Abstract
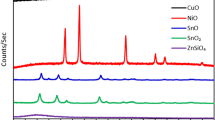
In this study, four different metal/non-metal oxide nanoparticles including CuO, Fe3O4, ZnO, and SiO2 were employed to improve CO2 absorption and desorption in methyl diethanolamine (MDEA)-based nanofluid. CO2 absorption experiment with various nanofluids was done in a bubble column reactor at ambient temperature. Also, CO2 stripping experiments for all nanofluids were done at 60 and 70 °C. The influence of nanoparticles type, nanoparticle concentration, and the stability of nanoparticles were studied on both CO2 absorption and stripping. The obtained results revealed that Fe3O4 nanoparticles at 0.01 wt.% concentration had the best influence on CO2 absorption and it improved the CO2 loading up to 36%. Also, CO2 stripping experiments for all nanofluids were done at 60 and 70 °C. The desorption experiments illustrated that metal oxide nanoparticles can be more efficient in improving CO2 desorption. In CO2 desorption, the CuO nanoparticles at 0.05 wt.% had higher efficiency, and enhanced CO2 concentration at outlet gas phase up to 44.2 vol.% at 70 °C. Finally, as an indication, the chemical stability of Fe3O4 NPs under optimum operational conditions was studied using XRD analysis and the result showed that the proposed operational condition did not have any negative effect on the chemical nature of Fe3O4 NPs.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Akachuku A, Osei PA, Decardi-Nelson B, Srisang W, Pouryousefi F, Ibrahim H, Idem R (2019) Experimental and kinetic study of the catalytic desorption of CO2 from CO2-loaded monoethanolamine (MEA) and blended monoethanolamine–Methyl-diethanolamine (MEA-MDEA) solutions. Energy 179:475–489
Awais M, Bhuiyan AA, Salehin S, Ehsan MM, Khan B, Rahman MH (2021) Synthesis, heat transport mechanisms and thermophysical properties of nanofluids: a critical overview International Journal of Thermofluids:100086
Bougie F, Fan X (2018) Microwave regeneration of monoethanolamine aqueous solutions used for CO2 capture. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 79:165–172
Choi SU, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. Argonne National Lab.(ANL), Argonne, IL (United States),
Chronopoulos T, Fernandez-Diez Y, Maroto-Valer MM, Ocone R, Reay DA (2014) CO2 desorption via microwave heating for post-combustion carbon capture microporous and mesoporous materials 197:288–290
Deiana P, Bassano C, Calì G, Miraglia P, Maggio E (2017) CO2 capture and amine solvent regeneration in Sotacarbo pilot plant. Fuel 207:663–670
Durán-Jiménez G, Stevens LA, Kostas ET, Hernández-Montoya V, Robinson JP, Binner ER (2020) Rapid, simple and sustainable synthesis of ultra-microporous carbons with high performance for CO2 uptake, via microwave heating. Chemical Engineering Journal 388:124309
Dutta A, Paul A, Chattopadhyay A (2016) The Effect of Temperature on the Aggregation Kinetics of Partially Bare Gold Nanoparticles RSC Advances 6:82138–82149
Elhambakhsh A, Keshavarz P (2020) Effects of different amin-based core-shell magnetic NPs on CO2 capture using NMP solution at high pressures. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 84:103645
Elhambakhsh A, Keshavarz P (2021) Enhanced CO 2 capture efficiency applying amine-based nano magnetite/sulfinol-M nano solvents at high pressures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:3455–3464
Elhambakhsh A, Zaeri MR, Mehdipour M, Keshavarz P (2020) Synthesis of different modified magnetic nanoparticles for selective physical/chemical absorption of CO2 in a bubble column reactor. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104195
Elhambakhsh A, Heidari S, Keshavarz P (2022) Experimental study of carbon dioxide absorption by Fe2O3@ glutamine/NMP nanofluid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:1060–1072
Elhambakhsh A, Keshavarz, Peyman (2022) Sono-hollow fiber membrane contactors: a new approach for CO2 separation by physical/chemical absorbents. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering
Elhambakhsh A, Zaeri MR, Mehdipour M, Keshavarz PJJoECE (2020b) Synthesis of different modified magnetic nanoparticles for selective physical/chemical absorption of CO2 in a bubble column reactor 8:104195
Elhambakhsh A, Ghanaatian A, Keshavarz PJJoNGS, Engineering (2021) Glutamine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for high-performance carbon dioxide absorption:104081
