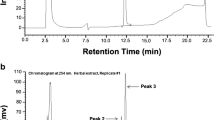
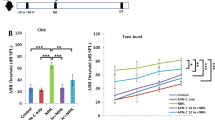
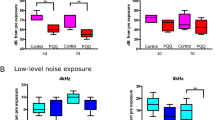
Abstract
Noise pollution has become one of the important social hazards that endanger the auditory system of residents, causing noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). Oxidative stress has a significant role in the pathogenesis of NIHL, in which the silent information regulator 1(SIRT1)/proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) signaling pathway is closely engaged. Ginsenoside Rd (GSRd), a main monomer extract from ginseng plants, has been confirmed to suppress oxidative stress. Therefore, the hypothesis that GSRd may attenuate noise-induced cochlear hair cell loss seemed promising. Forty-eight male guinea pigs were randomly divided into four groups: control, noise exposure, GSRd treatment (30 mg/kg Rd for 10d + noise), and experimental control (30 mg/kg glycerol + noise). The experimental groups received military helicopter noise exposure at 115 dB (A) for 4 h daily for five consecutive days. Hair cell damage was evaluated by using inner ear basilar membrane preparation and scanning electron microscopy. Terminal dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and immunofluorescence staining were conducted. Changes in the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway and other apoptosis-related markers in the cochleae, as well as oxidative stress parameters, were used as readouts. Loss of outer hair cells, more disordered cilia, prominent apoptosis, and elevated free radical levels were observed in the experimental groups. GSRd treatment markedly mitigated hearing threshold shifts, ameliorated outer hair cell loss and lodging or loss of cilia, and improved apoptosis through decreasing Bcl-2 associated X protein (Bax) expression and increasing Bcl-2 expression. In addition, GSRd alleviated the noise-induced cochlear redox injury by upregulating superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels, decreasing malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, and enhancing the activity of SIRT1 and PGC-1α messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and protein expression. In conclusion, GSRd can improve structural and oxidative damage to the cochleae caused by noise. The underlying mechanisms may be associated with the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All materials are commercially available.
Abbreviations
- 3-NT :
-
3-Nitrotyrosine
- 4-HNE :
-
4-Hydroxy-4-hydroxynonenal
- ABR :
-
Auditory brainstem response
- AHL :
-
Age-related hearing loss
- Bcl-2 :
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- Bax :
-
Bcl-2 associated X protein
- DAPI :
-
4,6-Diamino-2-phenylindole
- GO :
-
Gene ontology
- GSH-Px :
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSRd :
-
Ginsenoside Rd
- IgG :
-
Immunoglobulin G
- MDA :
-
Malondialdehyde
- NIHL :
-
Noise-induced hearing loss
- PBS :
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PBST :
-
Phosphate-buffered saline-Tween
- PGC-1α :
-
Proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1α
- RNA :
-
Ribonucleic acid
- RNS :
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS :
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SEM :
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SIRT1 :
-
Silent information regulator 1
- SOD :
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TUNEL :
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling assay
References
Andres AM, Stotland A, Queliconi BB, Gottlieb RA (2015) A time to reap, a time to sow: mitophagy and biogenesis in cardiac pathophysiology. J Mol Cell Cardiol 78:62–72
Basta D, Gröschel M, Ernst A (2018) Central and peripheral aspects of noise-induced hearing loss. HNO 66:342–349
Bielefeld EC (2015) Protection from noise-induced hearing loss with Src inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 20:760–765
Cai BX, Li XY, Chen JH, Tang YB, Wang GL, Zhou JG, Qui QY, Guan YY (2009) Ginsenoside-Rd, a new voltage-independent Ca2+ entry blocker, reverses basilar hypertrophic remodeling in stroke-prone renovascular hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 606:142–149
Chen XM, Ji SF, Liu YH, Xue XM, Xu J, Gu ZH, Deng SL, Liu CD, Wang H, Chang YM, Wang XC (2020) Ginsenoside Rd ameliorates auditory cortex injury associated with military aviation noise-induced hearing loss by activating SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Front Physiol 11:788
