Bioaerosolization behavior along sewage sludge biostabilization. Front Environ Sci Eng 15(3):1–14
Madsen AM, Frederiksen MW, Bjerregaard M, Tendal K (2020) Measures to reduce the exposure of waste collection workers to handborne and airborne microorganisms and inflammogenic dust. Waste Manage 101:241–249
Mbareche H, Brisebois E, Veillette M, Duchaine C (2017) Bioaerosol sampling and detection methods based on molecular approaches: no pain no gain. Sci Total Environ 599:2095–2104
Mbareche H, Morawska L, Duchaine C (2019) On the interpretation of bioaerosol exposure measurements and impacts on health. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 69(7):789–804
Ministry of Environmental Protection (2013) Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population. China Environmental Press, Beijing
Naddafi K, Nabizadeh R, Baghani AN, Fazlzadeh M (2019) Bioaerosols in the waterpipe cafés: genera, levels, and factors influencing their concentrations. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(20):20297–20307
Nadimpalli ML, Stewart JR, Pierce E, Pisanic N, Love DC, Hall D, Larsen J, Carroll KC, Tekle T, Perl TM, Heaney CD (2018) Face mask use and persistence of livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage among industrial hog operation workers and household contacts, USA. Environ Health Perspect 126(12):1–12
Nair AT (2021) Bioaerosols in the landfill environment: an overview of microbial diversity and potential health hazards. Aerobiologia 37(2):185–203
Niazi S, Hassanvand MS, Mahvi AH, Nabizadeh R, Alimohammadi M, Nabavi S, Faridi S, Dehghani A, Hoseini M, Moradi-Joo M (2015) Assessment of bioaerosol contamination (bacteria and fungi) in the largest urban wastewater treatment plant in the Middle East. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16014–16021
Pahari AK, Dasgupta D, Patil RS, Mukherji S (2016) Emission of bacterial bioaerosols from a composting facility in Maharashtra. India Waste Manage 52:22–31
Pasalari H, Ataei-Pirkooh A, Aminikhah M, Jafari AJ, Farzadkia M (2019) Assessment of airborne enteric viruses emitted from wastewater treatment plant: atmospheric dispersion model, quantitative microbial risk assessment, disease burden. Environ Pollut 253:464–473
Pasmionka I (2020) Evaluation of microbiological quality of atmospheric air in a selected sewage treatment plant in Lesser Poland. Aerobiologia 36:249–260
Piotrowski R, Ujazdowski T (2020) Designing control strategies of aeration system in biological WWTP. Energies 13(14):1–17
Piqueras P, Li F, Castelluccio V, Matsumoto M, Asa-Awuku A (2016) Real-time ultrafine aerosol measurements from wastewater treatment facilities. Environ Sci Technol 50(20):11137–11144
Sales-Ortells H, Medema G (2014) Screening-level microbial risk assessment of urban water locations: a tool for prioritization. Environ Sci Technol 48(16):9780–9789
Schoen ME, Jahne MA, Garland J, Ramirez L, Lopatkin AJ, Hamilton KA (2021) Quantitative microbial risk assessment of antimicrobial resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in reclaimed wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 55:15246–15255
Shi KW, Wang CW, Jiang SC (2018) Quantitative microbial risk assessment of greywater on-site reuse. Sci Total Environ 635:1507–1519
Sosnowski TR (2011) Importance of airway geometry and respiratory parameters variability for particle deposition in the human respiratory tract. J Thoracic Dis 3(3):153–155
Stuart BO (1984) Deposition and clearance of inhaled particles. Environ Health Perspect 55:369–390
Sun CX, Zhang B, Chen Z, Qin WT, Wen XH (2020) Sludge retention time affects the microbial community structure: a large-scale sampling of aeration tanks throughout China. Environ Pollut 261:1–10
Taha MPM, Drew GH, Tamer A, Hewings G, Jordinson GM, Longhurst PJ, Pollard SJT (2007) Improving bioaerosol exposure assessments of composting facilities-comparative modelling of emissions from different compost ages and processing activities. Atmos Environ 41(21):4504–4519
Teunis PFM, Moe CL, Liu P, Miller SE, Lindesmith L, Baric RS, Le Pendu J, Calderon RL (2008) Norwalk virus: how infectious is it? J Med Virol 80:1468–1476