Elhambakhsh A et al. (2022b) Absorption increment of various physical/chemical CO2 absorbents using CeO2/SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposite Chemical Papers:1–18
Eskandari M, Elhambakhsh A, Rasaie M, Keshavarz P, Mowla D (2022) Absorption of carbon dioxide in mixture of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and six different chemical solvents. J Mol Liq 364:119939
Esmaeilpour M, Javidi J, Dehghani F, Zahmatkesh S (2017) One-pot synthesis of multisubstituted imidazoles catalyzed by Dendrimer-PWA n nanoparticles under solvent-free conditions and ultrasonic irradiation. Res Chem Intermed 43:163–185
Fan J, Wang L (2011) Review of heat conduction in nanofluids. Journal of heat transfer 133
Golkhar A, Keshavarz P, Mowla DJJoms (2013) Investigation of CO2 removal by silica and CNT nanofluids in microporous hollow fiber membrane contactors. 433:17–24
Kars R, Best R (1979) Drinkenburg AJTCEJ. The Sorption of Propane in Slurries of Active Carbon in Water 17:201–210
Keblinski P, Phillpot S, Choi S, Eastman J (2002) Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids). Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:855–863
Kim W-g, Kang HU, Jung K-m, Kim SH (2008) Synthesis of silica nanofluid and application to CO2 absorption. Sep Sci Technol 43:3036–3055
Kim ES, Jung J-Y, Kang YT (2013a) The effect of surface area on pool boiling heat transfer coefficient and CHF of Al 2 O 3/water nanofluids. J Mech Sci Technol 27:3177–3182
Kim SH, Kang JY, Ahn HS, Jo HJ, Kim MH (2013b) Study of leidenfrost mechanism in droplet impacting on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Int J Air-Cond Refrig 21:1350028
Kim JH, Jung CW, Kang YT (2014) Mass transfer enhancement during CO2 absorption process in methanol/Al2O3 nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 76:484–491
Kluytmans J, Van Wachem B, Kuster B, Schouten J (2003) Mass transfer in sparged and stirred reactors: influence of carbon particles and electrolyte. Chem Eng Sci 58:4719–4728
Krishnamurthy S, Bhattacharya P, Phelan P, Prasher R (2006) Enhanced mass transport in nanofluids. Nano Lett 6:419–423
Kwark SM, Kumar R, Moreno G, Yoo J (2010) You SMJIJoH, Transfer M. Pool Boiling Characteristics of Low Concentration Nanofluids 53:972–981
Lee JS, Lee JW, Kang YT (2015) CO2 absorption/regeneration enhancement in DI water with suspended nanoparticles for energy conversion application. Appl Energy 143:119–129
Lee JW, Pineda IT, Lee JH, Kang YT (2016) Combined CO2 absorption/regeneration performance enhancement by using nanoabsorbents. Appl Energy 178:164–176
Lee S, Choi S-S, Li S, and, Eastman J (1999) Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles
Liang Z, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Yu F, Liu H, Rongwong W (2016) Experimental study on the solvent regeneration of a CO2-loaded MEA solution using single and hybrid solid acid catalysts. AIChE J 62:753–765
Linek V, Kordač M, Soni M (2008) Mechanism of gas absorption enhancement in presence of fine solid particles in mechanically agitated gas–liquid dispersion. Effect Mole Diffusivity Chem Eng Sci 63:5120–5128
Liu H, Yao C, Zhao Y, Chen G (2018) Heat transfer characteristics of CO2 desorption from N-methyldiethanolamine solution in a microchannel reactor. Chem Eng Technol 41:1398–1405
Ma S, Chen G, Gao R, Zhu S, Weng X, Jiao K (2016) Experimental research on desorption of ammonia decarbonization solution coupled sound wave. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 52:231–236
McGurk SJ, Martín CF, Brandani S, Sweatman MB, Fan X (2017) Microwave swing regeneration of aqueous monoethanolamine for post-combustion CO2 capture. Appl Energy 192:126–133
Mehdipour M, Elhambakhsh A, Keshavarz P, Rahimpour MR, Hasanzadeh Y (2021) CO2 separation by rotating liquid sheet contactor: a novel procedure to improve mass transfer characterization. Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Modak A, Bhaumik A (2015) Porous carbon derived via KOH activation of a hypercrosslinked porous organic polymer for efficient CO2, CH4, H2 adsorptions and high CO2/N2 selectivity. J Solid State Chem 232:157–162
Modak A, Nandi M, Mondal J, Bhaumik A (2012) Porphyrin based porous organic polymers: novel synthetic strategy and exceptionally high CO 2 adsorption capacity. Chem Commun 48:248–250