Chen XM, Xue XM, XU J, Deng SL, Chang YM, Wang XC, (2019) Effects of a military helicopter noise exposure on auditory function of guinea pigs. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering 32:406–411
Chen XM, Xue XM, Yu N, Guo WW, Yuan SL, Jiang QQ, Yang SM (2022) The role of genetic variants in the susceptibility of noise-induced hearing loss. Front Cell Neurosci 16:946206
Choi CH, Chen K, Du X, Floyd RA, Kopke RD (2011) Effects of delayed and extended antioxidant treatment on acute acoustic trauma. Free Radic Res 45:1162–1172
Ding DL (2010) Science of the inner ear. China science & technology press, Beijing
Ding T, Yan A, Liu K (2019) What is noise-induced hearing loss? Br J Hosp Med (lond) 80:525–529
Droge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82:47–95
Esterberg R, Hailey DW, Rubel EW, Raible DW (2014) ER-mitochondrial calcium flow underlies vulnerability of mechanosensory hair cells to damage. J Neurosci 34:9703–9719
Fredianelli L, Carpita S, Bernardini M, Del Pizzo LG, Brocchi F, Bianco F, Licitra G (2022) Traffic flow detection using camera images and machine learning methods in ITS for noise map and action plan optimization. Sensors (Basel) 22:1929
Fridberger A, Flock A, Ulfendahl M, Flock B (1998) Acoustic overstimulation increases outer hair cell Ca2+ concentrations and causes dynamic contractions of the hearing organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:7127–7132
Hahad O, Prochaska JH, Daiber A, Muenzel T (2019) Environmental noise-induced effects on stress hormones, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction: key factors in the relationship between cerebrocardiovascular and psychological disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:4623109
Halonen JI, Hansell AL, Gulliver J, Morley D, Blangiardo M, Fecht D, Toledano MB, Beevers SD, Anderson HR, Kelly FJ, Tonne C (2015) Road traffic noise is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and all-cause mortality in London. Eur Heart J 36:2653–2661
Han WJ, Shi XR, Nuttall A (2018) Distribution and change of peroxynitrite in the guinea pig cochlea following noise exposure. Biomed Rep 9:135–141
Henderson D, Bielefeld EC, Harris KC, Hu BH (2006) The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear 27:1–19
Honkura Y, Matsuo H, Murakami S, Sakiyama M, Mizutari K, Shiotani A, Yamamoto M, Morita I, Shinomiya N, Kawase T, Katori Y, Motohashi H (2016) NRF2 is a key target for prevention of noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative damage of cochlea. Sci Rep 6:19329
Hori YS, Kuno A, Hosoda R, Tanno M, Miura T, Shimamoto K, Horio Y (2011) Resveratrol ameliorates muscular pathology in the dystrophic mdx mouse, a model for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:784–794
Imam L, Hannan SA (2017) Noise-induced hearing loss: a modern epidemic? Br J Hosp Med (lond) 78:286–290
Jia H, Yu Z, Ge X, Chen Z, Huang X, Wei Y (2020) Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protects noise-induced apoptosis in cochlear cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. Med Mol Morphol 53:73–81
Jung E, Pyo MK, Kim J (2021) Pectin-lyase-modified ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rd inhibits high glucose-induced ROS production in mesangial cells and prevents renal dysfunction in db/db mice. Molecules 26:367
Karikura M, Tanizawa H, Hirata T, Miyase T, Takino Y (1992) Studies on absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins. VIII. Isotope labeling of ginsenoside Rb2. Chem Pharm Bull (tokyo) 40:2458–2460
Kim H, Kim JH, Lee PY, Bae KH, Cho S, Park BC, Shin H, Park SG (2013) Ginsenoside Rb1 is transformed into Rd and Rh2 by Microbacterium trichothecenolyticum. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1802–1805
Kim MS, Yu JM, Kim HJ, Kim HB, Kim ST, Jang SK, Choi YW, Lee DI, Joo SS (2014) Ginsenoside Re and Rd enhance the expression of cholinergic markers and neuronal differentiation in Neuro-2a cells. Biol Pharm Bull 37:826–833
Kowalski TJ, Pawelczyk M, Rajkowska E, Dudarewicz A, Sliwinska-Kowalska M (2014) Genetic variants of CDH23 associated with noise-induced hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 35:358–365
Ku S, You HJ, Park MS, Ji GE (2016) Whole-cell biocatalysis for producing ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1206–1215