Vantarakis A, Paparrodopoulos S, Kokkinos P, Vantarakis G, Fragou K, Detorakis I (2016) Impact on the quality of life when living close to a municipal wastewater treatment plant. J Environ Public Health 2016:1–9
Walser SM, Gerstner DG, Brenner B, Bunger J, Eikmann T, Janssen B, Eikmann T, Janssen B, Kolb S, Kolk A, Nowak D, Raulf M, Sagunski H, Sedlmaier N, Suchenwirth R, Wiesmuller G, Wollin KM, Tesseraux I, Herr CEW (2015) Evaluation of exposure-response relationships for health effects of microbial bioaerosols - a systematic review. Int J Hyg Environ Health 218(7):577–589
Wang CH, Chen BT, Han BC, Liu ACY, Hung PC, Chen CY, Chao HJ (2015) Field Evaluation of personal sampling methods for multiple bioaerosols. PLoS One 10(3):1–19
Wang YJ, Li L, Xue S, Han YP. Yang KX (2019) Characteristics and formation mechanism of intestinal bacteria particles emitted from aerated wastewater treatment tanks. Water Res 163:1–12
Wang RN, Yu AY, Qiu TL, Guo YJ, Gao HZ, Sun XB, Gao M, Wang XM (2022) Aerosolization behaviour of fungi and its potential health effects during the composting of animal manure. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(9):1–16
Wanner J (2020) The development in biological wastewater treatment over the last 50 years. Water Sci Technol 84(2):274–283
Wéry N (2014) Bioaerosols from composting facilities—a review. Front Cell Infection Microbiol 4:1–9
Wéry N, Galès A, Brunet Y (2018) Microbiology of Aerosols Book, First Edition: Part II Sources and Transport of Microbial Aerosols. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp 115–135
Viau E, Bibby K, Paez-Rubio T, Peccia J (2011) Toward a consensus view on the infectious risks associated with land application of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 45:5459–5469
Wolany MKJ, Płaza JSPG (2017) Characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in some Polish wastewater treatment plants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(10):2181–2192
Xing Y, Burdsall AC, Owens A, Magnuson M, Harper WF (2021) The effect of mixing and free-floating carrier media on bioaerosol release from wastewater: a multiscale investigation with Bacillus globigii. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 7(7):1240–1249
Yang T, Han Y, Liu J, Li L (2019a) Aerosols from a wastewater treatment plant using oxidation ditch process: characteristics, source apportionment, and exposure risks. Environ Pollut 250:627–638
Yang KX, Li L, Wang Y, Xue S, Han YP, Liu JX (2019b) Airborne bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant: emission characterization, source analysis and health risk assessment. Water Res 149:596–606
Zhou Y, Benson JM, Irvin C, Irshad H, Cheng YS (2007) Particle size distribution and inhalation dose of shower water under selected operating conditions. Inhalation Toxicol 19:333–342
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51608497), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (CUGGC07).
Funding
We declare that the sources of funding for this research include the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). The funding bodies only provide financial support in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cheng Yan: conceptualization; data curation; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; visualization; software; investigation; funding acquisition; resources. Xiao-yan Zhao: conceptualization; data curation; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; visualization. Xi Luo: methodology, writing—review and editing. Dong-zi An: project administration, supervision and validation, writing—review and editing. Hao Zhu: supervision and validation, writing—review and editing. Ming Li: supervision and validation, writing—review and editing. Xiao-Jun Ai: supervision and validation, writing—review and editing. Wajid Ali: validation, writing—review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, C., Zhao, Xy., Luo, X. et al. Quantitative microbial risk assessment with nasal/oral breathing pattern for S. aureus bioaerosol emission from aeration tanks and residual sludge storage yard in a wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 21252–21262 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23621-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23621-5