Nabipour M, Keshavarz P, Raeissi SJIJoR (2017) Experimental investigation on CO2 absorption in Sulfinol-M based Fe3O4 and MWCNT nanofluids 73:1–10
Nanda S, Reddy SN, Mitra SK, Kozinski JA (2016) The progressive routes for carbon capture and sequestration. Energy Science & Engineering 4:99–122
Nwaoha C et al (2016) Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture: absorption-desorption capabilities of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP), piperazine (PZ) and monoethanolamine (MEA) tri-solvent blends. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 33:742–750
Osei PA, Akachuku A, Decardi-Nelson B, Srisang W, Pouryousefi F, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Idem R (2017) Mass transfer studies on catalyst-aided CO2 desorption from CO2-loaded amine solution in a post-combustion CO2 capture plant. Chem Eng Sci 170:508–517
Peyravi A, Keshavarz P, Mowla D (2015) Experimental investigation on the absorption enhancement of CO2 by various nanofluids in hollow fiber membrane contactors. Energy Fuels 29:8135–8142
Pineda IT, Lee JW, Jung I, Kang YT (2012) CO2 absorption enhancement by methanol-based Al2O3 and SiO2 nanofluids in a tray column absorber. Int J Refrig 35:1402–1409
Prasher R, Bhattacharya P, Phelan PE (2006) Brownian-motion-based convective-conductive model for the effective thermal conductivity of nanofluids
Putnam SA, Cahill DG, Braun PV, Ge Z, Shimmin RG (2006) Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions. J Appl Phys 99:084308
Rasaie M, Elhambakhsh A, Eskandari M, Keshavarz P, Mowla D (2022) Highly selective physical/chemical CO2 separation by functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles in hollow fiber membrane contactors: experimental and modeling approaches
Ren X, Zhang C, Kou L, Wang R, Wang Y, Li R (2022) Hierarchical porous polystyrene-based activated carbon spheres for CO2 capture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:13098–13113
Sahoo PC, Kumar M, Singh A, Singh MP, Puri SK (2017) Biocatalyzed accelerated post-combustion CO2 capture and stripping in monoethanolamine. Energy Fuels 31:11007–11012
Salvinder K et al. (2019) An overview on control strategies for CO2 capture using absorption/stripping system 147:319–337
Santos SPd (2013) Comparative study of amine solutions used in CO2 absorption/desorption cycles. Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa
Schaetz A, Hager M, Reiser O (2009) Cu (II)-azabis (oxazoline)-complexes immobilized on superparamagnetic magnetite@ silica-nanoparticles: a highly selective and recyclable catalyst for the kinetic resolution of 1, 2-diols. Adv Func Mater 19:2109–2115
Shi H et al (2018) CO2 desorption tests of blended monoethanolamine–diethanolamine solutions to discover novel energy efficient solvents. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 13:e2186
Silva C, Esperança M, Cruz A, Moura L, Badino A (2015) Stripping of ethanol with CO2 in bubble columns: effects of operating conditions and modeling. Chem Eng Res Des 102:150–160
Song C et al (2019) Bio-regeneration of different rich CO2 absorption solvent via microalgae cultivation. Biores Technol 290:121781
Srisang W, Pouryousefi F, Osei PA, Decardi-Nelson B, Akachuku A, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Idem R (2018) CO2 capture efficiency and heat duty of solid acid catalyst-aided CO2 desorption using blends of primary-tertiary amines. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 69:52–59
Tinge J, Drinkenburg A (1992) Absorption of gases into activated carbon—water slurries in a stirred cell. Chem Eng Sci 47:1337–1345
Tsubaki S, Furusawa K, Yamada H, Kato T, Higashii T, Fujii S, Wada Y (2020) Insights into the dielectric-heating-enhanced regeneration of CO2-rich aqueous amine solutions. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 8:13593–13599
Tumuluri U et al. (2017) Effect of surface structure of TiO2 nanoparticles on CO2 adsorption and SO2 resistance 5:9295–9306
Wang X, Xu X, Choi SU (1999) Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture. J Thermophys Heat Transfer 13:474–480
Wang T, Yu W, Liu F, Fang M, Farooq M, Luo Z (2016) Enhanced CO2 absorption and desorption by monoethanolamine (MEA)-based nanoparticle suspensions. Industrial Eng Chem Res 55:7830–7838
Wenzel RN (1949) Surface roughness and contact angle. J Phys Chem 53:1466–1467
White SB (2010) Enhancement of boiling surfaces using nanofluid particle deposition.