Kudryavtseva AV, Krasnov GS, Dmitriev AA, Alekseev BY, Kardymon OL, Sadritdinova AF, Fedorova MS, Pokrovsky AV, Melnikova NV, Kaprin AD, Moskalev AA, Snezhkina AV (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in aging and cancer. Oncotarget 7:44879–44905
Le TN, Straatman LV, Lea J, Westerberg B (2017) Current insights in noise-induced hearing loss: a literature review of the underlying mechanism, pathophysiology, asymmetry, and management options. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 46:41
Li X, Cao J, Wang J, Song H, Ji G, Dong Q, Wei C, Cao Y, Wang B, Zhu B, Xiao H (2016) PON2 and ATP2B2 gene polymorphisms with noise-induced hearing loss. J Thorac Dis 8:430–438
Liu HJ, Jiang XX, Guo YZ, Sun FH, Kou XH, Bao Y, Zhang ZQ, Lin ZH, Ding TB, Jiang L, Lei XS, Yang YH (2017) The flavonoid TL-2-8 induces cell death and immature mitophagy in breast cancer cells via abrogating the function of the AHA1/Hsp90 complex. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:1381–1393
Liu ZQ, Luo XY, Liu GZ, Chen YP, Wang ZC, Sun YX (2003) In vitro study of the relationship between the structure of ginsenoside and its antioxidative or prooxidative activity in free radical induced hemolysis of human erythrocytes. J Agric Food Chem 51:2555–2558
Maillet A, Pervaiz S (2012) Redox regulation of p53, redox effectors regulated by p53: a subtle balance. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:1285–1294
Mercken EM et al (2014) SRT2104 extends survival of male mice on a standard diet and preserves bone and muscle mass. Aging Cell 13:787–796
Mitchell SJ, Martin-Montalvo A, Mercken EM, Palacios HH, Ward TM, Abulwerdi G, Minor RK, Vlasuk GP, Ellis JL, Sinclair DA, Dawson J, Allison DB, Zhang Y, Becker KG, Bernier M, de Cabo R (2014) The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 extends lifespan and improves health of mice fed a standard diet. Cell Rep 6:836–843
Moore BCJ (2020) Diagnosis and quantification of military noise-induced hearing loss. J Acoust Soc Am 148:884
Mungan Durankaya S, Olgun Y, Aktas S, Eskicioglu HE, Gurkan S, Altun Z, Mutlu B, Kolatan E, Dogan E, Yilmaz O, Kirkim G (2021) Effect of Korean red ginseng on noise-induced hearing loss. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 59:111–117
Munzel T, Kroller-Schon S, Oelze M, Gori T, Schmidt FP, Steven S, Hahad O, Roosli M, Wunderli JM, Daiber A, Sorensen M (2020) Adverse cardiovascular effects of traffic noise with a focus on nighttime noise and the new WHO noise guidelines. Annu Rev Public Health 41:309–328
Murphy E, King EA (2014) An assessment of residential exposure to environmental noise at a shipping port. Environ Int 63:207–215
Nemoto S, Fergusson MM, Finkel T (2005) SIRT1 functionally interacts with the metabolic regulator and transcriptional coactivator PGC-1{alpha}. J Biol Chem 280:16456–16460
Oberdoerffer P, Michan S, McVay M, Mostoslavsky R, Vann J, Park SK, Hartlerode A, Stegmuller J, Hafner A, Loerch P, Wright SM, Mills KD, Bonni A, Yankner BA, Scully R, Prolla TA, Alt FW, Sinclair DA (2008) SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging. Cell 135:907–918
Pawelczyk M, Van Laer L, Fransen E, Rajkowska E, Konings A, Carlsson PI, Borg E, Van Camp G, Sliwinska-Kowalska M (2009) Analysis of gene polymorphisms associated with K ion circulation in the inner ear of patients susceptible and resistant to noise-induced hearing loss. Ann Hum Genet 73:411–421
Petri D, Licitra G, Vigotti MA, Fredianelli L (2021) Effects of exposure to road, railway, airport and recreational noise on blood pressure and hypertension. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:9145
Phi LTH, Sari IN, Wijaya YT, Kim KS, Park K, Cho AE, Kwon HY (2019) Ginsenoside Rd inhibits the metastasis of colorectal cancer via epidermal growth factor receptor signaling axis. IUBMB Life 71:601–610
Qi M, Qiu Y, Zhou X, Tian K, Zhou K, Sun F, Yue B, Chen F, Zha D, Qiu J (2018) Regional up-regulation of NOX2 contributes to the differential vulnerability of outer hair cells to neomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500:110–116
Rabiei H, Ramezanifar S, Hassanipour S, Gharari N (2021) Investigating the effects of occupational and environmental noise on cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:62012–62029
Ren K, Li S, Ding J, Zhao S, Liang S, Cao X, Su C, Guo J (2021) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates mouse experimental autoimmune neuritis by modulating monocyte subsets conversion. Biomed Pharmacother 138:111489
Ren T (2002) Longitudinal pattern of basilar membrane vibration in the sensitive cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:17101–17106
Santi PA, Aldaya R, Brown A, Johnson S, Stromback T, Cureoglu S, Rask-Andersen H (2016) Scanning electron microscopic examination of the extracellular matrix in the decellularized mouse and human cochlea. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 17:159–171
Seidman M, Babu S, Tang W, Naem E, Quirk WS (2003) Effects of resveratrol on acoustic trauma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:463–470
Singh CK, Chhabra G, Ndiaye MA, Garcia-Peterson LM, Mack NJ, Ahmad N (2018) The role of sirtuins in antioxidant and redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 28:643–661
Smith MG, Croy I, Ogren M, Hammar O, Lindberg E, Persson Waye K (2017) Physiological effects of railway vibration and noise on sleep. J Acoust Soc Am 141:3262
Song X, Wang L, Fan D (2022) Insights into recent studies on biotransformation and pharmacological activities of ginsenoside Rd. Biomolecules 12(4):512
Stansfeld S (2013) Airport noise and cardiovascular disease. BMJ 347:f5752
Su YT, Guo YB, Cheng YP, Zhang X, Xie XP, Chang YM, Bao JX (2019) Hyperbaric oxygen treatment ameliorates hearing loss and auditory cortex injury in noise exposed mice by repressing local ceramide accumulation. Int J Mol Sci 20:4675
Sung CM, Kim HC, Cho YB, Shin SY, Jang CH (2018) Evaluating the ototoxicity of an anti-MRSA peptide KR-12-a2. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 84:441–447
Szklarczyk D, Santos A, von Mering C, Jensen LJ, Bork P, Kuhn M (2016) STITCH 5: augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D380–D384
Takumida M, Takumida H, Katagiri Y, Anniko M (2016) Localization of sirtuins (SIRT1-7) in the aged mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 136:120–131
Tennen RI, Michishita-Kioi E, Chua KF (2012) Finding a target for resveratrol. Cell 148:387–389
Tian K, Song Y, Zhou K, Yue B, Qiu Y, Sun F, Wang R, Zha D, Qiu J (2018) Upregulation of HSP60 expression in the postnatal rat cochlea and rats with drug-induced hearing loss. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:1311–1317
Tuerdi A, Kinoshita M, Kamogashira T, Fujimoto C, Iwasaki S, Shimizu T, Yamasoba T (2017) Manganese superoxide dismutase influences the extent of noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Neurosci Lett 642:123–128
Xiong H, Dai M, Ou Y, Pang J, Yang H, Huang Q, Chen S, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Cai Y, Liang M, Zhang X, Lai L, Zheng Y (2014) SIRT1 expression in the cochlea and auditory cortex of a mouse model of age-related hearing loss. Exp Gerontol 51:8–14
Xiong H, Pang J, Yang H, Dai M, Liu Y, Ou Y, Huang Q, Chen S, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Lai L, Zheng Y (2015) Activation of miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 signaling contributes to cochlear hair cell apoptosis: implications for age-related hearing loss. Neurobiol Aging 36:1692–1701
Xiong H, Ou Y, Xu Y, Huang Q, Pang J, Lai L, Zheng Y (2017) Resveratrol promotes recovery of hearing following intense noise exposure by enhancing cochlear SIRT1 activity. Audiol Neurootol 22:303–310
Xu HY, Zhang YQ, Liu ZM, Chen T, Lv CY, Tang SH, Zhang XB, Zhang W, Li ZY, Zhou RR, Yang HJ, Wang XJ, Huang LQ (2019) ETCM: an encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D976–D982
Xue T, Wei L, Zha DJ, Qiu JH, Chen FQ, Qiao L, Qiu Y (2016) miR-29b overexpression induces cochlear hair cell apoptosis through the regulation of SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling: implications for age-related hearing loss. Int J Mol Med 38:1387–1394
Yamashita D, Jiang HY, Schacht J, Miller JM (2004) Delayed production of free radicals following noise exposure. Brain Res 1019:201–209
Yan X, Hu G, Yan W, Chen T, Yang F, Zhang X, Zhao G, Liu J (2017) Ginsenoside Rd promotes non-amyloidogenic pathway of amyloid precursor protein processing by regulating phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha. Life Sci 168:16–23
Yang H, Chen J, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Ge B, Hong L (2021) Sirt1 activation negatively regulates overt apoptosis in Mtb-infected macrophage through Bax. Int Immunopharmacol 91:107283