Wu Z, Liu S, Gao H, Yin Q, Liang Z (2019) A study of structure-activity relationships of aqueous diamine solutions with low heat of regeneration for post-combustion CO2 capture. Energy 167:359–368
Xing X, Feng C (2018) Enhancing CO2 desorption from crude oil by ultrasound. Ultrasonics 84:74–80
Yang J, Tan H, Low Q, Binks B, Chin J (2015) CO 2 capture by dry alkanolamines and an efficient microwave regeneration process. J Mater Chem A 3:6440–6446
Ying J, Eimer DA, Brakstad F, Haugen HA (2018) Ultrasound intensified CO2 desorption from pressurized loaded monoethanolamine solutions. I Parameters Investig Model Energy 163:168–179
Yoon S, Chung JT, Kang YT (2014) The particle hydrodynamic effect on the mass transfer in a buoyant CO2-bubble through the experimental and computational studies. Int J Heat Mass Transf 73:399–409
Yu W, Wang T, Fang M, Hei H, Luo ZCO (2015) 2 absorption/desorption enhanced by nanoparticles in post-combustion CO 2 capture. International Symposium on Coal Combustion. Springer, pp 591–596
Zandahvifard MJ, Elhambakhsh A, Ghasemi MN, Esmaeilzadeh F, Parsaei R, Keshavarz P, Wang X (2021) Effect of modified Fe3O4 magnetic NPs on the absorption capacity of CO2 in water, wettability alteration of carbonate rock surface, and water–oil interfacial tension for oilfield applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 60:3421–3434
Zhang R, Zhang X, Yang Q, Yu H, Liang Z, Luo X (2017a) Analysis of the reduction of energy cost by using MEA-MDEA-PZ solvent for post-combustion carbon dioxide capture (PCC). Appl Energy 205:1002–1011
Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu H, Li W, Xiao M, Gao H, Liang Z (2017b) Reduction of energy requirement of CO2 desorption from a rich CO2-loaded MEA solution by using solid acid catalysts. Appl Energy 202:673–684
Zhang X, Liu H, Liang Z, Idem R, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Al-Marri MJ, Benamor A (2018a) Reducing energy consumption of CO2 desorption in CO2-loaded aqueous amine solution using Al2O3/HZSM-5 bifunctional catalysts. Appl Energy 229:562–576
Zhang X, Zhang R, Liu H, Gao H, Liang Z (2018b) Evaluating CO2 desorption performance in CO2-loaded aqueous tri-solvent blend amines with and without solid acid catalysts. Appl Energy 218:417–429
Zhou W et al (2017) Bio-mitigation of carbon dioxide using microalgal systems: advances and perspectives. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:1163–1175
Funding
This work was financially supported by Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran (No. 7134851154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fariba Zarei: methodology, data curation, investigation, resources, and writing—review and editing.
Peyman Keshavarz: conceptualization, visualization, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, F., Keshavarz, P. Intensification of CO2 absorption and desorption by metal/non-metal oxide nanoparticles in bubble columns. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 19278–19291 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23577-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23577-6