Yang J, Zhang J, Wang X, Wang C, Chen J, Qian Y, Duan Z (2015) Identification of functional tag single nucleotide polmorphisms within the entire CAT gene and their clinical relevance in patients with noise-induced hearing loss. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:2852–2863
Yang L, Deng Y, Xu S, Zeng X (2007) In vivo pharmacokinetic and metabolism studies of ginsenoside Rd. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 854:77–84
Yang ZG, Sun HX, Ye YP (2006) Ginsenoside Rd from Panax notoginseng is cytotoxic towards HeLa cancer cells and induces apoptosis. Chem Biodivers 3:187–197
Ye R, Han J, Kong X, Zhao L, Cao R, Rao Z, Zhao G (2008) Protective effects of ginsenoside Rd on PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1923–1927
Ye R, Li N, Han J, Kong X, Cao R, Rao Z, Zhao G (2009) Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rd against oxygen-glucose deprivation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Res 64:306–310
Ye R, Zhao G, Liu X (2013) Ginsenoside Rd for acute ischemic stroke: translating from bench to bedside. Expert Rev Neurother 13:603–613
Yoon JH, Choi YJ, Cha SW, Lee SG (2012) Anti-metastatic effects of ginsenoside Rd via inactivation of MAPK signaling and induction of focal adhesion formation. Phytomedicine 19:284–292
Yu P, Jiao J, Chen G, Zhou W, Zhang H, Wu H, Li Y, Gu G, Zheng Y, Yu Y, Yu S (2018) Effect of GRM7 polymorphisms on the development of noise-induced hearing loss in Chinese Han workers: a nested case-control study. BMC Med Genet 19:4
Yu SE, Mwesige B, Yi YS, Yoo BC (2019) Ginsenosides: the need to move forward from bench to clinical trials. J Ginseng Res 43:361–367
Yuan H, Wang X, Hill K, Chen J, Lemasters J, Yang SM, Sha SH (2015) Autophagy attenuates noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 22:1308–1324
Zeng X, Deng Y, Feng Y, Liu Y, Yang L, Huang Y, Sun J, Liang W, Guan Y (2010) Pharmacokinetics and safety of ginsenoside Rd following a single or multiple intravenous dose in healthy Chinese volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 50:285–292
Zhang N, An X, Lang P, Wang F, Xie Y (2019) Ginsenoside Rd contributes the attenuation of cardiac hypertrophy in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1016–1023
Zhang X, Shi M, Bjoras M, Wang W, Zhang G, Han J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang B, Chen J, Zhu Y, Xiong L, Zhao G (2013) Ginsenoside Rd promotes glutamate clearance by up-regulating glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 pathways. Front Pharmacol 4:152
Zhang X, Wang Y, Ma C, Yan Y, Yang Y, Wang X, Rausch WD (2016) Ginsenoside Rd and ginsenoside Re offer neuroprotection in a novel model of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Neurodegener Dis 5:52–61
Zhu D, Liu M, Yang Y, Ma L, Jiang Y, Zhou L, Huang Q, Pi R, Chen X (2014) Ginsenoside Rd ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. J Neurosci Res 92:1217–1226
Acknowledgements
Our deepest gratitude goes to colleagues from Senior Department of Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, led by Prof. Shi-ming Yang and Department of Otolaryngology, Xijing Hospital, led by Prof. Jian-hua Qiu for their valuable technical support.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Major Military Project (grant number AWS14L009) and Key Researcher and Development Plan in Shaanxi (grant number 2018SF-252).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XMC, YHL, YMC, and XCW conceived and designed the experiment methods. XMC and YHL drafted the manuscript. SFJ performed bioinformatic analysis. XMC and LLW performed phalloidin staining, SEM observation RT-qPCR, and western blot analysis. SFJ and XMX performed TUNEL staining. YHL and XMX performed immunofluorescence staining for 4-HNE and 3-NT. XMX examined SOD, MDA, and GSH-Px levels. XMC, SFJ, and LLW conducted the statistics. XMC and SFJ revised the manuscript. XCW takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Air Force Medical University (No. 20220331).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Xm., Liu, Yh., Ji, Sf. et al. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rd on military aviation noise-induced cochlear hair cell damage in guinea pigs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 23965–23981 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23504-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23504-9